在django中所有的路由最终都被保存到一个变量 urlpatterns.
1.路由
1.1 传统路由
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path from apps.web import views urlpatterns = [ path('home/', views.home),\ path('news/<int:nid>/edit/', views.news), # 可以传参 ]
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse def home(request): return HttpResponse("成功") def news(request, nid): print(nid) page = request.GET.get("page") return HttpResponse("新闻")
-
-
str,字符串 /
-
slug,字母+数字+下滑线+-
-
uuid,uuid格式
-
1.2 正则匹配路由
正则路由匹配 结合了正则的知识来进行匹配
re_path(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/$', views.year_archive), re_path(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/$', views.month_archive), re_path(r'^articles/(?P<year>[0-9]{4})/(?P<month>[0-9]{2})/$', views.month_archive2),
2.路由分发
在多app中,我们一般不会将所有的路由放在主项目的下的urls.py文件中,会将每个子app下的路由放在自身下的urls.py中,这需要通过主路由的分发
2.1 常规分发
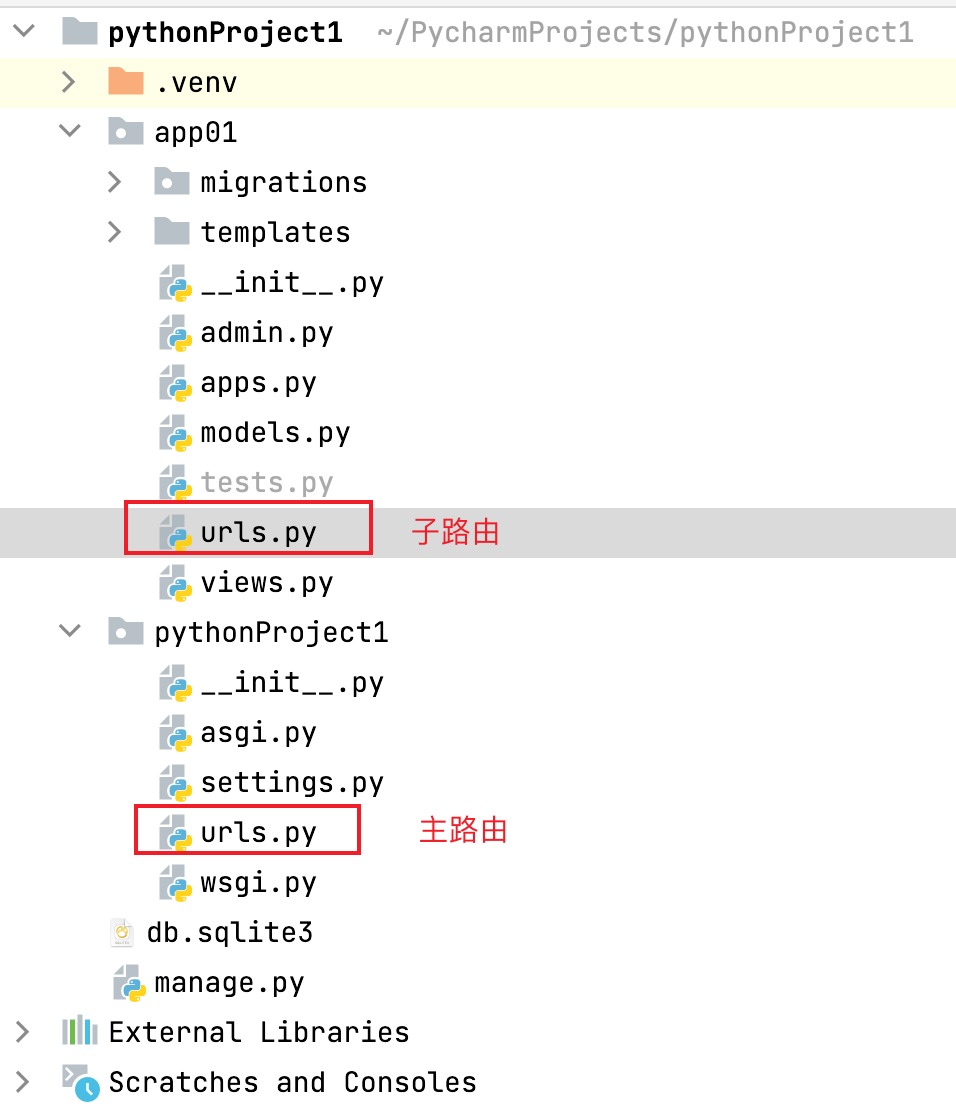
主路由
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, include urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('app01/', include('app01.urls')) ]
子路由
from django.urls import path,include from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ path('index/', views.index), ]
2.2 路由分发的本质
通过查看include函数的源码,我们会发现,include返回的是一个含有3个元素的元组

1 def include(arg, namespace=None): 2 app_name = None 3 if isinstance(arg, tuple): 4 # Callable returning a namespace hint. 5 try: 6 urlconf_module, app_name = arg 7 except ValueError: 8 if namespace: 9 raise ImproperlyConfigured( 10 'Cannot override the namespace for a dynamic module that ' 11 'provides a namespace.' 12 ) 13 raise ImproperlyConfigured( 14 'Passing a %d-tuple to include() is not supported. Pass a ' 15 '2-tuple containing the list of patterns and app_name, and ' 16 'provide the namespace argument to include() instead.' % len(arg) 17 ) 18 else: 19 # No namespace hint - use manually provided namespace. 20 urlconf_module = arg 21 22 if isinstance(urlconf_module, str): 23 urlconf_module = import_module(urlconf_module) 24 patterns = getattr(urlconf_module, 'urlpatterns', urlconf_module) 25 app_name = getattr(urlconf_module, 'app_name', app_name) 26 if namespace and not app_name: 27 raise ImproperlyConfigured( 28 'Specifying a namespace in include() without providing an app_name ' 29 'is not supported. Set the app_name attribute in the included ' 30 'module, or pass a 2-tuple containing the list of patterns and ' 31 'app_name instead.', 32 ) 33 namespace = namespace or app_name 34 # Make sure the patterns can be iterated through (without this, some 35 # testcases will break). 36 if isinstance(patterns, (list, tuple)): 37 for url_pattern in patterns: 38 pattern = getattr(url_pattern, 'pattern', None) 39 if isinstance(pattern, LocalePrefixPattern): 40 raise ImproperlyConfigured( 41 'Using i18n_patterns in an included URLconf is not allowed.' 42 ) 43 return (urlconf_module, app_name, namespace)
# 1. 不使用include函数 path('user/', ([ path('add/', views.login), path('delete/', views.login), # /user/delete/ path('edit/', views.login), path('list/', views.login), ], None, None)), # 2. 使用include,但是参数为字符串,也就是指定子路由的文件路径 path('user/', include("apps.api.urls")), # 一般是每个app中urls # 3. 使用include,使用一个元组为参数 path('user/', include(("apps.api.urls", None))), # 一般是每个app中urls
3.name/namespace
name就是给路由起一个别名,nameapce是为了辅助name的,防止在多app或者多人开发中name重名的问题
在实际开发中,一个url可能是非常长的,我们就可以利用name+ namespace的方式反向生成对应的URL
-
-
模板语法中使用
name的使用
urlpatterns = [ path('login/', views.login, name="v1"), path('auth/', views.auth, name="v2"), ]
namespace的使用
urlpatterns = [ path('api/', include("apps.api.urls",namespace='x1')), path('web/', include("apps.web.urls",namespace='x2')), ]
namespace在路由分发的过程是可以嵌套使用的
namespace1:namespace2:name
4.反向解析
反向解析就是根据路由的namespace和name生成对应的路由
主路由
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, include urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('app01/', include(('app01.urls', 'app01'), namespace='app01')) ]
注意:在指定namespace之后,需要指定app_name
子路由
from django.urls import path, include from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ path('index/<int:nid>', views.index, name='index'), ]
视图中的reverse使用反向解析
def index(request, nid): now_time = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") print(reverse("app01:index", kwargs={"nid": nid})) # /app01/index/88 return render(request, "index.html", {"now_time": now_time, "nid": nid})
模板语法中的url使用反向解析
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <p>{{ now_time }}</p> <p><a href="{% url "app01:index" nid %}">hello</a></p> </body> </html>
5.重定向
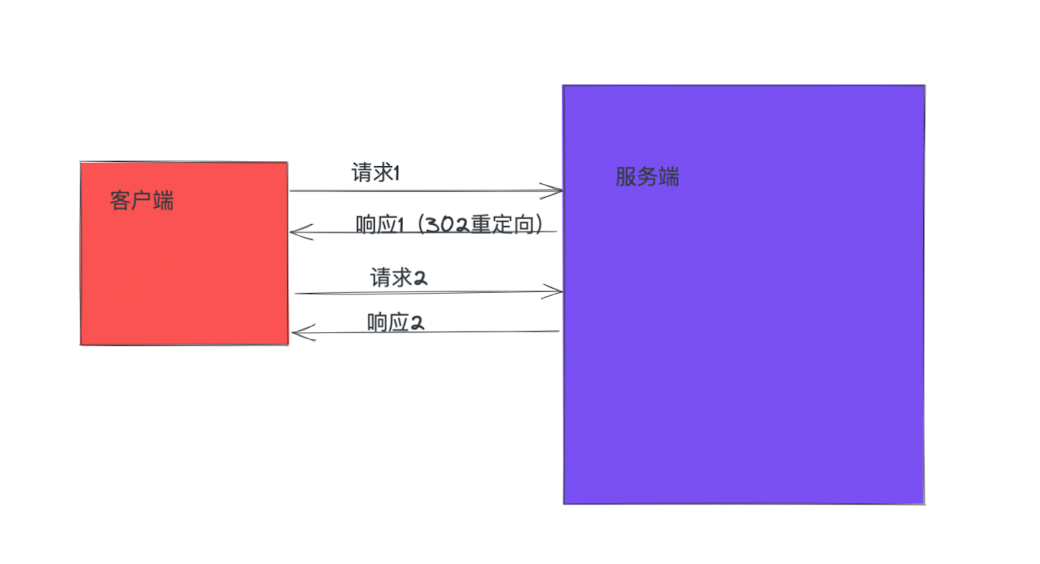
当我们希望客户端主动请求某一个URL的时候,就可以发起重定向,比如用户登录成功,重定到主页页面
通过redirect实现
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse, redirect
from datetime import datetime
from django.urls import reverse
# Create your views here.
def index(request, nid):
now_time = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
print(reverse("app01:index", kwargs={"nid": nid})) # /app01/index/88
# return redirect("https://www.baidu.com/") # 完整url
return redirect(reverse("app01:index", kwargs={"nid": nid})) # 反向生成
6.补充
6.1
路由
path('login/', views.login),
请求
http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/ 成功
http://127.0.0.1:8000/login django,重定向301,发送的是GET
http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/ 成功
path('login', views.login),
http://127.0.0.1:8000/login 成功
http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/ 失败
path('login/', views.login),
http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/ 成功
http://127.0.0.1:8000/login 失败
path('login', views.login),
http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/ 失败
http://127.0.0.1:8000/login 成功
ResolverMatch( func=app01.views.index, # 匹配的视图函数 args=(), # 列表参数 kwargs={'nid': 88}, # 字典参数 url_name=index, # url_name app_names=['app01'], # app_name namespaces=['app01'], # namespace route=app01/index/<int:nid> # router )
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse from datetime import datetime from django.urls import reverse # Create your views here. def index(request, nid): print(request.resolver_match) # 获取当前匹配路由的对象 """ ResolverMatch( func=app01.views.index, args=(), kwargs={'nid': 88}, url_name=index, app_names=['app01'], namespaces=['app01'], route=app01/index/<int:nid> ) """ now_time = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") print(reverse("app01:index", kwargs={"nid": nid})) # /app01/index/88 return render(request, "index.html", {"now_time": now_time, "nid": nid})




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端