VUE源码相关面试题汇总
1.谈一下你对MVVM原理的理解

传统的MVC指的是,用户操作会请求服务端路由,路由拦截分发请求,调用对应的控制器来处理。控制器会获取数据,然后数据与模板结合,将结果返回给前端,页面重新渲染。
数据流是单向的,view——>model——>view
MVVM:传统的前端会将数据手动渲染到页面上,MVVM模式不需要用户手动操作DOM元素,将数据绑定到viewModel层上,会自动将数据渲染到页面中。视图变化会通知viewModel层更新数据,viewModel就是MVVM模式的桥梁。
数据驱动数据流动时双向的,model——>viewModel<——>view
2.请说一下响应式数据的原理
vue2——核心点:Object.defineProperty —— 修改每一个属性
默认Vue在初始化数据时,会给data中的属性使用Object.defineProperty,在获取和设置的进行拦截,重新定义所有属性。当页面取到对应属性时,会进行依赖收集(收集当前组件的watcher)。如果属性发生变化会通知相关依赖进行更新操作。
依赖收集、派发更新的作用:如果没有这项操作,每个数据更新就会去渲染页面,极大的消耗性能。加了这项操作,去监听相关数据的改变,添加到队列里,当所有改变完事儿之后,一起进行渲染(详情见:https://www.dazhuanlan.com/2019/12/10/5dee72f414290/的3)。
vue3——核心点:proxy(代理)—— 直接处理对象
解决了vue2中的处理对象递归、处理数组麻烦的问题(详情见:https://www.dazhuanlan.com/2019/12/10/5dee72f414290/的1,2)
原理:

响应式原理图

源码:
export function defineReactive (
obj: Object,
key: string,
val: any,
customSetter?: ?Function,
shallow?: boolean
) {
const dep = new Dep()
const property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key)
if (property && property.configurable === false) {
return
}
// cater for pre-defined getter/setters
const getter = property && property.get
const setter = property && property.set
if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) {
val = obj[key]
}
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val)//递归处理子
//每一个对象属性添加get、set方法,变为响应式对象
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()//依赖收集
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {
customSetter()
}
// #7981: for accessor properties without setter
if (getter && !setter) return
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
dep.notify()//派发更新
}
})
}
3.vue中时如何检测数组变化的:使用了函数劫持的方式,重写了数组方法
Vue将data中的数组,进行了原型链重写,指向了自己定义的数组原型方法。这样当调用数组api时,可以通知依赖更新。如果数组中包含着引用类型,会对数组中的引用类型再次进行监控。
Object.create(),保存原有原型
原理:

源码:
import { def } from '../util/index'
const arrayProto = Array.prototype
export const arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto)//es6语法,相当于继承一个对象,添加的属性是在原型下
const methodsToPatch = [
'push',
'pop',
'shift',
'unshift',
'splice',
'sort',
'reverse'
]
/**
* Intercept mutating methods and emit events
*/
methodsToPatch.forEach(function (method) {
// cache original method
const original = arrayProto[method]//将原生方法存下来
def(arrayMethods, method, function mutator (...args) {//重写的方法
const result = original.apply(this, args)//原生的方法
const ob = this.__ob__
let inserted
switch (method) {
case 'push':
case 'unshift':
inserted = args
break
case 'splice':
inserted = args.slice(2)
break
}
if (inserted) ob.observeArray(inserted)//数组中新操作的对象进行响应式处理
// notify change
ob.dep.notify()//派发更新,渲染页面
return result
})
})
4.为何vue采用异步渲染?
vue是组件级更新,如果不采用异步更新,那么每次更新数据都会对当前组件重新渲染。为了性能考虑,vue会在本轮数据更新后,再去异步更新视图。
原理:

源码:
export function queueWatcher (watcher: Watcher) {
const id = watcher.id//判断watcher的id是否存在
if (has[id] == null) {
has[id] = true
if (!flushing) {
queue.push(watcher)
} else {
// if already flushing, splice the watcher based on its id
// if already past its id, it will be run next immediately.
let i = queue.length - 1
while (i > index && queue[i].id > watcher.id) {
i--
}
queue.splice(i + 1, 0, watcher)
}
// queue the flush
if (!waiting) {//wating默认为false
waiting = true
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) {
flushSchedulerQueue()
return
}
nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue)//调用nextTick方法,批量更新
}
}
}
5.nextTick实现原理?
nextTick主要是使用了宏任务和微任务,定义了一个异步方法。多次调用nextTick会将方法存入队列中,通过这个异步方法清空当前队列,所以nextTick就是异步方法。
原理:

源码:
export function nextTick (cb?: Function, ctx?: Object) {
let _resolve
callbacks.push(() => {//callbacks是一个数组
if (cb) {
try {
cb.call(ctx)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick')
}
} else if (_resolve) {
_resolve(ctx)
}
})
if (!pending) {//pengding默认为false
pending = true
timerFunc()//调用异步方法
}
// $flow-disable-line
if (!cb && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise(resolve => {
_resolve = resolve
})
}
}
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="initial-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no"> <title>Vue.js elastic header example</title> <!-- Delete ".min" for console warnings in development --> <script src="../../dist/vue.min.js"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css"> <!-- template for the component --> <script type="text/x-template" id="header-view-template"> <button @click="changeMsg" id="button" :style="{width:width+'px'}" v-if="isShow"> {{msg}} </button> </div> </script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <draggable-header-view> </draggable-header-view> </div> <script> Vue.component('draggable-header-view', { template: '#header-view-template', data: function () { return { msg: 'Hello Vue.', width:200, } }, computed: { }, methods: { changeMsg() { this.msg = "Hello world." this.width +=50; console.log("this.$nextTick前",document.getElementById('button').innerHTML); console.log("this.$nextTick前 width",document.getElementById('button').style.width); this.$nextTick(() => { console.log("this.$nextTick",document.getElementById('button').innerHTML); console.log("this.$nextTick width",document.getElementById('button').style.width); }) console.log("this.$nextTick后",document.getElementById('button').innerHTML); console.log("this.$nextTick后 width",document.getElementById('button').style.width); }, } }) new Vue({ el: '#app' }) </script> </body> </html>
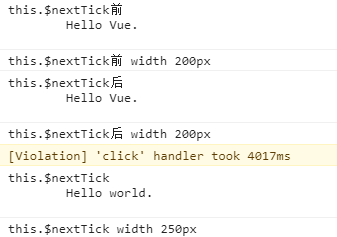
6.vue中computed的特点
默认computed也是一个watcher,具备缓存,只有当依赖的属性发生变化才会更新视图。
原理:

源码:
const computedWatcherOptions = { lazy: true } function initComputed (vm: Component, computed: Object) { ... if (!isSSR) { // create internal watcher for the computed property. watchers[key] = new Watcher( vm, getter || noop,//将用户定义传到watcher中 noop, computedWatcherOptions//lazy:true懒watcher ) } // component-defined computed properties are already defined on the // component prototype. We only need to define computed properties defined // at instantiation here. if (!(key in vm)) { defineComputed(vm, key, userDef) } else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { if (key in vm.$data) { warn(`The computed property "${key}" is already defined in data.`, vm) } else if (vm.$options.props && key in vm.$options.props) { warn(`The computed property "${key}" is already defined as a prop.`, vm) } } } } export function defineComputed ( target: any, key: string, userDef: Object | Function ) { const shouldCache = !isServerRendering() if (typeof userDef === 'function') { sharedPropertyDefinition.get = shouldCache ? createComputedGetter(key)//创建计算属性的getter,不是用用户传的 : createGetterInvoker(userDef) sharedPropertyDefinition.set = noop } else { sharedPropertyDefinition.get = userDef.get ? shouldCache && userDef.cache !== false ? createComputedGetter(key) : createGetterInvoker(userDef.get) : noop sharedPropertyDefinition.set = userDef.set || noop } if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && sharedPropertyDefinition.set === noop) { sharedPropertyDefinition.set = function () { warn( `Computed property "${key}" was assigned to but it has no setter.`, this ) } } Object.defineProperty(target, key, sharedPropertyDefinition) } function createComputedGetter (key) { return function computedGetter () {//用户取值的时候会调用此方法 const watcher = this._computedWatchers && this._computedWatchers[key] if (watcher) { if (watcher.dirty) {//dirty为true会去进行求值,这儿的dirty起到了缓存的作用 watcher.evaluate() } if (Dep.target) { watcher.depend() } return watcher.value } } }
7.watch中的deep:true是如何实现的?
当用户指定了watch中的deep属性为true时,如果当时监控的属性是数组类型,会对对象中的每一项进行求值,此时会将当前watcher存入到对应属性的依赖中,这样数组中对象发生变化时也会通知数据更新。
内部原理就是递归,耗费性能 。
traverse
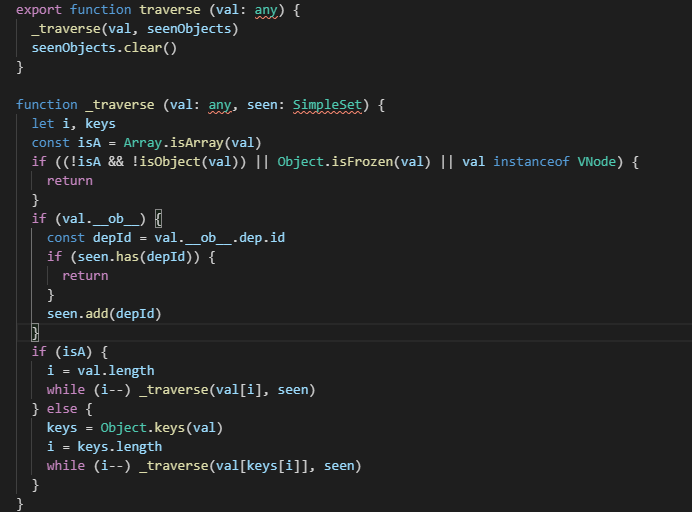
详解:https://www.cnblogs.com/vickylinj/p/14034909.html
8.vue组件的生命周期
每个生命周期什么时候被调用
- beforeCreate 在实例初始化new Vue()之后,数据观测(data observer)响应式处理之前被调用
- created 实例已经创建完成之后被调用,实例已完成以下的配置:数据观测(data observer)、属性和方法的运算、watch/event事件回调。数据可以拿到,但是没有$el。
- beforeMount 在挂载开始之前被调用:相关的render函数首次被调用。//template
- mounted el被新创建的vm.$el替换,并挂载到实例上去之后被调用。页面渲染完毕
- beforeUpdate 数据更新时调用,发生在虚拟DOM重新渲染和打补丁之前。
- updated 由于数据更改导致的虚拟DOM重新渲染和打补丁,在这之后会调用该钩子。
- beforeDestroy 实例销毁之前调用,在这一步,实例仍然完全可用。
- destroyed Vue实例销毁后调用。调用后,Vue实例指示的所有东西都会解绑定,所有的事件监听器会被移除,所有的子实例也会被销毁。该钩子在服务器端渲染期间不被调用。
每个生命周期内部可以做什么事
- created 实例已经创建完成,因为它时最早触发的,可以进行一些数据资源的请求。
- mounted 实例已经挂载完成,可以进行一些DOM操作。
- beforeUpdate 可以在这个钩子中进一步地更改状态,不会触发附加的重渲染过程。
- updated 可以执行依赖于DOM的操作,尽量避免在此期间更改状态,因为可能会导致更新无限循环。该钩子在服务器端渲染期间不被调用。
- destroyed 可以执行一些优化操作,清空定时器,解除绑定事件。

原理:


9.ajax请求放在哪个生命周期中?
在created的时候,视图中的dom并没有被渲染出来,所以此时如果直接去操作dom节点,无法找到相关元素。
在mounted中,由于此时的dom元素已经渲染出来了,所以可以直接使用dom节点。
因此,一般情况下,都放在mounted中,保证逻辑的统一性。因为生命周期是同步执行的,ajax是异步执行的。
但是,服务端渲染不支持mounted方法,所以在服务端渲染的情况下统一放在created中。
10.何时需要使用beforeDestroy?
可能在当前组件使用了$on方法,需要在组件销毁前解绑
清除自己定义的定时器
解除事件的原生绑定scroll、mousemove…
11.vue中模板编译原理
模板(template)》 ast语法树(抽象语法树)》 codegen方法 ==》render函数 ==》createElement方法 ==》 Virtual Dom(虚拟dom)
模板转语法树

模板结合数据,生成抽象语法树,描述html、js语法

语法树生成render函数

render函数
生成Virtual Dom(虚拟dom),描述真实的dom节点

渲染成真实dom

12.vue中v-if和v-show的区别
v-if如果条件不成立,不会渲染当前指令所在节点的dom元素

v-show切换当前dom的显示和隐藏,本质上display:none

13.为什么v-for和v-if不能连用?
v-for会比v-if的优先级高一些,如果连用的话,会把v-if给每个元素都添加一下,会造成性能问题。
如果确实需要判断每一个,可以用计算属性来解决,先用计算属性将满足条件的过滤出来,然后再去循环。
14.用vnode来描述一个dom结构


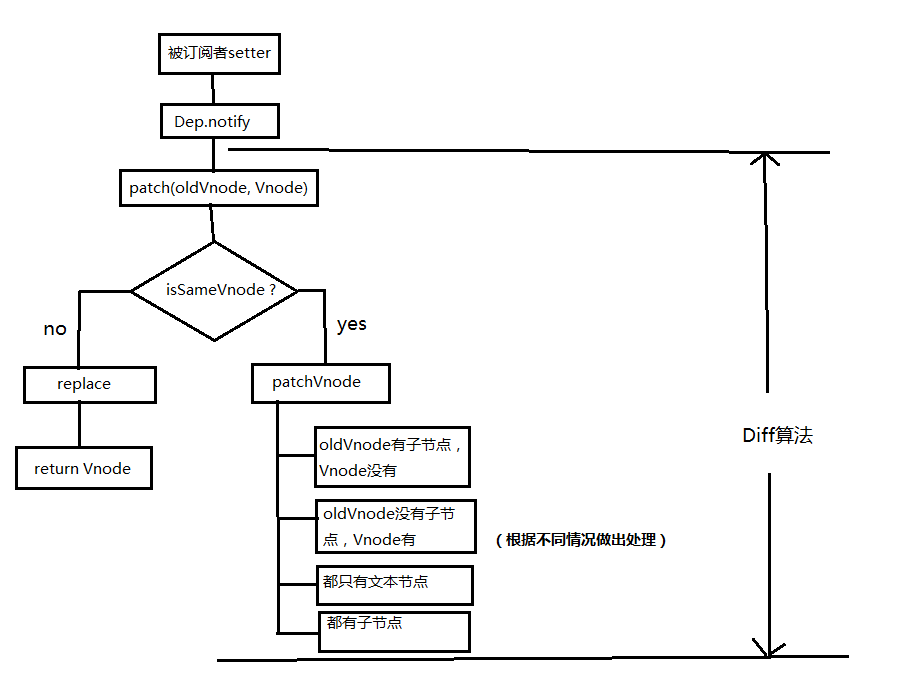
15.diff算法的时间复杂度
15.1、两个树完全diff算法的时间复杂度为O(n3):
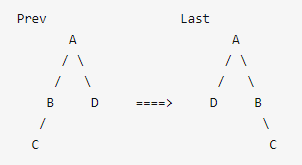
就上面两树的变化而言,若要达到最小更新,首先要对比每个节点是否相同,也就是:

查找不同就需要O(n^2),找到差异后还要计算最小转换方式,最终结果为O(n^3)。
15.2、Vue中的diff算法进行了优化,只考虑同级不考虑跨级,将时间复杂度降为O(n)。前端当中,很少会跨层级的移动Dom元素,所以Virtual Dom只会对同一个层级的元素进行对比。
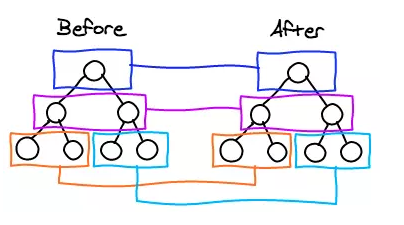
16.简述vue中diff算法原理
diff流程图
diff算法原理
1、先同级比较,再比较儿子节点
2、先判断一方有儿子一方没儿子的情况
3、比较都有儿子的情况
4、递归比较子节点
vue3中做了优化,只比较动态节点,略过静态节点,极大的提高了效率
双指针去确定位置
diff算法原理图

核心源码:
function updateChildren (parentElm, oldCh, newCh, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) { let oldStartIdx = 0 let newStartIdx = 0 let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1 let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0] let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx] let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1 let newStartVnode = newCh[0] let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx] let oldKeyToIdx, idxInOld, vnodeToMove, refElm // removeOnly is a special flag used only by <transition-group> // to ensure removed elements stay in correct relative positions // during leaving transitions const canMove = !removeOnly if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { checkDuplicateKeys(newCh) } while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) { if (isUndef(oldStartVnode)) { oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] // Vnode has been moved left } else if (isUndef(oldEndVnode)) { oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx] } else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) { patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx) oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx] } else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) { patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newEndIdx) oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx] newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx] } else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) { // Vnode moved right patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newEndIdx) canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, nodeOps.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm)) oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx] } else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) { // Vnode moved left patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx) canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm) oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx] newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx] } else { if (isUndef(oldKeyToIdx)) oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx) idxInOld = isDef(newStartVnode.key) ? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key] : findIdxInOld(newStartVnode, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx) if (isUndef(idxInOld)) { // New element createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx) } else { vnodeToMove = oldCh[idxInOld] if (sameVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode)) { patchVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx) oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, vnodeToMove.elm, oldStartVnode.elm) } else { // same key but different element. treat as new element createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx) } } newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx] } } if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) { //取得兄弟节点 refElm = isUndef(newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm
//oldCh先遍历完,将多余的节点根据index添加到dom中去 addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx, insertedVnodeQueue) } else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
//newCh先遍历完,那么就在真实dom中将区间为[oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx]的多余节点删掉
removeVnodes(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx) } }
17.v-for中为什么要用key?
解决vue中diff算法结构相同key相同,内容复用的问题,通过key(最好自定义id,不要用索引),明确dom元素,防止复用
源码:
function sameVnode (a, b) { return ( a.key === b.key && ( ( a.tag === b.tag && a.isComment === b.isComment && isDef(a.data) === isDef(b.data) && sameInputType(a, b) ) || ( isTrue(a.isAsyncPlaceholder) && a.asyncFactory === b.asyncFactory && isUndef(b.asyncFactory.error) ) ) ) }
详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/vickylinj/p/14036812.html
18.描述组件渲染和更新过程
渲染组件时,会通过Vue.extend方法构建子组件的构造函数,并进行实例化,最终手动调用$mount进行挂载,如下图。渲染组件时进行createElm流程分支,而更新组件时会进行patchVnode流程分支,核心就是diff算法。
图示:组件渲染流程
19.组件中的data为什么是个函数?
同一个组件被复用多次,会创建多个实例。这些实例用的是同一个构造函数,如果data是一个对象的话,所有组件共享了同一个对象。为了保证组件的数据独立性,要求每个组件都必须通过data函数返回一个对象作为组件的状态。
20.Vue中事件绑定的原理
Vue的事件绑定分为两种:一种是原生的事件绑定,一种是组件的事件绑定
原生dom事件绑定采用的是addEventListener
组件的事件绑定采用的是$on方法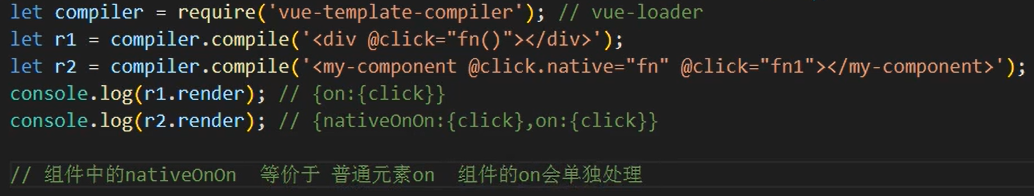

21.v-model的实现原理及如何自定义v-model?
v-model可以看成是value+input方法的语法糖



不同的标签去触发不同的方法
22.vue中的v-html会导致哪些问题
可能会导致XXS攻击
v-html会替换掉标签内的子元素
原理:
23.vue父子组件生命周期调用顺序
加载渲染过程
父beforeCreate ==> 父created ==> 父beforeMount ==> 子beforeCreat ==>子created ==> 子beforeMount ==> 子mounted ==> 父mounted
子组件更新过程
父beforeUpdate ==> 子beforeUpdate ==> 子updated ==> 父updated
父组件更新过程
父beforeUpdate ==> 父updated
销毁过程
父beforeDestroy ==> 子beforeDestroy ==> 子destroyed ==> 父destroyed
理解
组件的调用顺序都是先父后子,渲染完成的顺序是先子后父
组件的销毁操作是先父后子,销毁完成的顺序是先子后父
原理图

24.vue组件如何通信?(单向数据流)
- 父子间通信 父 ==> 子通过props ,子 ==> 父通过$on、$emit(发布订阅)
- 通过获取父子组件实例的方式$parent、$children
- 在父组件中提供数据,子组件进行消费 Provide、Inject(插件必备)
- Ref获取实例的方式调用组件的属性和方法
- Event Bus实现跨组件通信 Vue.prototype.$bus = new Vue,全局就可以使用$bus
- Vuex状态管理实现通信
25.vue中相同逻辑如何抽离
Vue.mixin用法给组件每个生命周期、函数都混入一些公共逻辑
Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate(){}//这儿定义的生命周期和方法会在每个组件里面拿到 })
源码:
import { mergeOptions } from '../util/index'
export function initMixin (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
Vue.mixin = function (mixin: Object) {
this.options = mergeOptions(this.options, mixin)//将当前定义的属性合并到每个组件中
return this
}
}
export function mergeOptions (
parent: Object,
child: Object,
vm?: Component
): Object {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
checkComponents(child)
}
if (typeof child === 'function') {
child = child.options
}
normalizeProps(child, vm)
normalizeInject(child, vm)
normalizeDirectives(child)
// Apply extends and mixins on the child options,
// but only if it is a raw options object that isn't
// the result of another mergeOptions call.
// Only merged options has the _base property.
if (!child._base) {
if (child.extends) {//递归合并extends
parent = mergeOptions(parent, child.extends, vm)
}
if (child.mixins) {//递归合并mixin
for (let i = 0, l = child.mixins.length; i < l; i++) {
parent = mergeOptions(parent, child.mixins[i], vm)
}
}
}
const options = {}//属性及生命周期的合并
let key
for (key in parent) {
mergeField(key)
}
for (key in child) {
if (!hasOwn(parent, key)) {
mergeField(key)
}
}
function mergeField (key) {
const strat = strats[key] || defaultStrat
options[key] = strat(parent[key], child[key], vm, key)
}
return options
}
26.为什么要使用异步组件?
如果组件功能多,打包出的结果会变大,可以采用异步组件的方式来加载组件。主要依赖import()这个语法,可以实现文件的分割加载。
27.插槽和作用域插槽
渲染的作用域不同,普通插槽是父组件,作用域插槽是子组件
插槽
- 创建组件虚拟节点时,会将组件的儿子的虚拟节点保存起来。当初始化组件时,通过插槽属性将儿子进行分类,{a:[vnode],b:[vnode]}
- 渲染组件时,会拿对应的slot属性的节点进行替换操作。(插槽的作用域为父组件)


作用域插槽
- 作用域插槽在解析的时候,不会作为组件的儿子节点,会解析成函数。当子组件渲染时,调用此函数进行渲染。(插槽的作用域为父组件)


原理:
28.谈谈你对keep-alive的理解(一个组件)
keep-alive可以实现组件的缓存,当组件切换时,不会对当前组件卸载
常用的2个属性include、exclude
常用的2个生命周期activated、deactivated
源码:
export default { name: 'keep-alive', abstract: true,//抽象组件 props: { include: patternTypes, exclude: patternTypes, max: [String, Number] }, created () { this.cache = Object.create(null)//创建缓存列表 this.keys = []//创建缓存组件的key列表 }, destroyed () {//keep-alive销毁时,会清空所有的缓存和key for (const key in this.cache) {//循环销毁 pruneCacheEntry(this.cache, key, this.keys) } }, mounted () {//会监控include和exclude属性,进行组件的缓存处理 this.$watch('include', val => { pruneCache(this, name => matches(val, name)) }) this.$watch('exclude', val => { pruneCache(this, name => !matches(val, name)) }) }, render () { const slot = this.$slots.default//默认拿插槽 const vnode: VNode = getFirstComponentChild(slot)//只缓存第一个组件 const componentOptions: ?VNodeComponentOptions = vnode && vnode.componentOptions if (componentOptions) { // check pattern const name: ?string = getComponentName(componentOptions)//取出组件的名字 const { include, exclude } = this if (//判断是否缓存 // not included (include && (!name || !matches(include, name))) || // excluded (exclude && name && matches(exclude, name)) ) { return vnode } const { cache, keys } = this const key: ?string = vnode.key == null // same constructor may get registered as different local components // so cid alone is not enough (#3269) ? componentOptions.Ctor.cid + (componentOptions.tag ? `::${componentOptions.tag}` : '') : vnode.key//如果组件没key,就自己通过组件的标签和key和cid拼接一个key if (cache[key]) { vnode.componentInstance = cache[key].componentInstance//直接拿到组件实例 // make current key freshest remove(keys, key)//删除当前的[b,c,d,e,a] //LRU最近最久未使用法 keys.push(key)//将key放到后面[b,a] } else { cache[key] = vnode//缓存vnode keys.push(key)//将key存入 // prune oldest entry if (this.max && keys.length > parseInt(this.max)) {//缓存的太多,超过了max就需要删除掉 pruneCacheEntry(cache, keys[0], keys, this._vnode)//要删除第0个,但是渲染的就是第0个 } } vnode.data.keepAlive = true//标准keep-alive下的组件是一个缓存组件 } return vnode || (slot && slot[0])//返回当前的虚拟节点 } }
29.Vue中常见性能优化
一个优秀的Vue团队代码规范是什么样子的?
1、编码优化
- 不要将所有的数据都放到data中,data中的数据都会增加getter、setter,会收集对应的watcher
- vue在v-for时给每项元素绑定事件需要用事件代理
- SPA页面采用keep-alive缓存组件
- 拆分组件(提高复用性、增加代码的可维护性,减少不必要的渲染)
- v-if当值为false时,内部指令不会执行,具有阻断功能。很多情况下使用v-if替换v-show
- key保证唯一性(默认vue会采用就地复用策略)
- Object.freeze冻结数据
- 合理使用路由懒加载、异步组件
- 数据持久化的问题,防抖、节流
2、Vue加载性能优化
-
- 第三方模块按需导入(babel-plugin-component)
- 滚动到可视区域动态加载(https://tangbc.github.io/vue-virtual-scroll-list)
- 图片懒加载(https://github.com/hilongjw/vue-lazyload.git)
3、用户体验
-
- app-skeleton骨架屏
- app shell app壳
- pwa
4、SEO优化
-
- 预渲染插件prerender-spa-plugin
- 服务端渲染ssr
5、打包优化
-
- 使用cdn的方式加载第三方模块
- 多线程打包happypack
- splitChunks抽离公共文件
- sourceMap生成
6、缓存压缩
-
- 客户端缓存、服务端缓存
- 服务端gzip压缩
30.Vue3.0的改进
- 采用了TS来编写
- 支持composition API
- 响应式数据原理改成了proxy
- diff对比算法更新,只更新vdom绑定了动态数据的部分
31.实现hash路由和history路由
- onhashchange #
- history.pushState h5 api
32.Vue-Router中导航守卫有哪些
完整的导航解析流程 runQueue
33.action和mutation区别
- mutation是同步更新数据(内部会进行是否为异步方式更新的数据检测)
- action异步操作,可以获取数据后调用mutation提交最终数据
34.简述Vuex工作原理
35.vue3今年发布了,请你说一下他们之间在响应式的实现上有什么区别?
vue2采用的是defineProperty去定义get,set,而vue3改用了proxy。也代表着vue放弃了兼容ie。
36.像vue-router,vuex他们都是作为vue插件,请说一下他们分别都是如何在vue中生效的?
通过vue的插件系统,用vue.mixin混入到全局,在每个组件的生命周期的某个阶段注入组件实例。
37.请你说一下vue的设计架构。
vue2采用的是典型的混入式架构,类似于express和jquery,各部分分模块开发,再通过一个mixin去混入到最终暴露到全局的类上。
简述一个框架的同时,说出他的设计来源、类似的框架。
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40970987/article/details/106396285
https://www.dazhuanlan.com/2019/12/10/5dee72f414290/
7.2queueWatcher(src\core\observer\scheduler.js):



