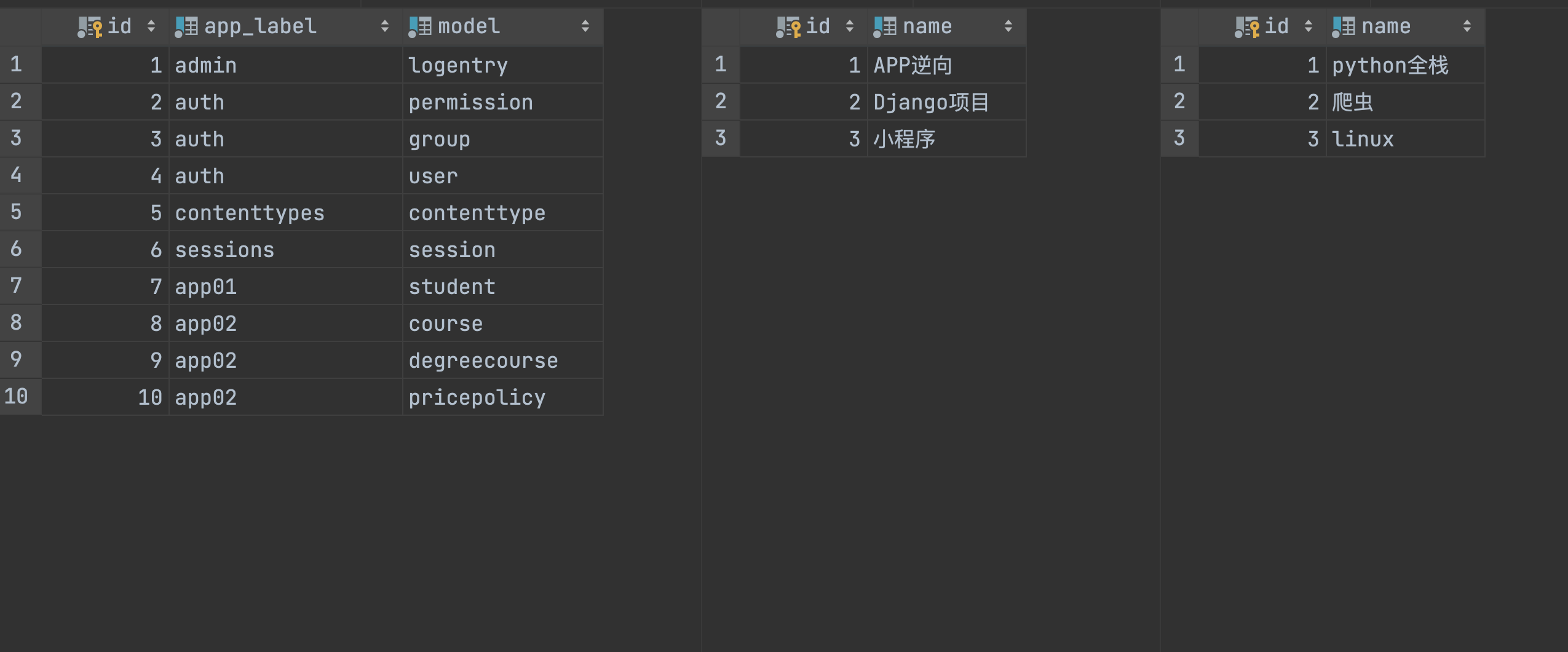
Contenttypes是一个app,将Django中的所有定义的表定义在一张表中
INSTALLED_APPS = [ 'django.contrib.admin', 'django.contrib.auth', 'django.contrib.contenttypes', # **** # 'django.contrib.sessions', 'django.contrib.messages', 'django.contrib.staticfiles', "app01.apps.App01Config", "rest_framework" ]
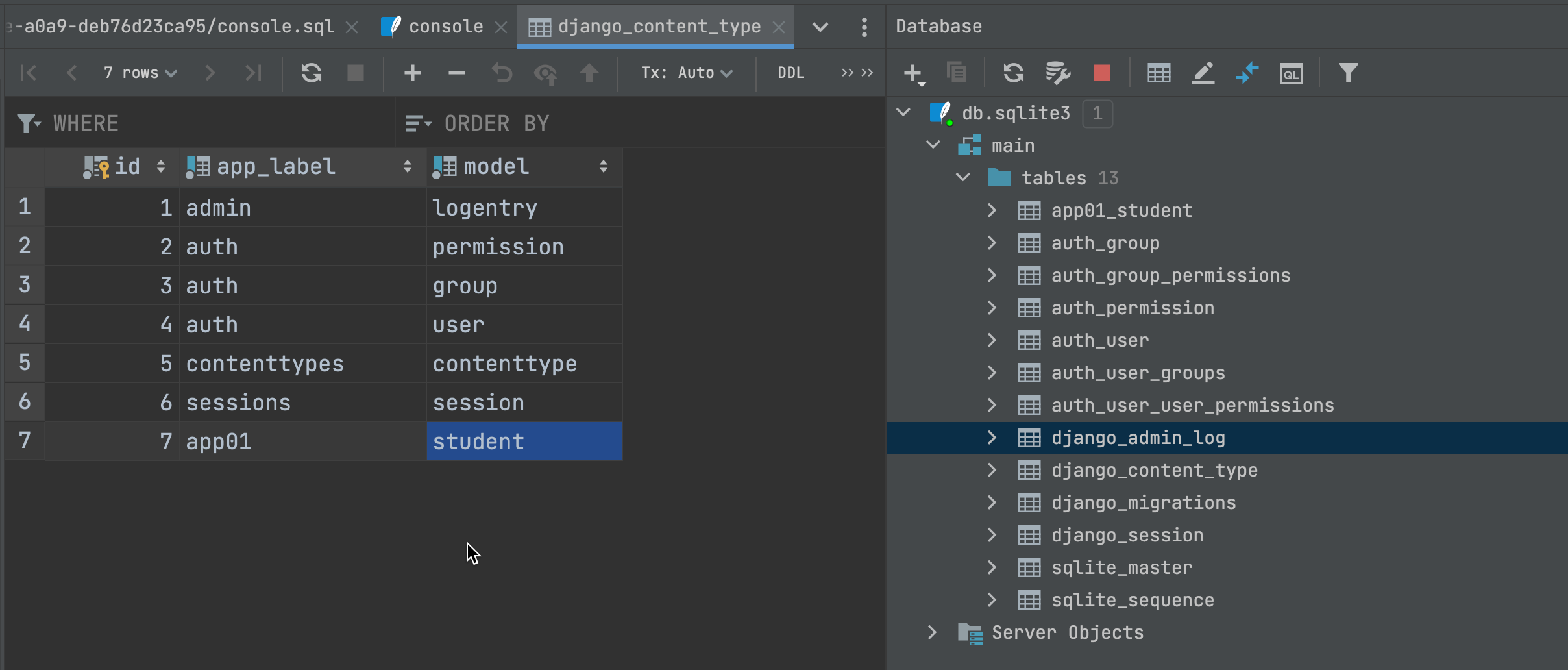
在这个表中最开始保存着每个app的名字和模型类的小写,两者拼接就是数据库中表的名字,如app01_student
使用场景
当一张表关联多张表的时候就可以很好的发挥这个组件的作用了,下面通过一个案例来展示
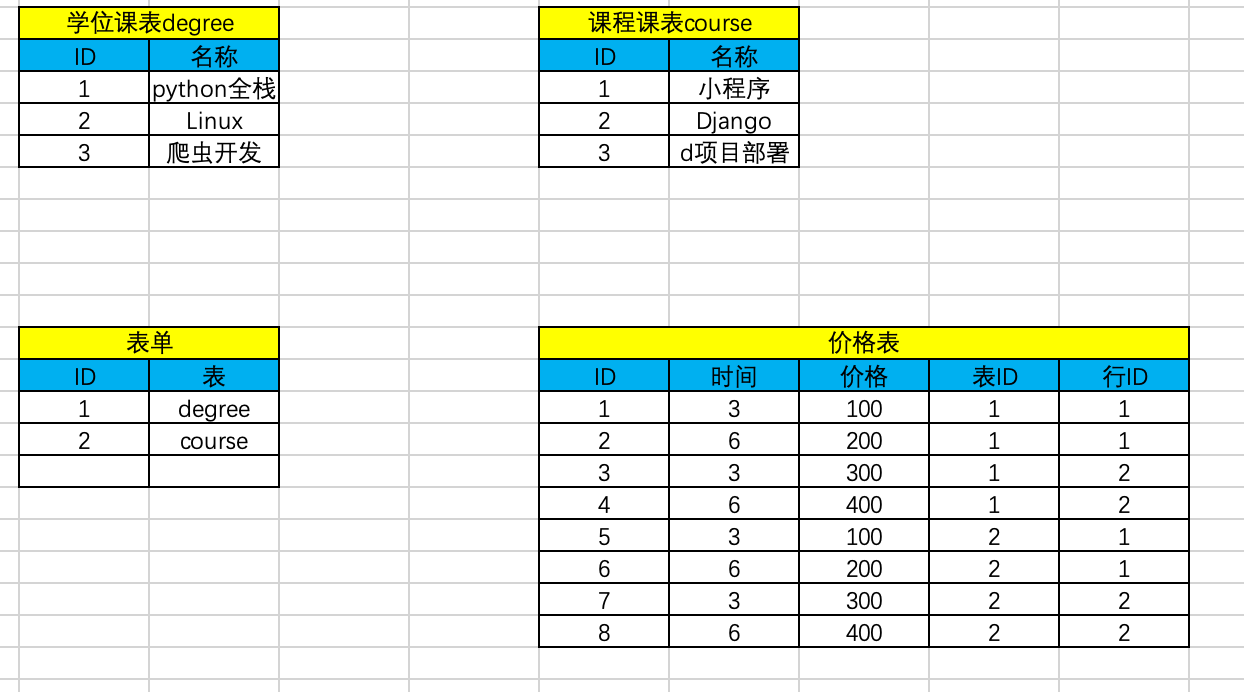
假如有以下两张表
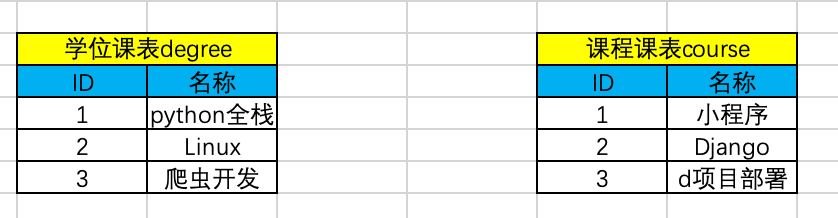
我们希望学位表和课程表中的课程都有不同时间对应的的价格,我们可以很好的想到如下方法
为课程表和学位表再各自创建一个表,实现二者的关系,虽然功能上可以实现,但会产生很多的表
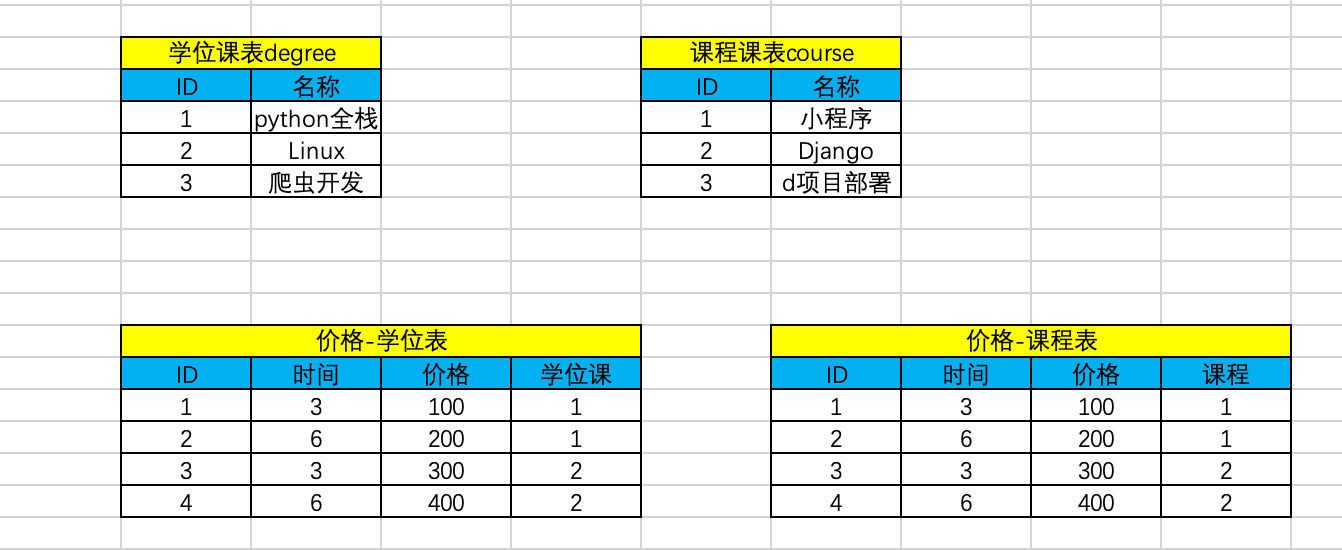
我们可以可改进如下
虽然表的数量减少了,但是会产生很多的NUll字段
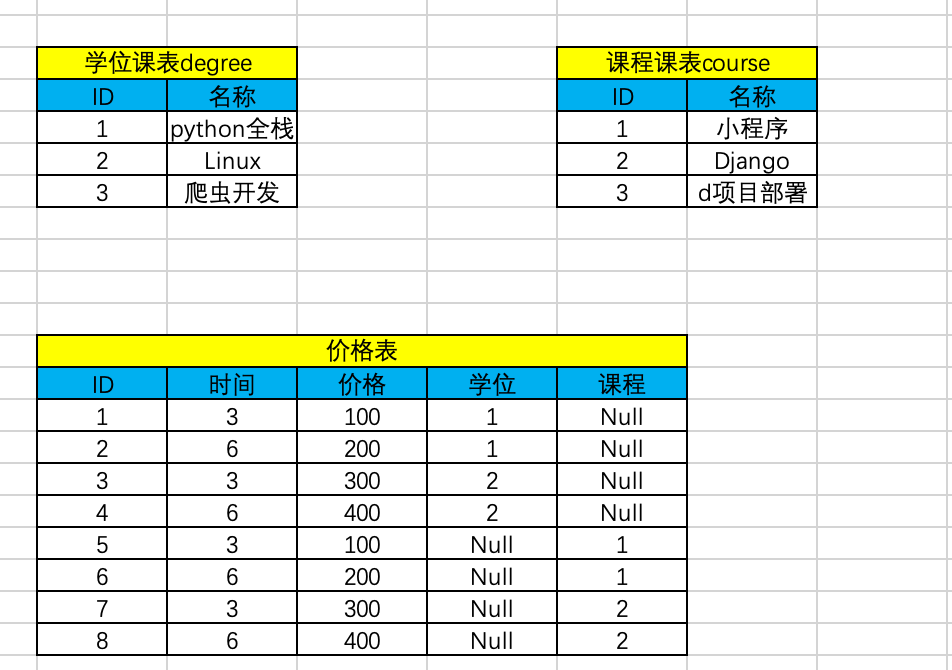
我们就可以使用contenttypes 表
代码展示
模型类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | from django.db import models# Create your models here.from django.db import modelsfrom django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericForeignKey, GenericRelationfrom django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentTypeclass DegreeCourse(models.Model): """学位课程""" name = models.CharField(max_length=128, unique=True)class Course(models.Model): """课程""" name = models.CharField(max_length=128, unique=True)class PricePolicy(models.Model): """价格与有课程效期表""" content_type_id = models.ForeignKey(ContentType, on_delete=models.CASCADE) object_id = models.PositiveIntegerField() time = models.CharField(verbose_name="时间段", max_length=32) price = models.IntegerField(verbose_name="价格") |
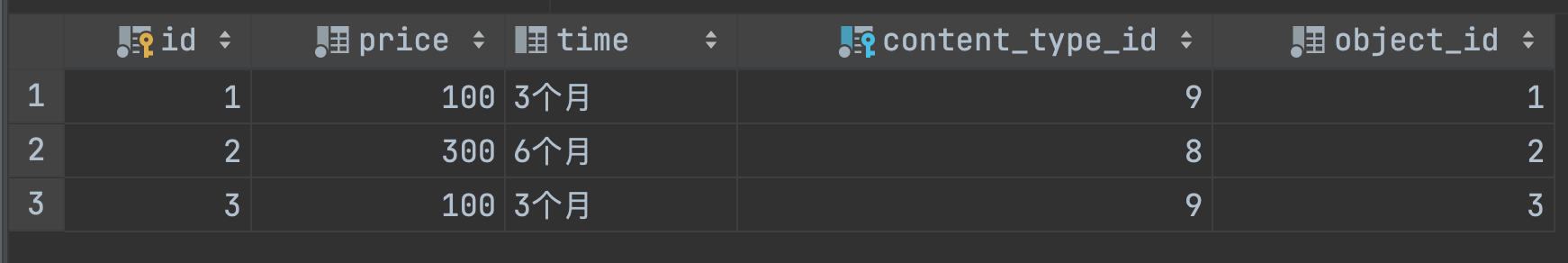
添加数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | def func(request): models.PricePolicy.objects.create( content_type_id=9, # 对应着django_content_type中 degreecourse表id object_id=1, # degreecourse表中的id=1的对象 time="3个月", price=100, ) models.PricePolicy.objects.create( content_type_id=8, object_id=2, time="6个月", price=300 ) |
但是我们还需要去contenttypes表中去寻找表的id和数据行的id,我们修改代码如下
模型类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | from django.db import models# Create your models here.from django.db import modelsfrom django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericForeignKey, GenericRelationfrom django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentTypeclass DegreeCourse(models.Model): """学位课程""" name = models.CharField(max_length=128, unique=True)class Course(models.Model): """课程""" name = models.CharField(max_length=128, unique=True)class PricePolicy(models.Model): """价格与有课程效期表""" content_type = models.ForeignKey(ContentType, on_delete=models.CASCADE) object_id = models.PositiveIntegerField() # 在数据库中不会创建该字段 content_type_object = GenericForeignKey("content_type", "object_id") time = models.CharField(verbose_name="时间段", max_length=32) price = models.IntegerField(verbose_name="价格") |
添加数据
1 2 3 4 5 | models.PricePolicy.objects.create( content_type_object=models.DegreeCourse.objects.filter(name="linux").first(), time="3个月", price=100,) |
查找数据
- 正向查询
12foriteminmodels.PricePolicy.objects.all():print(item.time, item.price, item.content_type_object,item.content_type_object.name)结果
1233个月100DegreeCourseobject(1) python全栈6个月300Courseobject(2) Django项目3个月100DegreeCourseobject(3) linux - 反向查询
需要将模型类代码修改为
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930fromdjango.dbimportmodels# Create your models here.fromdjango.dbimportmodelsfromdjango.contrib.contenttypes.fieldsimportGenericForeignKey, GenericRelationfromdjango.contrib.contenttypes.modelsimportContentTypeclassDegreeCourse(models.Model):"""学位课程"""name=models.CharField(max_length=128, unique=True)degree_price=GenericRelation(to="PricePolicy")classCourse(models.Model):"""课程"""name=models.CharField(max_length=128, unique=True)course_price=GenericRelation(to="PricePolicy")classPricePolicy(models.Model):"""价格与有课程效期表"""content_type=models.ForeignKey(ContentType, on_delete=models.CASCADE)object_id=models.PositiveIntegerField()# 在数据库中不会创建该字段content_type_object=GenericForeignKey("content_type","object_id")time=models.CharField(verbose_name="时间段", max_length=32)price=models.IntegerField(verbose_name="价格")查询代码
123obj=models.DegreeCourse.objects.filter(name="linux").first()foriteminobj.degree_price.all():print(item.price, item.time)
contenttype组件的设计可以帮助我们很好的应景一张表关联多张表,虽然操作简单,表的数量较少,但是却牺牲了查询效率



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」