检测中缀表达式的合法性
检测中缀表达式的合法性
前面我们对《中缀表达式的计算》以及《检测后缀表达式的合法性》进行了讨论,这里我们借助于之前对于两者的讨论,来对中缀表达式的合法性进行检测。如果中缀表达式是合法的,则返回该表达式的值;如果是非法的,则提示其非法。
我们对中缀表达式的合法性检测主要分为两个阶段:
1)中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式过程中是否存在错误;
2)后缀表达式的计算过程中是否存在错误
其中,第2阶段我们在《中缀表达式的计算》中已经做过讨论,这里重点在于第1阶段。
在第1阶段中主要涉及以下几个合法性检测:
<1>.操作数是否合法;
<2>.左括号和右括号是否匹配;
一、操作数是否合法
合法的操作数首个字符可以是“+”、“-”,也可以是“0”-“9”。后面的字符最多只包含一个“.”字符,其余字符都是“0”-“9”。
具体的实现相见程序。
二、左括号和右括号是否匹配
实现左括号和右括号是否匹配有两种方式:
<1>.设置一个记录项,当遇到“(”时,自动加1,,当遇到“)”时,自动减1,每当减1后,检测该记录项是否大于等于0,如果大于则说明没问题,如果小于0,则说明从左到右“)”的数目大于”(”的数目,也就是说二者不匹配,这时终止返回。
如果在扫描的过程中没有出现记录项小于0,当扫描完中缀表达式后,检测记录项是否大于0,如果大于则说明中缀表达式中“(”的数量大于”)”,说明左括号和右括号不匹配,终止返回。
<2>.第二种实现方式是:对“(”的情况不作处理,直接压栈,当遇到”)”时,设置一个标示符,用来记录弹栈循环中是否遇到了“(”,当弹栈循环结束后,检测该标示符,如果没有出现“(”,则说明左括号与右括号不匹配,右括号数量大于左括号数量,终止返回。
当扫描完中缀表达式后,在对操作符栈进行弹栈过程中检测栈中是否还有“(”,如果有则说明左括号与右括号不匹配,左括号数量大于右括号数量,终止返回。
在我们的实现中,我们采用第一种方式,因为第一种方式只计算了左括号和右括号出现的情况;而第二种情况为了检测左括号,必须计算栈中其他操作符的情况。所以,第一种方式的效率更高。
此外,还有N目操作符与其操作数的位置关系检测、空白中缀表达式的检测等。
具体程序如下:
// 中缀表达式的合法性检测 #include <iostream> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <map> using namespace std; string& replace_all_distinct(string& str, const string& src, const string& des) { for (string::size_type i = 0; i != string::npos; i += des.size()) { i = str.find(src, i); if (i != string::npos) { str.replace(i, src.size(), des); } else { break; } } return str; } string& n_replace(string& str, const vector<string>& src, const vector<string>& des) { assert(src.size() > 0 && src.size() == des.size()); for (vector<string>::size_type i = 0; i != src.size(); ++i) { replace_all_distinct(str, src[i], des[i]); } return str; } void get_infix(vector<string>& inf, const vector<string>& src, const vector<string>& des) { inf.clear(); string line; getline(cin, line); n_replace(line, src, des); istringstream sin(line); string tmp; while (sin >> tmp) { inf.push_back(tmp); } } void show(const vector<string>& hs) { for (vector<string>::size_type i = 0; i != hs.size(); ++i) { cout << hs[i] << ' '; } cout << endl; } void init_op(map<string, int>& ops) { ops.clear(); ops["+"] = 100; ops["-"] = 100; ops["*"] = 200; ops["/"] = 200; ops["("] = 1000; ops[")"] = 0; } bool is_operator(const string& hs, const map<string, int>& ops) { map<string, int>::const_iterator cit = ops.find(hs); if (cit != ops.end()) { return true; } else { return false; } } // 判断操作数是否合法 bool op_legal(const string& str, int& ill_id) { assert(str.size() > 0); string::size_type i = 0; if (str[i] == '+' || str[i] == '-') { ++i; if (i == str.size()) { ill_id = 3001; return false; } } int dot_num = 0; for (; i != str.size(); ++i) { if (isdigit(static_cast<int>(str[i]))) { ; } else if (str[i] == '.') { ++dot_num; } else { ill_id = 3002; return false; } } if (dot_num > 1) { ill_id = 3003; return false; } return true; } void in2post(const vector<string>& inf, vector<string>& postf, map<string, int>& ops, bool& leg, int& ill_id) { if (inf.size() == 0) { leg = false; ill_id = 6001; return; } postf.clear(); stack<string> op_st; // 记录左括号和右括号之间的数量关系 int brac = 0; int op_op = 0; for (vector<string>::size_type i = 0; i != inf.size(); ++i) { if (!is_operator(inf[i], ops)) { // 判断是否是正确的操作数 int tmp = 0; if (!op_legal(inf[i], tmp)) { leg = false; ill_id = tmp; return; } ++op_op; if (op_op > 1) { leg = false; ill_id = 5001; return; } postf.push_back(inf[i]); } else { if (inf[i] == "(") { ++brac; op_st.push(inf[i]); } else if (inf[i] == ")") { --brac; if (brac < 0) { leg = false; ill_id = 4001; return; } while (!op_st.empty()) { if (op_st.top() == "(") { op_st.pop(); // !勘误! // 如果inf[i] == ")",当遇到"(",将"("弹栈后必须终止弹栈循环。 break; } else { postf.push_back(op_st.top()); op_st.pop(); } } } else // 若为其他运算符 { --op_op; if (op_op < 0) { leg = false; ill_id = 5002; return; } if (op_st.empty()) // 若为空栈,则直接入栈 { op_st.push(inf[i]); } else { if (ops[inf[i]] > ops[op_st.top()]) { // 如果当前操作符优先级高于站定操作符优先级 // 则直接入栈 op_st.push(inf[i]); } else { // 否则弹出栈中优先级大于等于当前操作符优先级 // 的操作符,并最后将当前操作符压栈 while (!op_st.empty() && ops[op_st.top()] >= ops[inf[i]] && op_st.top() != "(") { /* 等价于 && op_st.top != "(" if (op_st.top() == "(") { // 如果当前栈顶操作符为 "(" // 则终止操作,继续保留 "(" 的栈顶位置 break; } */ postf.push_back(op_st.top()); op_st.pop(); } op_st.push(inf[i]); } } } } } if (brac > 0) { leg = false; ill_id = 4002; return; } if (op_op != 1) { leg = false; ill_id = 5003; return; } while (!op_st.empty()) { postf.push_back(op_st.top()); op_st.pop(); } leg = true; return; } double cal_post(const vector<string>& postf, const map<string, int>& ops, bool& leg, int& ill_id) { stack<double> or_st; double operand = 0.0, a = 0.0, b = 0.0, c = 0.0; for (vector<string>::size_type i = 0; i != postf.size(); ++i) { if (!is_operator(postf[i], ops)) { operand = static_cast<double>(atof(postf[i].c_str())); or_st.push(operand); } else { switch (postf[i][0]) { case '+': // 检测后缀表达式的合法性:操作数是否足够 if (or_st.size() < 2) { leg = false; ill_id = 1001; return -10000000000000.0; } b = or_st.top(); or_st.pop(); a = or_st.top(); or_st.pop(); c = a + b; or_st.push(c); break; case '-': // 检测后缀表达式的合法性:操作数是否足够 if (or_st.size() < 2) { leg = false; ill_id = 1002; return -10000000000000.0; } b = or_st.top(); or_st.pop(); a = or_st.top(); or_st.pop(); c = a - b; or_st.push(c); break; case '*': // 检测后缀表达式的合法性:操作数是否足够 if (or_st.size() < 2) { leg = false; ill_id = 1003; return -10000000000000.0; } b = or_st.top(); or_st.pop(); a = or_st.top(); or_st.pop(); c = a * b; or_st.push(c); break; case '/': // 检测后缀表达式的合法性:操作数是否足够 if (or_st.size() < 2) { leg = false; ill_id = 1004; return -10000000000000.0; } b = or_st.top(); or_st.pop(); a = or_st.top(); or_st.pop(); c = a / b; or_st.push(c); break; default: break; } } } if (or_st.size() == 1) { leg = true; return or_st.top(); } else // 检测后缀表达式的合法性:操作数是否有多余 { leg = false; ill_id = 2001; return -10000000000000.0; } } void init_src_des(vector<string>& src, vector<string>& des) { src.push_back("+"); src.push_back("-"); src.push_back("*"); src.push_back("/"); src.push_back("("); src.push_back(")"); des.push_back(" + "); des.push_back(" - "); des.push_back(" * "); des.push_back(" / "); des.push_back(" ( "); des.push_back(" ) "); } // 将中缀表达式转换后缀表达式和计算后缀表达式封装合并 double cal_inf(const vector<string>& inf, map<string, int>& ops, bool& leg_trans, bool& leg_cal, int& ill_id) { leg_trans = true; ill_id = 0; vector<string> postf; in2post(inf, postf, ops, leg_trans, ill_id); if (leg_trans) { show(postf); } else { cout << "Trans illegal: " << ill_id << '!' << endl << endl; return -10000000000000.0; } leg_cal = true; ill_id = 0; double ret = cal_post(postf, ops, leg_cal, ill_id); if (leg_cal) { return ret; } else { cout << "Cal illegal: " << ill_id << '!' << endl << endl; return -10000000000000.0; } } int main() { map<string, int> ops; init_op(ops); vector<string> inf; vector<string> src, des; init_src_des(src, des); while (1) { get_infix(inf, src, des); bool leg_trans = true; bool leg_cal = true; int ill_id = 0; double ret = cal_inf(inf, ops, leg_trans, leg_cal, ill_id); if (leg_trans && leg_cal) { cout << ret << endl << endl; } } /* map<string, int> ops; init_op(ops); vector<string> inf, postf; vector<string> src, des; init_src_des(src, des); while (1) { get_infix(inf, src, des); // show(inf); bool leg_trans = true; int ill_id_trans = 0; in2post(inf, postf, ops, leg_trans, ill_id_trans); if (leg_trans) { show(postf); } else { cout << "Trans illegal: " << ill_id_trans << '!' << endl << endl; continue; } bool leg_cal = true; int ill_id_cal = 0; double ret = cal_post(postf, ops, leg_cal, ill_id_cal); if (leg_cal) { cout << ret << endl << endl; } else { cout << "Cal illegal: " << ill_id_cal << '!' << endl << endl; } } */ system("PAUSE"); return 0; }
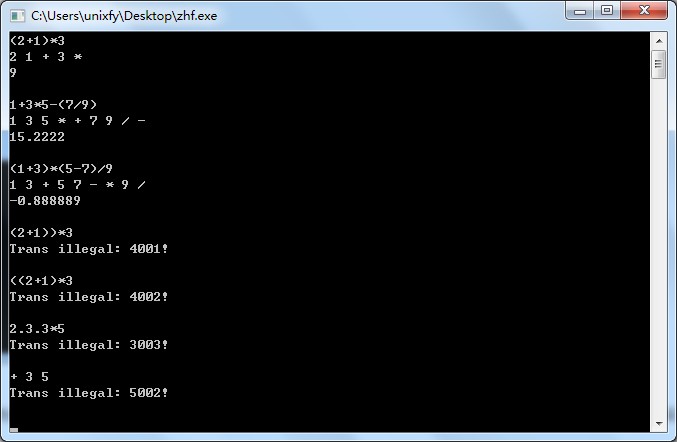
讨论
两个阶段检测的区别在于:第1阶段主要涉及操作数、操作符自身的检测;第2阶段检测的是操作数与操作符之间的关系是否合法,主要是数量上的。
从某种意义上讲,第1阶段主要是涉及词法方面的检测,第2阶段主要是涉及语法方面的检测。
(完)
文档信息
·版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名 | Creative Commons BY-NC-ND 3.0
·博客地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/unixfy
·博客作者:unixfy
·作者邮箱:goonyangxiaofang(AT)163.com
·如果你觉得本博文的内容对你有价值,欢迎对博主 小额赞助支持




