【Spring从入门到精通】02-AOP
AOP
1、AOP 概述
- 定义:AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming,面向切面编程),通过预编译和运行时动态代理扩展程序功能
- 作用:利用 AOP 可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,降低耦合性,提高程序可重用性和开发效率
- 场景:日志记录,性能统计,安全控制,事务处理,异常处理
- 通俗描述:不修改源代码,在主干功能中添加新功能
使用登录功能案例说明 AOP
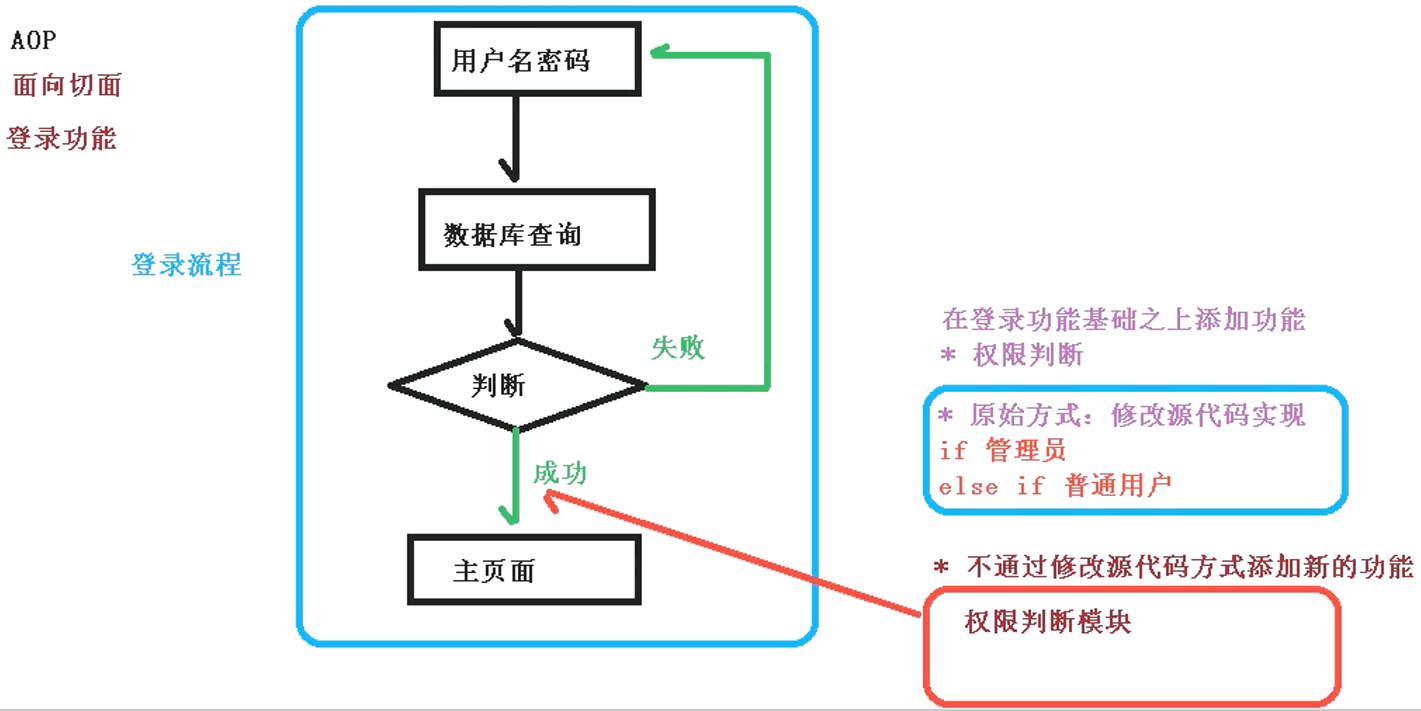
2、AOP 底层原理
- 底层原理:动态代理
- 有接口情况:JDK动态代理
- 无接口情况:CGLib动态代理
如果学习过设计模式,应该对上述两种代理方式非常了解了。没有学习过也没关系,我们接着往下看
2.1、JDK 动态代理
public interface UserDao {
void login();
}
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public void login(){
//登录实现过程
}
}
有接口情况:创建 UserDao 接口实现类代理对象
2.2、CGlib 动态代理
public class User {
public void add(){
//...
}
}
// 原始方法:通过子类继承,重写User类方法
public class Person extends User {
@Override
public void add(){
super.add();
//增强代码逻辑
}
}
无接口情况:创建 User 类子类代理对象
由于 Spring5 中对上述代理已经做了很好的封装,我们只需要通过最简单的方式进行配置即可
但仍然需要我们对原理有一定的认识,只有做到“知其然,知其所以然”,才能真正“以不变应万变”
3、JDK 动态代理实现
实现方式:使用Proxy中的方法创建代理对象

具体方法:newProxyInstance()
方法参数
ClassLoader loader:类加载器Class<?>[] interfaces:增强方法所在类实现的接口数组InvocationHandler h:实现InvocationHandler接口,创建代理对象,编写增强方法

常言道:“Talking is cheap, show me the code"。话不多说,下面上代码~
- 1)创建 UserDao 接口和对应实现类
public interface UserDao {
int add(int a, int b);
String update(String id);
}
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
@Override
public String update(String id) {
return id;
}
}
- 2)创建 UserDao 代理对象
public class UserDaoProxy {
private UserDao target;
public UserDaoProxy(UserDao target) {
this.target = target;
}
public UserDao newProxyInstance() {
Class<?> targetClass = target.getClass();
ClassLoader classLoader = targetClass.getClassLoader();
Class<?>[] interfaces = targetClass.getInterfaces();
return (UserDao) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, new UserDaoInvocationHandler());
}
class UserDaoInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 被代理对象方法前置逻辑
System.out.print("method=" + method.getName() + ", args=" + Arrays.toString(args));
// 被代理对象方法
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
// 被代理对象方法后置逻辑
System.out.println(", result=" + result);
return result;
}
}
}
- 3)测试
UserDao target = new UserDaoImpl();
UserDaoProxy userDaoProxy = new UserDaoProxy(target);
UserDao userDao = userDaoProxy.newProxyInstance();
userDao.add(1, 2);
userDao.update("UUID1");
// method=add, args=[1, 2], result=3
// method=update, args=[UUID1], result=UUID1
4、AOP 术语
-
连接点:类中可以被增强的方法,称为连接点
-
切入点:类中实际被增强的方法,称为切入点
-
通知(增强):实际增强的逻辑部分,称为通知
通知分为五种类型:
- 前置通知:方法执行之前的处理
- 后置通知:方法执行之后的处理
- 环绕通知:方法执行前后的处理
- 异常通知:方法抛出异常的处理
- 最终通知:方法执行最终的处理(相当于
try-catch-finally中的finally)
-
切面:是一个动作,即把通知应用到切入点的过程
5、AOP 准备工作
5.1、AspectJ 介绍
Spring 一般都是基于AspectJ实现 AOP 操作的
AspectJ不是 Spring 的一部分,而是一个独立的 AOP 框架- 一般会把
AspectJ和 Spring 搭配使用,进行 AOP 操作,因为这样更加方便
基于 AspectJ 进行 AOP 操作的两种方式:
- 基于 XML 配置文件方式实现
- 基于注解方式实现(推荐使用)
5.2、引入 AOP 相关依赖

<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>1.9.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.8</version>
</dependency>
5.3、切入点表达式
切入点表达式的作用:知道对哪个类的哪个方法进行增强
语法结构:execution([权限修饰符][返回类型][类全路径][方法名]([参数列表]))
举例
⭐ 举例1:对com.vectorx.dao.BookDao中的add()方法进行增强
execution(* com.vectorx.dao.BookDao.add(..))
⭐ 举例2:对com.vectorx.dao.BookDao中的所有方法进行增强
execution(* com.vectorx.dao.BookDao.*(..))
⭐ 举例3:对com.vectorx.dao包中所有类的所有方法进行增强
execution(* com.vectorx.dao.*.*(..))
6、AspectJ 注解实现
6.1、Spring 配置文件
- 1)引入
context和aop名称空间 - 2)配置组件扫描基础包
- 3)开启AspectJ生成代理对象
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--组件扫描配置-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.vectorx.spring5.s13_aspectj_annatation"/>
<!--开启AspectJ生成代理对象-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans>
6.2、创建被增强对象和增强对象
- 1)创建 User 对象,并添加
@Component注解 - 2)创建 UserProxy 对象,并添加
@Component注解
@Component
public class User {
public void add() {
System.out.println("add...");
}
}
@Component
public class UserProxy {
/**
* 前置通知
*/
public void before() {
System.out.println("before...");
}
/**
* 后置通知
*/
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning...");
}
/**
* 最终通知
*/
public void after() {
System.out.println("after...");
}
/**
* 异常通知
*/
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("afterThrowing...");
}
/**
* 环绕通知
*/
public void around() {
System.out.println("around...");
}
}
6.3、添加增强类注解和切入点表达式
@Component
@Aspect
public class UserProxy {
/**
* 前置通知
*/
@Before(value = "execution(* com.vectorx.spring5.s13_aspectj_annatation.User.add(..))")
public void before() {
System.out.println("before...");
}
/**
* 后置通知
*/
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* com.vectorx.spring5.s13_aspectj_annatation.User.add(..))")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning...");
}
/**
* 最终通知
*/
@After(value = "execution(* com.vectorx.spring5.s13_aspectj_annatation.User.add(..))")
public void after() {
System.out.println("after...");
}
/**
* 异常通知
*/
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.vectorx.spring5.s13_aspectj_annatation.User.add(..))")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("afterThrowing...");
}
/**
* 环绕通知
*/
@Around(value = "execution(* com.vectorx.spring5.s13_aspectj_annatation.User.add(..))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around before...");
// 执行被增强的方法
joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("around after...");
}
}
6.4、代码测试
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean11.xml");
User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);
user.add();
结果
around before...
before...
add...
afterReturning...
after...
around after...
为了演示异常通知,需要修改下被增强对象中的方法,模拟一个异常
@Component
public class User {
public void add() {
System.out.println("add...");
// 模拟一个异常
int i = 2 / 0;
}
}
运行结果
around before...
before...
add...
afterThrowing...
after...
对比正常情况下,发现少了afterReturning即后置异常和around after即环绕增强的后置处理
6.5、抽取相同切入点表达式
通过上述的例子,应该对AspectJ注解实现有了一定的了解
同时我们发现切入点表达式都是完全一样的,可以对这些相同的切入点表达式进行抽取,以达到重用切入点表达式定义的目的
- 1)首先想到的应该是定义成员变量
private final String execution = "execution(* com.vectorx.spring5.s13_aspectj_annatation.User.add(..))";
@Before(value = execution)
public void before() {
System.out.println("before...");
}
- 2)
AspectJ中提供了Pointcut注解(推荐)
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* com.vectorx.spring5.s13_aspectj_annatation.User.add(..))")
private void pointcut(){}
@Before(value = "pointcut()")
public void before() {
System.out.println("before...");
}
6.6、设置增强类优先级
如果有多个增强类对类中同一个方法进行增强,可以设置增强类的优先级,来决定哪个增强类先执行,哪个增强类后执行
使用@Order注解设置增强类的优先级,其中指定优先级数字,注解格式:@Order(数字类型值)
- 数字类型值越小,优先级越高
- 数字类型值越大,优先级越低
⭐最佳实践
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class PersonProxy {
//...
}
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(3)
public class UserProxy {
//...
}
测试结果
person around before...
person before...
user around before...
user before...
add...
user afterReturning...
user after...
user around after...
person afterReturning...
person after...
person around after...
我们发现:
- PersonProxy 中的前置通知先于 UserProxy 中的前置通知执行
- PersonProxy 中的后置通知晚于 UserProxy 中的后置通知执行
6.7、完全注解开发
如果要用完全注解的方式进行开发,可以使用注解类代替 Spring 配置文件
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.vectorx.spring5.s13_aspectj_annatation")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class AopConfig {
}
其中:
- 注解
@ComponentScan(value = "com.vectorx.spring5.s13_aspectj_annatation")代替了<context:component-scan base-package="com.vectorx.spring5.s13_aspectj_annatation"/>进行组件扫描的配置 - 注解
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)代替了<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>开启AspectJ生成代理对象
对应关系
| 注解方式 | 配置文件方式 |
|---|---|
@ComponentScan |
<context:component-scan> |
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy |
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy> |
7、AspectJ 配置文件实现
7.1、创建被增强对象和增强对象
public class Book {
public void buy() {
System.out.println("buy...");
}
}
public class BookProxy {
public void before() {
System.out.println("before...");
}
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning...");
}
public void after() {
System.out.println("after...");
}
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("afterThrowing...");
}
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around before...");
joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("around after...");
}
}
7.2、Spring 配置文件
- 1)引入
aop名称空间 - 2)配置被增强对象和增强对象创建
- 3)配置
aop增强
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--创建对象-->
<bean id="book" class="com.vectorx.spring5.s14_aspectj_xml.Book"></bean>
<bean id="bookProxy" class="com.vectorx.spring5.s14_aspectj_xml.BookProxy"></bean>
<!--配置aop增强-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="p" expression="execution(* com.vectorx.spring5.s14_aspectj_xml.Book.buy(..))"/>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:aspect ref="bookProxy">
<!--前置通知-->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="p"/>
<!--后置通知-->
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="p"/>
<!--最终通知-->
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="p"/>
<!--异常通知-->
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="p"/>
<!--环绕通知-->
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="p"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
其中,配置文件的标签与注解的对应关系如下表
| 配置文件方式 | 注解方式 |
|---|---|
<aop:pointcut> |
@Pointcut |
<aop:aspect> |
@Aspect |
<aop:before> |
@Before |
<aop:after-returning> |
@AfterReturning |
<aop:after> |
@After |
<aop:after-throwing> |
@AfterThrowing |
<aop:around> |
@Around |
7.3、代码测试
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean12.xml");
Book book = context.getBean("book", Book.class);
book.buy();
测试结果
before...
around before...
buy...
around after...
after...
afterReturning...
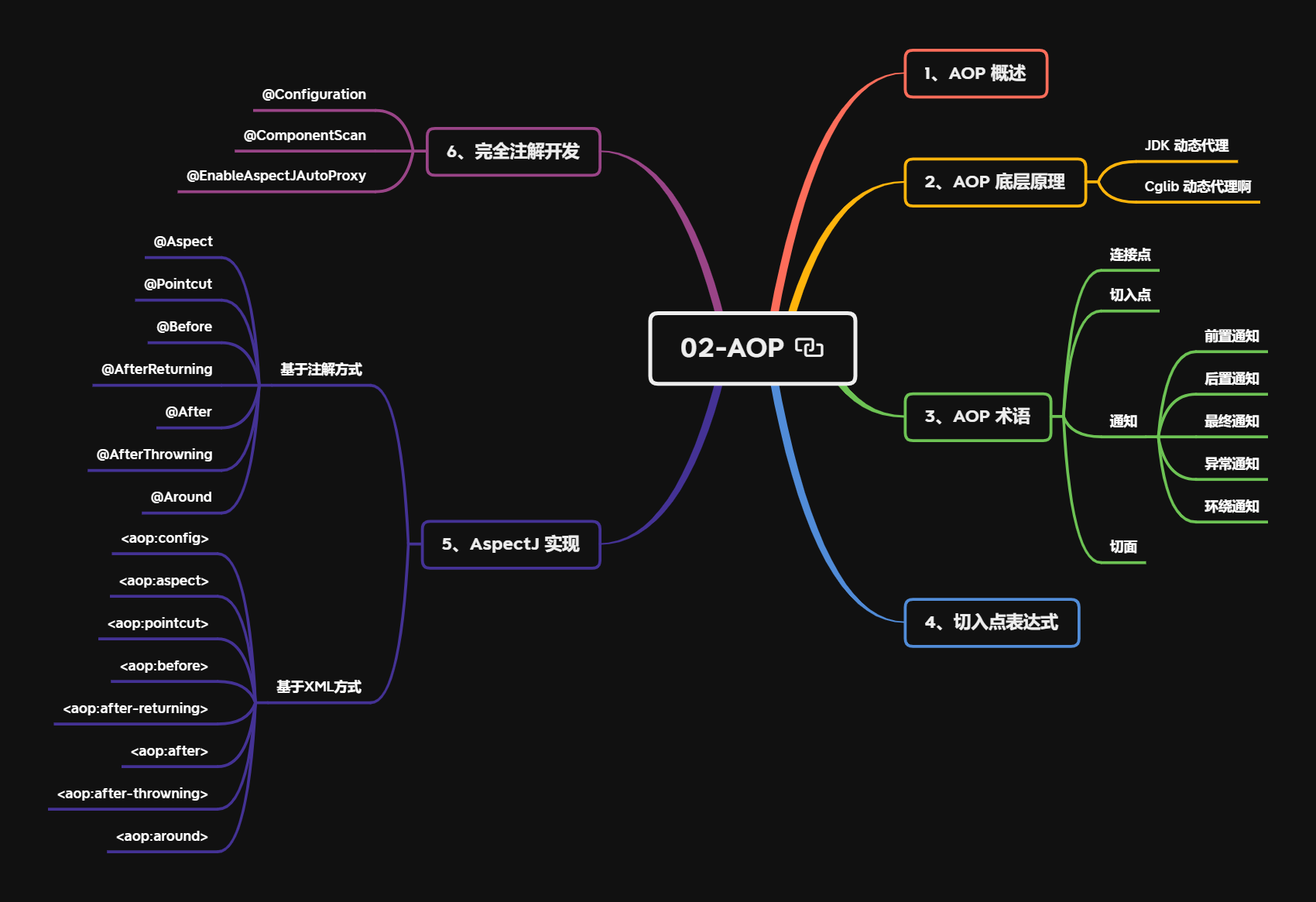
小结
本节重点
- AOP 概述
- AOP 底层原理
- AOP 术语
- 切入点表达式
- AspectJ 实现
- 完全注解开发
以下总结仅供参考


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号