设计模式之装饰器 Decorator Pattern
1. 定义
当需要扩展子类中的功能时,不修改原有子类A中的功能,采用继承自同一个父类新子类B,来增加原有子类A中功能。此时需要新的子类B持有子类A的引用。
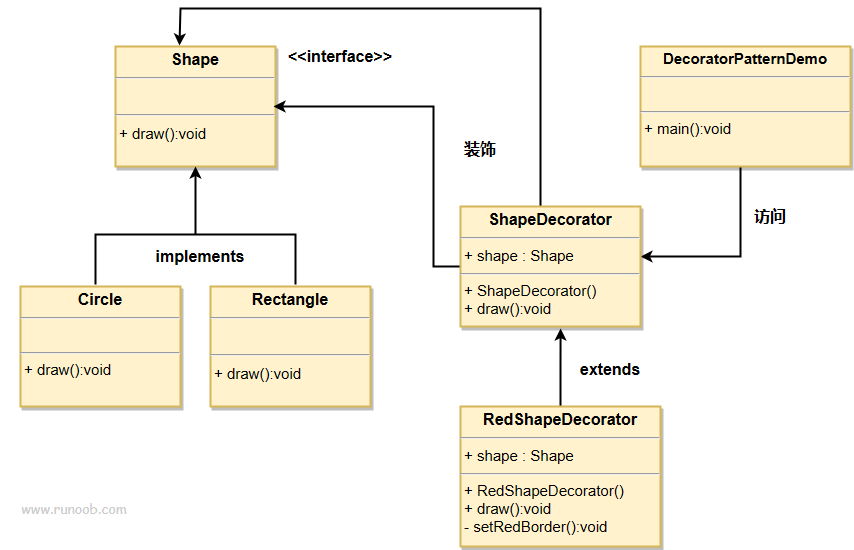
2. 解释
设计原则
- 对扩展开放,对修改封闭;
- 使用组合(接口)代替继承;
装饰模式特点:
- 装饰对象和真实对象有相同的接口。这样客户端对象就能以和真实对象相同的方式和装饰对象交互。
- 装饰对象包含一个真实对象的引用(reference)
- 装饰对象接受所有来自客户端的请求。它把这些请求转发给真实的对象。
- 装饰对象可以在转发这些请求以前或以后增加一些附加功能。这样就确保了在运行时,不用修改给定对象的结构就可以在外部增加附加的功能。在面向对象的设计中,通常是通过继承来实现对给定类的功能扩展。
装饰器模式与其他组合模式类似,不同的地方在于,装饰器模式没有引入其他父类型,即可实现运行时的行为扩展。
与其他设计模式的比较:[Design Pattern] Decorator 裝飾者模式
3. 举例
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class Ship : public enable_shared_from_this<Ship> {
public:
virtual void run() = 0;
virtual void shot() = 0;
virtual ~Ship() = default;
std::shared_ptr<Ship> getptr() {
return shared_from_this();
}
};
class NorthCarolina : public Ship {
public:
void run() override {
cout << "NorthCarolina is running." << endl;
};
void shot() override {
cout << "NorthCarolina is shotting." << endl;
};
};
class Iowa : public Ship {
public:
void run() override {
cout << "Iowa is running." << endl;
};
void shot() override {
cout << "Iowa is shotting." << endl;
};
};
class Decorator : public Ship {
public:
Decorator(std::shared_ptr<Ship> ship) : ship(ship) {}
void run() override {
ship->run();
}
void shot() override {
ship->shot();
}
protected:
std::shared_ptr<Ship> ship;
};
class ScoutPlane : public Decorator {
string scout;
public:
ScoutPlane(std::shared_ptr<Ship> ship) : Decorator(ship) {}
void setScout() {
scout = "Searching......";
};
void getScout() {
cout << scout << endl;
}
void run() override {
ship->run();
setScout();
getScout();
}
void shot() override {
ship->shot();
}
};
class Ammu : public Decorator {
string ammu;
public:
Ammu(std::shared_ptr<Ship> ship) : Decorator(ship) {}
void setAmmu() {
ammu = "AP";
};
void getAmmu() {
cout << "shotting " << ammu << "." << endl;
}
void run() override {
ship->run();
}
void shot() override {
ship->shot();
setAmmu();
getAmmu();
}
};
int main() {
std::shared_ptr<Ship> ship1 = std::make_shared<Iowa>();
std::shared_ptr<Ship> ship2 = std::make_shared<NorthCarolina>();
ship1->run();
ship1->shot();
cout << "----------------" << endl;
ship2->run();
ship2->shot();
cout << "----------------" << endl;
std::shared_ptr<Ship> ship3 = std::make_shared<Ammu>(ship1->getptr());
ship3->run();
ship3->shot();
cout << "----------------" << endl;
std::shared_ptr<Ship> ship4 = std::make_shared<ScoutPlane>(ship3->getptr());
ship4->run();
ship4->shot();
cout << "----------------" << endl;
std::shared_ptr<Ship> ship5 = std::make_shared<ScoutPlane>(ship2->getptr());
ship5->run();
ship5->shot();
}
Iowa is running.
Iowa is shotting.
----------------
NorthCarolina is running.
NorthCarolina is shotting.
----------------
Iowa is running.
Iowa is shotting.
shotting AP.
----------------
Iowa is running.
Searching......
Iowa is shotting.
shotting AP.
----------------
NorthCarolina is running.
Searching......
NorthCarolina is shotting.





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构