设计模式学习总结4 - 创建型4 - Prototype原型模式
Prototype原型模式(创建型)
作用:
原型模式通过克隆已存在的原型类实例新对象。原型模式有两点优势:1、因为复制对象比构造新对象要快,而且这些要复制的对象已加载在内存中,可以快速复制这些大对象来创建新的对象;2、可以保留大对象的固定的部分来复制新对象,简化子类的实例过程。
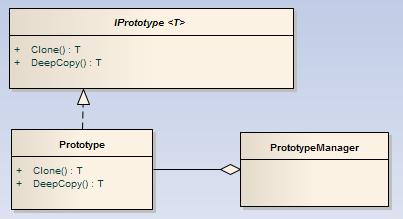
Role
The Prototype pattern creates new objects by cloning one of a few stored prototypes. The Prototype pattern has two advantages: it speeds up the instantiation of very large, dynamically loaded classes (when copying objects is faster), and it keeps a record of identifiable parts of a large data structure that can be copied without knowing the subclass from which they were created.
设计:
IPrototype,定义可以被克隆原型接口
Prototype,实现了原型接口,可以克隆出新对象
PrototypeManager,原型管理器,管理各种可克隆类型和他们的关键词
举例:
IPrototype:可复制的功能
Prototype:实现可复制功能的钢笔
PrototypeManager:管理各种具有克隆自己功能的钢笔
实现:
实例1
 代码
代码
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using PrototypePattern;
namespace Prototype
{
[Serializable()]
// Helper class used to create a second level data structure
class DeeperData
{
public string Data {get; set;}
public DeeperData(string s)
{
Data = s;
}
public override string ToString ()
{
return Data;
}
}
[Serializable()]
class Prototype : IPrototype <Prototype>
{
// Content members
public string Country {get; set;}
public string Capital {get; set;}
public DeeperData Language {get; set;}
public Prototype (string country, string capital, string language)
{
Country = country;
Capital = capital;
Language = new DeeperData(language);
}
public override string ToString()
{
return Country+"\t\t"+Capital+"\t\t->"+Language;
}
}
class PrototypeManager
{
public Dictionary <string, Prototype> prototypes
= new Dictionary <string, Prototype>
{
{"Germany",
new Prototype ("Germany", "Berlin", "German")},
{"Italy",
new Prototype ("Italy", "Rome", "Italian")},
{"Australia",
new Prototype ("Australia", "Canberra", "English")}
};
}
//引用类型
class RefTypeRectangle
{
public int Width;
public int Height;
}
class Program
{
static void Report (string s, Prototype a, Prototype b) {
Console.WriteLine("\n"+s);
Console.WriteLine("Prototype "+a+"\nClone "+b);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 测试引用类型
/*
//有该程序可以看出,引用类型是相互影响的,因为他们是指向相同的内存空间实际的是操作同一个堆栈中的数据
RefTypeRectangle refOne = new RefTypeRectangle();
RefTypeRectangle refTwo = refOne;
refOne.Width = 10;
refOne.Height = 20;
System.Console.WriteLine("引用类型测试:");
System.Console.WriteLine("refTwo.Width:" + refTwo.Width);
System.Console.WriteLine("refTwo.Height:" + refTwo.Height);
System.Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------");
refTwo.Width = 15;
refTwo.Height = 25;
System.Console.WriteLine("refOne.Width:" + refOne.Width);
System.Console.WriteLine("refOne.Height:" + refOne.Height);
System.Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------");
string s1 = "s1";
string s2 = s1;
Console.WriteLine(s1);
s2 = "s2";
Console.WriteLine(s1);
Console.ReadLine();
*/
#endregion
PrototypeManager manager = new PrototypeManager();
Prototype c2, c3;
// Make a copy of Australia's data
c2 = manager.prototypes["Australia"].Clone();
Report("Shallow cloning Australia\n===============",
manager.prototypes["Australia"], c2);
// Change the capital of Australia to Sydney
c2.Capital = "Sydney";
Report("Altered Clone's shallow state, prototype unaffected",
manager.prototypes["Australia"], c2);
// Change the language of Australia (deep data)
c2.Language.Data = "Chinese";
Report("Altering Clone deep state: prototype affected *****",
manager.prototypes["Australia"], c2);
// Make a copy of Germany's data
c3 = manager.prototypes["Germany"].DeepCopy();
Report("Deep cloning Germany\n============",
manager.prototypes["Germany"], c3);
// Change the capital of Germany
c3.Capital = "Munich";
Report("Altering Clone shallow state, prototype unaffected",
manager.prototypes["Germany"], c3);
// Change the language of Germany (deep data)
c3.Language.Data = "Turkish";
Report("Altering Clone deep state, prototype unaffected",
manager.prototypes["Germany"], c3);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
 代码
代码
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary;
using System.IO;
namespace PrototypePattern
{
// Prototype Pattern Judith Bishop Nov 2007
// Serialization is used for the deep copy option
// The type T must be marked with the attribute [Serializable()]
[Serializable()]
public abstract class IPrototype <T>
{
// Shallow copy
public T Clone()
{
return (T) this.MemberwiseClone();
}
//Deep Copy
public T DeepCopy()
{
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
formatter.Serialize(stream, this);
stream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
T copy = (T) formatter.Deserialize(stream);
stream.Close();
return copy;
}
}
}
使用场景:
1、隐藏具体的类,不让客户端知道
2、在运行时通过原型类添加或删除新类
3、在系统中保持最小数量的类
4、适用于在运行时改变数据的结构
5、在C#3.0中使用深度克隆是非常简单的
Use the Prototype pattern when…
You want to:
• Hide concrete classes from the client.
• Add and remove new classes (via prototypes) at runtime.
• Keep the number of classes in the system to a minimum.
• Adapt to changing structures of data at runtime.
总结:
Prototype原型模式是一种创建型模式,解决“结构复杂对象”的创建工作。《设计模式》:使用原型实例创建指定的对象类型,然后通过拷贝这些原型来创建新的对象。原型模式是通过拷贝一个已存在的实例来创建新的对象,这一点和其他创建型模式不相同。
Prototype原型模式的几个要点:
1、Prototype原型模式隔离对象的使用者和具体类型之间的耦合关系,它同样要求这些要使用的类拥有“稳定的接口”。
2、Prototype原型模式采用克隆原型的方法来创建对象,它使得我们可以非常灵活地动态创建“拥有某些稳定接口”的新对象——所需工作仅仅是注册一个新类的对象(即原型),然后在任何需要的地方不断地Clone克隆。
3、Prototype模式中的Clone方法可以利用Object类的浅拷贝MemberwiseClone()或者序列化来实现深拷贝DeepCopy()。
这里面我们再来说说浅拷贝和深拷贝。对于Prototype模式是很重要的。浅拷贝和深拷贝的关键区别是对于对象内引用类型数据的拷贝。
public class ClassB
{}
public class MainClass
{
int a;
ClassB b;
}
我们用浅拷贝实现了两个对象MainClass1和MainClass2,对于MainClass1.a和MainClass2.a,他们是值类型,在MainClass2.a是新分配的内存,他们所有的内存空间是不一样,值是相等的,但是MainClass1.b和MainClass2.b,由于它们是引用类型,在浅拷贝时只是拷贝了MainClass1.b的地址给MainClass2的b成员,实际上MainClass1.b和MainClass2.b指向同一块内存。
但如果我们用深拷贝,MainClass1.b和MainClass2.b指向的是不同的内存地址。一般利用序列化和反序列化来实现深拷贝来创建新的引用类型。
posted on 2010-03-01 19:37 Utopia Coming 阅读(1195) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报