排序算法(六)基数排序
时间复杂度:O(P(N+B))
空间复杂度:O(N+B)
稳定性:稳定
其他排序算法都假定排序记录只有一个关键字,基数排序讨论待排序记录有多个关键字的排序问题。
次位优先
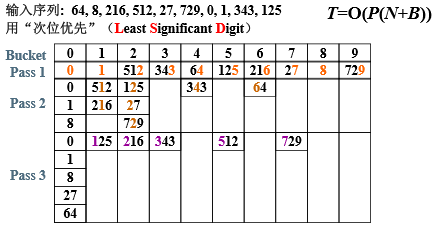
/* 基数排序 - 次位优先 */ /* 假设元素最多有MaxDigit个关键字,基数全是同样的Radix */ #define MaxDigit 4 #define Radix 10 /* 桶元素结点 */ typedef struct Node *PtrToNode; struct Node { int key; PtrToNode next; }; /* 桶头结点 */ struct HeadNode { PtrToNode head, tail; }; typedef struct HeadNode Bucket[Radix]; int GetDigit ( int X, int D ) { /* 默认次位D=1, 主位D<=MaxDigit */ int d, i; for (i=1; i<=D; i++) { d = X % Radix; X /= Radix; } return d; } void LSDRadixSort(ElementType A[], int N ) { /* 基数排序 - 次位优先 */ int D, Di, i; Bucket B; PtrToNode tmp, p, List = NULL; for (i=0; i<Radix; i++) /* 初始化每个桶为空链表 */ B[i].head = B[i].tail = NULL; for (i=0; i<N; i++) { /* 将原始序列逆序存入初始链表List */ tmp = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); tmp->key = A[i]; tmp->next = List; List = tmp; } /* 下面开始排序 */ for (D=1; D<=MaxDigit; D++) { /* 对数据的每一位循环处理 */ /* 下面是分配的过程 */ p = List; while (p) { Di = GetDigit(p->key, D); /* 获得当前元素的当前位数字 */ /* 从List中摘除 */ tmp = p; p = p->next; /* 插入B[Di]号桶尾 */ tmp->next = NULL; if (B[Di].head == NULL) B[Di].head = B[Di].tail = tmp; else { B[Di].tail->next = tmp; B[Di].tail = tmp; } } /* 下面是收集的过程 */ List = NULL; for (Di=Radix-1; Di>=0; Di--) { /* 将每个桶的元素顺序收集入List */ if (B[Di].head) { /* 如果桶不为空 */ /* 整桶插入List表头 */ B[Di].tail->next = List; List = B[Di].head; B[Di].head = B[Di].tail = NULL; /* 清空桶 */ } } } /* 将List倒入A[]并释放空间 */ for (i=0; i<N; i++) { tmp = List; List = List->next; A[i] = tmp->key; free(tmp); } }
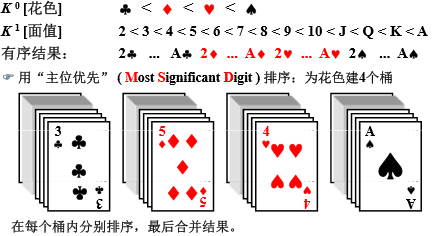
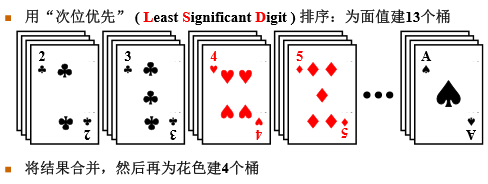
主位优先和次位优先


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号