1、vuex的入门案例
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="container"> <h1>{{$store.state.count}}</h1> <!--在界面上访问用的是$store进行访问,类似$router--> <bill></bill> </div> <template id="bill"> <div> <input type="button" value="add" @click="add"> <input type="button" value="del" @click="del"> </div> </template> <script src="./vue.js"></script> <script src="./vuex.js"></script> <script> //状态数据存储 let state = { count: 1 }; /** * 改变数据的方法集合 * @type {{add(*): void, del(*): void}} */ let mutations = { //注册到vuex后,在vue中访问需要用到this.$store.commit('name')方法进行访问 add(state) { state.count ++; }, del(state) { state.count --; console.log(this); //这里的this指向的是vuex的整个对象,从中也可以获取state数据 } }; let store = new Vuex.Store({state, mutations}); let bill = { template: '#bill', methods: { add(){ this.$store.commit('add'); //触发mutations里的方法 }, del() { this.$store.commit('del'); } } }; let app = new Vue({ el: '#container', components: { bill }, store //绑定vuex }) </script> </body> </html>
注意:当在全局注册了store后,组件与路由里都可以使用,无需再引入
2、vuex中的state
获取vuex里面state的五种方式,前提需要引入mapState: import { mapState } from 'vuex'
//方式一 computed: { count() { return this.$store.state.count; }, msg() { return this.$store.state.msg } }, //方式二 computed: mapState({ state: state => state.count }), //方式三 computed: mapState(['count', 'msg']), //方式四 computed: { ...mapState(['count', 'msg']) }, //方式五 computed: { ...mapState({ count: state => state.count, text: state => state.msg }) },
3、vuex中的mutations
获取vuex中mutitions的方法,前提需要引入相当的方法 import { mapMutations, mapState } from 'vuex'
// import mapState from 'vuex'; import { mapMutations, mapState } from 'vuex' export default { data: function () { return { 'text': 'this is msg' } }, computed: mapState(['count']), //方式一 methods: mapMutations({ check: 'update' }) //方式二 methods: mapMutations(['check']) //方式三 methods: { ...mapMutations(['update']), //方式四 ...mapMutations({ say: 'update' }), check() { //方式五 this.$store.commit('update', 'yes'); } } }
4、vuex中的getters
相当于vue中的computed属性,用于过滤vuex中state的值, 前提需要引入mapGetters import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
// 方式一 computed: mapGetters(['nList']), // 方式二 computed: { ...mapGetters(['nList']) }, // 方式三 computed: mapGetters({ list: 'nList' }), // 方式四 computed: { ...mapGetters({ list: 'nList' }) }, // 方式五 computed: { list() { return this.$store.getters.nList } },
5、vuex中的actions
vuex中的actions与mutations的作用类似,不同之前是action是异步的方式修改数据,mutations是同步的方式修改数据,通常来讲,vuex不直接操作state里的数据,是通过mutations进行操作state里的数据
methods: { // 方式二引入 ...mapActions(['getData']), // 方式三引入 ...mapActions({ getList: 'getData' }), check () { // 方式一 this.$store.dispatch('getData') //接收一个参数 // 方式二调用 this.getData(); // 方式三调用 this.getList(); } }
// 方式四 methods: mapActions(['getData']) // 方式五 methods: mapActions({ getList: 'getData' })
action所对应的vuex中的内容
export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { list: [] }, mutations: { setList (state, list) { state.list = list } }, getters: { titleList (state) { let arr = []; state.list.forEach( value => arr.push(value.title)); return arr; } }, actions: { async getData ({ commit }) { // 通过解构赋值的形式获取commit对象 let res = await axios.get('/main/v1');// 发送ajax请求 if (res.status === 200) { let { data: { data, code } } = res; if (code === 0) { commit('setList', data);// commit调用的是mutations里的方法,通常action是发送请求,mutations方法是本地方法 } } } }, modules: {} })
6、modules下的定义以及访问
在不使用命名空间的情况下,需要访问test模块下的state需要用 this.$store.state.test.变量名进行访问,而方法或者getters里的方法可以按上面的方法进行获取和访问。同时里层的getters可以通过第三个参数访问外层的state或者可以通过this指向进行获取和访问
export default { computed: { ...mapState({ list: state => state.list, count: state => state.test.count// 表示模块test下的count }), ...mapGetters({ titleList: 'titleList', getCount: 'getCount'// 这个可以直接访问子模块test下getter里的getCount方法 }) }, methods: { ...mapActions(['getData', 'inner']), // 可以直接访问子模块test下的inner方法 check() { // console.log(this.list, this.count, this.titleList); // console.log(this.getCount); this.$store.commit('add'); // this.inner(); } } }
所对应的vuex文件如下
export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { list: [] }, mutations: { setList (state, list) { state.list = list } }, getters: { titleList (state) { let arr = []; state.list.forEach( value => arr.push(value.title)); return arr; } }, actions: { async getData ({ commit }) { // 通过解构赋值的形式获取commit对象 let res = await axios.get('/main/v1');// 发送ajax请求 if (res.status === 200) { let { data: { data, code } } = res; if (code === 0) { commit('setList', data);// commit调用的是mutations里的方法,通常action是发送请求,mutations方法是本地方法 } } } }, modules: { test: { state: { count: 0 }, getters: { getCount(state, args, outState) {// outState表示外层的state console.log(arguments); return state.count + 2; } }, mutations: { add(test) { console.log(test, this); } }, actions: { inner() { console.log(arguments, this); } } } } })
利用命名空间对modules进行访问
访问:
import { mapGetters, mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapState('test', {
count: state => state.count// 表示模块test下的count
}),
...mapGetters('test', {
getCount: 'getCount'// 这个可以直接访问子模块test下getter里的getCount方法
})
},
methods: {
check() {
console.log(this.getCount);
console.log(this.$store.state.test.count); //这个方法也可以进行访问
console.log(this.count);
}
}
}
定义:
modules: { test: { namespaced: true, state: { count: 0 }, getters: { getCount(state, args, outState) {// outState表示外层的state console.log(arguments); return state.count + 2; } }, mutations: { add(test) { console.log(test, this); } }, actions: { inner({commit}) { console.log(arguments, this); } } } }
7、plugins的用法
定义一个plugin: 如下
export default store => { console.log('this is store plugin init'); store.subscribe((mutation, state) => { console.log(mutation, state); }) };
在vuex中注册plugins
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' import state from './state' import mutations from './mutations' import actions from './actions' import user from './module/user' import myPlugin from './plugin/myPlugin' Vue.use(Vuex) export default new Vuex.Store({ state, mutations, actions, modules: { user }, plugins: [myPlugin] })
初始化的时候会打印出那个console.log的内容,当每次commit的时候就会触发subscribe里的内容,以上情况结合socket的使用如下
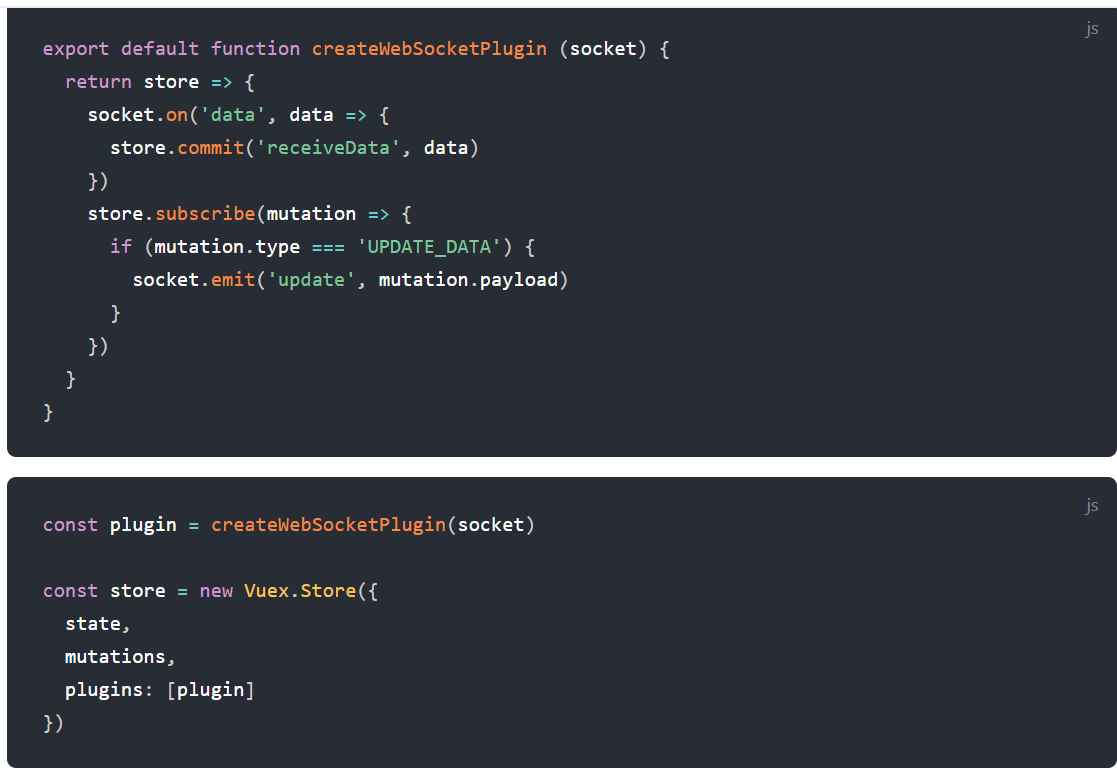
8、严格模式
当严格模式为true的时候是不允许直接修改state里的值,而是要通过mutations里的方法进行修改,可以按如下设置
export default new Vuex.Store({ // strict: true, strict: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development', state, mutations, actions, modules: { user }, plugins: [myPlugin] })
9、经典的模块引用
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' import getters from './getters' Vue.use(Vuex) // https://webpack.js.org/guides/dependency-management/#requirecontext const modulesFiles = require.context('./modules', true, /\.js$/) // you do not need `import app from './modules/app'` // it will auto require all vuex module from modules file const modules = modulesFiles.keys().reduce((modules, modulePath) => { // set './app.js' => 'app' const moduleName = modulePath.replace(/^\.\/(.*)\.\w+$/, '$1') const value = modulesFiles(modulePath) modules[moduleName] = value.default return modules }, {}) const store = new Vuex.Store({ modules, getters }) export default store


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号