Educational Codeforces Round 113 (Rated for Div. 2) A~D题解
A. Balanced Substring
-
题意
给定一个只包含a和b字符串,需要你判断是否存在连续子串使得a的数量和b的数量相等。 -
解题思路
如果给定字符串存在·ab或者ba那么即存在长度为 2 2 2的连续子串符合条件,否则则不存在。因为如果这种没有出现过,那么说明要么只出现a要么只出现b。
当然,如果你不太确定或者当时没有发现这种技巧,那么可以使用前缀和然后暴力枚举区间找到符合情况的区间即可。 -
AC代码
/**
*@filename:A_Balanced_Substring
*@author: pursuit
*@created: 2021-09-08 22:35
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(a) cout << "debug : " << (#a)<< " = " << a << endl
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const int P = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int t, n;
char s[N];
void solve(){
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++ i){
if(s[i] != s[i + 1]){
cout << i << " " << i + 1 << endl;
return;
}
}
cout << -1 << " " << -1 << endl;
}
int main(){
cin >> t;
while(t -- ){
cin >> n >> s + 1;
solve();
}
return 0;
}
B. Chess Tournament
-
题意
有一个围棋比赛,每个人都要与其他人进行一场比赛,结果有三种情况,赢、输、平局。每个人都有自己的结果期望,为以下两种之一:- 不想输掉任何一场比赛。
- 至少赢得一场比赛。
现给定这 n n n个人的结果期望,请你找出一种比赛结果使得每个人的结果符合自己的期望。
-
解题思路
不想输掉任何一场比赛实际上我们就可以理解为这个人和其他任何人比要么赢要么平局,这里为了简便利于处理,我们可以安排这种期望的人和其他任何人比都是平局(这样和其他也是这种期望的人也正好符合)。关键在于至少赢得一场比赛的人,既然赢不了不想输掉任何一场比赛的人,那么我们就可以赢至少赢得一场比赛的人,可以得知,如果这种类型的人小于等于两个,那么就形不成闭环。而如果有大于两个的人,例如abc,可以让a赢b,b赢c,c赢a。这样构造即可。 -
AC代码
/**
*@filename:B_Chess_Tournament
*@author: pursuit
*@created: 2021-09-08 22:40
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(a) cout << "debug : " << (#a)<< " = " << a << endl
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 60 + 10;
const int P = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int t, n;
char s[N];
char g[N][N];
void solve(){
vector<int> ans;
memset(g, '0', sizeof(g));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
if(s[i] == '2'){
ans.push_back(i);
}
}
int len = ans.size();
if(len >= 1 && len <= 2){
puts("NO");
}
else{
puts("YES");
for(int i = 0; i < len - 1; ++ i){
g[ans[i]][ans[i + 1]] = '+';
g[ans[i + 1]][ans[i]] = '-';
}
if(len != 0){
g[ans[len - 1]][ans[0]] = '+';
g[ans[0]][ans[len - 1]] = '-';
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++ j){
if(i == j){
printf("X");
}
else if(g[i][j] == '+' || g[i][j] == '-'){
printf("%c", g[i][j]);
}
else{
printf("=");
}
}
puts("");
}
}
}
int main(){
cin >> t;
while(t -- ){
cin >> n >> s + 1;
solve();
}
return 0;
}
C. Jury Meeting
-
题意
找出符合排列的个数,使得排列满足按顺序提问没有一个人连续讲述问题。 a i a_i ai代表问题数,没有问题可讲的人会跳过。 -
解题思路
我们发现,最大值影响着这个排列,如果存在两个及两个以上的最大值,那么不管怎么排列,都符合条件,那么方案数就是 n ! n! n!。那么如果最大值只有 1 1 1个,显然,最大值的那个人是最后被清除的,如果最大值 − - −次大值 > 1 >1 >1,说明不管怎么排列,最大值的那个人都要被连续提问两次,则方案数为 0 0 0。
如果满足,那么我们放置最大值一定要放在至少一个次大值前面,这样才能保证最大值不会被连续提问两次,我们来仔细分析一下:假设次大值的数量为 c n t cnt cnt,那么其他无关值的数量为 n − c n t − 1 n-cnt-1 n−cnt−1,这些值可以随便放,那么方案数则为 A n n − c n t − 1 A_n^{n-cnt-1} Ann−cnt−1,然后考虑次大值的排列,有 A c n t c n t A_{cnt}^{cnt} Acntcnt种排列,同时最大值放在次大值前面有 c n t cnt cnt种放法,则最终方案为: A n n − c n t − 1 × A c n t c n t × c n t A_n^{n-cnt-1}\times A_{cnt}^{cnt}\times cnt Ann−cnt−1×Acntcnt×cnt。 -
AC代码
/**
*@filename:C_Jury_Meeting
*@author: pursuit
*@created: 2021-09-08 23:04
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(a) cout << "debug : " << (#a)<< " = " << a << endl
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int P = 998244353;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//就是找出符合排列的个数,
//使得排列满足按顺序提问没有一个人连续讲述问题。ai代表问题数。没有问题的人会跳过
int t, n, a[N], fac[N];
void init(){
fac[0] = fac[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < N; ++ i){
fac[i] = 1LL * fac[i - 1] * i % P;
}
}
int ksm(int n, int q){
int ans = 1;
while(q){
if(q & 1){
ans = 1LL * ans * n % P;
}
n = 1LL * n * n % P;
q >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
void solve(){
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1, greater<int>() );
if(a[1] - a[2] > 1){
puts("0");
}
else{
ll res = 1;
if(a[1] == a[2]){
//说明怎么排列都没有关系。
res = fac[n];
}
else{
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++ i){
if(a[i] == a[2])++ cnt;
else break;
}
//Anm = n!/(n - m)!;
res = 1LL * fac[cnt] * cnt % P * fac[n] % P * ksm(fac[cnt + 1], P - 2) % P;
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &t);
init();
while(t -- ){
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
solve();
}
return 0;
}
D. Inconvenient Pairs
-
题意
给定 n n n条垂直线和 m m m条水平线,同时给定 k k k个点,这些点在垂直线上或水平线上。它们只能通过这些线来行走,现在你需要找出有多少点对 ( x , y ) (x,y) (x,y)它们之间的最短距离是大于曼哈顿距离的。 -
解题思路
对于处在垂直线和水平线的交叉点处,这到其他的点一定是曼哈顿距离的,因为这两条线中一定有一条和其他点所在的线有交点,所以我们不考虑这些点。
那么这里以在垂直线上的点为例,我们看这个图:
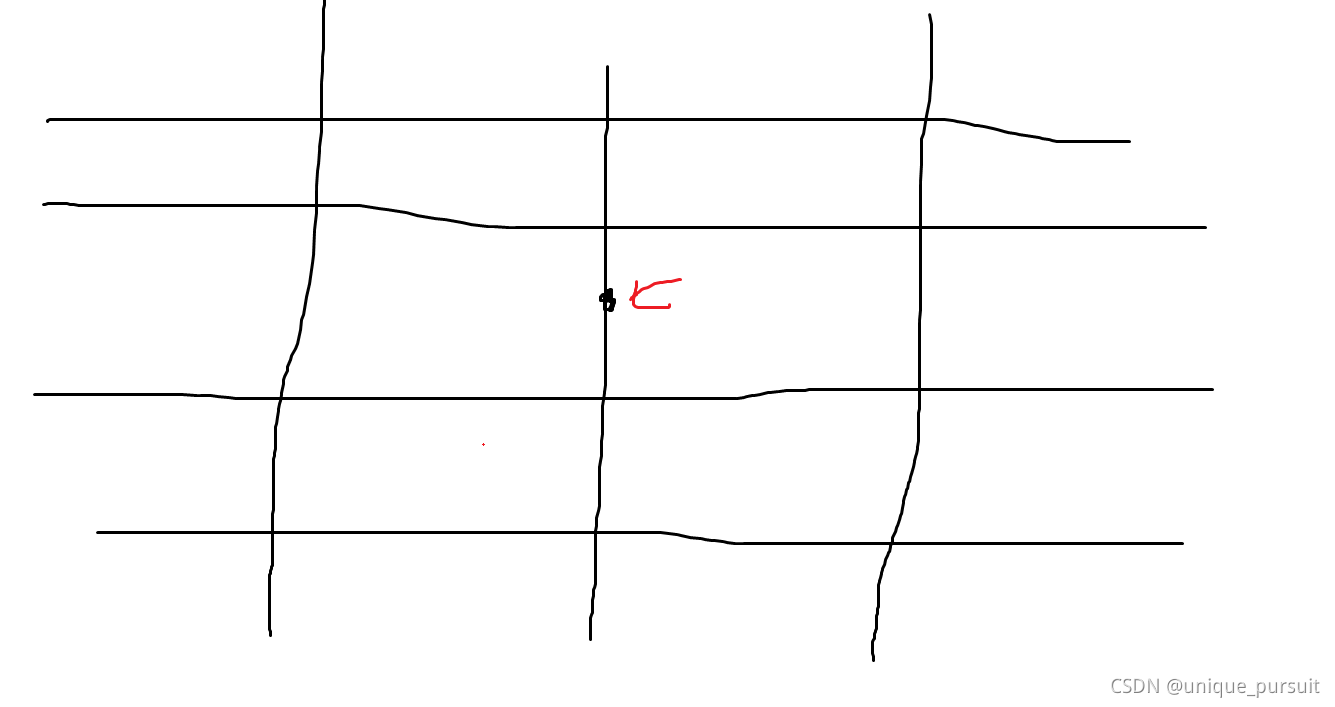
由于其和所有水平线都存在交点,故可以通过这些水平线到达其他各个点,那么特别的是出于第 i i i条水平线和第 i + 1 i+1 i+1条水平线中的点,这些点无法通过直接的曼哈顿距离到达,需要通过这两根水平线中转,故这些点的数量正是点对数,当然,我们需要排除和该点在同一根垂直线上的点即可。同理处理水平线上的点。
根据以上,我们需要处理出第 i i i条和第 i + 1 i+1 i+1条水平线和垂直线中有多少点,同时需要处理第 i i i条和第 i + 1 i+1 i+1条水平线中处于当前点的垂直线上的点的数量,这里我们可以利用 m a p map map使用滚动算法去写。
具体看AC代码。 -
AC代码
/**
*@filename:D_Inconvenient_Pairs
*@author: pursuit
*@created: 2021-09-09 11:13
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(a) cout << "debug : " << (#a)<< " = " << a << endl
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int P = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//如果一个人从另一个仅仅通过街道的最短路径严格大于它们的曼哈顿距离,那么这一对人就形成了不方便的人。
//计算不方便人的个数。
int t, n, m, k;//n条垂直和m条水平的线。k个点。
int x[N], y[N];
void solve(){
int xx, yy;
map<int, int> px, py;
map<pii, int> pxy, pyx;
ll res = 0;
while(k -- ){
scanf("%d%d", &xx, &yy);
int tx = lower_bound(x + 1, x + n + 1, xx) - x;
int ty = lower_bound(y + 1, y + m + 1, yy) - y;
if(x[tx] == xx && y[ty] == yy){
//说明落在横线和纵线上。这个时候到达任何点都是曼哈顿距离。
continue;
}
else if(x[tx] == xx){
//落在纵线上。那么此时的横线ty一定是大于yy的。
res += py[ty] - pxy[pii(tx, ty)];
++ py[ty];
++ pxy[pii(tx, ty)];
}
else{
//落在横线上,那么此时的纵线tx一定是大于xx的。
res += px[tx] - pyx[pii(ty, tx)];
++ px[tx];
++ pyx[pii(ty, tx)];
}
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t -- ){
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i){
scanf("%d", &x[i]);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++ i){
scanf("%d", &y[i]);
}
solve();
}
return 0;
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!