包子学系列——Java基础第七章_异常处理
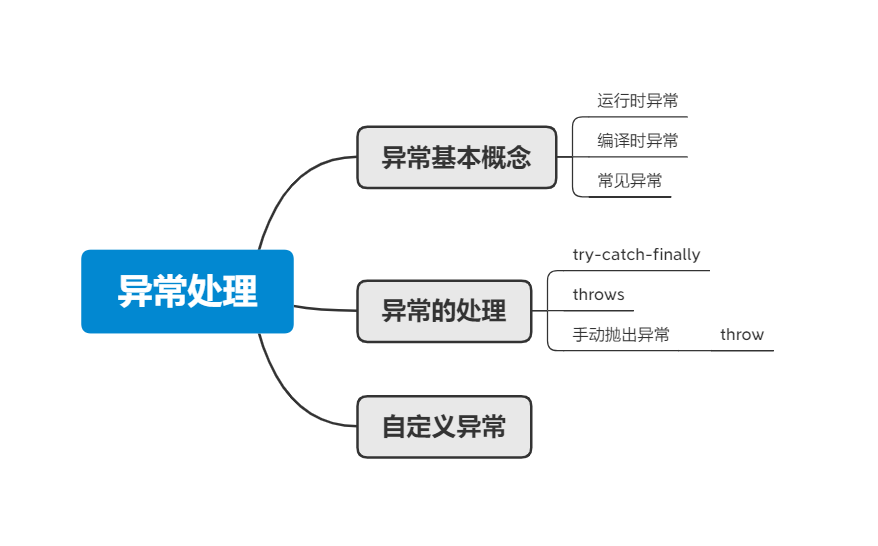
第七章 异常处理
Java程序在执行过程中所发生的异常事件可分为两类:
- Error:Java虚拟机无法解决的严重问题。如:JVM系统内部错误、资源 耗尽等严重情况。比如:StackOverflowError和OOM。一般不编写针对性 的代码进行处理
- Exception: 其它因编程错误或偶然的外在因素导致的一般性问题,可以使 用针对性的代码进行处理。例如
- 数组角标越界
- 空指针访问
捕获错误最理想的是在编译期间,但有的错误只有在运行时才会发生。 比如:除数为0,数组下标越界等
分类:编译时异常和运行时异常
* java.lang.Throwable
* |-----java.lang.Error:一般不编写针对性的代码进行处理。
* |-----java.lang.Exception:可以进行异常的处理
* |------编译时异常(checked)
* |-----IOException
* |-----FileNotFoundException
* |-----ClassNotFoundException
* |------运行时异常(unchecked,RuntimeException)
* |-----NullPointerException
* |-----ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
* |-----ClassCastException
* |-----NumberFormatException
* |-----InputMismatchException
* |-----ArithmeticException
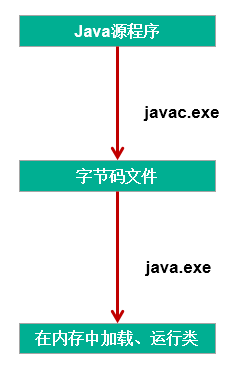
从程序执行过程,看编译时异常和运行时异常
编译时异常:执行javac.exe命名时,可能出现的异常
运行时异常:执行java.exe命名时,出现的异常
常见异常#
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException#
public class IndexOutExp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String friends[] = { "lisa", "bily", "kessy" };
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(friends[i]); // friends[4]?
}
System.out.println("\nthis is the end");
}
}
NullPointerException#
public void test1(){
// int[] arr = null;
// System.out.println(arr[3]);
String str = "abc";
str = null;
System.out.println(str.charAt(0));
}
ArithmeticException#
@Test
public void test6(){
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
System.out.println(a / b);
}
ClassCastException#
@Test
public void test3(){
Object obj = new Date();
String str = (String)obj;
}
异常的处理#
java异常处理的抓抛模型#
过程一:"抛":程序在正常执行的过程中,一旦出现异常,就会在异常代码处生成一个对应异常类的对象。
* 并将此对象抛出。
* 一旦抛出对象以后,其后的代码就不再执行。
*
* 关于异常对象的产生:① 系统自动生成的异常对象
* ② 手动的生成一个异常对象,并抛出(throw)
*
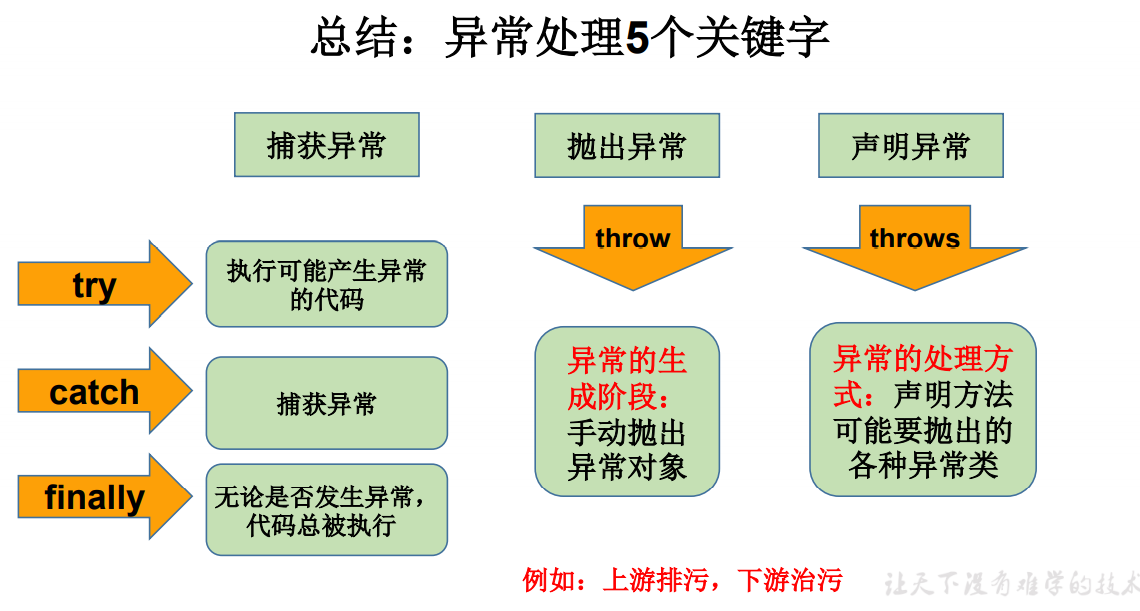
过程二:"抓":可以理解为异常的处理方式:① try-catch-finally ② throws
异常处理方式一:try-catch-finally#
try{
//可能出现异常的代码
}catch(异常类型1 变量名1){
//处理异常的方式1
}catch(异常类型2 变量名2){
//处理异常的方式2
}catch(异常类型3 变量名3){
//处理异常的方式3
}
....
finally{
//一定会执行的代码
}
- 使用try将可能出现异常代码包装起来,在执行过程中,一旦出现异常,就会生成一个对应异常类的对象,根据此对象的类型,去catch中进行匹配
- 一旦try中的异常对象匹配到某一个catch时,就进入catch中进行异常的处理。一旦处理完成,就跳出当前的try-catch结构(在没写finally的情况。继续执行其后的代码
- catch中的异常类型如果没子父类关系,则谁声明在上,谁声明在下无所谓。
- catch中的异常类型如果满足子父类关系,则要求子类一定声明在父类的上面。否则,报错
- 常用的异常对象处理的方式: ① String getMessage() ② printStackTrace()
- 在try结构中声明的变量,再出了try结构以后,就不能再被调用
- try-catch-finally结构可以嵌套
例子
public class IndexOutExp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String friends[] = { "lisa", "bily", "kessy" };
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(friends[i]);
}
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("index err");
}
System.out.println("\nthis is the end");
}
}
//=====================
程序IndexOutExp.java运行结果:java IndexOutExp
lisa
bily
kessy
index err
this is the end
public class DivideZero1 {
int x;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int y;
DivideZero1 c = new DivideZero1();
try {
y = 3 / c.x;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("divide by zero error!");
}
System.out.println("program ends ok!");
}
}
//=======================
程序DivideZero1运行结果:java DivideZero1
divide by zero error!
program ends ok!
如何看待代码中的编译时异常和运行时异常?#
- 体会1:使用try-catch-finally处理编译时异常,使得程序在编译时就不再报错,但是运行时仍可能报错。相当于我们使用try-catch-finally将一个编译时可能出现的异常,延迟到运行时出现。
- 体会2:开发中,由于运行时异常比较常见,所以我们通常就不针对运行时异常编写try-catch-finally了。针对于编译时异常,我们说一定要考虑异常的处理。
finally的再说明#
- finally是可的
- finally中声明的是一定会被执行的代码。即使catch中又出现异常了,try中return语句,catch中return语句等情况。
- 像数据库连接、输入输出流、网络编程Socket等资源,JVM是不能自动的回收的,我们需要自己手动的进行资源的释放。此时的资源释放,就需要声明在finally中。
异常处理方式二:throws + 异常类型#
throws + 异常类型"写在方法的声明处。指明此方法执行时,可能会抛出的异常类型。
一旦当方法体执行时,出现异常,仍会在异常代码处生成一个异常类的对象,此对象满足throws后异常类型时,就会被抛出。异常代码后续的代码,就不再执行!
对比两种处理方式#
try-catch-finally:真正的将异常给处理掉了。
throws的方式只是将异常抛给了方法的调用者。并没真正将异常处理掉。
如何选择#
- 如果父类中被重写的方法没throws方式处理异常,则子类重写的方法也不能使用throws,意味着如果子类重写的方法中异常,必须使用try-catch-finally方式处理。
- 执行的方法a中,先后又调用了另外的几个方法,这几个方法是递进关系执行的。我们建议这几个方法使用throws的方式进行处理。而执行的方法a可以考虑使用try-catch-finally方式进行处理。
手动抛出异常#
在程序执行中,除了自动抛出异常对象的情况之外,我们还可以手动的throw一个异常类的对象。
throw 和 throws区别:
- throw 表示抛出一个异常类的对象,生成异常对象的过程。声明在方法体内。
- throws 属于异常处理的一种方式,声明在方法的声明处。
class Student{
private int id;
public void regist(int id) throws Exception {
if(id > 0){
this.id = id;
}else{
//手动抛出异常对象
// throw new RuntimeException("您输入的数据非法!");
// throw new Exception("您输入的数据非法!");
throw new MyException("不能输入负数");
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + "]";
}
}
自定义异常#
/*
* 如何自定义异常类?
* 1. 继承于现的异常结构:RuntimeException 、Exception
* 2. 提供全局常量:serialVersionUID
* 3. 提供重载的构造器
*
*/
public class MyException extends Exception{
static final long serialVersionUID = -7034897193246939L;
public MyException(){
}
public MyException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET 9 new features-C#13新的锁类型和语义
· Linux系统下SQL Server数据库镜像配置全流程详解
· 现代计算机视觉入门之:什么是视频
· 你所不知道的 C/C++ 宏知识
· 聊一聊 操作系统蓝屏 c0000102 的故障分析
· DeepSeek V3 两周使用总结
· 回顾我的软件开发经历(1)
· C#使用yield关键字提升迭代性能与效率
· 低成本高可用方案!Linux系统下SQL Server数据库镜像配置全流程详解
· 4. 使用sql查询excel内容