2-1 购物车程序
1.需求
程序:购物车程序
需求:
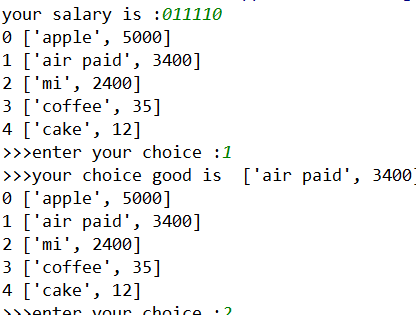
启动程序后,让用户输入工资,然后打印商品列表
允许用户根据商品编号购买商品
用户选择商品后,检测余额是否够,够就直接扣款,不够就提醒
可随时退出,退出时,打印已购买商品和余额
2.个人思路
定义商品列表database
用户输入工资 (str 如何转化int)
循环
打印商品列表 (index,items循环打印)
选择商品 if choice in (0,1,2,3):
if price <= salary:
add 购物车
salary -= price
else 余额不足
if choice is q: break
退出
打印购物车,余额
实现代码
# coding=utf-8
shopping_cart = []
sala = input("your salary is :").strip()
if sala.isdigit():
salary = int(sala)
goods = [['apple',5000],['air paid',3400],
['mi',2400],['coffee',35],['cake',12]
]
while True:
for index,items in enumerate(goods):
print(index,items)
choice = input(">>>enter your choice :" )
if choice in ('0','1','2','3','4'):
print('>>>your choice good is ',goods[int(choice)])
price = goods[int(choice)][-1:][0]
if price <= salary:
salary -= price
shopping_cart.append(goods[int(choice)])
else:
print("\033[1m余额不足,your salary is %s\033[0m"%salary)
elif choice == 'q':
break
else: print("\033[1menter error!!!\033[0m")
print('-----the shopping_cart ----')
for i in shopping_cart:
print(i)
print('---------------------------\n your salary:',salary)
else:print("\033[1menter error!!!\033[0m")
3.个人心得
3.1 定义一个空 字符串,列表,元组,字典
# a_str = ""
# a_list = []
# a_tuple= ()
# a_dict = {}
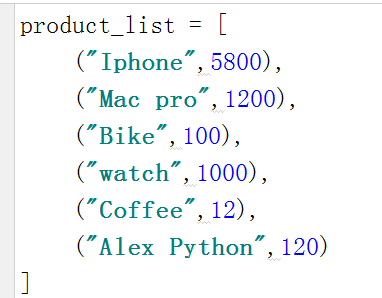
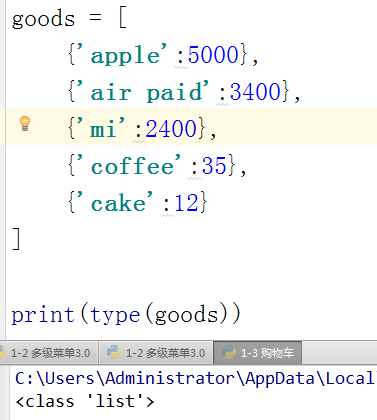
3.2 复合列表。复合字典
复合字典需要key:value 一一对应,goods1 没有key 所以显示错误
最外面为[ ] 就是list
最外面为{ } 就是dict
下图分别为,复合list,复合list,错误演示

三维字典正确演示
data_base = {
'shaanxi':{
"xi'an":{
'yantaqu':['dongyilu','dianzierlu','taibailu'],
'weiyangqu':['ziwulu','dahualu'],
'changanqu':['changanlu','jinhualu']
},
'xianyang':{},
'weinan':{}
},
'jiangsu':{},
'nanjing':{}
}
复合列表正确演示
goods = [{'apple':5000},{'air paid':3400},
{'mi':2400},{'coffee':35},{'cake':12}
]
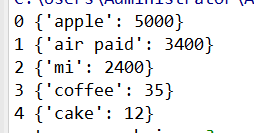
3.3 循环获取index,items
emumerate 是python中的内建函数,可以共同获取index,和items
goods = [{'apple':5000},{'air paid':3400},
{'mi':2400},{'coffee':35},{'cake':12}
]
for index,items in enumerate(goods):
print(index,items)
3.5 只获取index (或items)
比如:获取商品清单的全部序号,判断choice是否在index中,使用 len判断list的长度
如果goods为字典,获取price 只能用key,不能打印全部的
错误演示
if choice in ('0','1','2','3','4'):
print('>>>your choice good is ',goods[int(choice)])
正确演示
if choice <len(goods) and choice >= 0:
print('>>>your choice good is ',goods[int(choice)])
3.6 list内,string类型和int类型转换
['air paid',3400] 和 ['air paid',’3400‘] 区别
取出商品价格
['air paid',3400] 在list 中3400类型默认为int,取出商品价格 data[1] 即可,不能用 join
['air paid',’3400‘] 在list中“3400”,为字符串,取出商品价格 price = "".join(data[1])
# join() 方法用于将序列中的元素以指定的字符连接生成一个新的字符串。
# coding=utf-8 goods = [['apple','5000'],['air paid',3400],] print(goods) #[['apple', '5000'], ['air paid', 3400]] print(type(goods)) #<class 'list'> print(goods[1][1]+2) #3402 print(type(goods[1][1])) #<class 'int'> print(goods[1][-1:]) # [3400] print(type(goods[1][-1:])) #<class 'list'> g0 = ''.join(goods[1][-1:]) #TypeError: sequence item 0: expected str instance, int found # print(g0) # print(type(g0)) print(goods[0][1]) #5000 print(type(goods[0][1])) #<class 'str'> g = ''.join(goods[0][1]) #5000 print(g) print(type(g)) #<class 'str'> print(goods[0][-1:]) #['5000'] print(type(goods[0][-1:])) #<class 'list'>
# join() 方法用于将序列中的元素以指定的字符连接生成一个新的字符串。 #字符串 g1 = ''.join(goods[0][-1:]) #5000 print(g1) print(type(g1)) #<class 'str'>
3.4 用户输入 str ---》 int
用户输入为str(python默认为string),转换成int
sala = input("your salary is :").strip()
if sala.isdigit(): #是否为数字
salary = int(sala)
4.完整代码
个人修正代码完整版
# coding=utf-8
shopping_cart = []
sala = input("your salary is :").strip()
if sala.isdigit():
salary = int(sala)
goods = [['apple',5000],['air paid',3400],
['mi',2400],['coffee',35],['cake',12]
]
print(len(goods))
while True:
for index,items in enumerate(goods):
print(index,items)
choice1 = input(">>>enter your choice :" )
if choice1.isdigit():
choice = int(choice1)
if choice < len(goods) and choice >= 0:
print('>>>your choice good is ',goods[choice])
price = goods[choice][1]
#print('\tit is price is ',price)
if price <= salary:
salary -= price
shopping_cart.append(goods[choice])
else:
print("\033[1m余额不足,your salary is %s\033[0m"%salary)
else: print("\033[1menter error!!!\033[0m")
elif choice1 == 'q':
break
else: print("\033[1menter error!!!\033[0m")
print('-----the shopping_cart ----')
for i in shopping_cart:
print(i)
print('---------------------------\n your salary:',salary)
else:print("\033[1menter error!!!\033[0m")
alex答案完整版
# coding=utf-8
product_list = [
("Iphone",5800),
("Mac pro",1200),
("Bike",100),
("watch",1000),
("Coffee",12),
("Alex Python",120)
]
shopping_list = []
salary = input("Input your salary: ")
if salary.isdigit():
salary = int(salary)
while True:
for index,item in enumerate(product_list):
#print(product_list.index(item),item)
print(index,item)
user_choic = input("选择要买的?》》》:")
if user_choic.isdigit():
user_choic = int(user_choic)
if user_choic < len(product_list) and user_choic >= 0:
p_item = product_list[user_choic]
if p_item[1] <= salary: #买的起
shopping_list.append(p_item)
salary -= p_item[1]
print("Added %s into your shopping cart,your current balance is \033[31;1m%s\033[0m" %(p_item,salary) )
else:
print("\033[32;1m你的余额不足,只有[%s]\033[0m"%(salary))
else:
print("product code [%s] is not exist",user_choic)
elif user_choic == "q":
print("--------shopping list-------")
for p in shopping_list:
print(p)
print("----------------------------")
print("Your current balance:",salary)
exit()
else:
print("invalid option")
else:
print("please enter number,try again...")


