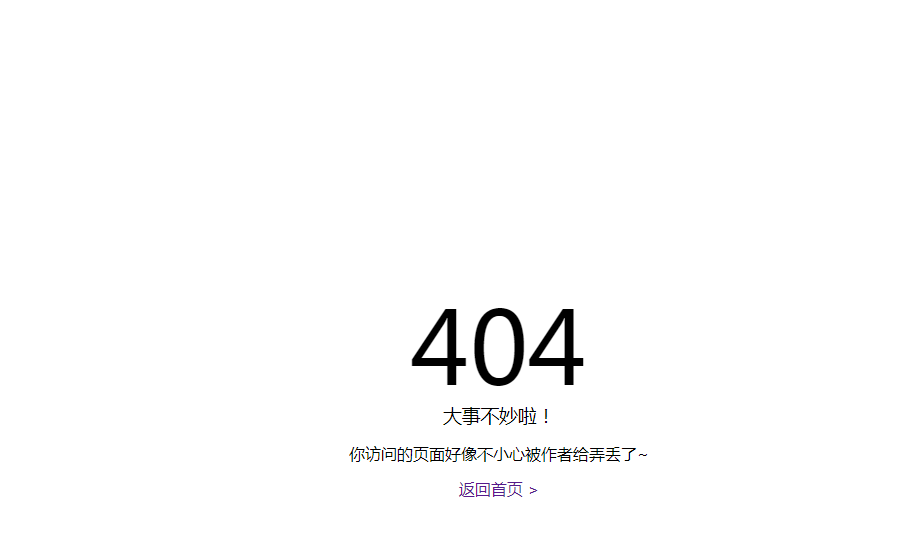
Django - 自定义错误页面
Django输入错误url,跳转错误页面
django404,500错误自定义页面:
将
改为
1.修改settings文件
DEBUG = False ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*'] 或者 ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['127.0.0.1', 'localhost']
改成ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*'] 就可以
2.配置urls文件
from django.conf.urls import handler404, handler500 #错误页面400 path('page_not_found/', views.page_not_found), #错误页面500 path('page_not_found/', views.page_not_found),
handler400 = bad_request handler403 = permission_denied handler404 = page_not_found handler500 = server_error
3.在views文件中定义函数page_not_found和page_error
from django.shortcuts import render_to_response def page_not_found(request): return render_to_response('404.html') def page_error(request): return render_to_response('500.html')
4.在app的templates下建立404.html和500.html文件(文件内就是你自定义的404或者500页面)
400.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"/> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <meta name="robots" content="none"/> <title>404 Not Found</title> <style> *{font-family:"Microsoft Yahei";margin:0;font-weight:lighter;text-decoration:none;text-align:center;line-height:2.2em;} html,body{height:100%;} h1{font-size:100px;line-height:1em;} table{width:100%;height:100%;border:0;} </style> </head> <body> <table cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0"> <tr> <td> <table cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0"> <tr> <td> <h1>404</h1> <h3>大事不妙啦!</h3> <p>你访问的页面好像不小心被作者给弄丢了~<br/> <a href="/login/">请返回首页 ></a> #这里直接返回登录页面 </p> </td> </tr> </table> </td> </tr> </table> </body> </html>
500.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>出错了</title> </head> <body> <h1>程序员又要加班了。。。。。</h1> </body> </html>
DEBUG修改为False时,static会出现加载失败,需要修改settings.py
STATIC_URL = '/static/' STATIC_ROOT = 'app01/statics' # 新增行 # Default primary key field type # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.2/ref/settings/#default-auto-field DEFAULT_AUTO_FIELD = 'django.db.models.BigAutoField' # STATICFILES_DIRS = [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'app01/statics')] STATICFILES_DIRS = [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, '/app01/statics/')] # 前后多加两个/ AUTH_USER_MODEL = 'app01.UserInfo' # 配置用户上传的文件存储位置 MEDIA_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'app01/face') # 文件名 随你 自己
# url.py修改
from django.views.static import serve
re_path(r'^face/(?P<path>.*)$', serve, {'document_root': settings.MEDIA_ROOT}),
re_path(r'^static/(?P<path>.*)$', serve, {'document_root': settings.STATIC_ROOT}),
before
Django2.2 + Python3.6.8
在Django的调试环境,遇到404、403、500等等,这些错误的页面都是使用Django内置的错误页面。但在上线环境中,却需要我们配置自定义的美观、简洁的错误页面,那怎么玩呢?
这里提供两种方式,
- 第一种是创建特殊名称的模板文件,这种方式写法固定,但很简单。
- 第二种是使用句柄的方式,也是我推荐的方式,这种方式不拘泥于模板文件名和位置,相对灵活。
声明:示例以Django2.2版本为准,其他版本套路也类似。
Django都支持自定义哪些错误页面
在研究具体配置之前,要知道我们都可以自定义哪些错误页面,通过Django的源码,源码在你Python解释器安装目录下的\Lib\site-packages\django\conf\urls\__init__.py中:
from django.urls import include, re_path from django.views import defaults __all__ = ['handler400', 'handler403', 'handler404', 'handler500', 'include', 'url'] handler400 = defaults.bad_request handler403 = defaults.permission_denied handler404 = defaults.page_not_found handler500 = defaults.server_error def url(regex, view, kwargs=None, name=None): return re_path(regex, view, kwargs, name)
可以看到,支持400、403、404、500这几个错误页面的自定制。
接下来,来看具体怎么配置吧!
settings配置
无论是哪一种配置,都需要先配置settings,在settings.py中:
# 将DEBUG模式设置为False # DEBUG = True DEBUG = False # 指定 ALLOWED_HOSTS 地址 # ALLOWED_HOSTS = [] # 这是搭配DEBUG = True模式用的 # 线上环境使用 ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['具体的IP/域名'] # 供客户端访问 # 我为了演示,使用 ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['127.0.0.1'] # 然后保证模板文件路径配置好了 TEMPLATES = [ { 'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates', 'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')] # 保证路径配置正确 , 'APP_DIRS': True, 'OPTIONS': { 'context_processors': [ 'django.template.context_processors.debug', 'django.template.context_processors.request', 'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth', 'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages', ], }, }, ]
接下来,就看两种自定义错误页面怎么配置的吧。
方法1:创建特殊命名的文件
这种方式说白了,这种方式是借助了 Django 的模板查找规则进行的。
具体配置
除了上面的settings配置之外,什么路由、视图统统不用管,直接在你项目下的templates目录中新建:
400.html 403.html 404.html 500.html
注意,文件名必须是这几个指定的,别的不识别.....然后你在各自的文件中写你的自定义内容即可。
方法2:使用句柄
在你的项目总路由文件urls.py中:
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, re_path, include from app01 import views # 路由这里不变,该怎么写怎么写 urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('app01/', include('app01.urls', namespace='app01')), path('app02/', include('app02.urls', namespace='app02')), path('books/', views.books, name='book'), # 无名分组 re_path('add_book/(\d+)/', views.add_book, name='add_book'), re_path('t1/(\d+)/(\d+)/', views.t1, name='t1'), # 有名分组 re_path('edit_book/(?P<book_id>\d+)/', views.edit_book, name='edit_book'), re_path('t2/(?P<id_1>\d+)/(?P<id_2>\d+)/', views.t2, name='t2'), ] # 以下自定义几个视图函数来处理自定义错误类型,模板文件名和文件内容可以自定义 from django.shortcuts import render def bad_request(request, exception): """ 400 error handler. """ return render(request, '400.html') def permission_denied(request, exception): """ Permission denied (403) handler. """ return render(request, '403.html') def page_not_found(request, exception): """ 404 handler. """ return render(request, '404.html') def server_error(request): """ 500 error handler. """ return render(request, '500.html') handler400 = bad_request handler403 = permission_denied handler404 = page_not_found handler500 = server_error