2-15 购物车程序
1.需求
数据结构: goods = [ {"name": "电脑", "price": 1999}, {"name": "鼠标", "price": 10}, {"name": "游艇", "price": 20}, {"name": "美女", "price": 998}, ...... ] 功能要求: 基础要求: 1、启动程序后,输入用户名密码后,让用户输入工资,然后打印商品列表 2、允许用户根据商品编号购买商品 3、用户选择商品后,检测余额是否够,够就直接扣款,不够就提醒 4、可随时退出,退出时,打印已购买商品和余额 5、在用户使用过程中, 关键输出,如余额,商品已加入购物车等消息,需高亮显示 扩展需求: 1、用户下一次登录后,输入用户名密码,直接回到上次的状态,即上次消费的余额什么的还是那些,再次登录可继续购买 2、允许查询之前的消费记录
2.普通流程图
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- product = [['Iphone8', 6888], ['MacPro', 14800], ['小米6', 2499], ['Coffee', 31], ['Book', 80], ['Nike Shoes', 799]] shopping_cart = [] flag = False # 标志位 while not flag: print("----------商品列表 --------") for index, item in enumerate(product): msg = "%s. %s %s" % (index, item[0], item[-1]) print(msg) choice = input("输入你要买的商品编号|退出q :") if choice.isdigit(): choice = int(choice) if choice < len(product): shopping_cart.append(product[choice]) print('-----你购买了',product[choice]) else: print('你输入的商品不存在') elif choice == 'q': if len(shopping_cart) > 0: print("------你的购物车---------") for index, item in enumerate(shopping_cart): msg = "%s. %s %s" % (index, item[0], item[-1]) print(msg) flag = True # break else: print('你输入的有误,请重新输入')
3.流程图
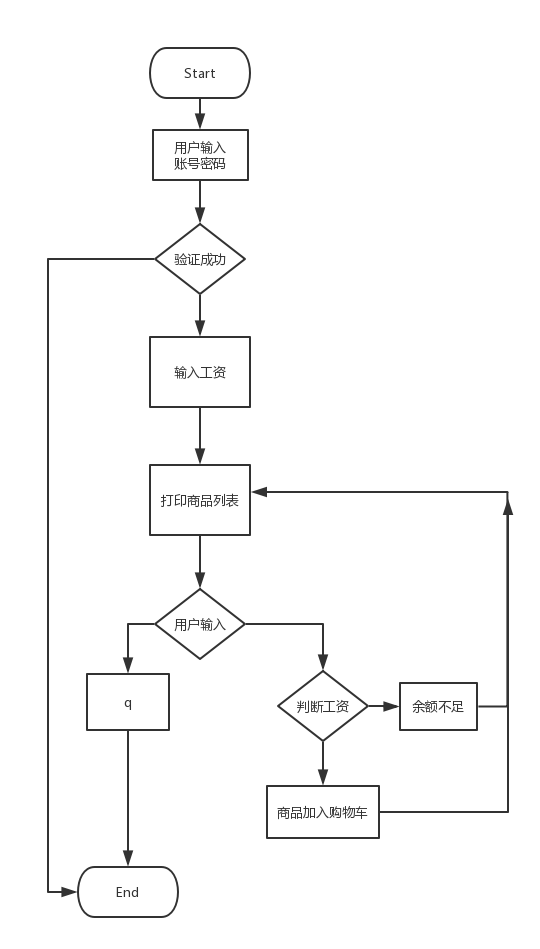
4.基本需求版本
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*- goods = [ {"name": "电脑", "price": 1999}, {"name": "鼠标", "price": 10}, {"name": "游艇", "price": 20}, {"name": "美女", "price": 998} ] shopping_cart = [] _username = 'alex' _password = '123' while True: # 用户名密码循环1 username = input("请您输入用户名:").strip() password = input("请您输入密码:").strip() if username == _username and password == _password: print("\033[1;34m-----登录成功,欢迎%s\033[0m"%username) while True: # 工资循环2 salary = input("请输入你的工资:").strip() if not salary: continue if salary.isdigit(): salary = int(salary) while True: # 商品列表循环3 print("----------商品列表 --------") for index, item in enumerate(goods): print("%s %s %s" % (index, item['name'], item['price'])) choice = input("输入你要买的商品编号|退出q :").strip() if not choice: continue if choice.isdigit(): choice = int(choice) if choice < len(goods): if salary >= goods[choice]['price']: shopping_cart.append([goods[choice]['name'], goods[choice]['price']]) # 加入商品名,price print('\033[1;32m>你购买了%s\033[0m'%goods[choice]['name']) salary -= goods[choice]['price'] print('\033[1;31m>余额剩余%s\033[0m'%salary) else: print("\033[1;31m余额不足,请重新选择\033[0m") else: print('\033[1;31;47m你输入的商品不存在\033[0m') elif choice == 'q': if len(shopping_cart) > 0: print("\033[1;34m------你的购物车---------") for index, item in enumerate(shopping_cart): print(index, item[0], item[-1]) print("------------------------") print("你的余额:%s\033[0m"%salary) exit() else: print("\033[1;34;47m你的购物车为空,你的余额:%s\033[0m"%salary) exit() else: print('\033[1;31;47m你输入的有误,请重新输入\033[0m') else: print('\033[1;31m你输入的有误,请重新输入\033[0m') else: print("\033[1;31;47m用户名或密码错误\033[0m")
5.高亮显示
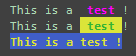
我们可以通过对有用的信息设置不同颜色来达到醒目的效果,因为我平时都是在linux下开发,
而linux终端中的颜色是用转义序列控制的,转义序列是以ESC开头,可以用\033完成相同的工作(ESC的ASCII码用十进制表示就是27,等于用八进制表示的33)。
显示颜色格式:\033[显示方式;字体色;背景色m......[\033[0m
print('This is a \033[1;35m test \033[0m!') print('This is a \033[1;32;43m test \033[0m!') print('\033[1;33;44mThis is a test !\033[0m')
------------------------------- 显示方式 | 效果 ------------------------------- 0 | 终端默认设置 1 | 高亮显示 4 | 使用下划线 5 | 闪烁 7 | 反白显示 8 | 不可见 -------------------------------
------------------------------------------- ------------------------------------------- 字体色 | 背景色 | 颜色描述 ------------------------------------------- 30 | 40 | 黑色 31 | 41 | 红色 32 | 42 | 绿色 33 | 43 | 黃色 34 | 44 | 蓝色 35 | 45 | 紫红色 36 | 46 | 青蓝色 37 | 47 | 白色 -------------------------------------------
6.扩展需求
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import time goods = [ {"name": "电脑", "price": 1999}, {"name": "鼠标", "price": 10}, {"name": "游艇", "price": 20}, {"name": "美女", "price": 998} ] shopping_cart = [] _username = 'alex' _password = '123' while True: # 用户名密码循环1 username = input("\033[1;32m请您输入用户名:\033[0m").strip() password = input("\033[1;32m请您输入密码:\033[0m").strip() if username == _username and password == _password: print("\033[1;34m-----登录成功,欢迎%s\033[0m"%username) while True: # 工资循环2 with open('salary', 'r') as f1: salary = f1.read() if salary: print('\033[1;31m你的余额还有:%s\033[0m' % salary) else: salary = input("\033[1;32m请输入你的工资:\033[0m").strip() if not salary: continue if salary.isdigit(): salary = int(salary) with open('salary', 'w') as f2: f2.write(str(salary)) while True: # 商品列表循环3 print("----------商品列表 --------") for index, item in enumerate(goods): print("%s %s %s" % (index, item['name'], item['price'])) choice = input("\033[1;34m输入你要买的商品编号|查看消费记录b|退出q:\033[0m").strip() if not choice: continue if choice.isdigit(): choice = int(choice) if choice < len(goods): if salary >= goods[choice]['price']: shopping_cart.append([goods[choice]['name'], goods[choice]['price']]) # 消费记录加入文件 with open('shopping_records', 'a') as f: now_time = time.ctime() goods_choice = [goods[choice]['name'], goods[choice]['price']] record = str(now_time) + '\t' + str(goods_choice) + '\n' f.write(record) print('\033[1;32m>你购买了%s\033[0m'%goods[choice]['name']) salary -= goods[choice]['price'] print('\033[1;31m>余额剩余%s\033[0m'%salary) else: print("\033[1;31m余额不足,请重新选择\033[0m") else: print('\033[1;31m你输入的商品不存在\033[0m') elif choice == 'b': with open('shopping_records', 'r') as f: records = f.read() if len(records): print('-------消费记录------') print(records) else: print('\033[1;31m>>你还没有买过东西\033[0m') elif choice == 'q': if len(shopping_cart) > 0: print("\033[1;32m------你的购物车---------") for index, item in enumerate(shopping_cart): print(index, item[0], item[-1]) print("------------------------") print("你的余额:%s\033[0m"%salary) with open('salary', 'w') as f2: f2.write(str(salary)) exit() else: print("\033[1;31m你的购物车为空,你的余额:%s\033[0m"%salary) exit() else: print('\033[1;31;47m你输入的有误,请重新输入\033[0m') else: print('\033[1;31m你输入的有误,请重新输入\033[0m') else: print("\033[1;31;47m用户名或密码错误\033[0m")
8.修改后
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import time goods = [ {"name": "电脑", "price": 1999}, {"name": "鼠标", "price": 10}, {"name": "游艇", "price": 20}, {"name": "美女", "price": 998} ] shopping_cart = [] _username = 'alex' _password = '123' count = 0 while count<3 : # 用户名密码循环1 username = input("\033[1;32m请您输入用户名:\033[0m").strip() password = input("\033[1;32m请您输入密码:\033[0m").strip() if username == _username and password == _password: print("\033[1;34m-----登录成功,欢迎%s\033[0m"%username) # 得到工资 with open('salary', 'r') as f1: data = f1.read() if data: salary = float(data) print('\033[1;31m你的余额还有:%s\033[0m' % salary) else: while True: # 工资循环2 salary = input("\033[1;32m请输入你的工资:\033[0m").strip() if salary.isdigit(): # 只能够把 3456转换,不能转换 3456.444, salary = float(salary) break else: print('你输入的有误,请重新输入') while True: # 商品列表循环3 print("----------商品列表 --------") for index, item in enumerate(goods): print("%s %s %s" % (index, item['name'], item['price'])) choice = input("\033[1;34m输入你要买的商品编号|查看消费记录b|退出q:\033[0m").strip() if choice.isdigit(): choice = int(choice) if choice < len(goods): if salary >= float(goods[choice]['price']): shopping_cart.append([goods[choice]['name'], goods[choice]['price']]) # 消费记录加入文件 with open('shopping_records', 'a') as f: now_time = time.ctime() goods_choice = [goods[choice]['name'], goods[choice]['price']] record = str(now_time) + '\t' + str(goods_choice) + '\n' f.write(record) print('\033[1;32m>你购买了%s\033[0m'%goods[choice]['name']) salary -= float(goods[choice]['price']) print('\033[1;31m>余额剩余%s\033[0m'%salary) else: print("\033[1;31m余额不足,请重新选择\033[0m") else: print('\033[1;31m你输入的商品不存在\033[0m') elif choice == 'b': with open('shopping_records', 'r') as f: records = f.read() if len(records): print('-------消费记录------') print(records) else: print('\033[1;31m>>你还没有买过东西\033[0m') elif choice == 'q': if len(shopping_cart) > 0: print("\033[1;32m------你的购物车---------") for index, item in enumerate(shopping_cart): print(index, item[0], item[-1]) print("------------------------") print("你的余额:%s\033[0m"%salary) with open('salary', 'w') as f2: f2.write(str(salary)) exit() else: print("\033[1;31m你的购物车为空,你的余额:%s\033[0m"%salary) with open('salary', 'w') as f2: f2.write(str(salary)) exit() else: print('\033[1;31;47m你输入的有误,请重新输入\033[0m') else: print("\033[1;31;47m用户名或密码错误\033[0m") count += 1 print("you have try more times")

