ARP, Fragmentation and Reassembly
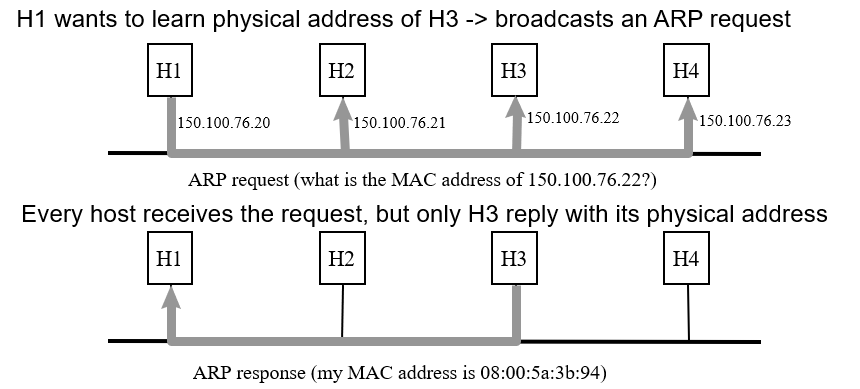
Address Resolution Protocol
- IP addresses are said to be logical, because they are defined in terms of logical topology of the routers and end systems.
- The logical IP addresses need to be converted into specific physical addresses that identify the physical endpoints for the Ethernet sender and receiver
- ARP: conversion between IP address and Physical address
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- How to map an IP address to a physical address? How to speed up? How fresh?
- How to map:First, broadcast. Second, specific host reply.
- How to speed up:cache the mac address
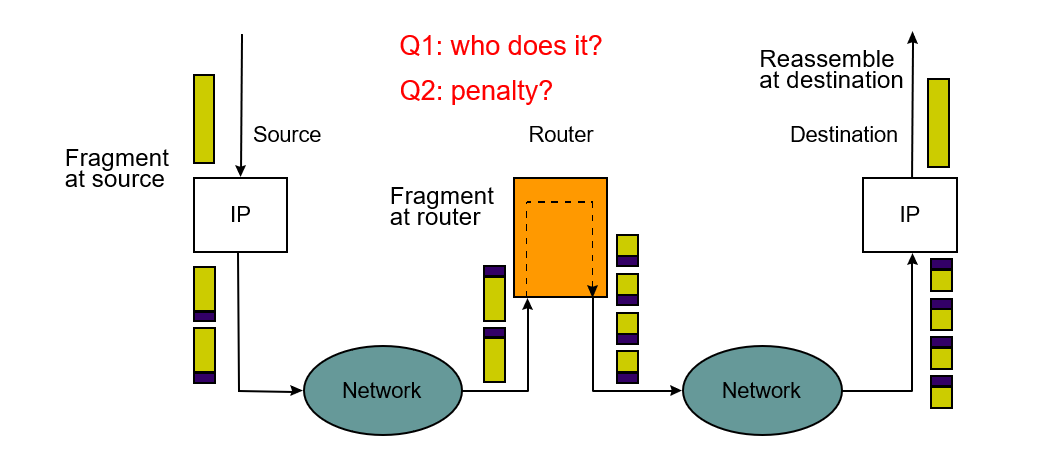
Fragmentation(分裂) and Reassembly
- Each physical network imposes(强加) a certain packet size limitation on the packet to be carried, called maximum transmission unit MTU.
- Router will devide packet into smaller pakcet according to the MTU.
RE: IP Packet Header
- Identification, Flags, and Fragment Offset: used for fragmentation and reassembly
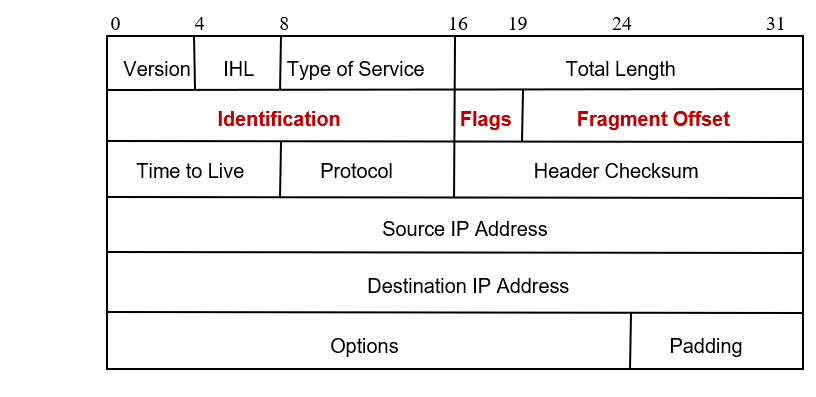
- Identification is used to identify which packet a particular fragment belongs to.
- Flag:contain tree
- unsed bit:
- don't fragment is set to one :it will force the router not to fragment the pakcet.
- more fragment is set to one:tell the estination host that there are more fragments to follow.
- The Fragment Offset field identidies the location of a fragment in the packet.
- Fragment offset(分段偏移) is 13 bits; total length is 16 bits, what does it imply?
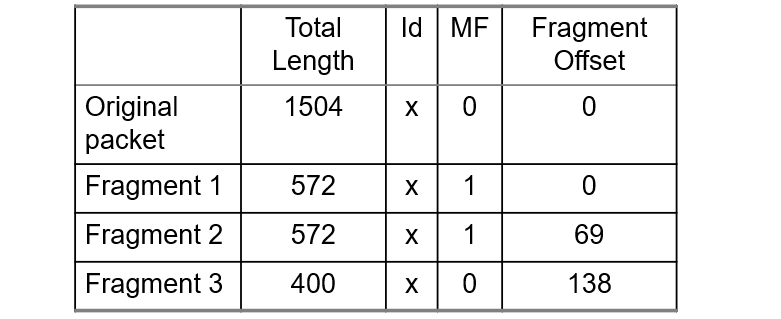
Example: Fragmenting a Packet
-
Packet is to be forwarded to a network with MTU of 576 bytes. The packet has an IP header of 20 bytes and a data part of 1484 bytes.
-
Maximum data length per fragment = 576 - 20 = 556 bytes.
-
Set maximum data length to 552 bytes to get multiple of 8.
-
All the value except the header checksum are the same as in original packet.



