alluxio源码解析-netty部分(2)
netty简介
Netty是 一个异步事件驱动的网络应用程序框架,用于快速开发可维护的高性能协议服务器和客户端。
netty作为alluxio中重要的通讯组件
在常见的客户端上传,下载中,都会有netty的参与
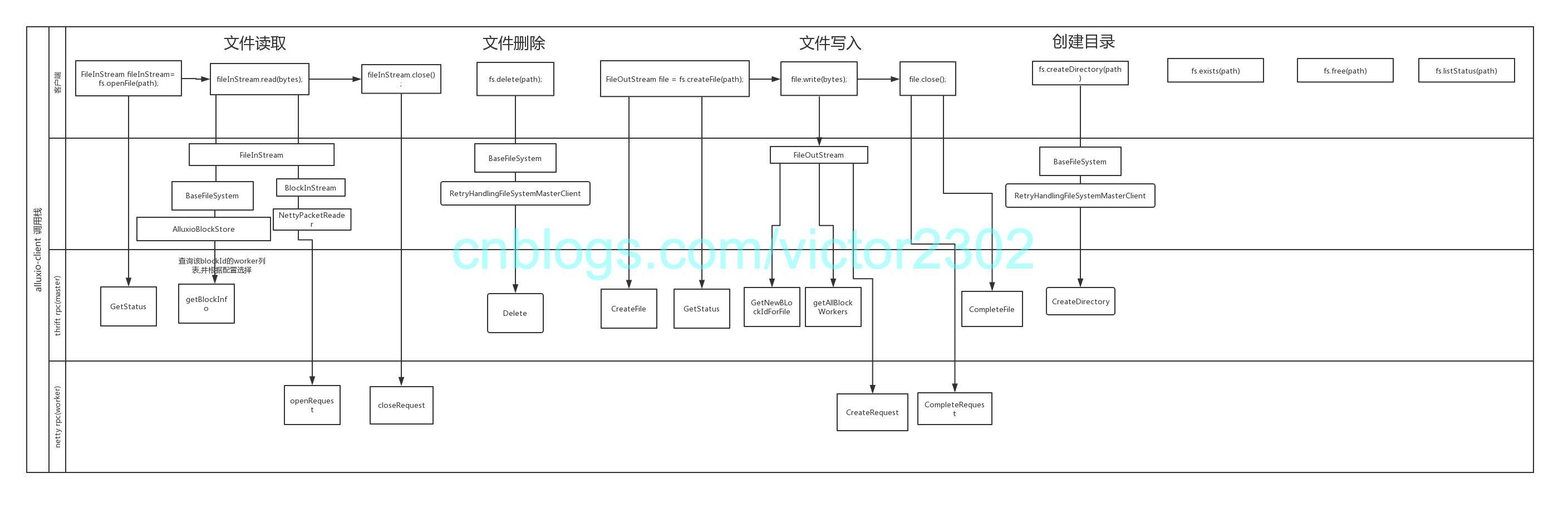
关于这个图,可以看上篇文章的介绍:
https://www.cnblogs.com/victor2302/p/10490253.html
netty作为alluxio交互重要的组件,扮演者重要的角色:
- 解耦ufs和worker缓存的功能
- 解耦 BlockHandler和 ShortCircuitBlockHandler
- 解耦异步上传,同步上传
- 高性能传输
netty客户端部分:
1.固定的处理器:alluxio.network.netty.NettyClient
final Bootstrap boot = new Bootstrap(); boot.group(WORKER_GROUP) .channel(NettyUtils.getClientChannelClass(!(address instanceof InetSocketAddress))); boot.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); boot.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true); boot.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT); if (NettyUtils.USER_CHANNEL_TYPE == ChannelType.EPOLL) { boot.option(EpollChannelOption.EPOLL_MODE, EpollMode.LEVEL_TRIGGERED); } // After 10 missed heartbeat attempts and no write activity, the server will close the channel. final long timeoutMs = Configuration.getMs(PropertyKey.NETWORK_NETTY_HEARTBEAT_TIMEOUT_MS); final long heartbeatPeriodMs = Math.max(timeoutMs / 10, 1); boot.handler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() { @Override public void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(RPCMessage.createFrameDecoder()); pipeline.addLast(ENCODER); pipeline.addLast(DECODER); pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(0, heartbeatPeriodMs, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)); pipeline.addLast(new IdleWriteHandler()); } });
2.临时的处理器:针对通用response注册回调(ShortCircuitBlockHandler 调用)
public static ProtoMessage call(final NettyRPCContext context, ProtoMessage request) throws IOException { Channel channel = Preconditions.checkNotNull(context.getChannel()); final Promise<ProtoMessage> promise = channel.eventLoop().newPromise(); channel.pipeline().addLast(new RPCHandler(promise)); channel.writeAndFlush(new RPCProtoMessage(request)).addListener((ChannelFuture future) -> { if (future.cause() != null) { future.channel().close(); promise.tryFailure(future.cause()); } }); ProtoMessage message; try { message = promise.get(context.getTimeoutMs(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } catch (ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) { CommonUtils.closeChannel(channel); throw new IOException(e); } catch (InterruptedException e) { CommonUtils.closeChannel(channel); throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { if (channel.isOpen()) { channel.pipeline().removeLast(); } } if (message.isResponse()) { CommonUtils.unwrapResponseFrom(message.asResponse(), context.getChannel()); } return message; }
3.临时的处理器:针对读写操作注册回调(BlockHandler)
private NettyPacketReader(FileSystemContext context, WorkerNetAddress address, Protocol.ReadRequest readRequest) throws IOException { mContext = context; mAddress = address; mPosToRead = readRequest.getOffset(); mReadRequest = readRequest; mChannel = mContext.acquireNettyChannel(address); mChannel.pipeline().addLast(new PacketReadHandler()); mChannel.writeAndFlush(new RPCProtoMessage(new ProtoMessage(mReadRequest))) .addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE); } private NettyPacketWriter(FileSystemContext context, final WorkerNetAddress address, long id, long length, long packetSize, Protocol.RequestType type, OutStreamOptions options, Channel channel) { mContext = context; mAddress = address; mLength = length; Protocol.WriteRequest.Builder builder = Protocol.WriteRequest.newBuilder().setId(id).setTier(options.getWriteTier()).setType(type); if (type == Protocol.RequestType.UFS_FILE) { Protocol.CreateUfsFileOptions ufsFileOptions = Protocol.CreateUfsFileOptions.newBuilder().setUfsPath(options.getUfsPath()) .setOwner(options.getOwner()).setGroup(options.getGroup()) .setMode(options.getMode().toShort()).setMountId(options.getMountId()).build(); builder.setCreateUfsFileOptions(ufsFileOptions); } mPartialRequest = builder.buildPartial(); mPacketSize = packetSize; mChannel = channel; mChannel.pipeline().addLast(new PacketWriteResponseHandler()); }
netty服务端:
注册处理器列表:
alluxio.worker.netty.PipelineHandler
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); final long timeoutMs = Configuration.getMs(PropertyKey.NETWORK_NETTY_HEARTBEAT_TIMEOUT_MS); // Decoders & Encoders pipeline.addLast("frameDecoder", RPCMessage.createFrameDecoder()); pipeline.addLast("RPCMessageDecoder", new RPCMessageDecoder()); pipeline.addLast("RPCMessageEncoder", new RPCMessageEncoder()); // Idle Event Handlers pipeline.addLast("idleEventHandler", new IdleStateHandler(timeoutMs, 0, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)); pipeline.addLast("idleReadHandler", new IdleReadHandler()); pipeline.addLast("heartbeatHandler", new HeartbeatHandler()); // Block Handlers pipeline.addLast("blockReadHandler", new BlockReadHandler(NettyExecutors.BLOCK_READER_EXECUTOR, mWorkerProcess.getWorker(BlockWorker.class), mFileTransferType)); pipeline.addLast("blockWriteHandler", new BlockWriteHandler( NettyExecutors.BLOCK_WRITER_EXECUTOR, mWorkerProcess.getWorker(BlockWorker.class), mWorkerProcess.getUfsManager())); pipeline.addLast("shortCircuitBlockReadHandler", new ShortCircuitBlockReadHandler(NettyExecutors.RPC_EXECUTOR, mWorkerProcess.getWorker(BlockWorker.class))); pipeline.addLast("shortCircuitBlockWriteHandler", new ShortCircuitBlockWriteHandler(NettyExecutors.RPC_EXECUTOR, mWorkerProcess.getWorker(BlockWorker.class))); pipeline.addLast("asyncCacheHandler", new AsyncCacheHandler(mRequestManager)); // UFS Handlers pipeline.addLast("ufsFileWriteHandler", new UfsFileWriteHandler( NettyExecutors.FILE_WRITER_EXECUTOR, mWorkerProcess.getUfsManager())); // Unsupported Message Handler pipeline.addLast("unsupportedMessageHandler", new UnsupportedMessageHandler()); }
写入或者读取配置
alluxio.client.file.options.CreateFileOptions是FileSystem类createFile的第二个参数,可以选定不同的写入策略
例如:
- MUST_CACHE(只写入Alluxio,必须存储在Alluxio中)
- CACHE_THROUGH(尝试缓存,同步写入到UnderFS)
- THROUGH(无缓存,同步写入到UnderFS)
- ASYNC_THROUGH(异步写入到UnderFS,实现特性)
FileOutStream createFile(AlluxioURI path, CreateFileOptions options) throws FileAlreadyExistsException, InvalidPathException, IOException, AlluxioException;
而这种写入选项,就是通过在传递netty message时,设置不同的标识,然后在netty中分派到不同的pipeline节点,处理各自的特性的
代码实例:
是否需要写入到ufs,则在UfsFileWriteHandler的acceptMessage方法中进行判断的
alluxio.worker.netty.UfsFileWriteHandler#acceptMessage
protected boolean acceptMessage(Object object) { if (!super.acceptMessage(object)) { return false; } Protocol.WriteRequest request = ((RPCProtoMessage) object).getMessage().asWriteRequest(); return request.getType() == Protocol.RequestType.UFS_FILE; }
欢迎大家访问:
我的博客


