
DHCP
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol(动态主机配置协议) (RFC 2131)
- Bootstrap Protocol BOOTP(引导程序协议) allows a diskless(无盘) workstation to be remotely booted up in a network
- UDP port 67 (server) & port 68 (client)
- DHCP builds on BOOTP to allow servers to deliver configuration information to a host
- Used extensively to assign temporary IP addresses to hosts
- Allows ISP(Internet Service Provider)(互联网服务提供商) to maximize usage of their limited IP addresses
- Time thresholds(阈值) to enforce lease time(增加租赁时间)
Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Class A, B, and C addresses have been set aside for use within private Internets
- Private IP addresses are sufficient for use inside of private networks
- But packets with private (“unregistered”) addresses are discarded by routers in the global Internet
- NAT (RFC 1631): method for mapping packets from hosts in private internets into packets that can traverse(穿过) the Internet
- A device (computer, router, firewall) acts as an agent between a private network and a public network
- A number of hosts can share(共享) a limited number of registered IP addresses
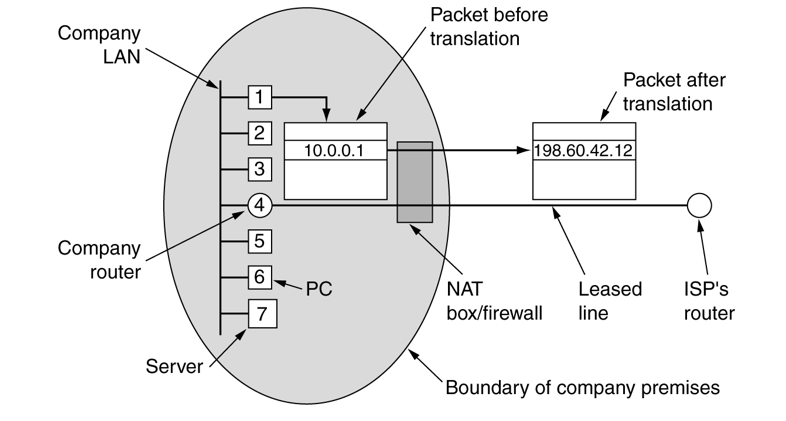
Placement of Operation of a NAT Box
- NAT: provides mapping between public IP address and private IP addresses
NAT Operations
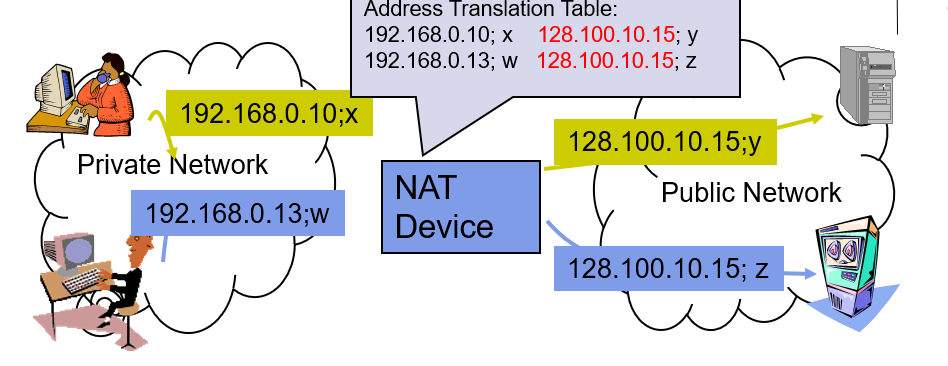
- Hosts inside private networks generate packets with private IP address & TCP/UDP port #s
- NAT maps each private IP address & port # into shared global IP address & available port #
- Translation table allows packets to be routed unambiguously(明确地)
NAT Discussions
- In theory, up to 2^16 private IP addresses supported by a single public IP address in NAT box
- Overhead in NAT operation
- TCP/UDP Port number used for NAT mapping at IP layer, violating OSI layer architecture principle
- The principle is that a higher layer utilize a service provided by the lower lever but not vice versa(反).
posted @
2017-10-17 17:27
范加索尔拉
阅读(
270)
评论()
编辑
收藏
举报





