pytest简易教程(11):pytest的配置文件(pytest.ini)
pytest简易教程汇总,详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/p/17982846
简介
pytest.ini是pytest的主配置文件,可以添加配置改变pytest的默认行为,这样不用我们每次执行都在命令行中指定很多参数;
此配置文件通常放到项目根目录下。
配置项
执行pytest -h,查看可用于pytest.ini的配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 | [pytest] ini-options in the first pytest.ini|tox.ini|setup.cfg|pyproject.toml file found: markers (linelist): Markers for test functions empty_parameter_set_mark (string): Default marker for empty parametersets norecursedirs (args): Directory patterns to avoid for recursion testpaths (args): Directories to search for tests when no files or directories are given on the command line filterwarnings (linelist): Each line specifies a pattern for warnings.filterwarnings. Processed after -W/--pythonwarnings. usefixtures (args): List of default fixtures to be used with this project python_files (args): Glob-style file patterns for Python test module discovery python_classes (args): Prefixes or glob names for Python test class discovery python_functions (args): Prefixes or glob names for Python test function and method discovery disable_test_id_escaping_and_forfeit_all_rights_to_community_support (bool): Disable string escape non-ASCII characters, might cause unwanted side effects(use at your own risk) console_output_style (string): Console output: "classic", or with additional progress information ("progress" (percentage) | "count" | "progress-even-when-capture-no" (forces progress even when capture=no) xfail_strict (bool): Default for the strict parameter of xfail markers when not given explicitly (default: False) tmp_path_retention_count (string): How many sessions should we keep the `tmp_path` directories, according to `tmp_path_retention_policy`. tmp_path_retention_policy (string): Controls which directories created by the `tmp_path` fixture are kept around, based on test outcome. (all/failed/none) enable_assertion_pass_hook (bool): Enables the pytest_assertion_pass hook. Make sure to delete any previously generated pyc cache files. junit_suite_name (string): Test suite name for JUnit report junit_logging (string): Write captured log messages to JUnit report: one of no|log|system-out|system-err|out-err|all junit_log_passing_tests (bool): Capture log information for passing tests to JUnit report: junit_duration_report (string): Duration time to report: one of total|call junit_family (string): Emit XML for schema: one of legacy|xunit1|xunit2 doctest_optionflags (args): Option flags for doctests doctest_encoding (string): Encoding used for doctest files cache_dir (string): Cache directory path log_level (string): Default value for --log-level log_format (string): Default value for --log-format log_date_format (string): Default value for --log-date-format log_cli (bool): Enable log display during test run (also known as "live logging") log_cli_level (string): Default value for --log-cli-level log_cli_format (string): Default value for --log-cli-format log_cli_date_format (string): Default value for --log-cli-date-format log_file (string): Default value for --log-file log_file_level (string): Default value for --log-file-level log_file_format (string): Default value for --log-file-format log_file_date_format (string): Default value for --log-file-date-format log_auto_indent (string): Default value for --log-auto-indent pythonpath (paths): Add paths to sys.path faulthandler_timeout (string): Dump the traceback of all threads if a test takes more than TIMEOUT seconds to finish addopts (args): Extra command line options minversion (string): Minimally required pytest version required_plugins (args): Plugins that must be present for pytest to run render_collapsed (string): row(s) to render collapsed on open. max_asset_filename_length (string): set the maximum filename length for assets attached to the html report. environment_table_redact_list (linelist): a list of regexes corresponding to environment table variables whose values should be redacted from the report initial_sort (string): column to initially sort on. generate_report_on_test (bool): the HTML report will be generated after each test instead of at the end of the run. reruns (string): number of times to re-run failed tests. defaults to 0. reruns_delay (string): add time (seconds) delay between reruns. |
配置文件样例
pytest.ini
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | [pytest]# 命令行执行参数addopts = -vs --strict-markers# 排除目录norecursedirs = xxx# 默认执行目录testpaths = case# 执行规则:classpython_classes = Test*# 执行规则:py文件python_files = test_* *_test# 执行规则:functionpython_functions = test_*# 自定义注册标记markers = user: 用户模块 order: 订单模块 |
addopts:命令行参数
pytest命令行运行参数可以写入到pytest.ini中的addopts参数值中,addopts参数几乎支持所有参数,这样避免每一次运行的时候都需要输入参数;
多个参数用空格分隔。
说明:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | [pytest]addopts = -vs --strict-markers等价于命令行参数:pytest -vs --strict-markers等价于main:if __name__ == "__main__": pytest.main(["-vs","--strict-markers"]) |
目录规则
1 2 | norecursedirs = sub_casetestpaths = case |
规则
-
1. norecursedirs:配置测试不搜索路径(也就是不访问哪些目录)
-
2. testpaths:配置测试搜索路径(也就是要访问的目录)
-
3. 当两者有冲突时,比如二者配置的一样,testpaths优先,也就是执行testpaths下的所有用例
-
4. testpaths包含norecursedirs,执行testpaths下除了norecursedirs的用例
-
5. norecursedirs包含testpaths,不执行任何用例,并给出警告
- 6.testpaths可以配置多个路径,用空格分隔
验证
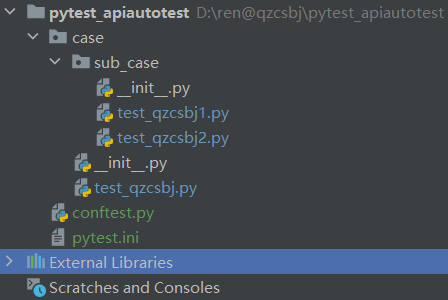
pytest.ini配置文件内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | [pytest]# 命令行执行参数addopts = -vs --strict-markers# 排除目录; norecursedirs = casenorecursedirs = sub_case# 默认执行目录testpaths = case; testpaths = sub_case# 执行规则:classpython_classes = Test*# 执行规则:py文件python_files = test_* *_test# 执行规则:functionpython_functions = test_* |
test_qzcsbj.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytestclass Test01: def test_case2(self): print("--------------test_case2") def test_case1(self): print("--------------test_case1") |
test_qzcsbj1.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytestclass TestCase: def test_a(self): print("---test_a") def test_b(self): print("---test_b") |
test_qzcsbj2.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/def test_c(): print("---test_c") assert 1 == 1 |
如果配置
1 2 | norecursedirs = sub_casetestpaths = case |
结果是:执行case下除了sub_case的用例
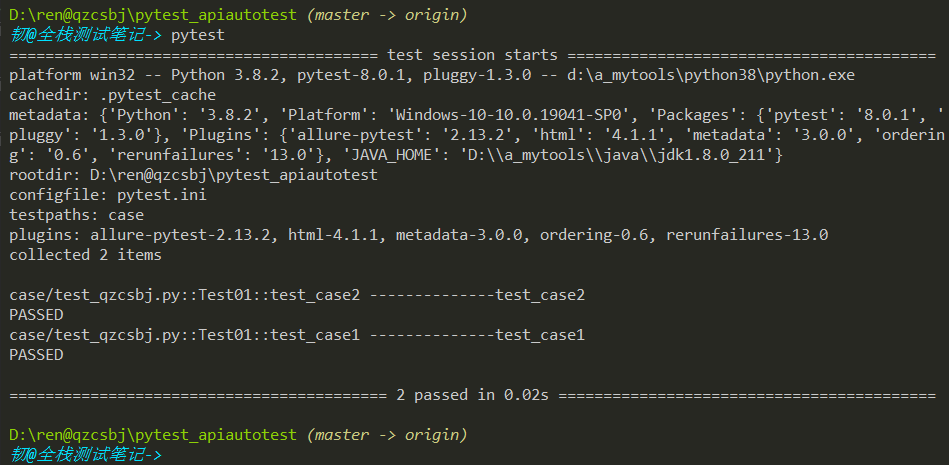
如果配置(实际不会这么配置,这里只是为了测试)
1 2 | norecursedirs = casetestpaths = case |
结果是:执行case下所有用例
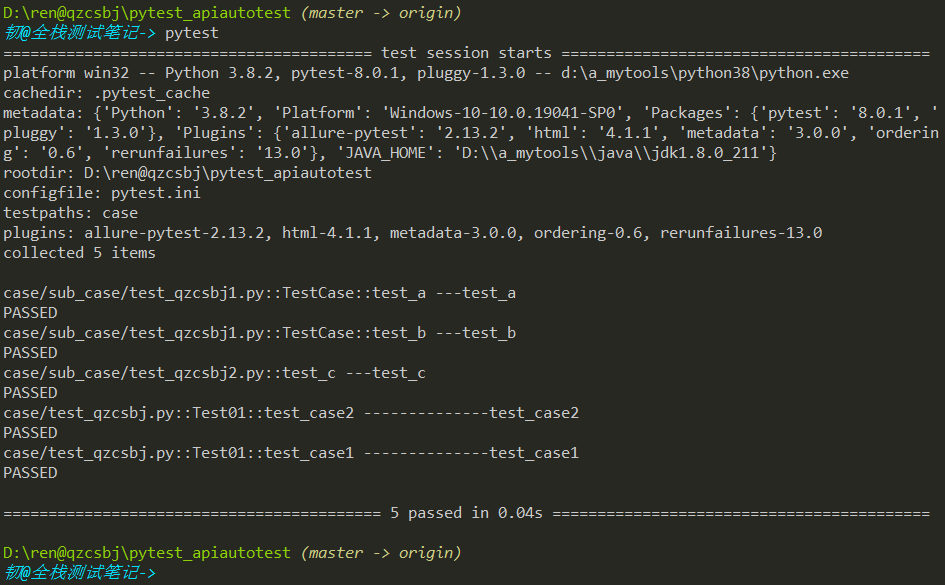
如果配置
1 2 | norecursedirs = casetestpaths = sub_case |
结果是:不执行任何用例
补充1:关于搜索
如果仅配置testpaths
1 | testpaths = ./case |
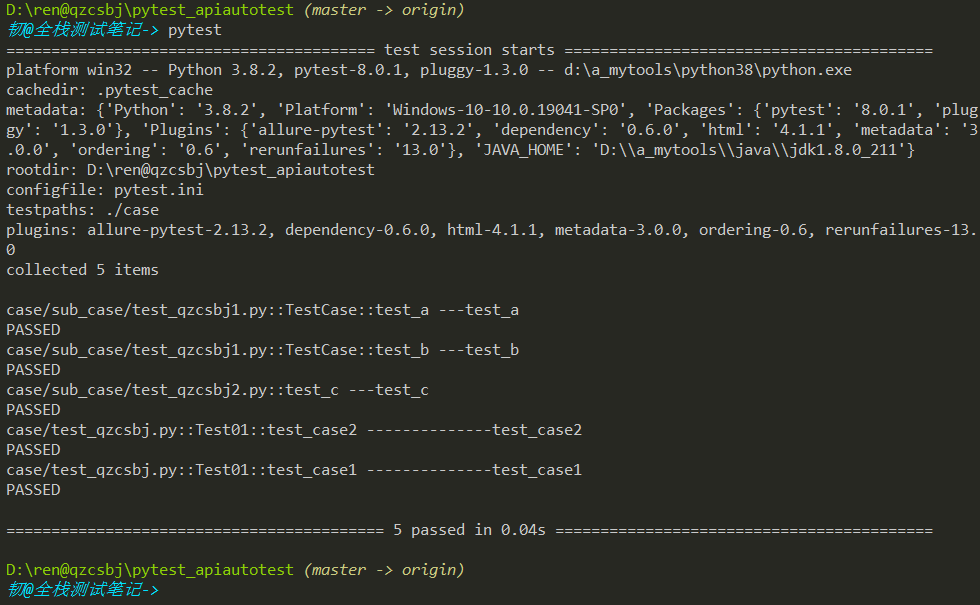
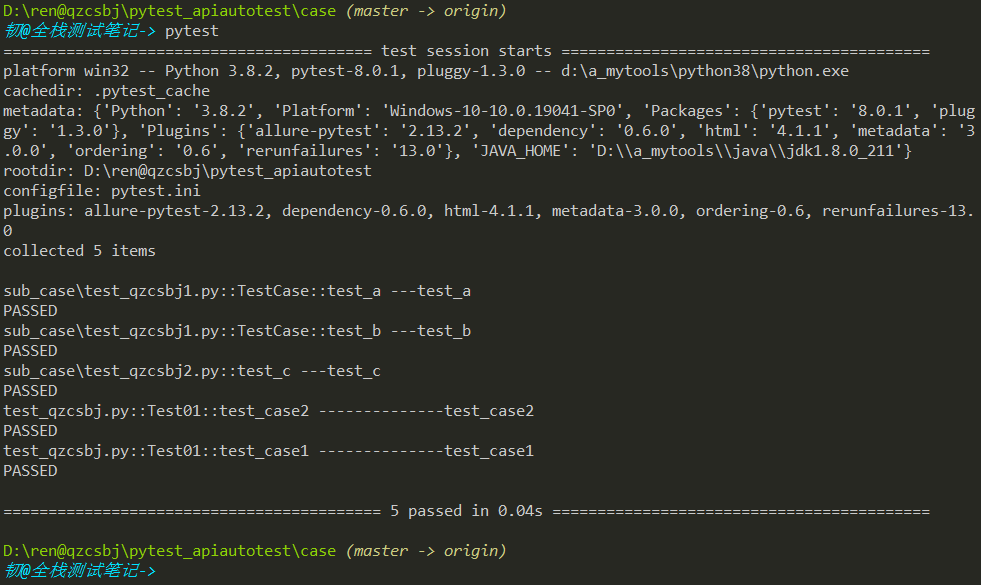
在项目根目录执行,结果是执行了5条
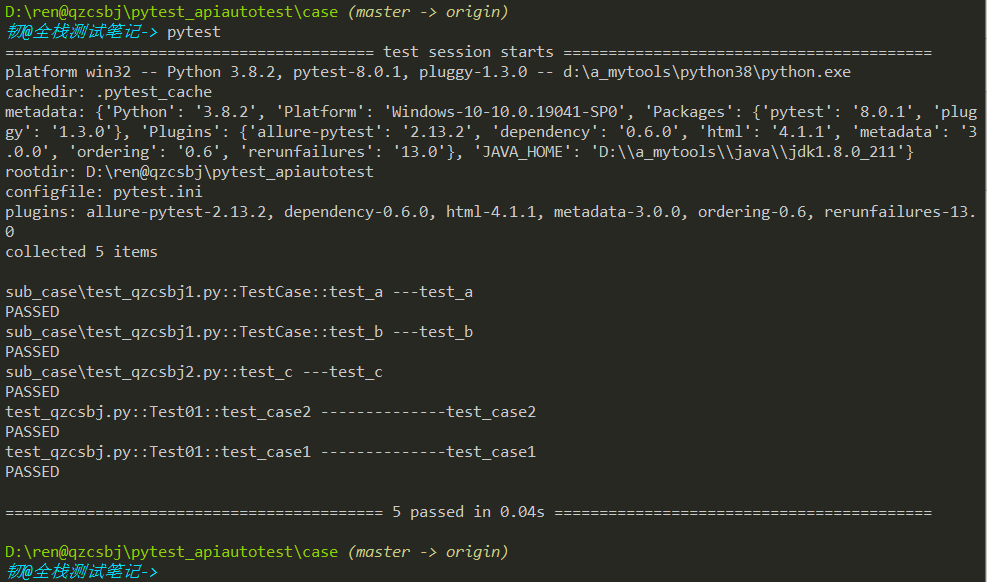
在case目录执行,结果是执行了5条
在sub_case目录执行,结果是执行了3条
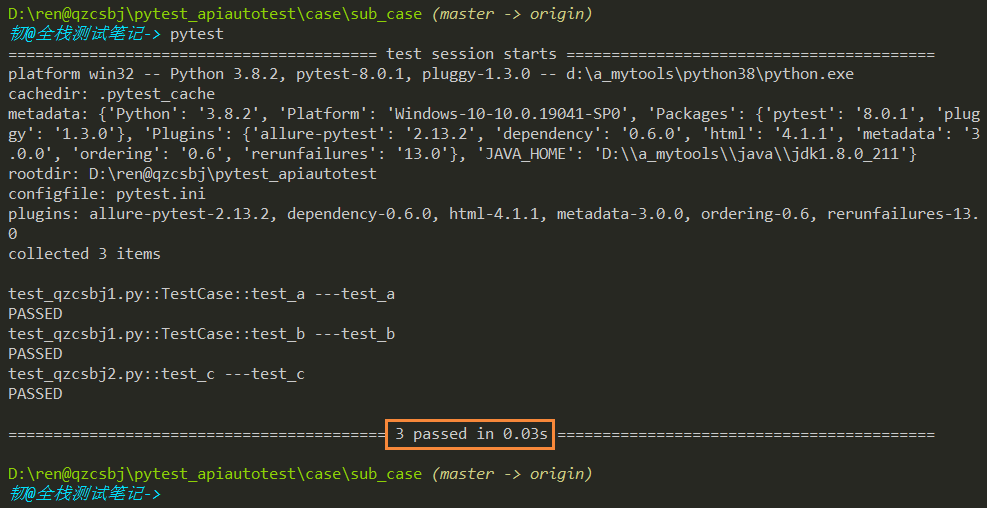
结论:从命令执行的目录开始搜索在testpaths下的用例
补充2:关于搜索
如果仅配置testpaths
1 | testpaths = ./case/sub_case |
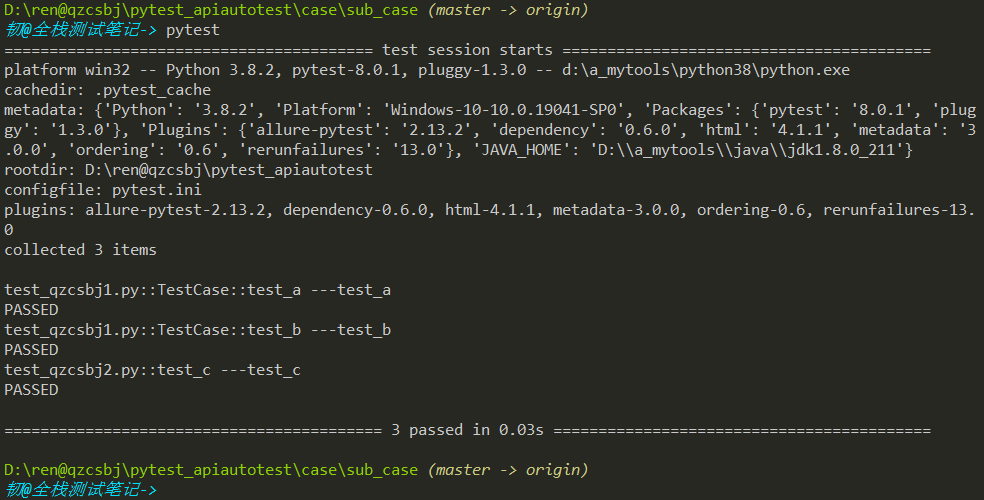
结果执行了3条用例
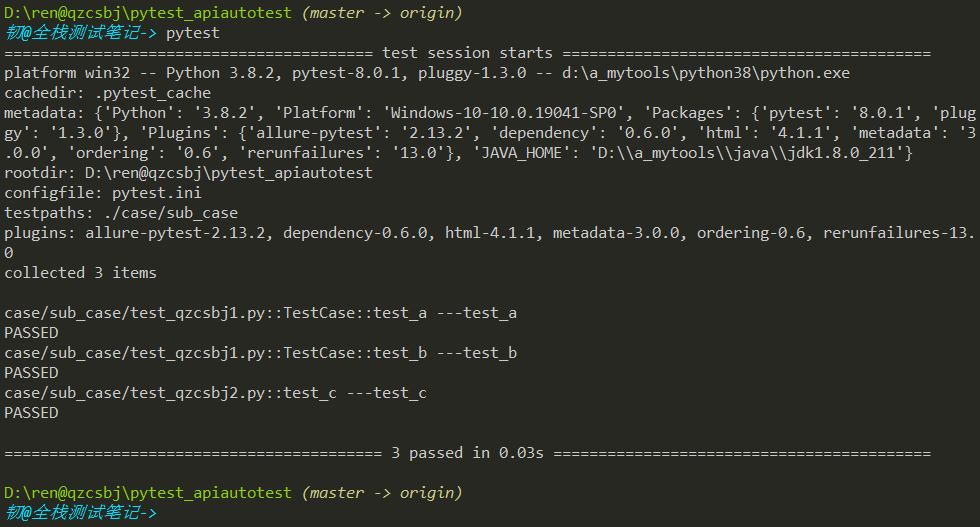
结果执行了5条用例,说明也执行当前目录下py文件中用例,因为py文件在testpaths路径的case下(如果py文件在项目根目录,pytest也在根目录下执行,不会执行根目录下这个py文件中用例,因为此文件不在testpaths路径的任何一级)。建议:不同用例放同级下不同的目录即可。
结果执行了3条用例
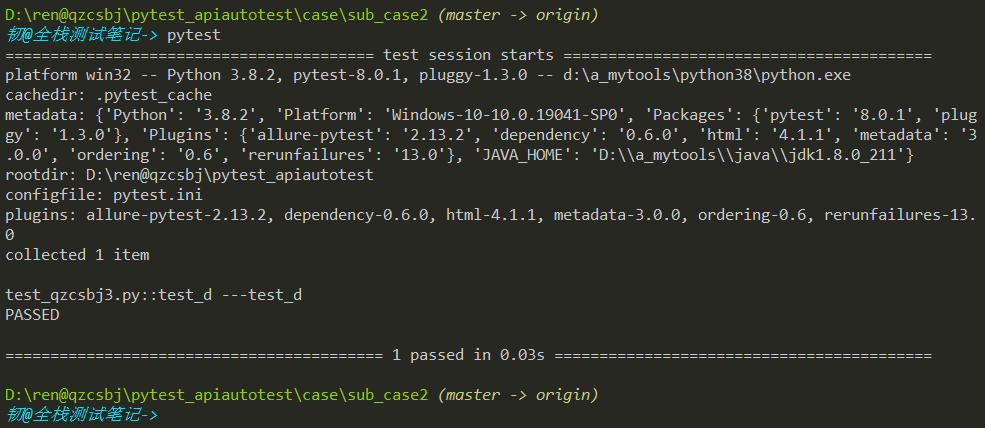
和sub_test同级,创建sub_test2,下面创建test_qzcsbj3.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog : https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/def test_d(): print("---test_d") assert 1 == 1 |
结果:虽然testpaths只配置了sub_case目录,在sub_case2下执行,依然会执行此目录下用例,因为sub_case2在配置中./case/sub_case的case下
执行规则
1 2 3 | python_classes = Test*python_files = test_*.py *_test.pypython_functions = test_* qzcsbj_* |
说明:
python_files = test_*.py,表示配置测试搜索的文件名
python_classes = Test*,表示配置测试搜索的类名
python_functions = test_*,表示配置测试搜索的函数名
我们可以修改规则,比如function除了test_开头,还可以qzcsbj_开头,不过,不建议修改。
另外,如果不加通配符,表示执行指定内容,比如python_files = test_qzcsbj.py,表示执行test_qzcsbj.py文件。
xfail:标志规则
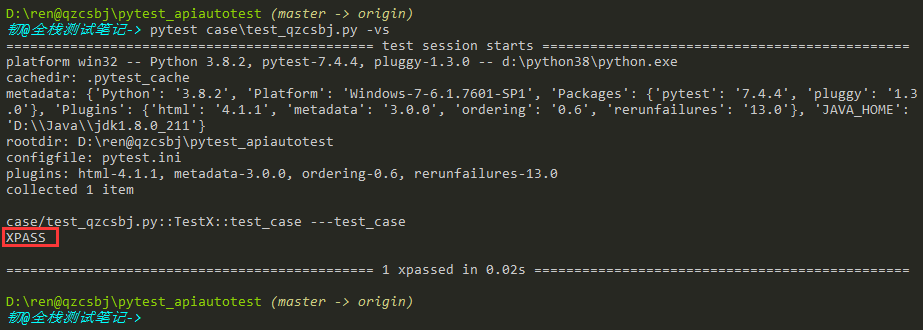
设置xfail_strict = true,标记为@pytest.mark.xfail且实际是通过(显示XPASS)的测试用例会被报告为失败FAILED
xfail_strict默认是false,标记为@pytest.mark.xfail的测试用例,如果是通过,显示XPASS
添加配置:
1 2 | [pytest]xfail_strict = true |
结果:如果通过,显示FAILED
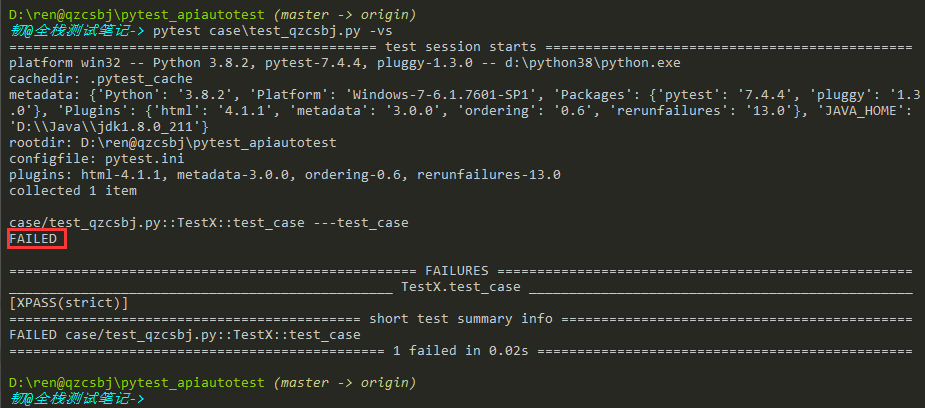
markers:自定义注册标志
测试用例加了@pytest.mark.xxx修饰器(下面示例加在测试类上了),如果配置文件中没有配置markers就会报warnings
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytest@pytest.fixture(params=['韧', '全栈测试笔记', '性能测试', '自动化测试', '测试开发'])def fun(request): # 必须是request这个参数名 return request.param # 依次取列表中的每个值返回@pytest.mark.caseclass TestX: def test_case(self, fun): print(f"---test_case,data={fun}") |
结果:是因为我们给测试方法打的标签,pytest识别不到
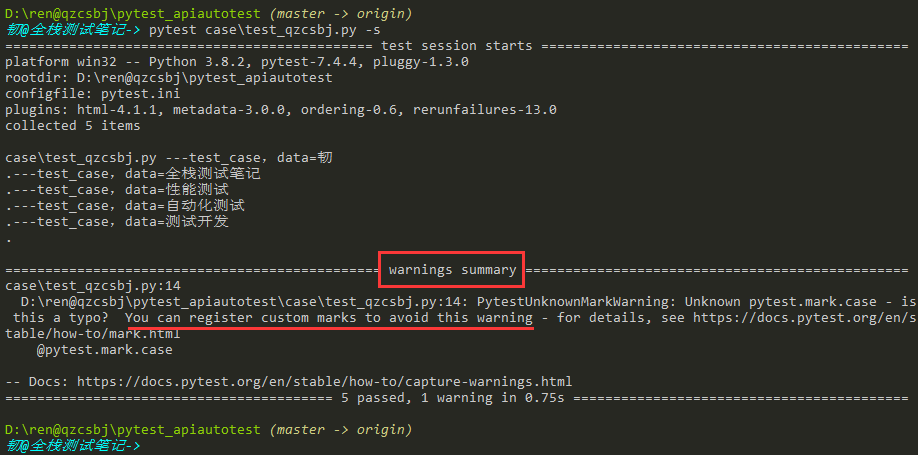
解决方案:https://docs.pytest.org/en/stable/how-to/mark.html
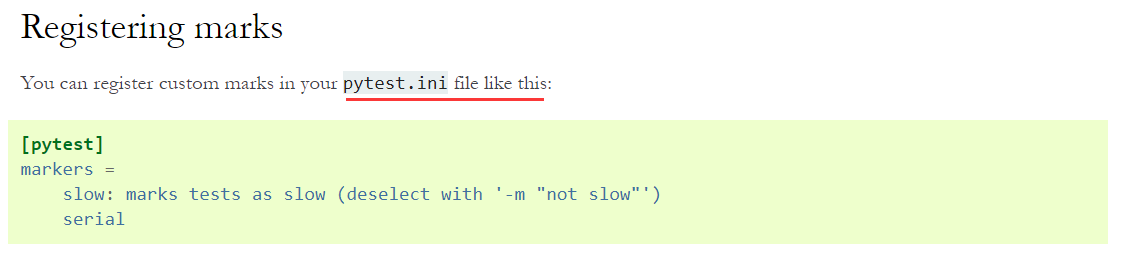
加上配置(可以加多个)
1 2 3 | [pytest]markers = case |
后面还可以加上说明
1 2 3 | [pytest]markers = case: case marker |
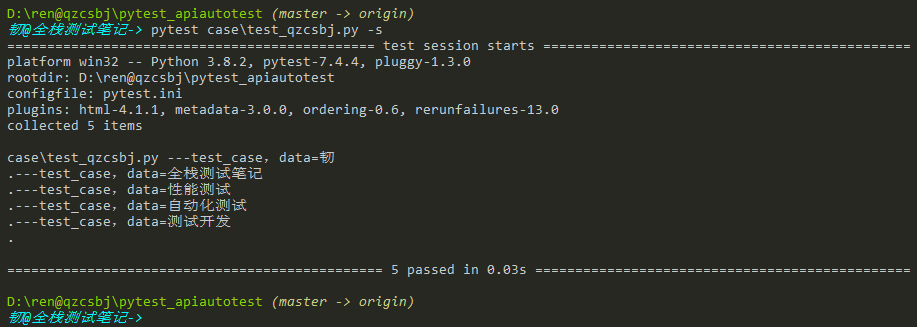
结果:没有warning了
log-cli:控制台实时输出日志
默认是false,log-cli=false,等价于:log_cli=0
示例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytest@pytest.mark.xfailclass TestX: def test_case(self): print(f"---test_case") assert 1==1 |
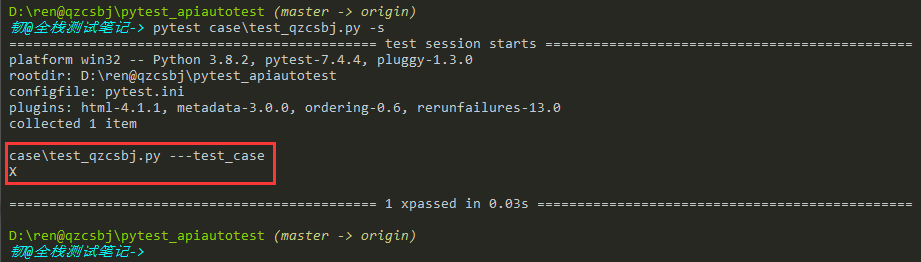
配置0
1 2 | [pytest]log_cli=0 |
结果:
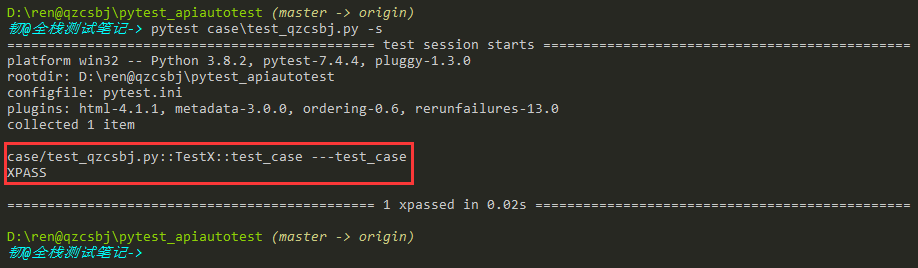
配置1
1 2 | [pytest]log_cli=1 |
结果:展示更细了,可以看到测试类和测试方法
日志格式配置,详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/p/18017483
disable_test_id_escaping_and_forfeit_all_rights_to_community_support = True
示例
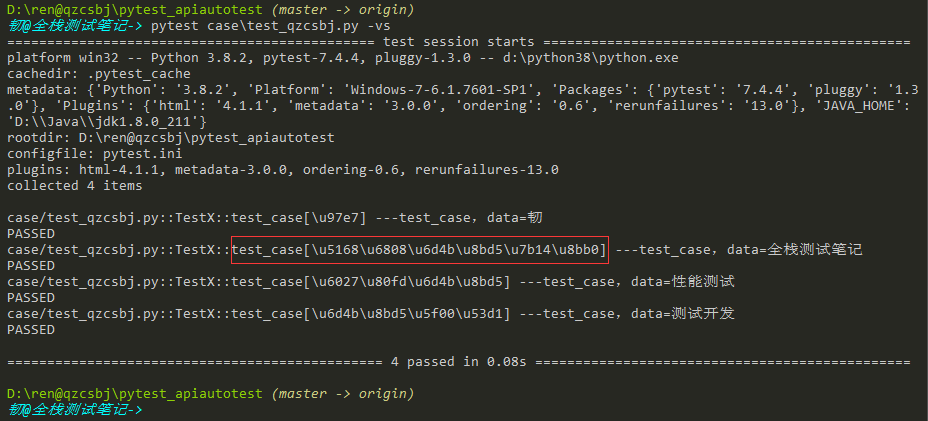
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author : 韧# @wx :ren168632201# @Blog :https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/import pytest@pytest.fixture(params=['韧', '全栈测试笔记', '性能测试', '测试开发'])def fun(request): # 必须是request这个参数名 return request.param # 依次取列表中的每个值返回class TestX: def test_case(self, fun): print(f"---test_case,data={fun}") |
结果:用例名unicode编码展示
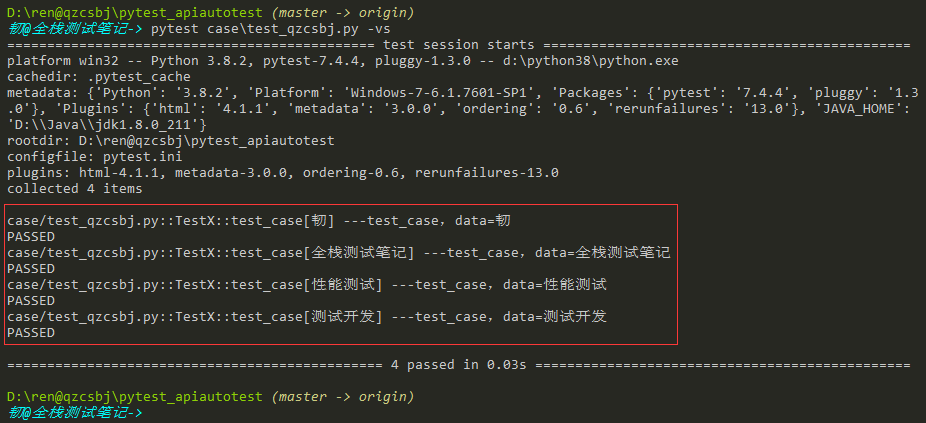
解决方案是配置文件中加上:
1 | disable_test_id_escaping_and_forfeit_all_rights_to_community_support = True |
结果:中文正常显示
其它方案,详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/p/18022091
__EOF__

关于博主:擅长性能、全链路、自动化、企业级自动化持续集成(DevTestOps)、测开等
面试必备:项目实战(性能、自动化)、简历笔试,https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/p/15777706.html
测试提升:从测试小白到高级测试修炼之路,https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/p/10530261.html
欢迎分享:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,欢迎转载、分享,也可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下!



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)
2022-02-23 答疑记录:jmeter从返回的html中提取指定内容