IP Addressing
IP Addressing(处理)
- Each host on Internet has unique 32 bit IP address
- Each address has two parts: netid and hostid
- netid(网络号) is unique & administered(管理) by Internet registration(注册)
- netid facilitates(促进) routing and reduces routing table
- A separate address is required for each physical connection of a host to a network; “multi-homed” hosts
- Dotted-Decimal Notation:
int1.int2.int3.int4 where intj = integer value of jth octet - IP address of 10000000 10000111 01000100 00000101
is 128.135.68.5 in dotted-decimal notation
Reflections
- How to reduces routing table: The netid sorts IP Addresses, combing the IP Addresses which belong to the same places to the same netid.
Classful Addresses

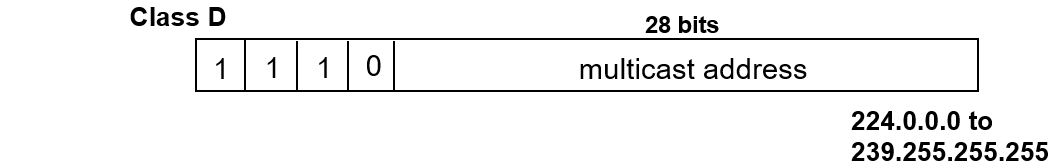
- Up to 250 million multicast groups at the same time
- Permanent group addresses
- All systems in LAN; All routers in LAN;
- All OSPF routers on LAN; All designated OSPF routers on a LAN, etc.
- Temporary groups addresses created as needed
- Special multicast routers
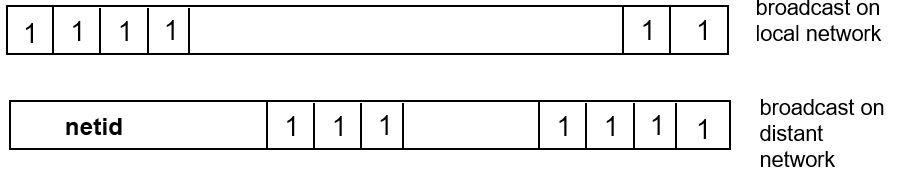
Reserved Host IDs (all 0s & 1s)
-
Internet address used to refer to network has hostid set to all 0s

-
Broadcast address has hostid set to all 1s
Private IP Addresses
- Specific ranges of IP addresses set aside for use in private networks (RFC 1918)
- Use restricted to private internets; routers in public Internet discard packets with these addresses
- Range 1: 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
- Range 2: 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
- Range 3: 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
- Network Address Translation (NAT)** used to convert** between private & global IP addresses
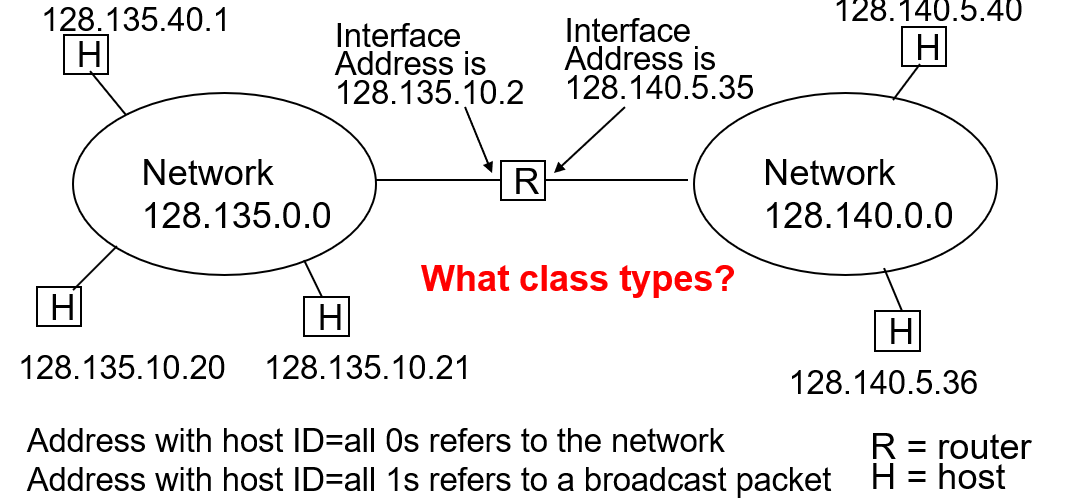
Example of IP Addressing
Subnets

- Subnets allow a network to be split into several parts for internal use, but the network still act like a single network to the outside.



