Scrum Guide 2020 (中英文对照)
Scrum 指南的目的
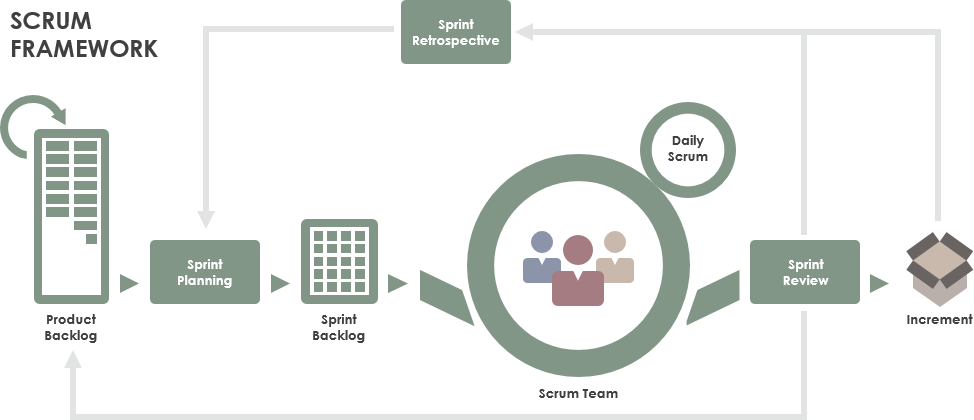
我们在 1990 年代初期开发了 Scrum。我们在 2010 年编写了第一版 Scrum 指南,以帮助全世界的人们了解 Scrum。从那时起,我们通过小的、功能性的更新改进了指南。我们一起支持它。
Scrum 指南包含 Scrum 的定义。框架的每个元素都有一个特定的目的,这对于使用 Scrum 实现的整体价值和结果至关重要。改变 Scrum 的核心设计或思想、遗漏元素或不遵循 Scrum 规则,会掩盖问题并限制 Scrum 的好处,甚至可能使其变得无用。
我们关注在不断增长的复杂世界中越来越多地使用 Scrum。我们很惭愧地看到 Scrum 被许多领域采用,这些领域具有本质上复杂的工作,超出了 Scrum 发源地的软件产品开发。随着 Scrum 的广泛使用,开发人员、研究人员、分析师、科学家和其他专家开始工作。我们在 Scrum 中使用“开发人员”这个词不是为了排除,而是为了简化。如果您从 Scrum 中获得价值,请考虑将自己包括在内。
在使用 Scrum 时,可以找到、应用和设计适合本文档中描述的 Scrum 框架的模式、流程和见解。它们的描述超出了 Scrum 指南的目的,因为它们是上下文敏感的,并且在 Scrum 使用之间存在很大差异。在 Scrum 框架内使用的此类策略差异很大,并在别处进行了描述。
Purpose of the Scrum Guide
We developed Scrum in the early 1990s. We wrote the first version of the Scrum Guide in 2010 to help people worldwide understand Scrum. We have evolved the Guide since then through small, functional updates. Together, we stand behind it.
The Scrum Guide contains the definition of Scrum. Each element of the framework serves a specific purpose that is essential to the overall value and results realized with Scrum. Changing the core design or ideas of Scrum, leaving out elements, or not following the rules of Scrum, covers up problems and limits the benefits of Scrum, potentially even rendering it useless.
We follow the growing use of Scrum within an ever-growing complex world. We are humbled to see Scrum being adopted in many domains holding essentially complex work, beyond software product development where Scrum has its roots. As Scrum’s use spreads, developers, researchers, analysts, scientists, and other specialists do the work. We use the word “developers” in Scrum not to exclude, but to simplify. If you get value from Scrum, consider yourself included.
As Scrum is being used, patterns, processes, and insights that fit the Scrum framework as described in this document, may be found, applied and devised. Their description is beyond the purpose of the Scrum Guide because they are context sensitive and differ widely between Scrum uses. Such tactics for using within the Scrum framework vary widely and are described elsewhere.
Scrum 定义
Scrum 是一个轻量级框架,可帮助人员、团队和组织通过针对复杂问题的自适应解决方案创造价值。
简而言之,Scrum 需要一个 Scrum Master 来营造这样一个环境:
Scrum 很简单。按原样尝试并确定其哲学、理论和结构是否有助于实现目标和创造价值。Scrum 框架故意不完整,只定义了实现 Scrum 理论所需的部分。Scrum 建立在使用它的人们的集体智慧之上。Scrum 规则不是为人们提供详细的说明,而是指导他们的关系和互动。
可以在该框架内采用各种过程、技术和方法。Scrum 环绕现有实践或使其变得不必要。Scrum 使当前管理、环境和工作技术的相对效率可见,以便进行改进。
Scrum Definition
Scrum is a lightweight framework that helps people, teams and organizations generate value through adaptive solutions for complex problems.
In a nutshell, Scrum requires a Scrum Master to foster an environment where:
- A Product Owner orders the work for a complex problem into a Product Backlog.
- The Scrum Team turns a selection of the work into an Increment of value during a Sprint.
- The Scrum Team and its stakeholders inspect the results and adjust for the next Sprint.
- Repeat
Scrum is simple. Try it as is and determine if its philosophy, theory, and structure help to achieve goals and create value. The Scrum framework is purposefully incomplete, only defining the parts required to implement Scrum theory. Scrum is built upon by the collective intelligence of the people using it. Rather than provide people with detailed instructions, the rules of Scrum guide their relationships and interactions.
Various processes, techniques and methods can be employed within the framework. Scrum wraps around existing practices or renders them unnecessary. Scrum makes visible the relative efficacy of current management, environment, and work techniques, so that improvements can be made.
Scrum 理论
Scrum 建立在经验主义和精益思想之上。经验主义断言,知识来自经验,并根据观察到的东西做出决定。精益思想减少浪费并专注于基本要素。
Scrum 采用迭代的、增量的方法来优化可预测性和控制风险。Scrum 让一群人共同拥有完成工作的所有技能和专业知识,并根据需要分享或获得这些技能。
Scrum 结合了四个正式事件,以便在一个包含事件(Sprint)中进行检查和调整。这些事件之所以有效,是因为它们实现了透明、检查和适应的经验 Scrum 支柱。
Scrum Theory
Scrum is founded on empiricism and lean thinking. Empiricism asserts that knowledge comes from experience and making decisions based on what is observed. Lean thinking reduces waste and focuses on the essentials.
Scrum employs an iterative, incremental approach to optimize predictability and to control risk. Scrum engages groups of people who collectively have all the skills and expertise to do the work and share or acquire such skills as needed.
Scrum combines four formal events for inspection and adaptation within a containing event, the Sprint. These events work because they implement the empirical Scrum pillars of transparency, inspection, and adaptation.
透明度
紧急过程和工作必须对执行工作的人和接受工作的人可见。使用 Scrum,重要的决策是基于其三个正式工件的感知状态。透明度低的工件可能会导致做出降低价值和增加风险的决策。
透明度使检查成为可能。不透明的检查是误导和浪费的。
Transparency
The emergent process and work must be visible to those performing the work as well as those receiving the work. With Scrum, important decisions are based on the perceived state of its three formal artifacts. Artifacts that have low transparency can lead to decisions that diminish value and increase risk.
Transparency enables inspection. Inspection without transparency is misleading and wasteful.
检查
Scrum 工件和达成一致目标的进度必须经常和勤奋地检查,以发现潜在的不受欢迎的差异或问题。为了帮助检查,Scrum 以五个事件的形式提供了节奏。
检查使适应成为可能。没有适应的检查被认为是没有意义的。Scrum 事件旨在激发变革。
Inspection
The Scrum artifacts and the progress toward agreed goals must be inspected frequently and diligently to detect potentially undesirable variances or problems. To help with inspection, Scrum provides cadence in the form of its five events.
Inspection enables adaptation. Inspection without adaptation is considered pointless. Scrum events are designed to provoke change.
适应
如果过程的任何方面超出可接受的范围,或者如果产生的产品不可接受,则必须调整正在应用的过程或正在生产的材料。必须尽快进行调整,以尽量减少进一步的偏差。
当相关人员没有被授权或自我管理时,适应变得更加困难。Scrum 团队应该在通过检查学习任何新事物的那一刻进行调整。
Adaption
If any aspects of a process deviate outside acceptable limits or if the resulting product is unacceptable, the process being applied or the materials being produced must be adjusted. The adjustment must be made as soon as possible to minimize further deviation.
Adaptation becomes more difficult when the people involved are not empowered or self-managing. A Scrum Team is expected to adapt the moment it learns anything new through inspection.
Scrum 价值观
Scrum 的成功使用取决于人们更加精通以下五个价值观:
承诺、专注、开放、尊重和勇气
Scrum 团队致力于实现其目标并相互支持。他们的主要重点是 Sprint 的工作,以尽可能实现这些目标。Scrum 团队及其利益相关者对工作和挑战持开放态度。Scrum 团队成员相互尊重,成为有能力、独立的人,并受到与他们一起工作的人的尊重。Scrum 团队成员有勇气做正确的事情,解决棘手的问题。
这些价值观为 Scrum 团队的工作、行动和行为指明了方向。做出的决定、采取的步骤和使用 Scrum 的方式应该加强这些价值观,而不是削弱或削弱它们。Scrum 团队成员在处理 Scrum 事件和工件时学习和探索价值。当这些价值观被 Scrum 团队和与他们一起工作的人体现时,透明度、检查和适应的经验性 Scrum 支柱就会建立信任。
Scrum Values
Successful use of Scrum depends on people becoming more proficient in living five values:
Commitment, Focus, Openness, Respect, and Courage
The Scrum Team commits to achieving its goals and to supporting each other. Their primary focus is on the work of the Sprint to make the best possible progress toward these goals. The Scrum Team and its stakeholders are open about the work and the challenges. Scrum Team members respect each other to be capable, independent people, and are respected as such by the people with whom they work. The Scrum Team members have the courage to do the right thing, to work on tough problems.
These values give direction to the Scrum Team with regard to their work, actions, and behavior. The decisions that are made, the steps taken, and the way Scrum is used should reinforce these values, not diminish or undermine them. The Scrum Team members learn and explore the values as they work with the Scrum events and artifacts. When these values are embodied by the Scrum Team and the people they work with, the empirical Scrum pillars of transparency, inspection, and adaptation come to life building trust.
Scrum 团队
Scrum 的基本单位是一个小团队,一个 Scrum 团队。Scrum 团队由一名 Scrum Master、一名产品负责人和开发人员组成。在 Scrum 团队中,没有子团队或层次结构。它是一个由专业人士组成的有凝聚力的单位,一次专注于一个目标,即产品目标。
Scrum 团队是跨职能的,这意味着成员拥有在每个 Sprint 中创造价值所需的所有技能。他们也是自我管理的,这意味着他们在内部决定谁做什么、什么时候做什么以及如何做。
Scrum 团队负责所有与产品相关的活动,包括利益相关者协作、验证、维护、运营、实验、研究和开发,以及任何其他可能需要的活动。他们由组织构建并授权来管理自己的工作。以可持续的速度在 Sprint 中工作可以提高 Scrum 团队的注意力和一致性。
整个 Scrum 团队负责在每个 Sprint 中创建有价值的、有用的增量。Scrum 在 Scrum 团队中定义了三个特定的职责:开发人员、产品负责人和 Scrum Master
Scrum Team
The fundamental unit of Scrum is a small team of people, a Scrum Team. The Scrum Team consists of one Scrum Master, one Product Owner, and Developers. Within a Scrum Team, there are no sub-teams or hierarchies. It is a cohesive unit of professionals focused on one objective at a time, the Product Goal.
Scrum Teams are cross-functional, meaning the members have all the skills necessary to create value each Sprint. They are also self-managing, meaning they internally decide who does what, when, and how.
The Scrum Team is responsible for all product-related activities from stakeholder collaboration, verification, maintenance, operation, experimentation, research and development, and anything else that might be required. They are structured and empowered by the organization to manage their own work. Working in Sprints at a sustainable pace improves the Scrum Team’s focus and consistency.
The entire Scrum Team is accountable for creating a valuable, useful Increment every Sprint. Scrum defines three specific accountabilities within the Scrum Team: the Developers, the Product Owner, and the Scrum Master.
团队规模
Scrum 团队小到可以保持敏捷,大到可以在 Sprint 中完成重要工作,通常是 10 人或更少。总的来说,我们发现较小的团队沟通更好,效率更高。
Team Size
The Scrum Team is small enough to remain nimble and large enough to complete significant work within a Sprint, typically 10 or fewer people. In general, we have found that smaller teams communicate better and are more productive.
多个团队
如果 Scrum 团队变得太大,他们应该考虑重组为多个有凝聚力的 Scrum 团队,每个团队都专注于相同的产品。因此,他们应该共享相同的产品目标、产品待办列表和产品负责人。
[…]
如果有多个 Scrum 团队一起开发一个产品,他们必须相互定义并遵守相同的完成定义。
Multiple teams
If Scrum Teams become too large, they should consider reorganizing into multiple cohesive Scrum Teams, each focused on the same product. Therefore, they should share the same Product Goal, Product Backlog, and Product Owner.
If there are multiple Scrum Teams working together on a product, they must mutually define and comply with the same Definition of Done.
开发人员
开发人员是 Scrum 团队中致力于在每个 Sprint 中创建可用增量的任何方面的人员。
开发人员所需的特定技能通常很广泛,并且会因工作领域而异。但是,开发人员始终负责:
为 Sprint 制定计划,即 Sprint Backlog;
通过坚持完成的定义来灌输质量;
每天根据 Sprint 目标调整他们的计划;和,
作为专业人士相互问责。
Developers
Developers are the people in the Scrum Team that are committed to creating any aspect of a usable Increment each Sprint.
The specific skills needed by the Developers are often broad and will vary with the domain of work. However, the Developers are always accountable for:
- Creating a plan for the Sprint, the Sprint Backlog;
- Instilling quality by adhering to a Definition of Done;
- Adapting their plan each day toward the Sprint Goal; and,
- Holding each other accountable as professionals.
产品拥有者
产品负责人负责最大化由 Scrum 团队工作产生的产品价值。如何做到这一点可能因组织、Scrum 团队和个人而异。
产品负责人还负责有效的产品待办列表管理,其中包括:
- 制定并明确传达产品目标;
- 创建并清楚地传达产品待办事项列表项;
- 订购产品待办列表项;和,
- 确保产品待办列表透明、可见和理解。
- 产品负责人可以完成上述工作,也可以将责任委托给其他人。无论如何,产品负责人仍然负责。
- 产品负责人要取得成功,整个组织都必须尊重他们的决定。这些决定在产品待办列表的内容和顺序中是可见的,并且通过 Sprint 评审中的可检查增量可见。
- 产品负责人是一个人,而不是一个委员会。产品负责人可能代表产品待办列表中许多利益相关者的需求。那些想要更改产品待办列表的人可以通过尝试说服产品负责人来实现。
Product Owner
The Product Owner is accountable for maximizing the value of the product resulting from the work of the Scrum Team. How this is done may vary widely across organizations, Scrum Teams, and individuals.
The Product Owner is also accountable for effective Product Backlog management, which includes:
- Developing and explicitly communicating the Product Goal;
- Creating and clearly communicating Product Backlog items;
- Ordering Product Backlog items; and,
- Ensuring that the Product Backlog is transparent, visible and understood.
- The Product Owner may do the above work or may delegate the responsibility to others. Regardless, the Product Owner remains accountable.
- For Product Owners to succeed, the entire organization must respect their decisions. These decisions are visible in the content and ordering of the Product Backlog, and through the inspectable Increment at the Sprint Review.
- The Product Owner is one person, not a committee. The Product Owner may represent the needs of many stakeholders in the Product Backlog. Those wanting to change the Product Backlog can do so by trying to convince the Product Owner.
Scrum Master
Scrum Master 负责建立 Scrum 指南中定义的 Scrum。他们通过帮助 Scrum 团队和组织内的每个人了解 Scrum 理论和实践来做到这一点。
Scrum Master 对 Scrum 团队的有效性负责。他们通过让 Scrum 团队在 Scrum 框架内改进其实践来做到这一点。
Scrum Master 是真正的领导者,为 Scrum 团队和更大的组织服务。
Scrum Master
The Scrum Master is accountable for establishing Scrum as defined in the Scrum Guide. They do this by helping everyone understand Scrum theory and practice, both within the Scrum Team and the organization.
The Scrum Master is accountable for the Scrum Team’s effectiveness. They do this by enabling the Scrum Team to improve its practices, within the Scrum framework.
Scrum Masters are true leaders who serve the Scrum Team and the larger organization.
为团队服务
Scrum Master 以多种方式为 Scrum 团队服务,包括:
- 指导团队成员进行自我管理和跨职能;
- 帮助 Scrum 团队专注于创造满足完成定义的高价值增量;
- 消除阻碍 Scrum 团队进展的障碍;和,
- 确保所有 Scrum 事件发生并且是积极的、富有成效的,并保持在时间范围内。
Service to the Team
- The Scrum Master serves the Scrum Team in several ways, including:
- Coaching the team members in self-management and cross-functionality;
- Helping the Scrum Team focus on creating high-value Increments that meet the Definition of Done;
- Causing the removal of impediments to the Scrum Team’s progress; and,
- Ensuring that all Scrum events take place and are positive, productive, and kept within the timebox.
为产品负责人服务
Scrum Master 以多种方式为组织服务,包括:
- 领导、培训和指导组织采用 Scrum;
- 计划和建议组织内的 Scrum 实施;
- 帮助员工和利益相关者理解和制定复杂工作的经验方法;和,
- 消除利益相关者和 Scrum 团队之间的障碍。
Service to the Product Owner
The Scrum Master serves the Product Owner in several ways, including:
- Helping find techniques for effective Product Goal definition and Product Backlog management;
- Helping the Scrum Team understand the need for clear and concise Product Backlog items;
- Helping establish empirical product planning for a complex environment; and,
- Facilitating stakeholder collaboration as requested or needed.
为本组织服务
Scrum Master 以多种方式为组织服务,包括:
- 领导、培训和指导组织采用 Scrum;
- 计划和建议组织内的 Scrum 实施;
- 帮助员工和利益相关者理解和制定复杂工作的经验方法;和,
- 消除利益相关者和 Scrum 团队之间的障碍。
Service to the Organization
The Scrum Master serves the organization in several ways, including:
- Leading, training, and coaching the organization in its Scrum adoption;
- Planning and advising Scrum implementations within the organization;
- Helping employees and stakeholders understand and enact an empirical approach for complex work; and,
- Removing barriers between stakeholders and Scrum Teams.
Scrum 事件
Sprint 是所有其他事件的容器。Scrum 中的每个事件都是检查和调整 Scrum 工件的正式机会。这些事件专门设计用于实现所需的透明度。未能按规定操作任何事件会导致失去检查和适应的机会。在 Scrum 中使用事件来创建规律性并最小化 Scrum 中未定义的会议的需求。
最理想的是,所有活动都在同一时间和地点举行,以降低复杂性。
Scrum Events
The Sprint is a container for all other events. Each event in Scrum is a formal opportunity to inspect and adapt Scrum artifacts. These events are specifically designed to enable the transparency required. Failure to operate any events as prescribed results in lost opportunities to inspect and adapt. Events are used in Scrum to create regularity and to minimize the need for meetings not defined in Scrum.
Optimally, all events are held at the same time and place to reduce complexity.
冲刺 (Sprint)
Sprint 是 Scrum 的心跳,在这里将想法转化为价值。
它们是一个月或更短的固定长度事件,以创建一致性。新的 Sprint 在上一个 Sprint 结束后立即开始。
实现产品目标所需的所有工作,包括 Sprint 计划、每日 Scrums、Sprint 审查和 Sprint 回顾,都在 Sprint 中进行。
在 Sprint 期间:
- 没有进行会危及 Sprint 目标的更改;
- 质量不下降;
- 产品待办列表根据需要进行细化;和,
- 随着了解的更多,范围可能会被澄清并与产品负责人重新协商。
- 冲刺通过确保至少每个日历月检查和调整产品目标的进度来实现可预测性。当 Sprint 的期限太长时,Sprint 目标可能会失效,复杂性可能会增加,风险可能会增加。可以采用更短的 Sprint 来产生更多的学习周期,并将成本和努力的风险限制在更短的时间范围内。每个 Sprint 都可以被视为一个短期项目。
- 存在各种用于预测进度的实践,例如燃尽、燃尽或累积流量。虽然被证明是有用的,但这些并不能取代经验主义的重要性。在复杂的环境中,会发生什么是未知的。只有已经发生的事情才能用于前瞻性决策。
The Sprint
Sprints are the heartbeat of Scrum, where ideas are turned into value. They are fixed length events of one month or less to create consistency. A new Sprint starts immediately after the conclusion of the previous Sprint.
All the work necessary to achieve the Product Goal, including Sprint Planning, Daily Scrums, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective, happen within Sprints.
- During the Sprint:
- No changes are made that would endanger the Sprint Goal;
- Quality does not decrease;
- The Product Backlog is refined as needed; and,
- Scope may be clarified and renegotiated with the Product Owner as more is learned.
Sprints enable predictability by ensuring inspection and adaptation of progress toward a Product Goal at least every calendar month. When a Sprint’s horizon is too long the Sprint Goal may become invalid, complexity may rise, and risk may increase. Shorter Sprints can be employed to generate more learning cycles and limit risk of cost and effort to a smaller time frame. Each Sprint may be considered a short project.
Various practices exist to forecast progress, like burn-downs, burn-ups, or cumulative flows. While proven useful, these do not replace the importance of empiricism. In complex environments, what will happen is unknown. Only what has already happened may be used for forward-looking decision making.
冲刺取消
如果 Sprint 目标过时,则 Sprint 可能会被取消。只有产品负责人有权取消 Sprint。
Sprint Cancellation
A Sprint could be cancelled if the Sprint Goal becomes obsolete. Only the Product Owner has the authority to cancel the Sprint.
冲刺计划
Sprint 计划通过布置要为 Sprint 执行的工作来启动 Sprint。这个最终计划是由整个 Scrum 团队的协作工作创建的。
产品负责人确保与会者准备好讨论最重要的产品待办事项列表项目以及它们如何映射到产品目标。Scrum 团队还可以邀请其他人参加 Sprint 计划以提供建议。
Sprint 计划涉及以下主题:
主题一:为什么这个 Sprint 有价值?
产品负责人提议产品如何在当前 Sprint 中增加其价值和效用。然后,整个 Scrum 团队协作定义一个 Sprint 目标,以传达为什么 Sprint 对利益相关者有价值。Sprint 目标必须在 Sprint 计划结束之前完成。
主题二:这个 Sprint 可以做什么?
通过与产品负责人的讨论,开发人员从产品待办列表中选择要包含在当前 Sprint 中的项目。Scrum 团队可能会在此过程中细化这些项目,从而增加理解和信心。
选择在 Sprint 中可以完成多少可能具有挑战性。然而,开发人员对他们过去的表现、即将到来的容量以及他们的完成定义了解得越多,他们对 Sprint 的预测就越有信心。
主题三:选择的工作将如何完成?
对于每个选定的产品待办列表项,开发人员计划创建满足完成定义的增量所需的工作。这通常是通过将产品待办列表项分解为一天或更短的更小的工作项来完成的。如何做到这一点由开发人员自行决定。没有人告诉他们如何将产品待办列表项转化为价值增量。
Sprint 目标、为 Sprint 选择的产品待办列表项以及交付它们的计划统称为 Sprint 待办列表。
Sprint 计划的时间限制为一个月的 Sprint 最多 8 小时。对于较短的 Sprint,事件通常较短。
Sprint Planning
Sprint Planning initiates the Sprint by laying out the work to be performed for the Sprint. This resulting plan is created by the collaborative work of the entire Scrum Team.
The Product Owner ensures that attendees are prepared to discuss the most important Product Backlog items and how they map to the Product Goal. The Scrum Team may also invite other people to attend Sprint Planning to provide advice.
Sprint Planning addresses the following topics:
Topic One: Why is this Sprint valuable? The Product Owner proposes how the product could increase its value and utility in the current Sprint. The whole Scrum Team then collaborates to define a Sprint Goal that communicates why the Sprint is valuable to stakeholders. The Sprint Goal must be finalized prior to the end of Sprint Planning.
Topic Two: What can be Done this Sprint? Through discussion with the Product Owner, the Developers select items from the Product Backlog to include in the current Sprint. The Scrum Team may refine these items during this process, which increases understanding and confidence.
Selecting how much can be completed within a Sprint may be challenging. However, the more the Developers know about their past performance, their upcoming capacity, and their Definition of Done, the more confident they will be in their Sprint forecasts.
Topic Three: How will the chosen work get done? For each selected Product Backlog item, the Developers plan the work necessary to create an Increment that meets the Definition of Done. This is often done by decomposing Product Backlog items into smaller work items of one day or less. How this is done is at the sole discretion of the Developers. No one else tells them how to turn Product Backlog items into Increments of value.
The Sprint Goal, the Product Backlog items selected for the Sprint, plus the plan for delivering them are together referred to as the Sprint Backlog.
Sprint Planning is timeboxed to a maximum of eight hours for a one-month Sprint. For shorter Sprints, the event is usually shorter.
每日站会
Daily Scrum 的目的是检查实现 Sprint 目标的进度并根据需要调整 Sprint Backlog,调整即将到来的计划工作。
每日 Scrum 是 Scrum 团队开发人员的 15 分钟活动。为了降低复杂性,它在 Sprint 的每个工作日在同一时间和地点举行。如果产品负责人或 Scrum Master 正在积极处理 Sprint 待办列表中的项目,他们作为开发人员参与。
开发人员可以选择他们想要的任何结构和技术,只要他们的 Daily Scrum 专注于实现 Sprint 目标的进展并为第二天的工作制定可操作的计划。这创造了焦点并改善了自我管理。
每日 Scrums 改善沟通,识别障碍,促进快速决策,从而消除其他会议的需要。
Daily Scrum 并不是唯一一次允许开发人员调整他们的计划。他们经常全天开会,就调整或重新规划 Sprint 的其余工作进行更详细的讨论。
Daily Scrum
The purpose of the Daily Scrum is to inspect progress toward the Sprint Goal and adapt the Sprint Backlog as necessary, adjusting the upcoming planned work.
The Daily Scrum is a 15-minute event for the Developers of the Scrum Team. To reduce complexity, it is held at the same time and place every working day of the Sprint. If the Product Owner or Scrum Master are actively working on items in the Sprint Backlog, they participate as Developers.
The Developers can select whatever structure and techniques they want, as long as their Daily Scrum focuses on progress toward the Sprint Goal and produces an actionable plan for the next day of work. This creates focus and improves self-management.
Daily Scrums improve communications, identify impediments, promote quick decision-making, and consequently eliminate the need for other meetings.
The Daily Scrum is not the only time Developers are allowed to adjust their plan. They often meet throughout the day for more detailed discussions about adapting or re-planning the rest of the Sprint’s work.
Sprint Review
Sprint Review 的目的是检查 Sprint 的结果并确定未来的调整。Scrum 团队向主要利益相关者展示他们的工作结果,并讨论实现产品目标的进展。
在活动期间,Scrum 团队和利益相关者审查在 Sprint 中完成的内容以及他们的环境中发生了什么变化。根据这些信息,与会者就下一步做什么进行协作。产品待办列表也可能会进行调整以迎接新的机会。Sprint Review 是一个工作会议,Scrum 团队应避免将其限制为演示。
Sprint Review 是 Sprint 的倒数第二个事件,并且在为期一个月的 Sprint 中将时间限制为最多四个小时。对于较短的 Sprint,事件通常较短。
Sprint Review
The purpose of the Sprint Review is to inspect the outcome of the Sprint and determine future adaptations. The Scrum Team presents the results of their work to key stakeholders and progress toward the Product Goal is discussed.
During the event, the Scrum Team and stakeholders review what was accomplished in the Sprint and what has changed in their environment. Based on this information, attendees collaborate on what to do next. The Product Backlog may also be adjusted to meet new opportunities. The Sprint Review is a working session and the Scrum Team should avoid limiting it to a presentation.
The Sprint Review is the second to last event of the Sprint and is timeboxed to a maximum of four hours for a one-month Sprint. For shorter Sprints, the event is usually shorter.
冲刺回顾
Sprint 回顾的目的是计划提高质量和有效性的方法。
Scrum 团队检查上一个 Sprint 在个人、交互、流程、工具及其完成定义方面的进展情况。检查的元素通常随着工作领域的不同而变化。确定了导致他们误入歧途的假设并探索了它们的起源。Scrum 团队讨论了 Sprint 中哪些方面做得好,遇到了哪些问题,以及这些问题是如何(或没有)解决的。
Scrum 团队确定最有帮助的更改以提高其有效性。尽快解决最具影响力的改进。它们甚至可能被添加到下一个 Sprint 的 Sprint Backlog 中。
Sprint 回顾会结束 Sprint。对于一个月的 Sprint,时间限制为最多三个小时。对于较短的 Sprint,事件通常较短。
Sprint Retrospective
The purpose of the Sprint Retrospective is to plan ways to increase quality and effectiveness.
The Scrum Team inspects how the last Sprint went with regards to individuals, interactions, processes, tools, and their Definition of Done. Inspected elements often vary with the domain of work. Assumptions that led them astray are identified and their origins explored. The Scrum Team discusses what went well during the Sprint, what problems it encountered, and how those problems were (or were not) solved.
The Scrum Team identifies the most helpful changes to improve its effectiveness. The most impactful improvements are addressed as soon as possible. They may even be added to the Sprint Backlog for the next Sprint.
The Sprint Retrospective concludes the Sprint. It is timeboxed to a maximum of three hours for a one-month Sprint. For shorter Sprints, the event is usually shorter.
Scrum 工件
Scrum 的工件代表工作或价值。它们旨在最大限度地提高关键信息的透明度。因此,每个检查它们的人都有相同的适应基础。
每个工件都包含一个承诺,以确保它提供的信息可以提高透明度和重点,可以衡量进度:
- 对于产品待办列表,它是产品目标。
- 对于 Sprint Backlog,它是 Sprint 目标。
- 对于增量,它是完成的定义。
这些承诺的存在是为了加强 Scrum 团队及其利益相关者的经验主义和 Scrum 价值观。
Scrum Artifacts
Scrum’s artifacts represent work or value. They are designed to maximize transparency of key information. Thus, everyone inspecting them has the same basis for adaptation.
Each artifact contains a commitment to ensure it provides information that enhances transparency and focus against which progress can be measured:
- For the Product Backlog it is the Product Goal.
- For the Sprint Backlog it is the Sprint Goal.
- For the Increment it is the Definition of Done.
These commitments exist to reinforce empiricism and the Scrum values for the Scrum Team and their stakeholders.
产品积压
产品待办列表是一个紧急的、有序的清单,列出了改进产品所需的内容。它是 Scrum 团队承担的工作的唯一来源。
可以由 Scrum 团队在一个 Sprint 内完成的产品待办事项列表项目被视为已准备好在 Sprint 计划活动中进行选择。他们通常在提炼活动后获得这种程度的透明度。产品待办列表细化是将产品待办列表项分解并进一步定义为更小更精确的项的行为。这是添加详细信息(例如描述、订单和尺寸)的持续活动。属性通常因工作领域而异。
将进行工作的开发人员负责调整大小。产品负责人可以通过帮助开发人员理解和选择权衡来影响他们。
Product Backlog
The Product Backlog is an emergent, ordered list of what is needed to improve the product. It is the single source of work undertaken by the Scrum Team.
Product Backlog items that can be Done by the Scrum Team within one Sprint are deemed ready for selection in a Sprint Planning event. They usually acquire this degree of transparency after refining activities. Product Backlog refinement is the act of breaking down and further defining Product Backlog items into smaller more precise items. This is an ongoing activity to add details, such as a description, order, and size. Attributes often vary with the domain of work.
The Developers who will be doing the work are responsible for the sizing. The Product Owner may influence the Developers by helping them understand and select trade-offs.
产品目标
产品待办事项承诺:产品目标
产品目标描述了产品的未来状态,可以作为 Scrum 团队计划的目标。产品目标在产品待办列表中。产品待办列表的其余部分出现以定义“什么”将实现产品目标。
产品是传递价值的载体。它有明确的边界、已知的利益相关者、明确定义的用户或客户。产品可以是服务、实物产品或更抽象的东西。
产品目标是 Scrum 团队的长期目标。他们必须先完成(或放弃)一个目标,然后才能开始下一个目标。
Product Goal
Product backlog Commitment: Product Goal
The Product Goal describes a future state of the product which can serve as a target for the Scrum Team to plan against. The Product Goal is in the Product Backlog. The rest of the Product Backlog emerges to define “what” will fulfill the Product Goal.
A product is a vehicle to deliver value. It has a clear boundary, known stakeholders, well-defined users or customers. A product could be a service, a physical product, or something more abstract.
The Product Goal is the long-term objective for the Scrum Team. They must fulfill (or abandon) one objective before taking on the next.
冲刺积压
因此,随着学到的更多,Sprint Backlog 在整个 Sprint 中都会更新。它应该有足够的细节,以便他们可以在 Daily Scrum 中检查他们的进度。
Sprint Backlog
The Sprint Backlog is composed of the Sprint Goal (why), the set of Product Backlog items selected for the Sprint (what), as well as an actionable plan for delivering the Increment (how).
The Sprint Backlog is a plan by and for the Developers. It is a highly visible, real-time picture of the work that the Developers plan to accomplish during the Sprint in order to achieve the Sprint Goal.
冲刺目标
Sprint backlog 承诺:Sprint 目标
Sprint 目标是 Sprint 的唯一目标。尽管 Sprint 目标是开发人员的承诺,但它在实现它所需的确切工作方面提供了灵活性。Sprint 目标还创造了一致性和重点,鼓励 Scrum 团队一起工作而不是单独的计划。
Sprint 目标是在 Sprint 计划活动期间创建的,然后添加到 Sprint 待办事项列表中。当开发人员在 Sprint 期间工作时,他们牢记 Sprint 目标。如果工作结果与他们预期的不同,他们会与产品负责人合作,在不影响 Sprint 目标的情况下协商 Sprint 中 Sprint Backlog 的范围。
Sprint Progress
Consequently, the Sprint Backlog is updated throughout the Sprint as more is learned. It should have enough detail that they can inspect their progress in the Daily Scrum.
冲刺目标
Sprint backlog 承诺:Sprint 目标
Sprint 目标是 Sprint 的唯一目标。尽管 Sprint 目标是开发人员的承诺,但它在实现它所需的确切工作方面提供了灵活性。Sprint 目标还创造了一致性和重点,鼓励 Scrum 团队一起工作而不是单独的计划。
Sprint 目标是在 Sprint 计划活动期间创建的,然后添加到 Sprint 待办事项列表中。当开发人员在 Sprint 期间工作时,他们牢记 Sprint 目标。如果工作结果与他们预期的不同,他们会与产品负责人合作,在不影响 Sprint 目标的情况下协商 Sprint 中 Sprint Backlog 的范围。
Sprint Goal
Sprint backlog Commitment: Sprint Goal
The Sprint Goal is the single objective for the Sprint. Although the Sprint Goal is a commitment by the Developers, it provides flexibility in terms of the exact work needed to achieve it. The Sprint Goal also creates coherence and focus, encouraging the Scrum Team to work together rather than on separate initiatives.
The Sprint Goal is created during the Sprint Planning event and then added to the Sprint Backlog. As the Developers work during the Sprint, they keep the Sprint Goal in mind. If the work turns out to be different than they expected, they collaborate with the Product Owner to negotiate the scope of the Sprint Backlog within the Sprint without affecting the Sprint Goal.
增量
增量是实现产品目标的具体垫脚石。每个增量都是所有先前增量的相加并经过彻底验证,确保所有增量协同工作。为了提供价值,增量必须是可用的。
可以在一个 Sprint 中创建多个增量。增量的总和在 Sprint Review 中呈现,从而支持经验主义。但是,增量可能会在 Sprint 结束之前交付给利益相关者。Sprint Review 永远不应被视为释放价值的大门。
工作不能被视为增量的一部分,除非它符合完成的定义。
Increment
An Increment is a concrete stepping stone toward the Product Goal. Each Increment is additive to all prior Increments and thoroughly verified, ensuring that all Increments work together. In order to provide value, the Increment must be usable.
Multiple Increments may be created within a Sprint. The sum of the Increments is presented at the Sprint Review thus supporting empiricism. However, an Increment may be delivered to stakeholders prior to the end of the Sprint. The Sprint Review should never be considered a gate to releasing value.
Work cannot be considered part of an Increment unless it meets the Definition of Done.
完成的定义
增量承诺:完成的定义
完成的定义是当增量满足产品要求的质量措施时对增量状态的正式描述。
产品待办列表项满足完成定义的那一刻,增量就诞生了。
完成的定义通过为每个人提供对作为增量的一部分完成的工作的共同理解来创建透明度。如果一个产品待办列表项不符合完成的定义,它就不能发布,甚至不能在 Sprint 评审中展示。相反,它返回到产品待办列表以供将来考虑。
如果增量的完成定义是组织标准的一部分,则所有 Scrum 团队必须至少遵循它。如果它不是组织标准,Scrum 团队必须创建适合产品的完成定义。
开发人员必须符合完成的定义。如果有多个 Scrum 团队一起开发一个产品,他们必须相互定义并遵守相同的完成定义。
Definition of Done
Increment Commitment: Definition of Done
The Definition of Done is a formal description of the state of the Increment when it meets the quality measures required for the product.
The moment a Product Backlog item meets the Definition of Done, an Increment is born.
The Definition of Done creates transparency by providing everyone a shared understanding of what work was completed as part of the Increment. If a Product Backlog item does not meet the Definition of Done, it cannot be released or even presented at the Sprint Review. Instead, it returns to the Product Backlog for future consideration.
If the Definition of Done for an increment is part of the standards of the organization, all Scrum Teams must follow it as a minimum. If it is not an organizational standard, the Scrum Team must create a Definition of Done appropriate for the product.
The Developers are required to conform to the Definition of Done. If there are multiple Scrum Teams working together on a product, they must mutually define and comply with the same Definition of Done.
尾注
Scrum 是免费的,并在本指南中提供。如本文所述,Scrum 框架是不可变的。虽然只实施部分 Scrum 是可能的,但结果不是 Scrum。Scrum 仅作为整体存在,并且作为其他技术、方法和实践的容器发挥作用。
End Note The Scrum
Scrum is free and offered in this Guide. The Scrum framework, as outlined herein, is immutable. While implementing only parts of Scrum is possible, the result is not Scrum. Scrum exists only in its entirety and functions well as a container for other techniques, methodologies, and practices.
- How to Prioritize Product Backlog Using MoSCoW Method
- How to Prioritize Product Backlog Using 100 Points Methods?
- What is Burndown Chart in Scrum?
- What is the Role-Feature-Reason Template?
- Write SMART Goals & INVEST for User Stories
- What is Agile Estimation?
- What is Story Point in Agile? How to Estimate a User Story?
- User Story Splitting - Vertical Slice vs Horizontal Slice
- Effective User Stories - 3C's and INVEST Guide
posted on 2021-11-16 10:07 Lynch_Warren 阅读(1676) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报


