1、react在进行props的祥细配置
react在进行props祥细配置的时候,可以配置默认值,参数的类型,以及是否是一定要传
import {Component} from 'react'
import reactDom from 'react-dom'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types' //该库是react默认引入的
class Counter extends Component {
static defaultProps = { //配置参数
name: 'bill'
}
static propTypes = { //配置参数的类型以及是否必要
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
age: PropTypes.number.isRequired
}
render() {
return <div>{this.props.name}{this.props.age}</div>
}
}
reactDom.render(<Counter name='this is title' age={12}/>, window.root) //注意:该写法,那么就是number类型的数据,如果用的是{'12'}则是字符串类型的数据
PropTypes的祥细类型配置
Son.propTypes = { optionalArray: PropTypes.array,//检测数组类型 optionalBool: PropTypes.bool,//检测布尔类型 optionalFunc: PropTypes.func,//检测函数(Function类型) optionalNumber: PropTypes.number,//检测数字 optionalObject: PropTypes.object,//检测对象 optionalString: PropTypes.string,//检测字符串 optionalSymbol: PropTypes.symbol,//ES6新增的symbol类型 }
propTypes其他类型配置示例
import {Component} from 'react'
import reactDom from 'react-dom'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types' //该库是react默认引入的
class Counter extends Component {
static defaultProps = { //配置参数
name: 'bill'
}
static propTypes = { //配置参数的类型以及是否必要
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
age: PropTypes.number,
str: PropTypes.oneOfType([PropTypes.number, PropTypes.bool]).isRequired, //表示这个是这两种类型里的任何一种都可以
num: PropTypes.oneOf([1,2]), //这个表示是指定数组里的一个值
arr: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.number), //表示这个是一个数组,并且是由数字组成的一个数组,如果是['1', 2]就会报错
obj: PropTypes.shape({ //这个表示指定一个对象里面的类型, 这个时候,如果下面传的是{'name': 'bill', age: '12'}就会报类型错误
name: PropTypes.string,
age: PropTypes.number
}).isRequired
}
render() {
return <div>{this.props.name}{this.props.age}</div>
}
}
reactDom.render(<Counter name='this is title' str={12} obj={{'name': 'bill', age: 12}}/>, window.root)
函数式组件的默认props的写法
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import ReactDom from 'react-dom'
class Index extends Component {
state = {
name: 'yfbill'
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<Counter name={this.state.name}/>
</div>
);
}
}
const Counter = props => {
let {name, age=10, list=['aaa', 'bbb']} = props //函数式组件中props中进行解构默认值的写法
return <div>
<h2>{name}{age}</h2>
{list.map(val => <span>{val}</span>)}
</div>
}
ReactDom.render(<Index/>, window.root)
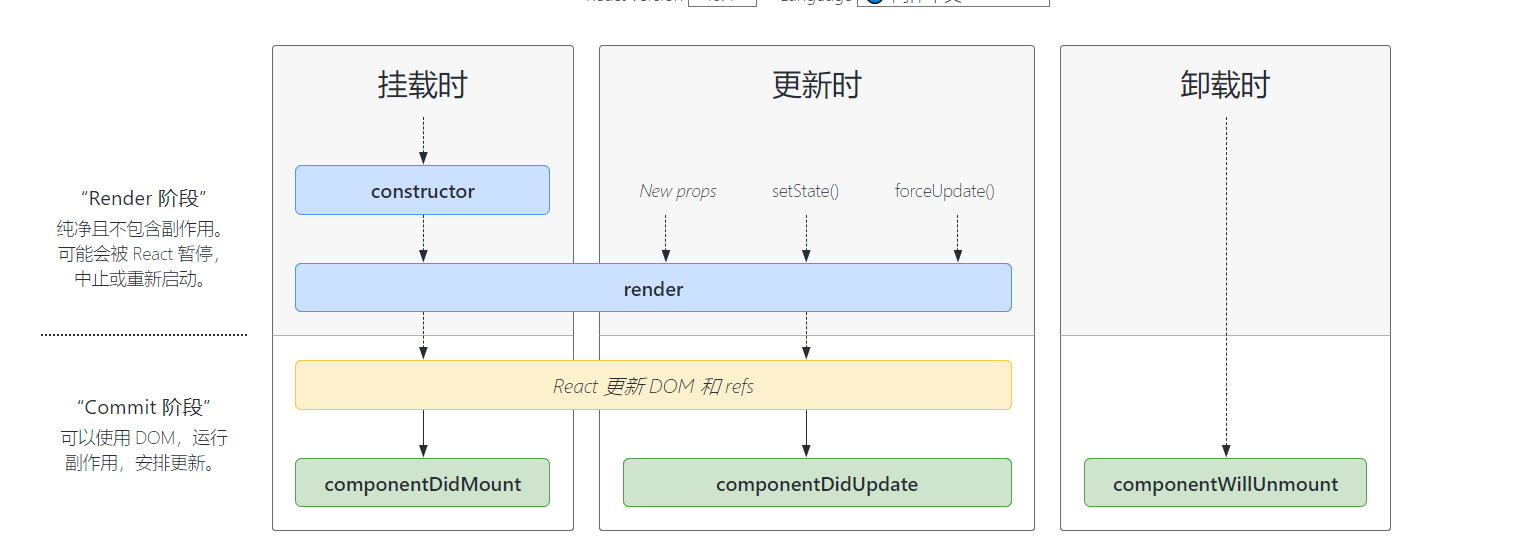
2、react的生命周期函数
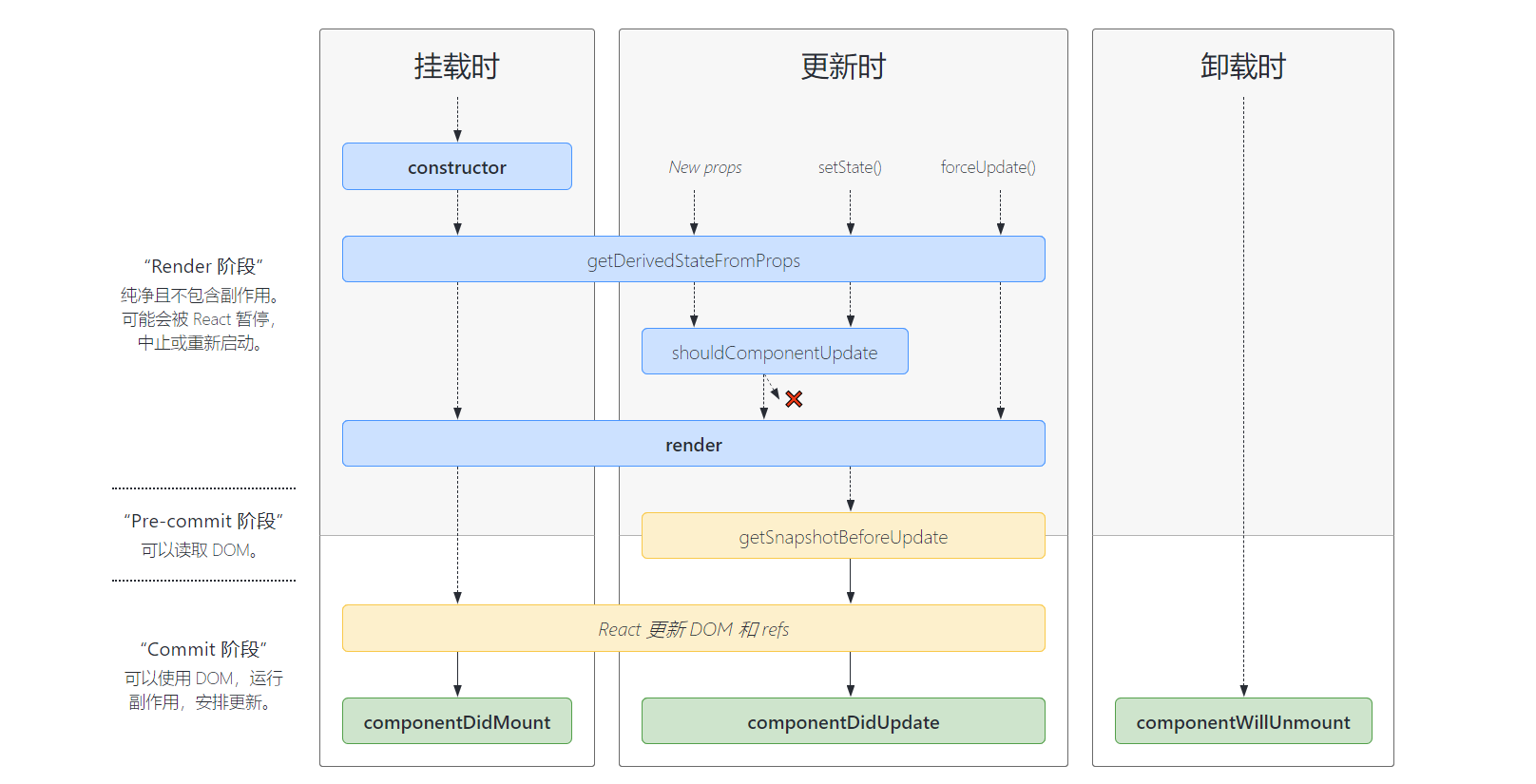
常用的生命周期函数
getDerivedStateFromProps 钩子
根据新的属性对象派生状态对象,也就表示在这个函数里面会接收两个参数,一个是传入的Props对象,一个是当前的state对象,并且该函数会返回一个对象或者null, 并且这个对象会被系统默认拿去更新当前的state,并且会触发页面的刷新
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import ReactDom from 'react-dom'
class Counter extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
num: 0
}
}
clickEvent = () => {
this.setState(state => ({num: state.num + 1}))
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>当前的数字是{this.state.num}</h2>
<button onClick={this.clickEvent}>按钮</button>
<Item num={this.state.num}/>
</div>
);
}
}
class Item extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
count: 0
}
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(currentProps, preState) { //注意:这个方法是静态方法
console.log(currentProps, preState)
return {
num: currentProps.num * 2 //该属性会被更新到state上,供使用
}
}
render() {
return <div>这个是子类的属性{this.state.count}, 传进来的值是{this.state.num}</div>
}
}
ReactDom.render(<Counter/>, window.root)
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 钩子
表示在更新前获取指定的状态,并且传入componentDidUpdate中的第三个参数以备调用,可以达到在组件更新的时候保持指定的状态
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import ReactDom from 'react-dom'
class Counter extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.wraper = React.createRef();
this.state = { messages: [] }
}
componentDidMount() {
setInterval(() => {
this.setState({messages: [this.state.messages.length, ...this.state.messages]})
}, 1000)
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
return this.wraper.current.scrollHeight
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
this.wraper.current.scrollTop = this.wraper.current.scrollTop + (this.wraper.current.scrollHeight - snapshot)
}
render () {
let style = {
height: '100px',
width: '200px',
border: '1px solid red',
overflow: 'auto'
}
return <ul style={style} ref={this.wraper}>
{
this.state.messages.map((val, ind) => <li key={ind}>{val}</li>)
}
</ul>
}
}
ReactDom.render(<Counter/>, window.root)
componentDidUpdate 钩子
表示组件更新后立即调用该方法,但是组件在初次渲染的时候不会调用该方法
接收三个参数, prevProps, prevState, snapshot, 前面两个分别是更新前的props对象,更新前的state对象,以及getSnapshotBeforeUpdate返回的结果,该方法可以用于监听指定属性的变化 ,但是需要作个条件限制以防走入死循环
componentDidMount 钩子
componentWillUnmount 钩子
componentDidCatch 捕获错误的钩子
render
注意:在旧版的react中通常来讲react在获取数据的时候会把获取数据这个操作放在componentDidMount里面进行操作,不放在constructor是因为,如果请求报错,会导致整个react组件崩溃,不放在componentWillMount是因为在SSR(服务端渲染)componentWillMount会执行两次,一次在服务端, 一次在客户端并且在react16后采用了Fiber架构,componentWillMount有可能被执行多次,而componentDidMount则永远只执行一次
3、react中的context
在某些场景下,你想在整个组件树中传递数据, 但却不想手动地在每一层传递属性, 你可以直接在React中使用强大的context Api解决上述问题
在老版本(17版本以前)的用法
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import ReactDom from 'react-dom'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
class Father extends Component {
static childContextTypes = { //定义父级需要传递的context值的类型
mark: PropTypes.string,
app: PropTypes.instanceOf(Father)
}
getChildContext() { //实现当前context传值的实例
return {
mark: this.props.mark,
app: this
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>this is father</h1>
<Son/>
</div>
);
}
}
class Son extends Component {
// constructor(props, context){ //第二参数是表示传递的上下文,这里的context相当于props如果没有写明constructor,那么默认是this.context
// super(props, context)
// }
static contextTypes = { //子类接收父级传递过来的context上下文,如果没有接收,那么就拿不到对应的值
mark: PropTypes.string,
app: PropTypes.instanceOf(Father)
}
render(){
console.log(this.context.app)
return <div>{this.context.mark}</div>
}
}
ReactDom.render(<Father mark='yfbill' />, window.root)
新版本context的使用
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import ReactDom from 'react-dom'
import MyContext from './context'
//注意:这里用MyContext.Provider来包所对应需要引入context的子组件
class Father extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>this is father</h1>
<MyContext.Provider value={{'name': 'yfbill', age: 20, app: this}}><Son/></MyContext.Provider>
</div>
);
}
}
class Son extends Component {
static contextType = MyContext //固定写法用contextType来接收context
render(){
console.log(this.context)
return <div>{this.context.name}</div>
}
}
ReactDom.render(<Father mark='yfbill' />, window.root)
注意:
//如果是函数式组件,那么接收context用的是useContext来接收 const Son = () => { const context = useContext(MyContext) //注意:这里的useContext需要从react中引入 console.log(context) return <div>{context.name}</div> }
context文件
import React from 'react' export default React.createContext()
如果在类组件中,那么不能使用useContext,但可以用以下方法,并且以下方法也可以使用在函数组件中
import styled from '@emotion/styled' import MyContext from './context' const StyleWrap = styled.div` color: red; background: #eee; `; const Item = () => { return <MyContext.Consumer> {value => { return <StyleWrap>{/*注意这里的样式组件也接收参数,用法与常规组件一样*/} <h2>this is item---{value.name}</h2> <span>this is sub item---{value.age}</span> </StyleWrap> }} </MyContext.Consumer> } export default Item
使用useContext代码如下
import { FC, ReactElement, useContext } from 'react';
import { userInfoContext } from '../context/context';
const Content: FC = (): ReactElement => {
const userInfo = useContext<{ name: string; age: number }>(userInfoContext);
console.log(userInfo);
return <div>this is content</div>;
};
export default Content;
注意:在react中进行跨层级的通信,或者是平行组件之前的通信,可以使用 hy-event-store 这个库来完成
import { HYEventBus } from 'hy-event-store'
const eventBus = new HYEventBus()
export default eventBus
// 对外暴露 on emit off三个方法进行调用
4、react中表单元素的使用举例
import { PureComponent, ReactElement, ChangeEvent, MouseEvent } from 'react';
interface IAppState {
username: string;
password: string;
checkList: Array<{ label: string; value: string; checked: boolean }>;
radioList: Array<{ label: string; value: string }>;
radioValue: string;
singleOptions: Array<{ label: string; value: string }>;
singleValue: string;
multipleValue: string[];
}
class App extends PureComponent<{}, IAppState> {
public state: IAppState = {
username: '',
password: '',
checkList: [
{ label: '语文', value: '1', checked: false },
{ label: '数学', value: '2', checked: false },
{ label: '电脑', value: '3', checked: false },
{ label: '英语', value: '4', checked: false },
],
radioList: [
{ label: '今天', value: '0' },
{ label: '昨天', value: '1' },
{ label: '明天', value: '2' },
],
radioValue: '',
singleOptions: [
{ label: 'javascript', value: 'js' },
{ label: 'php', value: 'php' },
{ label: 'node', value: 'node' },
{ label: 'python', value: 'python' },
{ label: 'shell', value: 'shell' },
],
singleValue: 'js',
multipleValue: [],
};
// 受控组件input的做法
public inputChangeEvent(e: ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>): void {
const { value, name } = e.target;
this.setState({ [name]: value } as Pick<
IAppState,
'username' | 'password'
>);
}
// 受控组件checkbox的做法
public checkSelectEvent(e: ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>): void {
const { value, checked } = e.target;
const target = this.state.checkList.find((item) => item.value === value);
if (target) target.checked = checked;
this.setState({
checkList: [...this.state.checkList],
});
}
// 受控组件radio的做法
public radioSelectEvent(e: ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>): void {
this.setState({
radioValue: e.target.value,
});
}
// 受控组件select的单项做法
public optionSelectEvent(e: ChangeEvent<HTMLSelectElement>): void {
this.setState({
singleValue: e.target.value,
});
}
// 受控组件的多项选择
public muliOptionEvent(e: ChangeEvent<HTMLSelectElement>): void {
const list = Array.from(e.target.selectedOptions).map((item) => item.value);
this.setState({
multipleValue: list,
});
}
// 提交按钮
public submitEvent(e: MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>): void {
e.preventDefault();
e.stopPropagation();
console.log(this.state);
}
public render(): ReactElement {
const {
username,
password,
checkList,
radioList,
radioValue,
singleValue,
singleOptions,
multipleValue,
} = this.state;
return (
<div>
<form>
<label htmlFor="username">用户名:</label>
<input
type="text"
id="username"
name="username"
value={username}
onChange={(e) => this.inputChangeEvent(e)}
/>
<label htmlFor="password">密码:</label>
<input
type="password"
id="password"
name="password"
value={password}
autoComplete="off"
onChange={(e) => this.inputChangeEvent(e)}
/>
{/* 多项选择 */}
<div>
{checkList.map((item) => (
<label key={'check' + item.value} htmlFor={'check' + item.value}>
{item.label}
<input
type="checkbox"
id={'check' + item.value}
value={item.value}
checked={item.checked}
onChange={(e) => this.checkSelectEvent(e)}
/>
</label>
))}
</div>
{/* 单项选择 */}
<div>
{radioList.map((item) => (
<label key={'radio' + item.value} htmlFor={'radio' + item.value}>
{item.label}
<input
type="radio"
id={'radio' + item.value}
value={item.value}
checked={radioValue === item.value}
name="day"
onChange={(e) => this.radioSelectEvent(e)}
/>
</label>
))}
</div>
{/* 单项选择框 */}
<select
value={singleValue}
onChange={(e) => this.optionSelectEvent(e)}
>
{singleOptions.map((item) => (
<option key={'option' + item.value} value={item.value}>
{item.label}
</option>
))}
</select>
{/* 多项选择框 */}
<select
multiple
value={multipleValue}
onChange={(e) => this.muliOptionEvent(e)}
>
{singleOptions.map((item) => (
<option key={'mulOption' + item.value} value={item.value}>
{item.label}
</option>
))}
</select>
{/* 点击提交按钮 */}
<div>
<button onClick={(e) => this.submitEvent(e)}>提交</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号