私有化主备文件同步方案
Rsync
用于实现数据增量同步:
1. 例如备份NAS或其它存储服务器上的文件;
2. 例如从发布服务器推数据到其它服务器。
基于sshd服务器,并client使用server的OS帐号同步数据,可以结合ssh公钥认证。
Server端启动rsyncd服务,并创建专用的rsync帐号(最终也要映射到系统帐号,对应一定的权限)
安装
curl http://mirror.centos.org/centos/7/os/x86_64/Packages/rsync-3.1.2-10.el7.x86_64.rpm -O
rpm -ivh rsync-3.1.2-10.el7.x86_64.rpm
systemctl start rsyncd
systemctl enable rsyncd
使用参数
# rsync --help
-v, --verbose increase verbosity
-u, --update skip files that are newer on the receiver
--inplace update destination files in-place (SEE MAN PAGE)
--append append data onto shorter files
--append-verify like --append, but with old data in file checksum
-r, --recursive recurse into directories
-l, --links copy symlinks as symlinks
-p, --perms preserve permissions
-t, --times preserve modification times
-o, --owner preserve owner (super-user only)
-g, --group preserve group
--devices preserve device files (super-user only)
--specials preserve special files
-D same as --devices --specials
-a, --archive archive mode; equals -rlptgoD (no -H,-A,-X)
-H, --hard-links preserve hard links
-A, --acls preserve ACLs (implies --perms)
-X, --xattrs preserve extended attributes
-z, --compress compress file data during the transfer
--delete delete extraneous files from destination dirs
--exclude=pattern 同步时忽略什么样的文件
同步目录注意事项
源:
目录以"/"结尾 #仅传输目录下的内容
目录不以"/"结尾 #传输目录及目录下所有的内容
目标:
目标目录不存在 #先创建目录,再传输. 如果创建时父目录不存在, 则报错
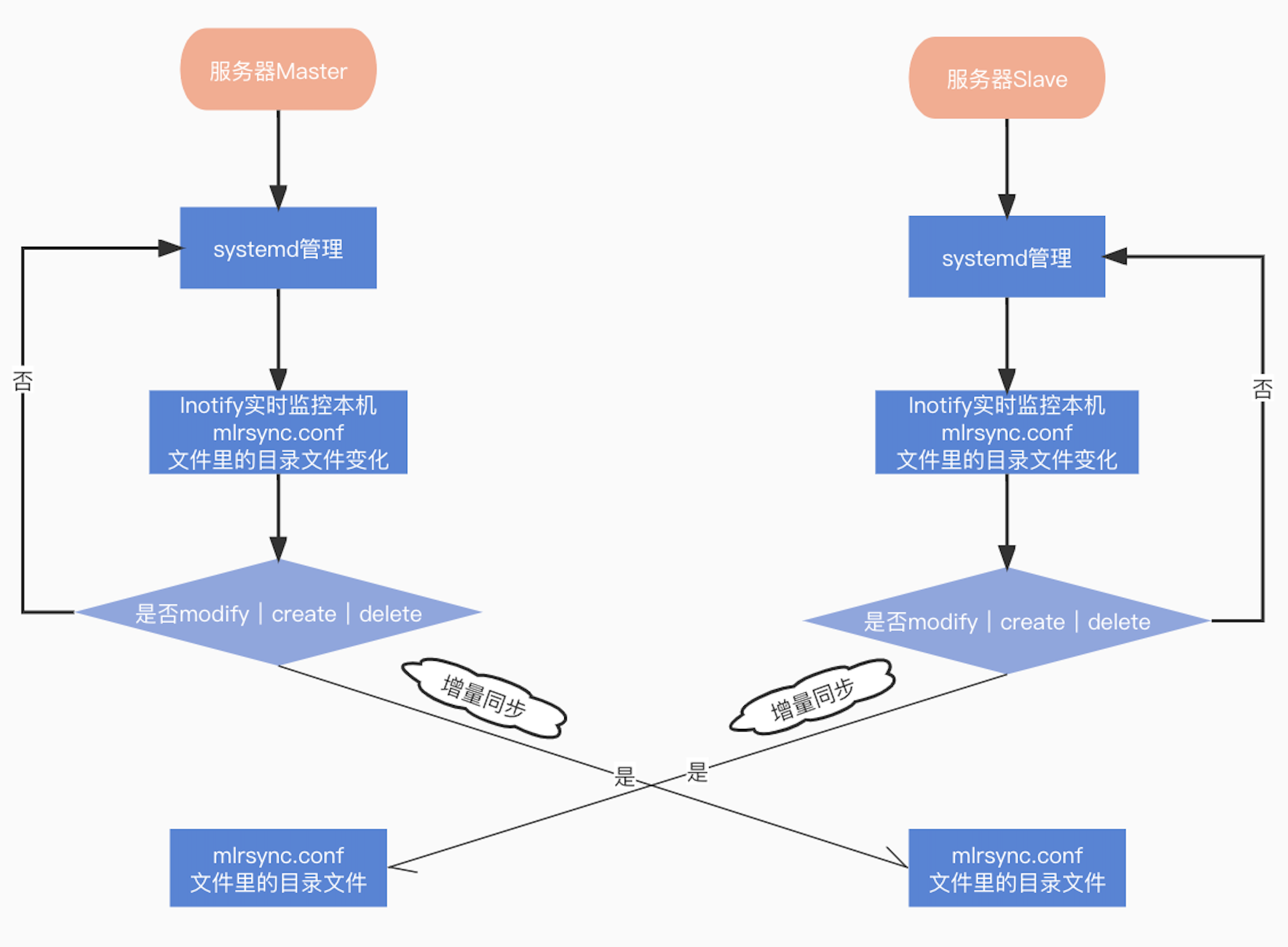
Inotify
Inotify 是一种强大的、细粒度的、异步的文件系统事件监控机制,linux内核从2.6.13起,加入了Inotify支持,
通过Inotify可以监控文件系统中添 加、删除,修改、移动等各种细微事件,
利用这个内核接口,第三方软件就可以监控文件系统下文件的各种变化情况,而inotify-tools就是这样的一 个第三方软件。
rsync可以实现触发式的文件同步,但是通过crontab守护进程方式进行触发,同步的数据和实际数据会有差异,
而inotify可以监控文件系统的各种变化,当文件有任何变动时,就触发rsync同步,这样刚好解决了同步数据的实时性问题。
安装inotify工具inotify-tools
rpm -ivh inotify-tools-3.14-9.el7.x86_64.rpm
Inotifywait相关参数
-m ,--monitor 表示始终保持事件监听状态
-r ,--recursive 表示递归查询目录
-q 即--quiet,表示不打印监控事件
-e 即--event,通过此参数可以指定要监控的事件,常见的事件有modify、delete、create、attrib等
-e omitted 监控所有事件
|
Events
|
含义
|
|
access
|
文件或目录被读取
|
|
modify
|
文件或目录内容被修改
|
|
attrib
|
文件或目录属性被改变
|
|
close
|
文件或目录封闭,无论读/写模式
|
|
open
|
文件或目录被打开
|
|
moved_to
|
文件或目录被移动至另外一个目录
|
|
move
|
文件或目录被移动到另一个目录或从另一个目录移动至当前目录
|
|
create
|
文件或目录被创建在当前目录
|
|
delete
|
文件或目录被删除
|
|
umount
|
文件系统被卸载
|
rsync+inotify 实时同步(触发式)
rsync+cron的优点与不足:与传统的cp、scp、tar备份方式相比,rsync具有安全性高、备份迅速、支持增量备份等优点,通过rsync可以解决对实时性要求不高的数据备份 需求,例如定期的备份文件服务器数据到远端服务器,对本地磁盘定期做数据镜像等。
随着应用系统规模的不断扩大,对数据的安全性和可靠性也提出的更好的要求,rsync在高端业务系统中也逐渐暴露出了很多不足,首先,rsync同步数据时,需要扫描所有文件后进行比对,进行增量传输。如果文件数量达到了百万甚至千万量级,扫描所有文件将是非常耗时的。而且正在发生变化的往往是其中很少的一部分,这是非常低效的方式。其次,rsync不能实时的去监测、同步数据,虽然它可以通过linux守护进程的方式进行触发同步,但是两次触发动作一定会有时间差,这样就导致了服务端和客户端数据可能出现不一致,无法在应用故障时完全的恢复数据
配置示例:
服务器
master:10.23.7.132
slave: 10.23.7.133
1、互信ssh免密
2、master服务器ansible
$ tree ha-base-install-rsync
ha-base-install-rsync
├── files
│ ├── inotify-tools-3.14-9.el7.x86_64.rpm
│ ├── mlrsync.conf#配置目录文件
│ ├── mlrsync.service
│ └── rsync-3.1.2-10.el7.x86_64.rpm
├── tasks
│ └── main.yml
└── templates
└── mlrsync.sh.j2
main.yml
---
# Install mlrsync
- name: copy rsync and inotify rpm files
copy:
src: '{{ item.src }}'
dest: '{{ item.dest }}'
with_items:
- { src: 'rsync-3.1.2-10.el7.x86_64.rpm', dest: '/tmp/' }
- { src: 'inotify-tools-3.14-9.el7.x86_64.rpm', dest: '/tmp/' }
tags:
- install mlrsync
- name: Finding RPM files
find:
paths: "/tmp"
patterns: "*.rpm"
register: rpm_result
tags:
- install mlrsync
- name: Install RPM
yum:
name: "{{ item.path }}"
state: present
with_items: "{{ rpm_result.files }}"
tags:
- install mlrsync
- name: systemd started rsyncd
systemd:
name: rsyncd
state: started
enabled: yes
daemon_reload: yes
tags:
- install mlrsync
- name: create mlrsync directory
file:
path: /usr/local/mlrsync
state: directory
tags:
- install mlrsync
- name: copy mlrsync.sh from template
template:
src: mlrsync.sh.j2
dest: /usr/local/mlrsync/mlrsync.sh
mode: +x
tags:
- install mlrsync
- Configuration regeneration
- name: copy mlrsync.conf and mlrsync.service
copy:
src: '{{ item.src }}'
dest: '{{ item.dest }}'
with_items:
- { src: 'mlrsync.conf', dest: '/usr/local/mlrsync/mlrsync.conf' }
- { src: 'mlrsync.service', dest: '/usr/lib/systemd/system/mlrsync.service' }
tags:
- install mlrsync
- Configuration regeneration
- name: systemd started mlrsync
systemd:
name: mlrsync
state: restarted
enabled: yes
daemon_reload: yes
tags:
- install mlrsync
- Configuration regeneration
mlrsync.sh.j2
#!/bin/bash logfile=/var/log/mlrsync.log PID_FILE_NAME=/var/run/mlrsync.pid [ -f $PID_FILE_NAME ] && rm -rf $PID_FILE_NAME remote_ip={{(MASTER_1_IP+MASTER_2_IP).replace(ansible_ssh_host, '')}} while read dirline;do dir=$dirline desc=$dirline { inotifywait -mrq -e modify,delete,create,attrib --format "[%T] %e %w%f" --timefmt "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" $dir |while read line;do echo "$line" >> $logfile rsync -azPu —delete $dir $remote_ip:$desc >> $logfile done } & echo $! >> $PID_FILE_NAME done < /usr/local/mlrsync/mlrsync.conf
mlrsync.conf#配置同步的目录文件
$MARINES_HOME/marines/application/paas/licence/app/licence/
$MARINES_HOME/upload/
/home/marines/application/paas/licence/app/licence/
/home/marines/upload/
mlrsync.service
[Unit] Description=mlrsync After=network.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/var/run/mlrsync.pid ExecStart=/usr/local/mlrsync/mlrsync.sh ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID Restart=always PrivateTmp=true StartLimitInterval=60 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
ha-install-after.yml
- name: install common component
hosts: common_consul_iaas
remote_user: root
become: yes
gather_facts: yes
# serial: 1
vars_files:
- vars.yml
- vars-ha-hosts.yml
- vars-middleware.yml
- vars-node.yml
roles:
- { role: ha-base-install-rsync, tags: install-mlrsync }
ansible-playbook -i inventory/hosts-ha playbook/ha-install-after.yml
3、测试验证
|
|
A 服务器master
|
|||
|
B
服务器slave
|
同一文件
|
modify
|
create
|
delete
|
|
modify
|
AB——两边modify都生效,modify同一处以最新时间modify为准,无法匹配到的modify无效
|
AB-最后modify为准
|
AB——第一个delete为准
|
|
|
create
|
AB——第一个modify为准
|
AB——最后create为准
|
AB——最后create为准
|
|
|
delete
|
AB——最后delete为准
|
AB——最后delete为准
|
AB——第一个delete为准
|
|





