07 -模型层ORM
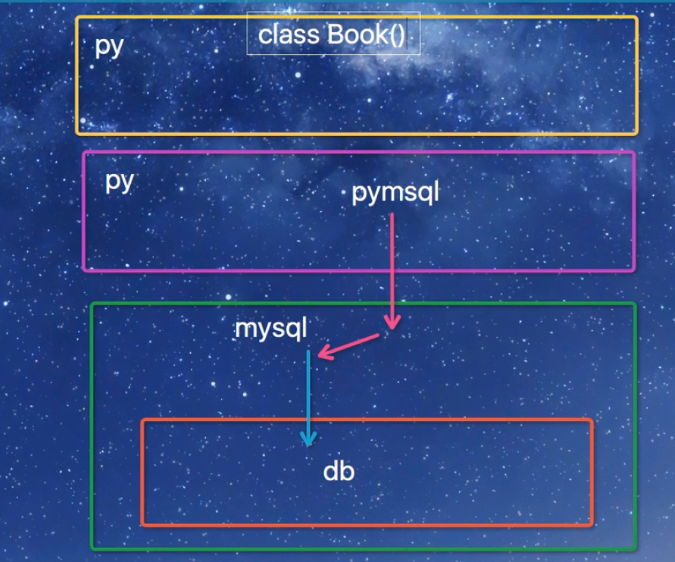
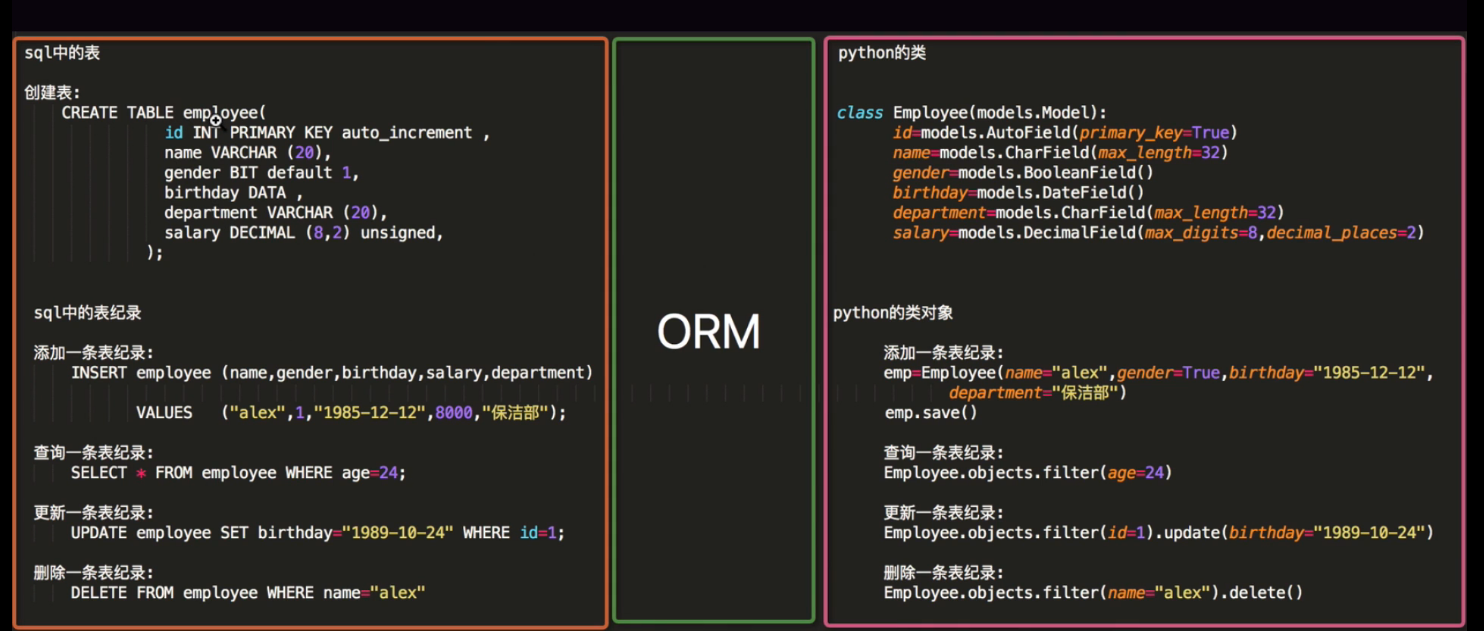
1、orm简介
2、
models.py
from django.db import models # Create your models here. class Book(models.Model): id = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) title = models.CharField(max_length=32, unique=True) state = models.BooleanField() pub_date = models.DateField() price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=8, decimal_places=2) # 999999.00 publish = models.CharField(max_length=22) # 10000000.00 溢出
C:\Windows\system32>mysql -uroot -proot mysql> create database orm; # 创建orm数据库 Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
settings默认sqlite3数据库

设置database为mysql
DATABASES = { 'default': { 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql', 'NAME': 'orm', # 要连接的数据库,连接前需要创建好 'USER': 'root', # 连接数据库的用户名 'PASSWORD': 'root', # 连接数据库的密码 'HOST': '127.0.0.1', # 连接主机,默认本级 'PORT': 3306, # 端口 默认3306 } }
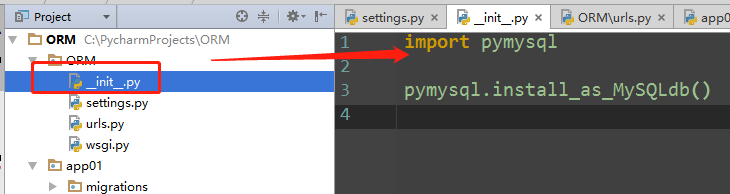
(3)django调用的是pymysql
报错:
E:\PycharmProjects\cnblog>python manage.py makemigrations Traceback (most recent call last): File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\db\backends\mysql\base.py", line 15, in <module> import MySQLdb as Database ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'MySQLdb' The above exception was the direct cause of the following exception: Traceback (most recent call last): File "manage.py", line 15, in <module> execute_from_command_line(sys.argv) File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\core\management\__init__.py", line 371, in execute_from_command_line utility.execute() File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\core\management\__init__.py", line 347, in execute django.setup() File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\__init__.py", line 24, in setup apps.populate(settings.INSTALLED_APPS) File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\apps\registry.py", line 112, in populate app_config.import_models() File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\apps\config.py", line 198, in import_models self.models_module = import_module(models_module_name) File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\importlib\__init__.py", line 126, in import_module return _bootstrap._gcd_import(name[level:], package, level) File "<frozen importlib._bootstrap>", line 994, in _gcd_import File "<frozen importlib._bootstrap>", line 971, in _find_and_load File "<frozen importlib._bootstrap>", line 955, in _find_and_load_unlocked File "<frozen importlib._bootstrap>", line 665, in _load_unlocked File "<frozen importlib._bootstrap_external>", line 678, in exec_module File "<frozen importlib._bootstrap>", line 219, in _call_with_frames_removed File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\contrib\auth\models.py", line 2, in <module> from django.contrib.auth.base_user import AbstractBaseUser, BaseUserManager File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\contrib\auth\base_user.py", line 47, in <module> class AbstractBaseUser(models.Model): File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\db\models\base.py", line 114, in __new__ new_class.add_to_class('_meta', Options(meta, app_label)) File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\db\models\base.py", line 315, in add_to_class value.contribute_to_class(cls, name) File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\db\models\options.py", line 205, in contribute_to_class self.db_table = truncate_name(self.db_table, connection.ops.max_name_length()) File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\db\__init__.py", line 33, in __getattr__ return getattr(connections[DEFAULT_DB_ALIAS], item) File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\db\utils.py", line 202, in __getitem__ backend = load_backend(db['ENGINE']) File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\db\utils.py", line 110, in load_backend return import_module('%s.base' % backend_name) File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\importlib\__init__.py", line 126, in import_module return _bootstrap._gcd_import(name[level:], package, level) File "C:\Users\Venicid\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\lib\site-packages\django\db\backends\mysql\base.py", line 20, in <module> ) from err django.core.exceptions.ImproperlyConfigured: Error loading MySQLdb module.
解决:
__init__.py
import pymysql pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()
注意2:确保配置文件中的INSTALLED_APPS中写入我们创建的app名称
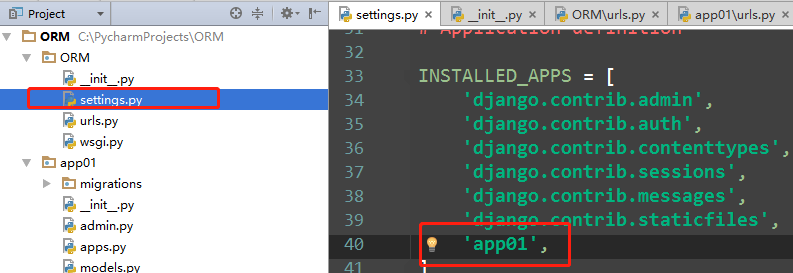
注意3:如果报错的话
django.core.exceptions.ImproperlyConfigured: mysqlclient 1.3.3 or newer is required; you have 0.7.11.None
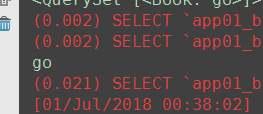
注意4: 如果想打印orm转换过程中的sql,需要在settings中进行如下配置:
LOGGING = { 'version': 1, 'disable_existing_loggers': False, 'handlers': { 'console':{ 'level':'DEBUG', 'class':'logging.StreamHandler', }, }, 'loggers': { 'django.db.backends': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'propagate': True, 'level':'DEBUG', }, } }

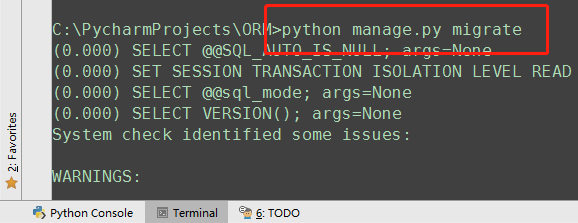
最后通过两条数据库迁移命令即可在指定的数据库中创建表 :
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
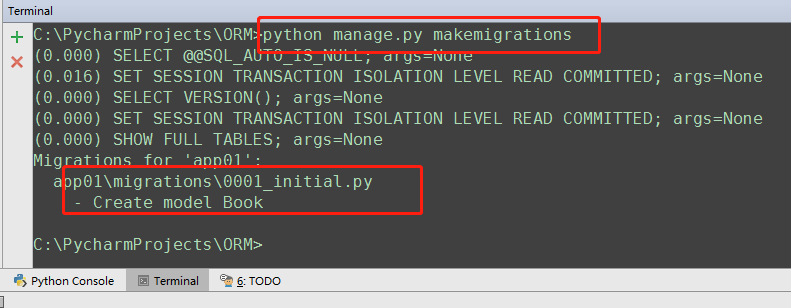
插入数据,创建表
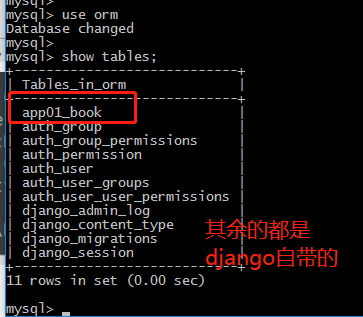
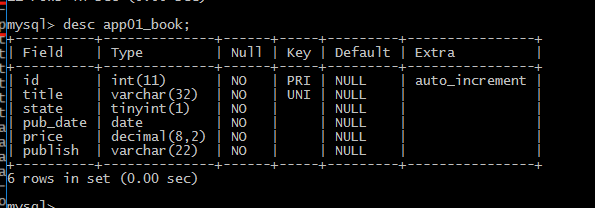
3、单表操作之添加记录
url
from django.urls import path, re_path, include from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ re_path(r'^index/$', views.index, name='index') ]
方法1:
view
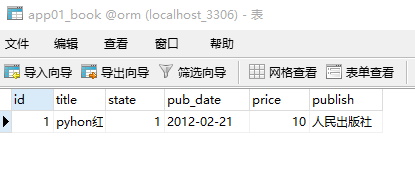
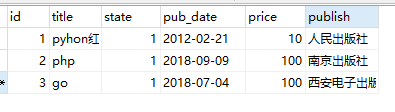
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse # Create your views here. from app01.models import Book # 导入Book对象 def index(request): # 添加表记录 # 方式1: # 所有字段必须和modles的一一对应 book_obj = Book( id=1, title='pyhon红宝书', state=True, price=10, pub_date='2012-02-21', publish='人民出版社' ) book_obj.save() # 相当于commit提交 return HttpResponse('<h1>数据操作成功</h1>')
启动django
方法2:
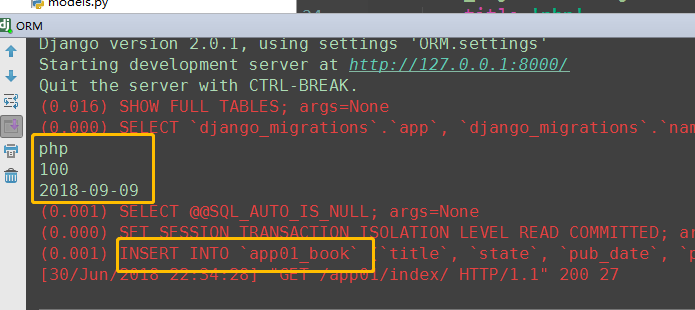
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse # Create your views here. from app01.models import Book def index(request): # 添加表记录 # 方式2: 推荐使用 Book.objects:表的管理器 book_obj = Book.objects.create( title='php', state=True, price=100, pub_date='2018-09-09', publish='南京出版社', ) # create返回值就是当前生成表的对象记录 print(book_obj.title) print(book_obj.price) print(book_obj.pub_date) return HttpResponse('<h1>数据操作成功</h1>')
4、单表操作之查询API
查询API
<1> all(): 查询所有结果 <2> filter(**kwargs): 它包含了与所给筛选条件相匹配的对象 <3> get(**kwargs): 返回与所给筛选条件相匹配的对象,返回结果有且只有一个, 如果符合筛选条件的对象超过一个或者没有都会抛出错误。 <4> exclude(**kwargs): 它包含了与所给筛选条件不匹配的对象 <5> order_by(*field): 对查询结果排序 <6> reverse(): 对查询结果反向排序 <8> count(): 返回数据库中匹配查询(QuerySet)的对象数量。 <9> first(): 返回第一条记录 <10> last(): 返回最后一条记录 <11> exists(): 如果QuerySet包含数据,就返回True,否则返回False <12> values(*field): 返回一个ValueQuerySet——一个特殊的QuerySet,运行后得到的并不是一系列 model的实例化对象,而是一个可迭代的字典序列 <13> values_list(*field): 它与values()非常相似,它返回的是一个元组序列,values返回的是一个字典序列 <14> distinct(): 从返回结果中剔除重复纪录

modles
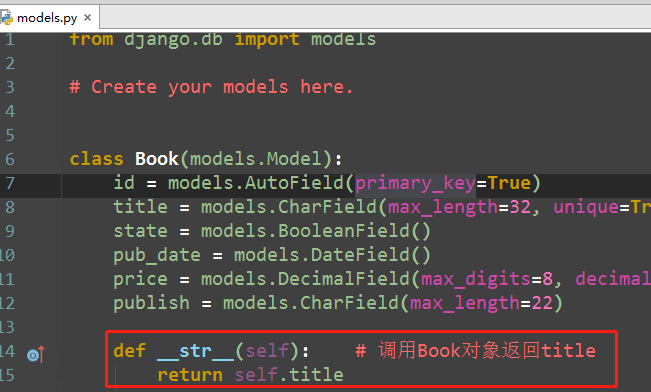
from django.db import models # Create your models here. class Book(models.Model): id = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) title = models.CharField(max_length=32, unique=True) state = models.BooleanField() pub_date = models.DateField() price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=8, decimal_places=2) # 999999.00 publish = models.CharField(max_length=22) # 10000000.00 溢出 def __str__(self): # 调用Book对象返回title return self.title
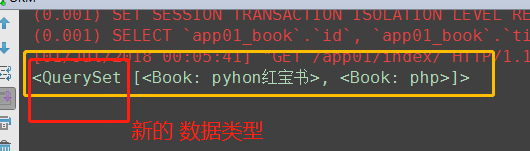
QuerySet:新的数据类型
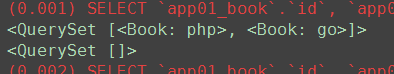
<QuerySet [<Book: pyhon红宝书>, <Book: php>]>
# ###### 查询表记录 """ 1.方法的返回值 2.方法的调用者 """
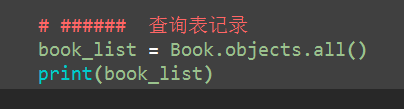
(1)all方法
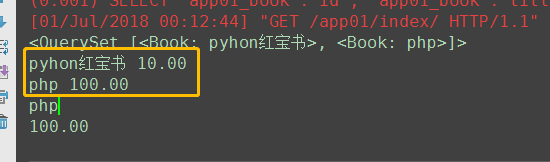
# 1. all() 调用者:Book.objects 返回值QuerySet对象 book_list = Book.objects.all() print(book_list) # [obj1, obj2, ....] for obj in book_list: print(obj.title, obj.price) print(book_list[1].title) print(book_list[1].price)
(2)first last
# 2. first,last() : 调用者QuerySet对象 返回值:model对象 book_obj1 = Book.objects.all().first() book_obj2 = Book.objects.all()[0] print(book_obj1) print(book_obj2)

(3)filter
# 3.filter() 调用者:Book.objects 返回值QuerySet对象 book_list = Book.objects.filter(price=100) # [obj1,obj2...] print(book_list) book_list1 = Book.objects.filter(price=100, title='go') print(book_list1)


(4)get方法
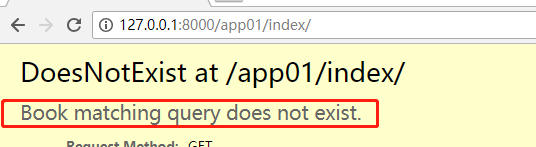
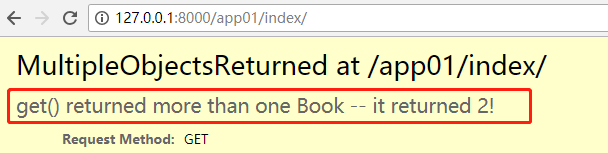
# 4.get() 有且只有一个返回值,才有意义 返回值model对象 book_obj1 = Book.objects.get(title='go') # book_obj1 = Book.objects.get(title='lalala') # 没有返回值,报错 # book_obj2 = Book.objects.get(price=100) # php go都是price=100 报错 print(book_obj1)
(5)exclude
# 5.exclude() 返回值QuerySet对象 book_obj = Book.objects.exclude(title='go') # 取反 print(book_obj)
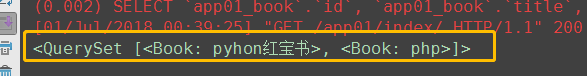
(6)order by
# 6. order by() 调用者QuerySet对象 返回值QuerySet对象 book_obj1 = Book.objects.order_by('id') book_obj2 = Book.objects.order_by('-id') # 反序 book_obj3 = Book.objects.order_by('price', 'id') # price一样的话,按照id排序 print(book_obj1) print(book_obj2) print(book_obj3)

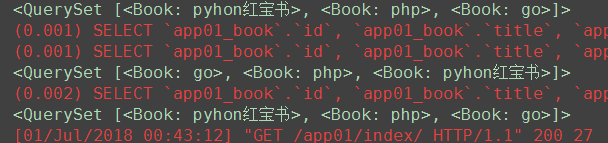
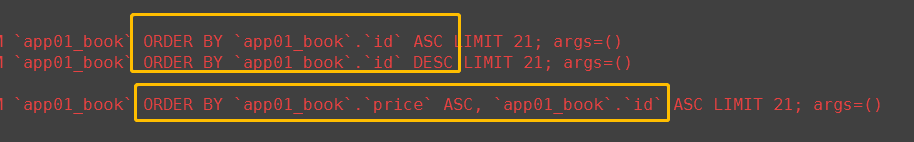
(7)count
# 7. count 调用者QuerySet对象 返回值int数字 ret = Book.objects.all().count() # 数字 print(ret)
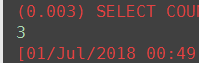
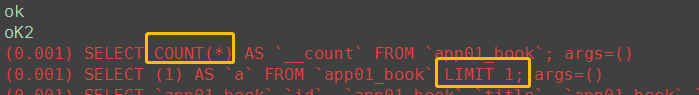
(8) exist
# 8. exist() ret = Book.objects.all() ret1 = Book.objects.all().exists() # limit 1 if ret: print('ok') if ret1: print('oK2')
(9)values
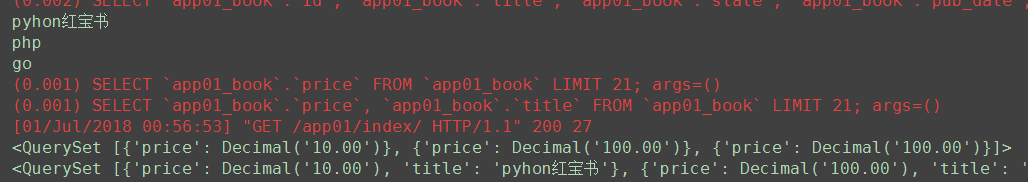
# 9. values() 调用者QuerySet对象 返回者QuerySet对象 ret = Book.objects.all() for item in ret: print(item.title) ret1 = Book.objects.all().values('price') # < QuerySet[{'price': Decimal('10.00')}, {'price': Decimal('100.00')}, {'price': Decimal('100.00')}] > print(ret1) ret2 = Book.objects.all().values('price', 'title') # <QuerySet [{'price': Decimal('10.00'), 'title': 'pyhon红宝书'}, {'price': Decimal('100.00'), 'title': 'php'}, {'price': Decimal('100.00'), 'title': 'go'}]> print(ret2) """ values: temp = [] for obj in Book.objects.all(): temp.append({ 'price'=obj.price, 'title'=obj.title, }) return temp """
(10)values_list
# 10. values_list方法 调用者QuerySet对象 返回值QuerySet对象 ret = Book.objects.all().values_list('price', 'title') # < QuerySet[(Decimal('10.00'), 'pyhon红宝书'), (Decimal('100.00'), 'php'), (Decimal('100.00'), 'go')] > print(ret)

""" values: list字典 <QuerySet [{'price': Decimal('10.00'), 'title': 'pyhon红宝书'}, {'price': Decimal('100.00'), 'title': 'php'}, {'price': Decimal('100.00'), 'title': 'go'}]> values_list: 元组 <QuerySet [(Decimal('10.00'), 'pyhon红宝书'), (Decimal('100.00'), 'php'), (Decimal('100.00'), 'go')]> """
(11)distinct
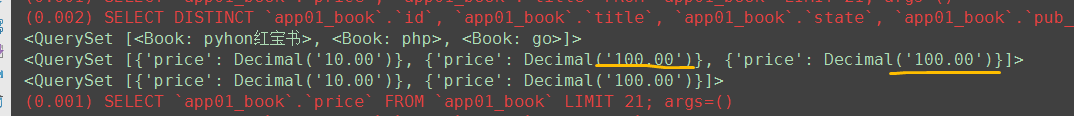
# 11. distinct ret = Book.objects.all().distinct() # id不同,不能去重 print(ret) ret1 = Book.objects.all().values('price') print(ret1) ret = Book.objects.all().values('price').distinct() # 存在相同price,可以去重 print(ret)
(12)点语法
# 12. 点语法 Book.objects.all().filter('price').order_by('id').filter('title').reverse().first()
5、单表查询之模糊查询
基于双下划线的模糊查询
Book.objects.filter(price__in=[100,200,300]) Book.objects.filter(price__gt=100) Book.objects.filter(price__lt=100) Book.objects.filter(price__range=[100,200]) Book.objects.filter(title__contains="python") Book.objects.filter(title__icontains="python") Book.objects.filter(title__startswith="py") Book.objects.filter(pub_date__year=2012)
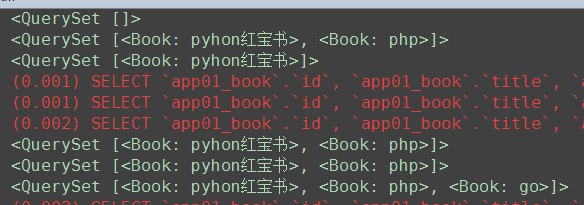
# ############ 单表查询 模糊查询 ret = Book.objects.filter(price__gt=100) # 大于100 print(ret) ret1 = Book.objects.filter(title__startswith='p') # 以p开头 print(ret1) ret2 = Book.objects.filter(title__startswith='py') print(ret2) ret3 = Book.objects.filter(title__contains='h') # 包含h就行 print(ret3) ret4 = Book.objects.filter(title__icontains='h') # 包含h,H就行 print(ret4) ret5 = Book.objects.filter(price__in=[10, 100]) # 价格是10 或者100 print(ret5) # 对于 pub_date = models.DateField() ret6 = Book.objects.filter(pub_date__year=2018) # year是2018 print(ret6) ret7 = Book.objects.filter(pub_date__month=6) # year是2018 print(ret7)
6、单表之删除与修改表记录
(1)delete
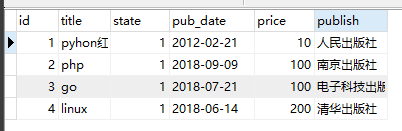
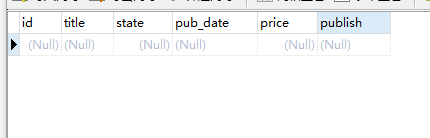
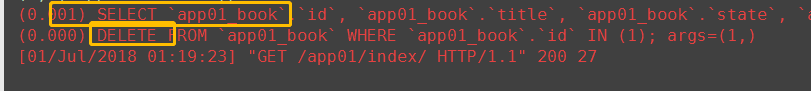
# 13. delete # 调用者QuerySet对象 Book.objects.filter(price=200).delete() # 直接过滤删除 ret = Book.objects.filter(price=100).delete() print(ret) # (2, {'app01.Book': 2}) 返回删除的数据2条 # 调用者models对象 Book.objects.filter(price=10).first().delete() # 先查询再删除

(2)update
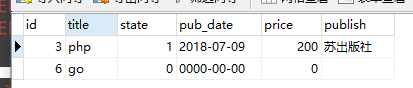
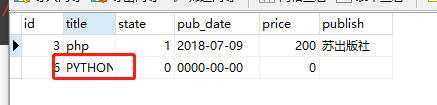
# 14. update 调用者QuerySet对象 ret = Book.objects.filter(title='go').update(title='PYTHON') print(ret)

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号