1.题型(找出数组中重复的数字)
在一个长度为 n 的数组 nums 里的所有数字都在 0~n-1 的范围内。数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字重复了,也不知道每个数字重复了几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shu-zu-zhong-zhong-fu-de-shu-zi-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解题思路:利用HashSet去重原理,遍历添加数组元素,添加失败则返回重复元素
代码
class Solution { public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) { HashSet<Integer> set=new HashSet<>(); for(int num:nums) { if(set.contains(num))return num; set.add(num); } return -1; } }
2.题型(在二维数组中找到指定的元素)
在一个 n * m 的二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个高效的函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
示例:
现有矩阵 matrix 如下:
[
[1, 4, 7, 11, 15],
[2, 5, 8, 12, 19],
[3, 6, 9, 16, 22],
[10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
[18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
]
给定 target = 5,返回 true。
给定 target = 20,返回 false。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/er-wei-shu-zu-zhong-de-cha-zhao-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解题思路:通过找出规律从左下角或者右上角可以矩阵类似于二叉搜索树(左边小于根节点右边大于根节点)
代码
class Solution { public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) { int i=matrix.length-1; int j=0; while(i>=0&&j<matrix[0].length) { if(matrix[i][j]>target) { i--; } else if(matrix[i][j]<target) { j++; } else { return true; } } return false; } }
3.替换空格(将字符串中的空格替换为指定的字符串)
请实现一个函数,把字符串 s 中的每个空格替换成"%20"。
示例 1:
输入:s = "We are happy."
输出:"We%20are%20happy."
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ti-huan-kong-ge-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解题思路:可以用StringBuilder重新拼接字符串
class Solution { public String replaceSpace(String s) { StringBuffer sb= new StringBuffer(); int len=s.length(); for(int i=0;i<len;i++) { if(s.charAt(i)==' ') { sb.append("%20"); } else sb.append(s.charAt(i)); } return sb.toString(); } }
4.从尾到头打印链表
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,3,2] 输出:[2,3,1]
解题思路1:反向输出可以考虑递归(借助LinkedList存数据,最后加入数组)
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { LinkedList<Integer> dic=new LinkedList(); public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) { rec(head); int[] res=new int[dic.size()]; for(int i=0;i<dic.size();i++) { res[i]=dic.get(i); } return res; } void rec(ListNode head){ if(head==null)return; rec(head.next); dic.add(head.val); } }
解题思路2.利用栈的先入后出特性
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { LinkedList<Integer> dic=new LinkedList(); public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) { Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack(); while(head!=null) { stack.push(head.val); head=head.next; } while(!stack.isEmpty()) { dic.add(stack.pop()); } int[] res= new int[dic.size()]; for(int i=0;i<dic.size();i++) { res[i]=dic.get(i); } return res; } }
5.重建二叉树
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请构建该二叉树并返回其根节点。
假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。
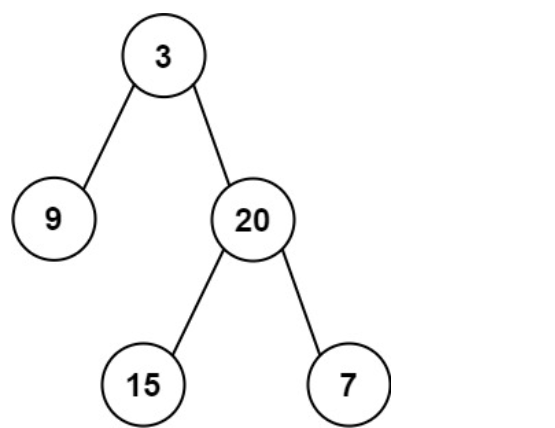
示例 1:
Input: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
Input: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1]
Output: [-1]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/zhong-jian-er-cha-shu-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution { HashMap<Integer,Integer> dic=new HashMap<>();//保留中序遍历集,以便获取到先序中根节点在中序中的范围 int[] preorder;//记录先序序列,以便在中序序列中划分范围和创建根节点 public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) { this.preorder=preorder; for(int i=0;i<inorder.length;i++) { dic.put(inorder[i],i); } return rec(0,0,inorder.length-1); } TreeNode rec(int pre_root,int in_left,int in_right){//pre_root记录先序序列中根节点的位置 if(in_left>in_right)return null;//以左边界为例,如果是最后一个节点,根节点下标为0,左边界为0,右边界为根节点位置-1,-1 TreeNode node= new TreeNode(preorder[pre_root]); int i= dic.get(preorder[pre_root]);//找到根节点在中序中的位置 node.left=rec(pre_root+1,in_left,i-1); node.right=rec(pre_root+i-in_left+1,i+1,in_right);//pre_root+i-in_left+1:表示先序中右子数根节点位置 return node; } }
6.包含min函数的栈
定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈的最小元素的 min 函数在该栈中,调用 min、push 及 pop 的时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
解题思路:题目要求查找最小值要为O(1),可以考虑空间换时间,利用非严格递减辅助栈
class MinStack { Stack<Integer> A; Stack<Integer> B; /** initialize your data structure here. */ public MinStack() { A=new Stack<>(); B=new Stack<>(); } public void push(int x) { A.push(x); if(B.isEmpty()||B.peek()>=x)//要注意=号,如果没有包含相等的入栈,比如3,3,只加入1个的话,弹出时会把最小值弹出 { B.push(x); } } public void pop() { if(B.peek().equals(A.pop()))//注意要使用equals比较,因为包装类有缓冲池,在范围内的数据可以比较,超出范围比较的是引用 { B.pop(); }, } public int top() { return A.peek(); } public int min() { return B.peek(); } } /** * Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such: * MinStack obj = new MinStack(); * obj.push(x); * obj.pop(); * int param_3 = obj.top(); * int param_4 = obj.min(); */
7.队列的最大值
请定义一个队列并实现函数 max_value 得到队列里的最大值,要求函数max_value、push_back 和 pop_front 的均摊时间复杂度都是O(1)。
若队列为空,pop_front 和 max_value 需要返回 -1
示例 1:
输入:
["MaxQueue","push_back","push_back","max_value","pop_front","max_value"]
[[],[1],[2],[],[],[]]
输出: [null,null,null,2,1,2]
示例 2:
输入:
["MaxQueue","pop_front","max_value"]
[[],[],[]]
输出: [null,-1,-1]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/dui-lie-de-zui-da-zhi-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解题思路:题目要求查找最大值要为O(1),可以考虑空间换时间,利用非严格递减辅助双向队列,队头就是最大值
class MaxQueue { Queue<Integer> queue; Deque<Integer> deque; public MaxQueue() { queue=new LinkedList<>(); deque=new LinkedList<>(); } public int max_value() { return deque.isEmpty()?-1:deque.peekFirst(); } public void push_back(int value) { queue.offer(value); while(!deque.isEmpty()&&deque.peekLast()<value)//入队时判断双端队列中的对位元素是否比要加入的元素小,如果小就将队列中小于要加入元素的值弹出,保证队列中元素始终能找到次大值,删除最大值后下次还有最大值 { deque.pollLast(); } deque.offerLast(value); } public int pop_front() { if(queue.isEmpty())return -1; if(queue.peek().equals(deque.peekFirst())) deque.pollFirst(); return queue.poll(); } } /** * Your MaxQueue object will be instantiated and called as such: * MaxQueue obj = new MaxQueue(); * int param_1 = obj.max_value(); * obj.push_back(value); * int param_3 = obj.pop_front(); */
8.构建乘积数组
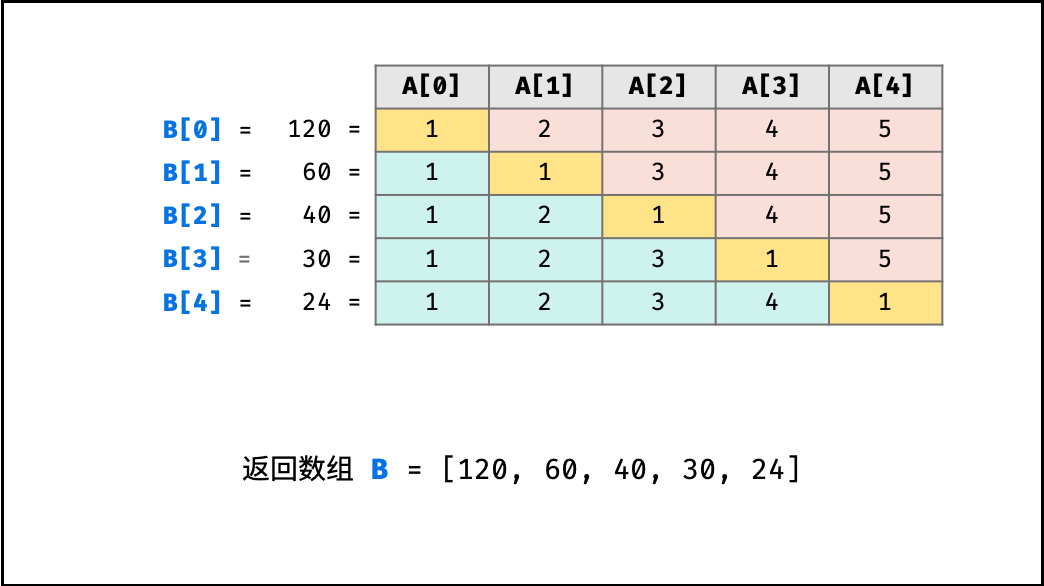
给定一个数组 A[0,1,…,n-1],请构建一个数组 B[0,1,…,n-1],其中 B[i] 的值是数组 A 中除了下标 i 以外的元素的积, 即 B[i]=A[0]×A[1]×…×A[i-1]×A[i+1]×…×A[n-1]。不能使用除法。
示例:
输入: [1,2,3,4,5]
输出: [120,60,40,30,24]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/gou-jian-cheng-ji-shu-zu-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解题思路:第一次循环算出i之前的,第二次循环算出之后的
图片来源于:剑指 Offer 66. 构建乘积数组(表格分区,清晰图解) - 构建乘积数组 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
class Solution { public int[] constructArr(int[] a) { int[] res=new int[a.length]; for(int i=0,p=1;i<a.length;i++) { res[i]=p;//本次计算以当前下标之前的为基础计算 p*=a[i];//计算到当前下标时元素之积,以备下次使用 } for(int i=a.length-1,p=1;i>=0;i--) { res[i]*=p;//计算下标之后元素的乘积与之前的积 p*=a[i];//把下标之后元素的乘积计算出来 } return res; } }

9.用两个栈实现队列
用两个栈实现一个队列。队列的声明如下,请实现它的两个函数 appendTail 和 deleteHead ,分别完成在队列尾部插入整数和在队列头部删除整数的功能。(若队列中没有元素,deleteHead 操作返回 -1 )
示例 1:
输入:
["CQueue","appendTail","deleteHead","deleteHead"]
[[],[3],[],[]]
输出:[null,null,3,-1]
解题思路:队列是先进先出,用栈模拟队列,入队就是入栈,出队要将栈底元素出去,可以先移动到另一个栈里面,再出栈
import java.util.Stack; public class Solution { Stack<Integer> A=new Stack<>(); Stack<Integer> B=new Stack<>(); public void push(int node) { A.add(node); } public int pop() { if(!B.isEmpty()) { return B.pop(); } else{ if(A.isEmpty())return -1; else { while(!A.isEmpty()) { B.push(A.pop()); } } } return B.pop(); } }






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!