初级5 二叉树
题目一:实现二叉树的先序、中序、后序遍历,包括递归方式和非递归方式

递归版:递归来到每个节点的顺序

前序遍历 打印时机放在第1次来到这个节点的时候
中序遍历 打印时机放在第2次来到这个节点的时候
后序遍历 打印时机放在第3次来到这个节点的时候
// 递归版本--先序遍历 public static void preOrderRecur(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } // System.out.print(head.value + " "); preOrderRecur(head.left); preOrderRecur(head.right); }
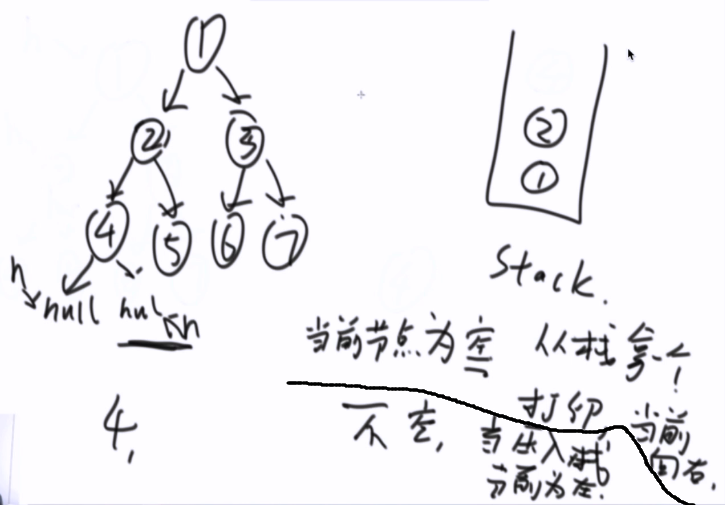
非递归版:stack栈



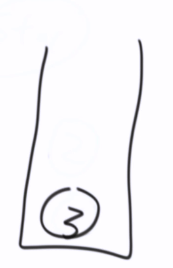
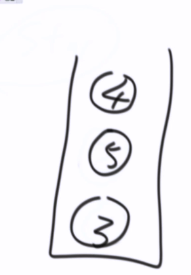
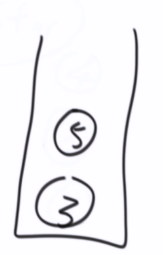
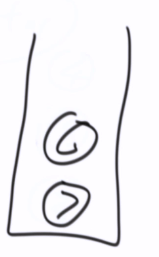
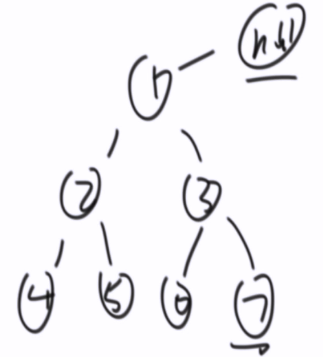
1,2,4,5,3,6,7
// 非递归--前序遍历 public static void preOrderUnRecur(Node head) { System.out.print("pre-order: "); if (head != null) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); stack.add(head); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { head = stack.pop(); System.out.print(head.value + " "); //如果有右孩子,先压右 // 如果有左孩子,后压左 if (head.right != null) { stack.push(head.right); } if (head.left != null) { stack.push(head.left); } } } System.out.println(); }
中左右被 模拟出来了
先压右后压左
先弹左,后弹右

为什么不用队列?
递归函数就是一种栈

二叉树只有从上到下的路径,没有回去的路径
非递归--中序遍历
public static void inOrderUnRecur(Node head) { System.out.print("in-order: "); if (head != null) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) { if (head != null) { stack.push(head); head = head.left; } else { head = stack.pop(); System.out.print(head.value + " "); head = head.right; } } } System.out.println(); }
head不等于空
当前节点会把自己左边界全部压入栈中,head = head.left
head == null 停止

当前节点为空,从栈中拿出一个,打印,往右移动
当前节点不为空,当前压入栈中,节点往左移动


极端例子

整棵树可以被左边界分解的

非递归--后序遍历
左右中 ---> 中右左----> 中左右(当前节点,先压左,再压右)
先不打印,放入栈中,然后逆序输出
方法1:两个栈
public static void posOrderUnRecur1(Node head) { System.out.print("pos-order: "); if (head != null) { Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<Node>(); Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<Node>(); s1.push(head); while (!s1.isEmpty()) { head = s1.pop(); // s2.push(head); 打印时机,放入辅助栈中, if (head.left != null) { s1.push(head.left); // 左不为空,先压左 } if (head.right != null) { s1.push(head.right); } } while (!s2.isEmpty()) { System.out.print(s2.pop().value + " "); // 逆序打印栈 } } System.out.println(); }
方法2:1个栈
纯属炫技
完整java代码
package class_04; import java.util.Stack; public class Code_01_PreInPosTraversal { public static class Node { public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } // 递归版本--先序遍历 public static void preOrderRecur(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } // System.out.print(head.value + " "); preOrderRecur(head.left); preOrderRecur(head.right); } public static void inOrderRecur(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } inOrderRecur(head.left); System.out.print(head.value + " "); inOrderRecur(head.right); } public static void posOrderRecur(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } posOrderRecur(head.left); posOrderRecur(head.right); System.out.print(head.value + " "); } // 非递归--前序遍历 public static void preOrderUnRecur(Node head) { System.out.print("pre-order: "); if (head != null) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); stack.add(head); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { head = stack.pop(); System.out.print(head.value + " "); //如果有右孩子,先压右 // 如果有左孩子,后压左 if (head.right != null) { stack.push(head.right); } if (head.left != null) { stack.push(head.left); } } } System.out.println(); } // 非递归---后序 // 方法1:两个栈 public static void inOrderUnRecur(Node head) { System.out.print("in-order: "); if (head != null) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) { if (head != null) { stack.push(head); head = head.left; } else { head = stack.pop(); System.out.print(head.value + " "); head = head.right; } } } System.out.println(); } // 方法2:一个栈,炫技 public static void posOrderUnRecur1(Node head) { System.out.print("pos-order: "); if (head != null) { Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<Node>(); Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<Node>(); s1.push(head); while (!s1.isEmpty()) { head = s1.pop(); // s2.push(head); 打印时机,放入辅助栈中, if (head.left != null) { s1.push(head.left); // 左不为空,先压左 } if (head.right != null) { s1.push(head.right); } } while (!s2.isEmpty()) { System.out.print(s2.pop().value + " "); // 逆序打印栈 } } System.out.println(); } public static void posOrderUnRecur2(Node h) { System.out.print("pos-order: "); if (h != null) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); stack.push(h); Node c = null; while (!stack.isEmpty()) { c = stack.peek(); if (c.left != null && h != c.left && h != c.right) { stack.push(c.left); } else if (c.right != null && h != c.right) { stack.push(c.right); } else { System.out.print(stack.pop().value + " "); h = c; } } } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node head = new Node(5); head.left = new Node(3); head.right = new Node(8); head.left.left = new Node(2); head.left.right = new Node(4); head.left.left.left = new Node(1); head.right.left = new Node(7); head.right.left.left = new Node(6); head.right.right = new Node(10); head.right.right.left = new Node(9); head.right.right.right = new Node(11); // recursive System.out.println("==============recursive=============="); System.out.print("pre-order: "); preOrderRecur(head); System.out.println(); System.out.print("in-order: "); inOrderRecur(head); System.out.println(); System.out.print("pos-order: "); posOrderRecur(head); System.out.println(); // unrecursive System.out.println("============unrecursive============="); preOrderUnRecur(head); inOrderUnRecur(head); posOrderUnRecur1(head); posOrderUnRecur2(head); } }
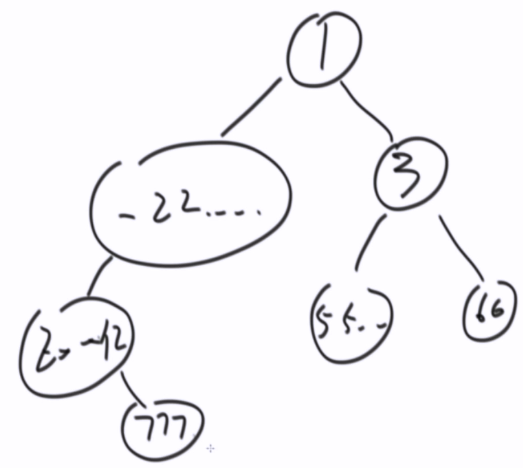
题目二:如何直观的打印一颗二叉树(福利)
还原不了整棵树

package class_04; public class Code_02_PrintBinaryTree { public static class Node { public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } public static void printTree(Node head) { System.out.println("Binary Tree:"); printInOrder(head, 0, "H", 17); System.out.println(); } public static void printInOrder(Node head, int height, String to, int len) { if (head == null) { return; } printInOrder(head.right, height + 1, "v", len); String val = to + head.value + to; int lenM = val.length(); int lenL = (len - lenM) / 2; int lenR = len - lenM - lenL; val = getSpace(lenL) + val + getSpace(lenR); System.out.println(getSpace(height * len) + val); printInOrder(head.left, height + 1, "^", len); } public static String getSpace(int num) { String space = " "; StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer(""); for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { buf.append(space); } return buf.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node head = new Node(1); head.left = new Node(-222222222); head.right = new Node(3); head.left.left = new Node(Integer.MIN_VALUE); head.right.left = new Node(55555555); head.right.right = new Node(66); head.left.left.right = new Node(777); printTree(head); head = new Node(1); head.left = new Node(2); head.right = new Node(3); head.left.left = new Node(4); head.right.left = new Node(5); head.right.right = new Node(6); head.left.left.right = new Node(7); printTree(head); head = new Node(1); head.left = new Node(1); head.right = new Node(1); head.left.left = new Node(1); head.right.left = new Node(1); head.right.right = new Node(1); head.left.left.right = new Node(1); printTree(head); } }

题目三:在二叉树中找到一个节点的后继节点
【题目】 现在有一种新的二叉树节点类型如下:
public class Node { public int value; public Node left;
public Node right; public Node parent;
public Node(int data) { this.value = data; }
}
该结构比普通二叉树节点结构多了一个指向父节点的parent指针。假
设有一 棵Node类型的节点组成的二叉树,树中每个节点的parent指针
都正确地指向 自己的父节点,头节点的parent指向null。只给一个在
二叉树中的某个节点 node,请实现返回node的后继节点的函数。在二
叉树的中序遍历的序列中, node的下一个节点叫作node的后继节点。
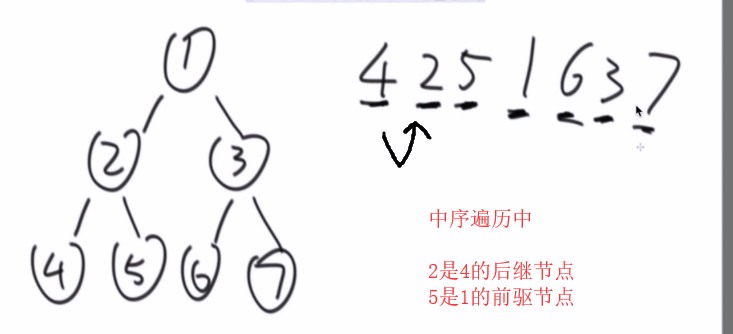
新类型节点

中序遍历中:
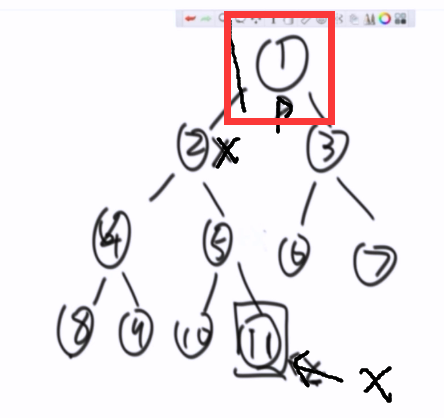
问题描述:如果给了5,如何找到1,不用遍历整棵树

结论:
X 如果有右孩子,右子树
X 的后继节点一定是它右子树上的最左节点
原因是:中序 : 左中右
X 没有右子树,
找他的parent,如果X是父的右子树,则继续
直到找到,X是父的左子树, 停止
则后继节点是parent

package class_04; public class Code_03_SuccessorNode { public static class Node { public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node parent; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } public static Node getSuccessorNode(Node node) { if (node == null) { return node; } if (node.right != null) { return getLeftMost(node.right); } else { // 没有右子树 Node parent = node.parent; while (parent != null && parent.left != node) { // 有些节点没有后继,7的后继是Null node = parent; parent = node.parent; } return parent; // 节点的后继 } } public static Node getLeftMost(Node node) { // 找到该子树的最左节点 if (node == null) { return node; } while (node.left != null) { node = node.left; } return node; } public static void main(String[] args) { Node head = new Node(6); head.parent = null; head.left = new Node(3); head.left.parent = head; head.left.left = new Node(1); head.left.left.parent = head.left; head.left.left.right = new Node(2); head.left.left.right.parent = head.left.left; head.left.right = new Node(4); head.left.right.parent = head.left; head.left.right.right = new Node(5); head.left.right.right.parent = head.left.right; head.right = new Node(9); head.right.parent = head; head.right.left = new Node(8); head.right.left.parent = head.right; head.right.left.left = new Node(7); head.right.left.left.parent = head.right.left; head.right.right = new Node(10); head.right.right.parent = head.right; Node test = head.left.left; System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value); test = head.left.left.right; System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value); test = head.left; System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value); test = head.left.right; System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value); test = head.left.right.right; System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value); test = head; System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value); test = head.right.left.left; System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value); test = head.right.left; System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value); test = head.right; System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value); test = head.right.right; // 10's next is null System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test)); } }
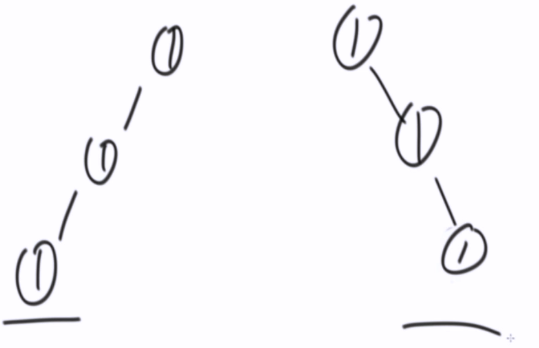
前驱节点
有左子树,左子树是最右节点
Node是当前父节点的右孩子,就停止
左神语录
面试5面, 2~3道题
迅速把面试官的题库挖空,还有吗,我要打10个

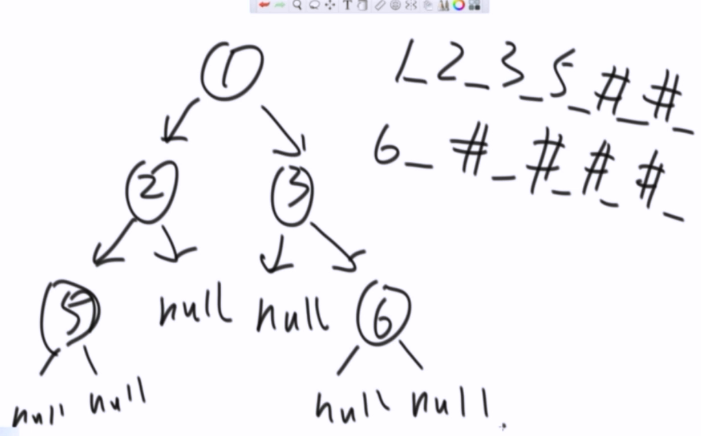
题目四:介绍二叉树的序列化和反序列化
data struct ----> 文件
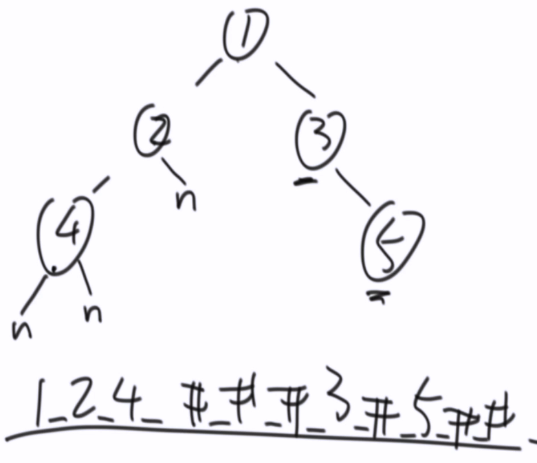
方法1:_ #
序列化

_ 代表 分割, # 代表Null
如何区分?
package class_04; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class Code_04_SerializeAndReconstructTree { public static class Node { public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } public static String serialByPre(Node head) { if (head == null) { return "#!"; } String res = head.value + "!"; res += serialByPre(head.left); // 当前节点的左树返回个字符串 res += serialByPre(head.right); // 右树返回个字符串 return res; } public static Node reconByPreString(String preStr) { String[] values = preStr.split("!"); Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>(); for (int i = 0; i != values.length; i++) { queue.offer(values[i]); } return reconPreOrder(queue); } public static Node reconPreOrder(Queue<String> queue) { String value = queue.poll(); if (value.equals("#")) { return null; } Node head = new Node(Integer.valueOf(value)); head.left = reconPreOrder(queue); head.right = reconPreOrder(queue); return head; } public static String serialByLevel(Node head) { if (head == null) { return "#!"; } String res = head.value + "!"; Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>(); queue.offer(head); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { head = queue.poll(); if (head.left != null) { res += head.left.value + "!"; queue.offer(head.left); } else { res += "#!"; } if (head.right != null) { res += head.right.value + "!"; queue.offer(head.right); } else { res += "#!"; } } return res; } public static Node reconByLevelString(String levelStr) { String[] values = levelStr.split("!"); int index = 0; Node head = generateNodeByString(values[index++]); Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>(); if (head != null) { queue.offer(head); } Node node = null; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { node = queue.poll(); node.left = generateNodeByString(values[index++]); node.right = generateNodeByString(values[index++]); if (node.left != null) { queue.offer(node.left); } if (node.right != null) { queue.offer(node.right); } } return head; } public static Node generateNodeByString(String val) { if (val.equals("#")) { return null; } return new Node(Integer.valueOf(val)); } // for test -- print tree public static void printTree(Node head) { System.out.println("Binary Tree:"); printInOrder(head, 0, "H", 17); System.out.println(); } public static void printInOrder(Node head, int height, String to, int len) { if (head == null) { return; } printInOrder(head.right, height + 1, "v", len); String val = to + head.value + to; int lenM = val.length(); int lenL = (len - lenM) / 2; int lenR = len - lenM - lenL; val = getSpace(lenL) + val + getSpace(lenR); System.out.println(getSpace(height * len) + val); printInOrder(head.left, height + 1, "^", len); } public static String getSpace(int num) { String space = " "; StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer(""); for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { buf.append(space); } return buf.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node head = null; printTree(head); String pre = serialByPre(head); System.out.println("serialize tree by pre-order: " + pre); head = reconByPreString(pre); System.out.print("reconstruct tree by pre-order, "); printTree(head); String level = serialByLevel(head); System.out.println("serialize tree by level: " + level); head = reconByLevelString(level); System.out.print("reconstruct tree by level, "); printTree(head); System.out.println("===================================="); head = new Node(1); printTree(head); pre = serialByPre(head); System.out.println("serialize tree by pre-order: " + pre); head = reconByPreString(pre); System.out.print("reconstruct tree by pre-order, "); printTree(head); level = serialByLevel(head); System.out.println("serialize tree by level: " + level); head = reconByLevelString(level); System.out.print("reconstruct tree by level, "); printTree(head); System.out.println("===================================="); head = new Node(1); head.left = new Node(2); head.right = new Node(3); head.left.left = new Node(4); head.right.right = new Node(5); printTree(head); pre = serialByPre(head); System.out.println("serialize tree by pre-order: " + pre); head = reconByPreString(pre); System.out.print("reconstruct tree by pre-order, "); printTree(head); level = serialByLevel(head); System.out.println("serialize tree by level: " + level); head = reconByLevelString(level); System.out.print("reconstruct tree by level, "); printTree(head); System.out.println("===================================="); head = new Node(100); head.left = new Node(21); head.left.left = new Node(37); head.right = new Node(-42); head.right.left = new Node(0); head.right.right = new Node(666); printTree(head); pre = serialByPre(head); System.out.println("serialize tree by pre-order: " + pre); head = reconByPreString(pre); System.out.print("reconstruct tree by pre-order, "); printTree(head); level = serialByLevel(head); System.out.println("serialize tree by level: " + level); head = reconByLevelString(level); System.out.print("reconstruct tree by level, "); printTree(head); System.out.println("===================================="); } }

反序列化
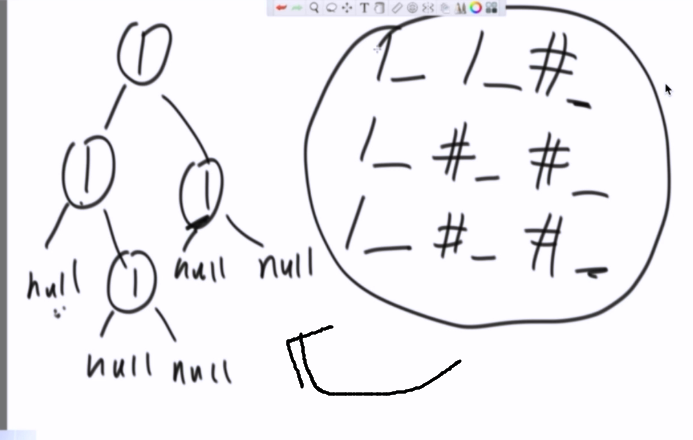
方法2:按层序列化
题目六:判断一棵二叉树是否是平衡二叉树

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号