baidu2
cf
red and blue
题目链接
题目大意:
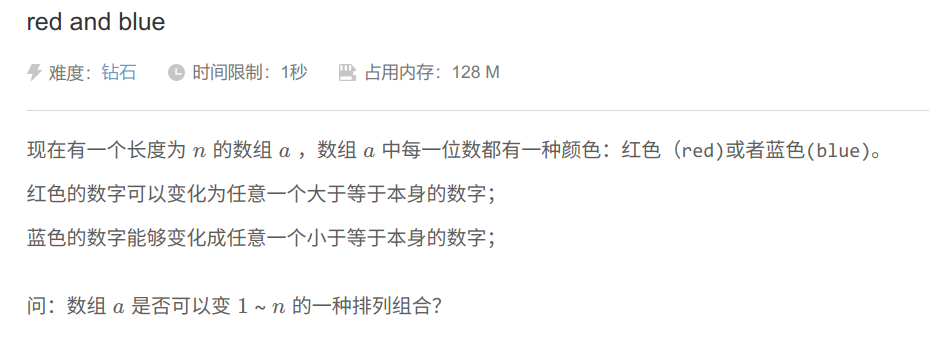
思路:
将数组先按颜色,再按大小升序排序所得形式类似于
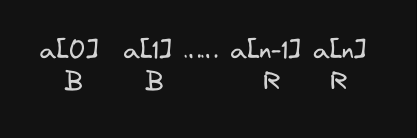
其中根据贪心只要能出现1~n的序列即可
在颜色B下,\(a[i] >= i + 1\) 因\(a[i]\)只能取不大于自身的数
在颜色R下,\(a[i] <= i + 1\) 因\(a[i]\)只能取不小于自身的数
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <array>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n,T;
struct Node{
int num;
char color;
};
Node node[N];
bool cmp(Node e1, Node e2) {
if(e1.color != e2.color) {
return e1.color < e2.color;
} else {
return e1.num < e2.num;
}
}
bool check(Node node[], int len) {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(node[i].color != 'B') {
break;
}
if(node[i].num < i + 1) {
return false;
}
}
for(int i = n - 1; i >=0; i--) {
if(node[i].color != 'R') {
break;
}
if(node[i].num > i + 1) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main() {
cin>>T;
while(T--) {
cin>>n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin>>node[i].num;
}
string s;
cin>>s;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
node[i].color=s[i];
}
sort(node, node + n, cmp);
// for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// cout<<node[i].num<<" "<<node[i].color<<endl;
// }
if(check(node, n)) {
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
} else {
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
正反卡牌
题目链接
题目大意:
思路:
在一张卡牌中假设有\(a[i] > b[i]\),将卡牌按照\(a[i] + b[i]\)排序,可以证明在两张卡牌中有\(b[j]-a[i]<b[i]-a[j]\)
\[\begin{equation}
\begin{aligned}
a[i] + b[i] < a[j] + b[j] \\
有 a[j] - b[i] < a[i] - b[j] \space (1)\\
b[j] - a[i] < b[i] - a[j] \space (2) \\
可以证明不等式左侧(2)<(1) \\
a[j] > b[j] \\
-b[i] > -a[i]
\end{aligned}
\end{equation}
\]
因此可以将\(a[i] + b[i] < a[j] + b[j]\)中选\(b[j] - a[i]\)来获得最优解
此时将正反面的和最大的一半序列取b[j]最小的一半取-a[i]来获得最优解
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <array>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 5e5+10;
struct Node {
int a;
int b;
};
Node card[N];
int n;
bool cmp(Node e1, Node e2) {
return e1.a + e1.b < e2.a + e2.b;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x,y;
cin>>x>>y;
card[i].a = max(x, y);
card[i].b = min(x, y);
}
sort(card, card + n, cmp);
LL ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < (n >> 1); i++) {
ans += card[i].b;
}
for(int i = (n >> 1); i < n; i++) {
ans -= card[i].a;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
战神小码哥
题目链接
题目大意:

思路
一种贪心的思路是尽可能按照时间边界来杀敌,但是在一下反例不成立
3
1 5
2 10
2 10
按照以上贪心思路最优解是15,但实际杀两个i=2的收益最高
此时在杀i = 1 时要求有反悔的选择,此时使用堆来存
将敌人按照时间界限进行升序排列,若此时堆内的元素小于当前时间界限那么可以杀这个敌人
如果大于等于当前时间界限那么就要考虑反悔,当堆中最小的价值小于当前考虑的敌人的价值,当然要反悔之前的操作。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <array>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q;
struct Node{
int t;
int val;
};
int n;
Node enemy[N];
LL res;
bool cmp(Node e1, Node e2) {
return e1.t < e2.t;
}
int main() {
cin>>n;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {
cin>>enemy[i].t>>enemy[i].val;
}
sort(enemy + 1, enemy + n + 1, cmp);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(q.size() < enemy[i].t) {
q.push(enemy[i].val);
} else {
if(enemy[i].val > q.top()) {
q.pop();
q.push(enemy[i].val);
}
}
}
while(!q.empty()) {
res += q.top();
// cout<<q.top();
q.pop();
}
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}
天梯赛
题目链接
题目大意:
思路
同样的反悔贪心,但这题在考虑一个人是否纳入时可能要多步操作(如样例)
如果考虑保存最优解的各个部分(选具体的能力为Ai的人会TLE)
此时只保留最优的结果即可
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <array>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5+10;
struct Node {
int val;
int limit;
};
Node stu[N];
int tmp[N];
int n;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q;
bool cmp(Node e1, Node e2) {
return e1.limit > e2.limit;
}
int main() {
cin>>n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin>>stu[i].val>>stu[i].limit;
}
sort(stu, stu + n,cmp);
LL sum = 0;
LL ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
q.push(stu[i].val);
sum += stu[i].val;
while(q.size() > stu[i].limit) {
sum -= q.top();
q.pop();
}
ans = max(ans, sum);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
硬币塔
题目链接
题目大意:
这里指从下到上一共有几个金币
思路
看清金币,银币。一个k级从下到上共有五级: 1银币,k-1级,n金币,k-1级,银币。按照分级递归即可。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <array>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 45;
LL n, k;
LL coin[N], gold[N];
void init(){
coin[0] = gold[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
coin[i] = (coin[i - 1] << 1) + i + 2;
gold[i] = (gold[i - 1] << 1) + i;
}
}
LL fd(int n, LL k) {
if(k == 0) return 0;
if(n == 0) return 1;
if(k <= 1) return 0;
else if(k > 1 && k <= 1 + coin[n - 1]) return fd(n - 1, k - 1);
else if(k > coin[n - 1] + 1 && k <= 1 + coin[n - 1] + n) return gold[n - 1] + k - (coin[n - 1] + 1);
else if(k > 1 + coin[n - 1] + n && k <= (coin[n - 1] << 1) + n + 1) return gold[n - 1] + n + fd(n - 1, k - (coin[n - 1] + 1 + n));
else return gold[n];
}
int main() {
cin>>n>>k;
init();
// for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// cout<<coin[i]<<" "<<gold[i]<<endl;
// }
cout<<fd(n, k);
return 0;
}
三角形个数
题目链接
题目大意:

思路
将三角形分为倒立和正三角形。
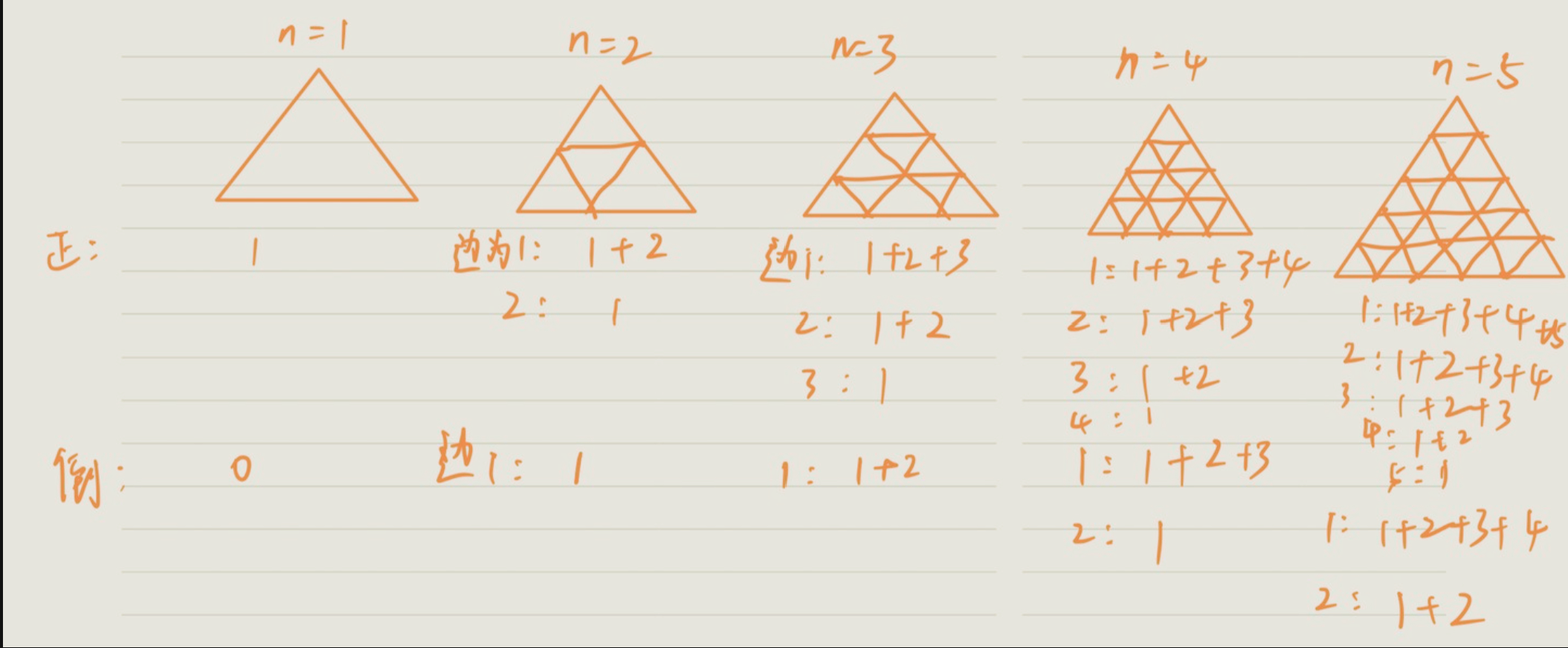
\[\begin{equation}
\begin{aligned}
sum(n等分) = sum(正) + sum(倒)\\
sum(正) = \sum^{n}_{j =1}\sum^{j}_{i = 1}i \\
sum(倒) = f(n) = f(n - 2) + \sum_{i =1}^{n-1}i
\end{aligned}
\end{equation}
\]
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <array>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 510;
int T;
int s[N],tol[N];
void init() {
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
s[i] = s[i - 1] + i;
tol[i] = tol[i - 1] + i;
}
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
tol[i] = tol[i - 1] + tol[i];
}
}
int dw(int n) {
if(n == 1) return 0;
if(n == 2) return 1;
return s[n - 1] + dw(n - 2);
}
int main() {
init();
cin>>T;
while(T --) {
int n;
cin>>n;
cout<<(tol[n] + dw(n))<<endl;
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号