4 进程间通信Queue [kjuː]
1.进程间通信-Queue
Process之间有时需要通信,操作系统提供了很多机制来实现进程间的通信。
说明
初始化Queue()对象时(例如:q=Queue()),若括号中没有指定最大可接收的消息数量,或数量为负值,那么就代表可接受的消息数量没有上限(直到内存的尽头);
-
Queue.qsize():返回当前队列包含的消息数量;
-
Queue.empty():如果队列为空,返回True,反之False ;
-
Queue.full():如果队列满了,返回True,反之False;
-
Queue.get([block[, timeout]]):获取队列中的一条消息,然后将其从列队中移除,block默认值为True;
1)如果block使用默认值,且没有设置timeout(单位秒),消息列队如果为空,此时程序将被阻塞(停在读取状态),直到从消息列队读到消息为止,如果设置了timeout,则会等待timeout秒,若还没读取到任何消息,则抛出"Queue.Empty"异常;
2)如果block值为False,消息列队如果为空,则会立刻抛出"Queue.Empty"异常;
-
Queue.get_nowait():相当Queue.get(False);
-
Queue.put(item,[block[, timeout]]):将item消息写入队列,block默认值为True;
1)如果block使用默认值,且没有设置timeout(单位秒),消息列队如果已经没有空间可写入,此时程序将被阻塞(停在写入状态),直到从消息列队腾出空间为止,如果设置了timeout,则会等待timeout秒,若还没空间,则抛出"Queue.Full"异常;
2)如果block值为False,消息列队如果没有空间可写入,则会立刻抛出"Queue.Full"异常;
- Queue.put_nowait(item):相当Queue.put(item, False);
In [1]: from multiprocessing import Queue In [2]: q = Queue(3) In [3]: q.qsize() Out[3]: 0 In [4]: q.put("haha") In [5]: q.put("haha1") In [6]: q.put("haha2") In [7]: q.put("haha3") #堵塞 In [8]: q.qsize() Out[8]: 3 In [9]: q.get() Out[9]: 'haha' In [10]: q.qsize() Out[10]: 2 In [11]: q.get() Out[11]: 'haha1' In [12]: q.get() Out[12]: 'haha2' In [13]: q.get() #堵塞 In [14]: q.empty() Out[14]: True In [15]: q.full() Out[15]: False In [17]: q.empty() Out[17]: True In [18]: q.get() #堵塞 In [3]: q.get_nowait() --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Empty Traceback (most recent call last) <ipython-input-3-4f5e3b567b9e> in <module>() ----> 1 q.get_nowait() In [4]: q.put("123") In [5]: q.get_nowait() Out[5]: '123' In [6]: q.get_nowait() --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Empty Traceback (most recent call last) <ipython-input-6-4f5e3b567b9e> in <module>() ----> 1 q.get_nowait() In [7]: q.put("2134") In [8]: q.put("wsdaf") In [9]: q.put([]) In [11]: q.put_nowait({}) --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Full Traceback (most recent call last) <ipython-input-11-cb0d653443e5> in <module>() ----> 1 q.put_nowait({})
2. Queue实例
我们以Queue为例,在父进程中创建两个子进程,一个往Queue里写数据,一个从Queue里读数据:
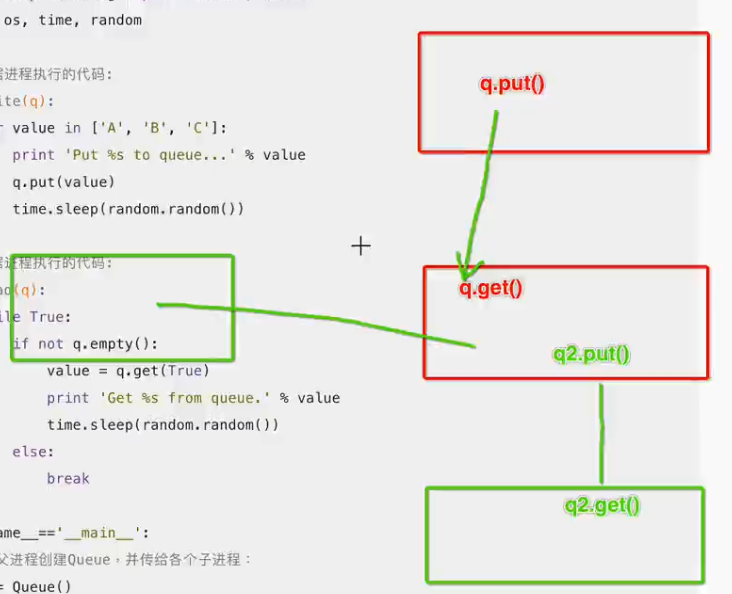
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue import os, time, random # 写数据进程执行的代码: def write(q): for value in ['A', 'B', 'C']: print 'Put %s to queue...' % value q.put(value) time.sleep(random.random()) # 读数据进程执行的代码: def read(q): while True: if not q.empty(): value = q.get(True) print 'Get %s from queue.' % value time.sleep(random.random()) else: break if __name__=='__main__': # 父进程创建Queue,并传给各个子进程: q = Queue() pw = Process(target=write, args=(q,)) pr = Process(target=read, args=(q,)) # 启动子进程pw,写入: pw.start() # 等待pw结束: pw.join() # 启动子进程pr,读取: pr.start() pr.join() # pr进程里是死循环,无法等待其结束,只能强行终止: print '' print '所有数据都写入并且读完'
Put A to queue... Put B to queue... Put C to queue... Get A from queue. Get B from queue. Get C from queue.
3. 进程池中的Queue
如果要使用Pool创建进程,就需要使用multiprocessing.Manager()中的Queue(),而不是multiprocessing.Queue(),否则会得到一条如下的错误信息:
RuntimeError: Queue objects should only be shared between processes through inheritance.
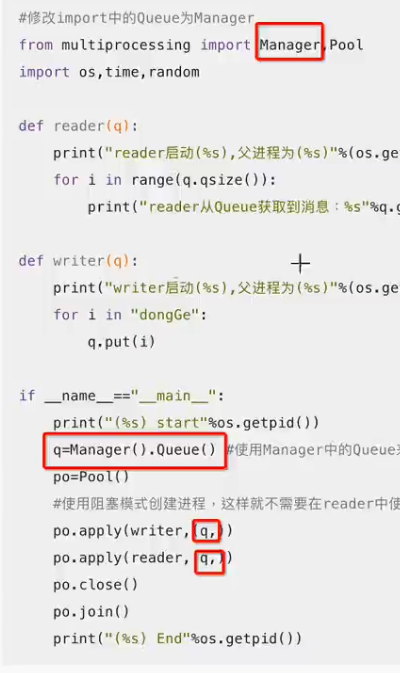
#coding=utf-8 #修改import中的Queue为Manager from multiprocessing import Manager,Pool import os,time,random def reader(q): print("reader启动(%s),父进程为(%s)"%(os.getpid(),os.getppid())) for i in range(q.qsize()): print("reader从Queue获取到消息:%s"%q.get(True)) def writer(q): print("writer启动(%s),父进程为(%s)"%(os.getpid(),os.getppid())) for i in "dongGe": q.put(i) if __name__=="__main__": print("(%s) start"%os.getpid()) q=Manager().Queue() #使用Manager中的Queue来初始化 po=Pool() #使用阻塞模式创建进程,这样就不需要在reader中使用死循环了,可以让writer完全执行完成后,再用reader去读取 po.apply(writer,(q,)) po.apply(reader,(q,)) po.close() po.join() print("(%s) End"%os.getpid())
(3630) start writer启动(3635),父进程为(3630) reader启动(3635),父进程为(3630) reader从Queue获取到消息:d reader从Queue获取到消息:o reader从Queue获取到消息:n reader从Queue获取到消息:g reader从Queue获取到消息:G reader从Queue获取到消息:e (3630) End
4.总结
- 进程和进程之间没有关联
- 如何完成1个进程处理的数据给另一个进程!这就是进程通信问题
- 有无管道,共享内存,队列,网路功能socket
其中一种实现方式就是Queue队列
- Process创建的进程 用Queue
2.进程池创建的进程用Manager().Queue()

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号