pytest简易教程(13):parametrize参数化
pytest简易教程汇总,详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/p/17982846
关于parametrize参数化
之前我们分享了通过fixture返回值实现参数化(详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/p/17957896)
今天我们分享parametrize参数化,也就是在测试函数/测试类进行参数化
parametrize是一个内置标记,在命令pytest --markers结果中可以看到@pytest.mark.parametrize(argnames, argvalues)

源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | class _ParametrizeMarkDecorator(MarkDecorator): def __call__( # type: ignore[override] self, argnames: Union[str, Sequence[str]], argvalues: Iterable[Union[ParameterSet, Sequence[object], object]], *, indirect: Union[bool, Sequence[str]] = ..., ids: Optional[ Union[ Iterable[Union[None, str, float, int, bool]], Callable[[Any], Optional[object]], ] ] = ..., scope: Optional[_ScopeName] = ..., ) -> MarkDecorator: ... |
方法:parametrize(argnames, argvalues, indirect=False, ids=None, scope=None)
常用参数:
- argnames:参数名,格式为:"arg1,arg2,arg3,...",通过逗号分隔多个参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | 多参数写法汇总:参数名可以是字符串、元组、列表、字符串放元组中@pytest.mark.parametrize("input,expected", [("1+1", 2), ("2-4", -2), ("2*3", 6)])@pytest.mark.parametrize(("input","expected"), [("1+1", 2), ("2-4", -2), ("2*3", 6)])@pytest.mark.parametrize(["input","expected"], [("1+1", 2), ("2-4", -2), ("2*3", 6)])@pytest.mark.parametrize(("input,expected"), [("1+1", 2), ("2-4", -2), ("2*3", 6)]) |
- argvalues:参数对应值,类型必须为list
当参数为一个时格式:[v1]
当参数个数大于一个时,格式为:[(v1_1, v2_1, ...), (v1_2, v2_2, ...)],一组参数值放元组或者列表中,也就是说,最外层列表可以嵌套元组或者列表
1 2 3 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("name,technology",[['韧','测试开发'],['全栈测试笔记','性能测试']]) # 列表嵌列表@pytest.mark.parametrize("name,technology",[('韧','测试开发'),('全栈测试笔记','性能测试')]) # 列表嵌套元组 |
- indirect:默认是False,如果设置成True,表示把被parametrize修饰器修饰的方法形参当函数执行(parametrize中参数名和这个形参同名),同时,必须有这个函数,且被@pytest.fixture()修饰,否则报错:fixture 'xxx' not found,xxx表示形参名
- ids:用例id,用于标识用例,增加可读性(测试结果中会展示id),是字符串列表,ids的长度要与测试数据列表长度一致
使用方法:
1、@pytest.mark.parametrize(argnames, argvalues)可以修饰函数、方法、测试类
2、修饰测试类时,会将测试数据传给此类下所有测试方法
3、函数、方法、测试类上可以加多个参数化修饰器
4、如果只有一个修饰器,参数值为N个(也就是列表长度),测试方法就会运行N次
5、如果多个修饰器,参数个数分别是X、Y、Z,会运行X*Y*Z次
单个参数的参数化
测试方法形参名要和parametrize里面的参数一样
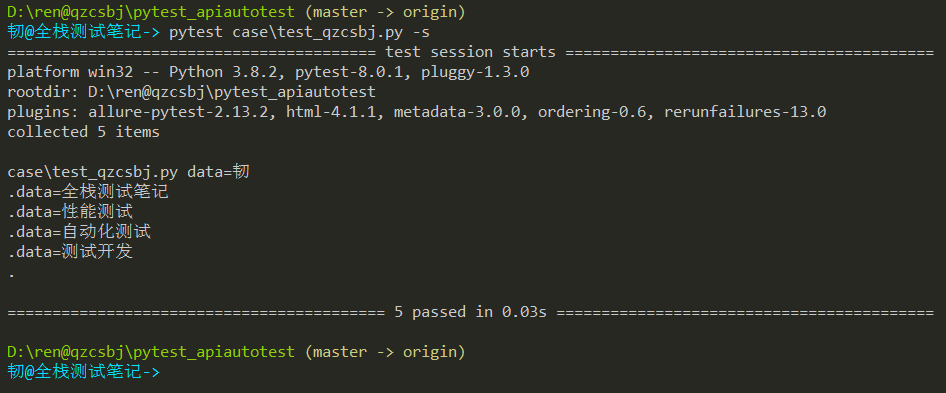
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytest@pytest.mark.parametrize("data",['韧','全栈测试笔记','性能测试','自动化测试','测试开发'])class TestQzcsbj: def test_case(self, data): print(f"data={data}") |
结果:
多个参数的参数化
参数放列表中,且列表嵌套元组或者列表
示例一:修饰器放函数上,参数值是基本类型
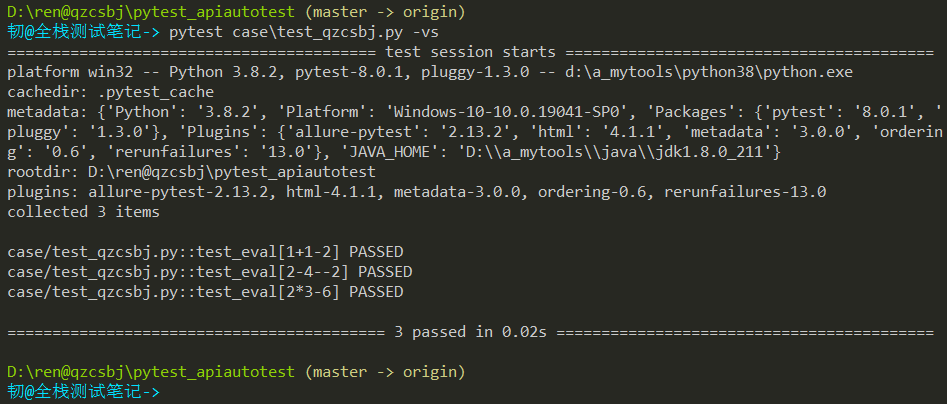
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytest@pytest.mark.parametrize("input,expected", [("1+1", 2), ("2-4", -2), ("2*3", 6)])def test_eval(input, expected): assert eval(input) == expected |
结果:
示例二:修饰器放函数上,参数值是字典
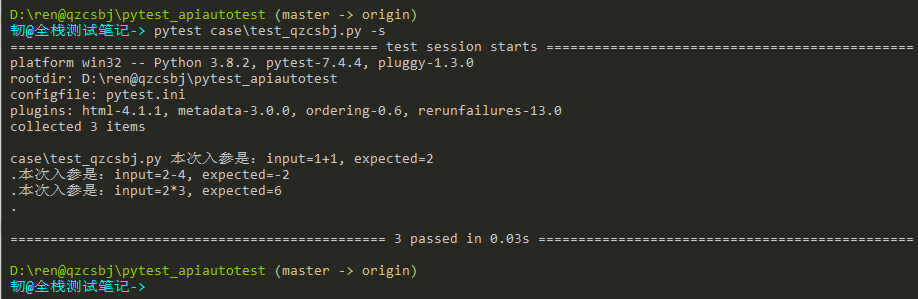
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytestdata = [ { "input": "1+1", "expected": 2 }, { "input": "2-4", "expected": -2 }, { "input": "2*3", "expected": 6 }]@pytest.mark.parametrize("par", data)def test_eval(par): print(f"本次入参是:input={par['input']}, expected={par['expected']}") assert eval(par['input']) == par['expected'] |
结果:
示例三:修饰器放测试类上
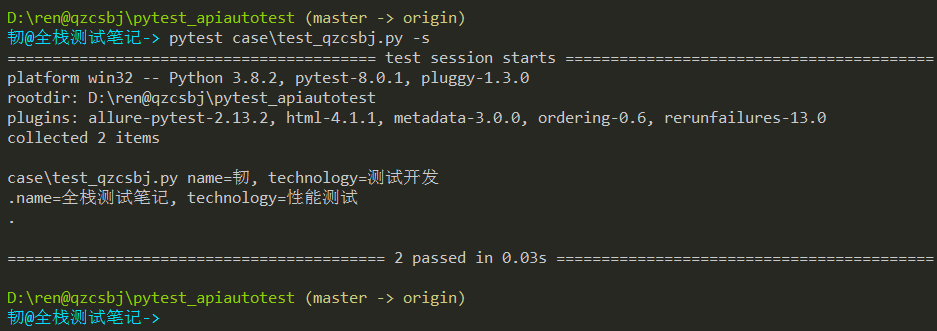
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytest# @pytest.mark.parametrize("name,technology",[['韧','测试开发'],['全栈测试笔记','性能测试']]) # 列表嵌列表@pytest.mark.parametrize("name,technology",[('韧','测试开发'),('全栈测试笔记','性能测试')]) # 列表嵌套元组class TestQzcsbj: def test_case(self, name, technology): print(f"name={name}, technology={technology}") |
结果:
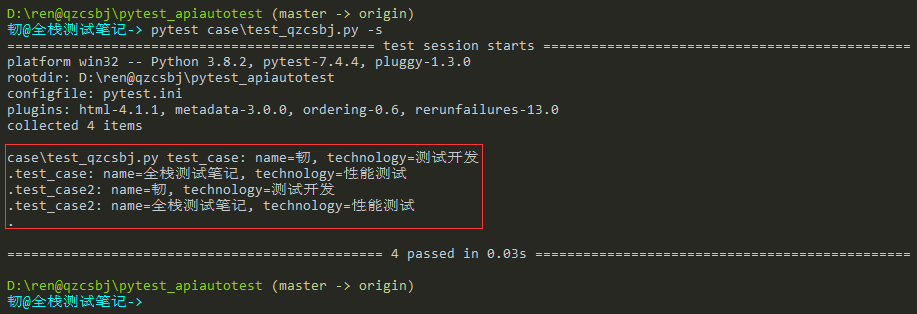
示例四:测试类下多个方法,会将测试数据传给此类下所有测试方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytest# @pytest.mark.parametrize("name,technology",[['韧','测试开发'],['全栈测试笔记','性能测试']]) # 列表嵌列表@pytest.mark.parametrize("name,technology",[('韧','测试开发'),('全栈测试笔记','性能测试')]) # 列表嵌套元组class TestQzcsbj: def test_case(self, name, technology): print(f"test_case: name={name}, technology={technology}") def test_case2(self, name, technology): print(f"test_case2: name={name}, technology={technology}") |
结果:
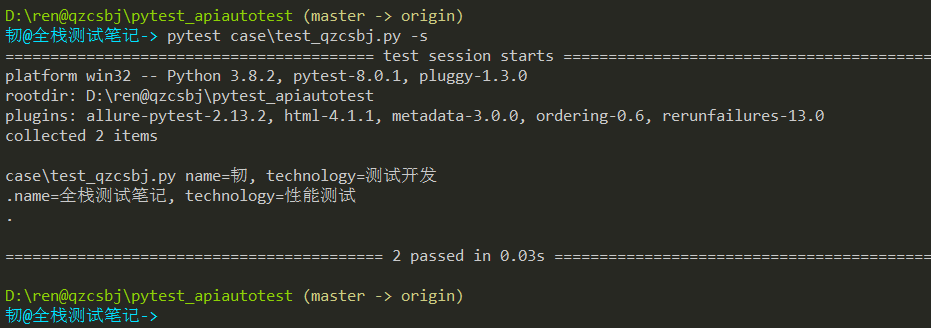
参数放变量中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytestdata = [('韧','测试开发'),('全栈测试笔记','性能测试')]@pytest.mark.parametrize("name,technology",data)class TestQzcsbj: def test_case(self, name, technology): print(f"name={name}, technology={technology}") |
结果:
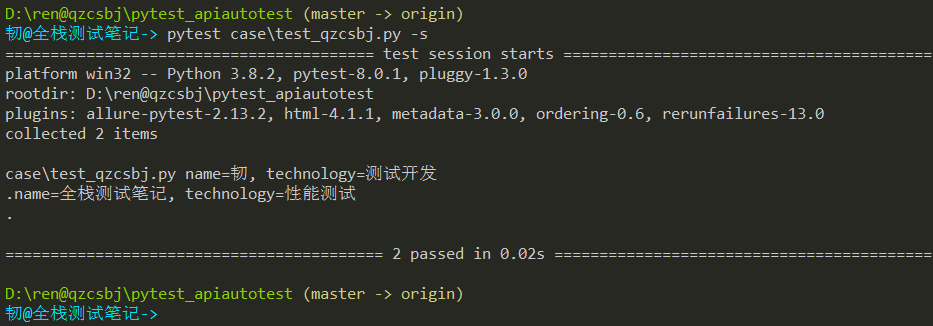
调用函数获取参数数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytestdef get_data(): return [('韧','测试开发'),('全栈测试笔记','性能测试')]@pytest.mark.parametrize("name,technology",get_data())class TestQzcsbj: def test_case(self, name, technology): print(f"name={name}, technology={technology}") |
结果:
mark标记参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytest@pytest.mark.parametrize( "input,expected", [ ("1+1", 2), pytest.param("2-4", -2, marks=[pytest.mark.minus, pytest.mark.xfail], id="input:2-4"), pytest.param("2*3", 6, marks=[pytest.mark.multiplication, pytest.mark.skip], id="input:2*3"), pytest.param("4/2", 2, marks=pytest.mark.division, id="input:4/2") ])def test_eval(input, expected): assert eval(input) == expected |
添加配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 | [pytest]addopts = -s --strict-markersmarkers = minus multiplication division |
结果:
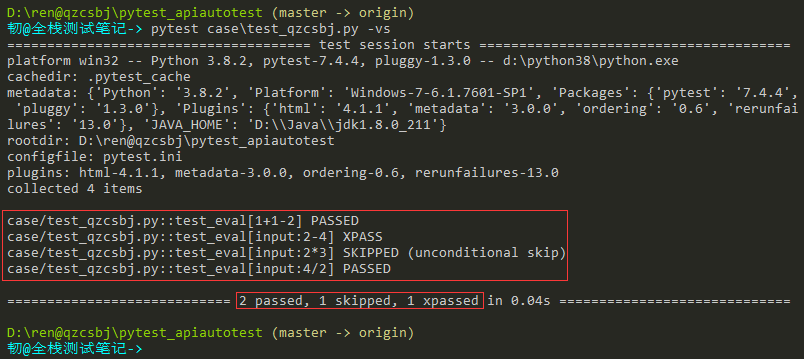
只执行某个标记的参数:pytest case\test_qzcsbj.py -vs -m division
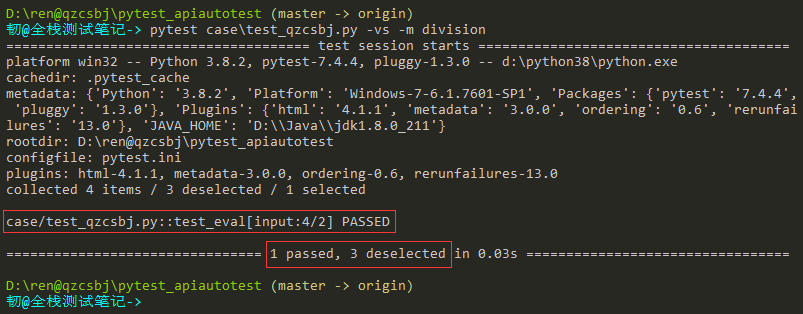
笛卡尔积:多个parametrize参数化修饰器
应用场景:比如注册接口,考虑不同入参的组合
示例:
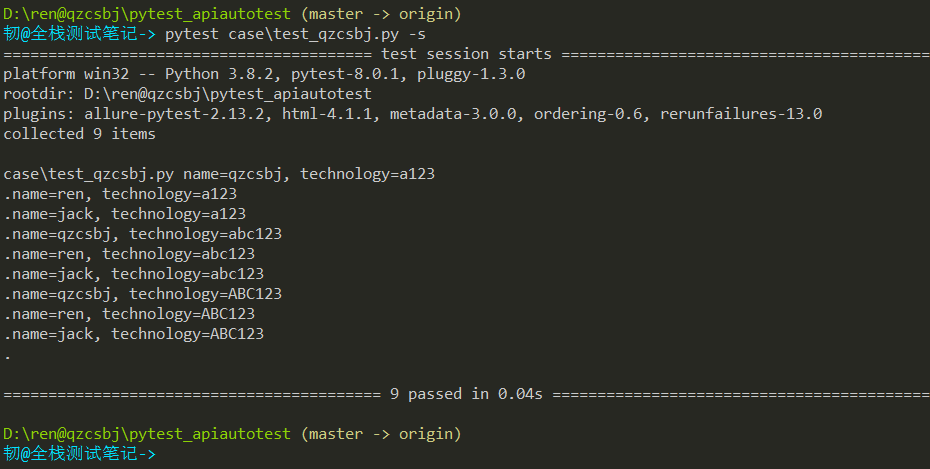
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytest@pytest.mark.parametrize("username",["qzcsbj","ren","jack"])@pytest.mark.parametrize("password",["a123","abc123","ABC123"])class TestQzcsbj: def test_case(self, username, password): print(f"name={username}, technology={password}") |
结果:运行9次
笛卡尔积:parametrize与fixture混合
注意:此时fixture修饰器中有params参数
示例:
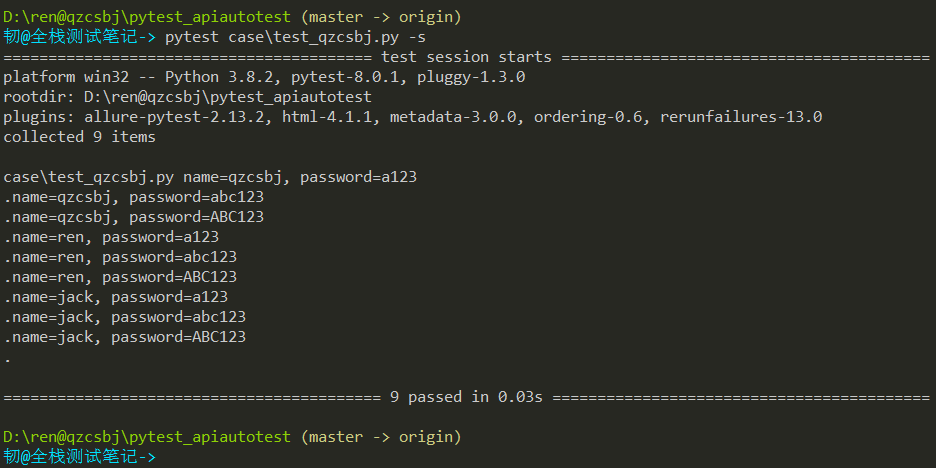
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytest@pytest.fixture(params=["qzcsbj","ren","jack"])def fun(request): return request.param@pytest.mark.parametrize("password", ["a123","abc123","ABC123"])def test_case(fun, password): print(f"name={fun}, password={password}") |
结果:
__EOF__

关于博主:擅长性能、全链路、自动化、企业级自动化持续集成(DevTestOps)、测开等
面试必备:项目实战(性能、自动化)、简历笔试,https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/p/15777706.html
测试提升:从测试小白到高级测试修炼之路,https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/p/10530261.html
欢迎分享:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,欢迎转载、分享,也可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下!



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)
2022-02-23 答疑记录:jmeter从返回的html中提取指定内容