微服务(二)hystrix
特性
1.延迟和失败容忍
防止级联错误,错误回退,优雅降级。快速失败和恢复
线程和信号量隔离
2.实时监控和配置更改
3.并发
并行执行,请求缓存,自动批处理失败请求
总运行流程
当你发出请求后,hystrix是这么运行的
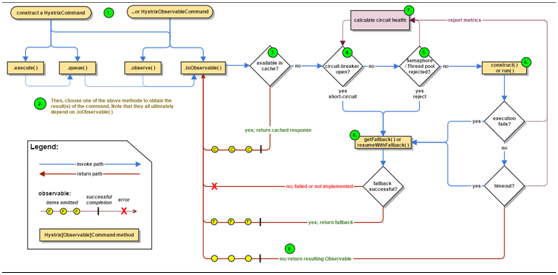
详细解释个步骤
1. Construct a HystrixCommand or HystrixObservableCommand Object
用于返回单一的响应
HystrixObservableCommand用于返回多个可自定义的响应
2. Execute the Command
对于HystrixCommand有4个执行方法
对于HystrixObservableCommand只有后两个
//阻塞方法,其实就是调用了queue().get() execute() — blocks, then returns the single response received from the dependency (or throws an exception in case of an error) //非阻塞方法,直接返回Future,可以先做自己的事情,做完再.get() queue() — returns a Future with which you can obtain the single response from the dependency //热观察,可以被立即执行,如果订阅了那么会重新通知,其实就是调用了toObservable()并内置ReplaySubject,详细可以参考RxJava observe() — subscribes to the Observable that represents the response(s) from the dependency and returns an Observable that replicates that source Observable //冷观察,返回一个Observable对象,当调用此接口,还需要自己加入订阅者,才能接受到信息,详细可以参考RxJava toObservable() — returns an Observable that, when you subscribe to it, will execute the Hystrix command and emit its responses 注:由于Hystrix底层采用了RxJava框架开发,所以没接触过的可能会一脸懵逼,需要再去对RxJava有所了解。
3. Is the Response Cached?
如果请求缓存可用,并且对于该请求的响应也在缓存中,那么命中的响应会以Observable直接返回
下图关于是请求缓存的整个生命周期

4. Is the Circuit Open?
执行command,hystrix会检查circuit是否打开,如果是打开的(失败率超过阈值)那么直接快速失败,否则进入下一流程
5. Is the Thread Pool/Queue/Semaphore Full?
线程池或者信号量是否已经满负荷,如果已经满负荷那么快速失败
6. HystrixObservableCommand.construct() or HystrixCommand.run()
两个断路器的入口,如果是继承HystrixObservableCommand,那么就调用construct()函数,如果是继承HystrixCommand,那么就调用run()函数。
7. Calculate Circuit Health
Hystrix记录了成功,失败,拒绝,超时四种报告
这些报告用于决定哪些用于断路,被断路的点在恢复周期内无法被后来的请求访问到。
8. Get the Fallback
快速失败会在以下几个场景触发
1.由construct() or run()抛出了一个异常
2.断路器已经打开的时候
3.没有空闲的线程池和队列或者信号量
4.一次命令执行超时
可以重写快速失败函数来自定义,
HystrixObservableCommand.resumeWithFallback()
HystrixCommand.getFallback()
9. 成功返回
整体的函数调用流程如下,其实这就是源码的调用流程
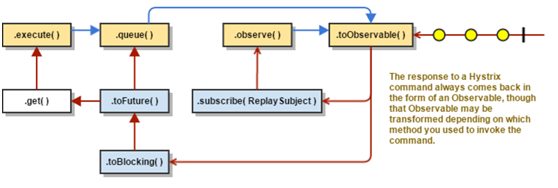
Coding
原生模式
基于hystrix的原生接口,也就是继承HystrixCommand或者HystirxObservableCommand。
public static class HelloHystrixCommand extends HystrixCommand<String>{ public HelloHystrixCommand() { super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ExampleGroup")); } /** * 实际操作的函数 * @return * @throws Exception */ public String run() throws Exception { Thread.sleep(1500); return "hello hystrix"; } /** * 快速失败后调用函数 * @return */ protected String getFallback(){ return "404 :)"; } }
注解模式
利用netflix的开源框架javanica,在需要使用断路器的方法上加上注解,参考代码如下
@Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; /** * 使用断路器的方法 * 其中fallback是快速失败的调用函数 * @return */ @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "fallback") public String post2AnotherService(){ HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); headers.set("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8"); HttpEntity<Object> formEntity = new HttpEntity<Object>(headers); //发送post请求 String res = restTemplate.postForObject("http://template/template/hello_world?",formEntity,String.class); return res; } /** * 当post2AnotherService函数出现问题,则调用此函数 * @return */ public String fallback(){ return "404 :)"; }
当调用post2AnotherService()的时候,由于函数返回超过规定时间默认是1s,就会执行fallback()函数,并返回。值得注意的是,如果对于fallback()也想使用降级机制,那么也可以加上@HystrixCommand
关于断路器
工作流程图
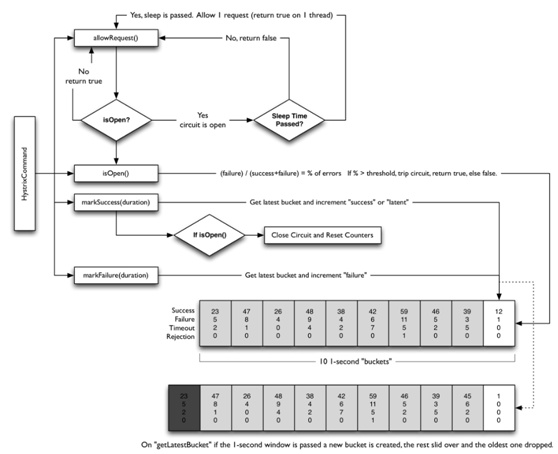
开关条件
关于断路器打开
·时间窗口内请求次数(限流)
如果在10s内,超过某个阈值的请求量,才会考虑断路(小于这个次数不会被断路)
配置是circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold
默认10s 20次
·失败率
默认失败率超过50%就会被断路
配置是circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage
关于断路器关闭
·重新尝试
在一定时间之后,重新尝试请求来决定是否继续打开或者选择关闭断路器
配置是circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds
默认5000ms
关于隔离
bulkhead pattern模式
Htstrix使用了bulkhead pattern模式,典型的例子就是线程隔离。
简单解释一下bulkhead pattern模式。一般情况我们都用一个线程池来管理所有线程,容易造成一个问题,粒度太粗,无法对线程进行分类管理,会导致局部问题影响全局。bulkhead pattern模式在于,采用多个线程池来管理线程,这样使得1个线程池资源出现问题时不会造成另一个线程池资源问题。尽量使问题最小化。
如图所示,采用了bulkhead pattern模式的效果
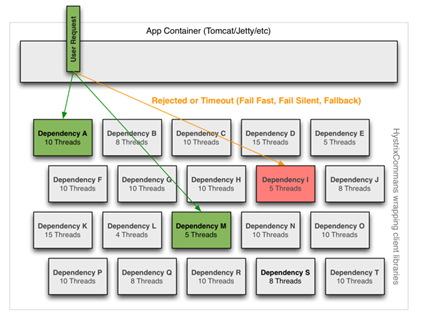
说完原理说实现,如何针对不同依赖采用不同的线程池管理呢
Hystrix给了我们三种key来用于隔离。
·CommandKey,针对相同的接口一般CommandKey值相同,目的是把HystrixCommand,HystrixCircuitBreaker,HytrixCommandMerics以及其他相关对象关联在一起,形成一个原子组。采用原生接口的话,默认值为类名;采用注解形式的话,默认值为方法名。
·CommandGroupKey,对CommandKey分组,用于真正的隔离。相同CommandGroupKey会使用同一个线程池或者信号量。一般情况相同业务功能会使用相同的CommandGroupKey。
·ThreadPoolKey,如果说CommandGroupKey只是逻辑隔离,那么ThreadPoolKey就是物理隔离,当没有设置ThreadPoolKey的时候,线程池或者信号量的划分按照CommandGroupKey,当设置了ThreadPoolKey,那么线程池和信号量的划分就按照ThreadPoolKey来处理,相同ThreadPoolKey采用同一个线程池或者信号量。
Coding
原生模式
可以通过HystrixCommand.Setter来自定义配置
HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey(""))
HystrixCommandKey.Factory.asKey("")
HystrixThreadPoolKey.Factory.asKey("")
注解模式
可以直接在方法名上添加
@HystrixCommand(groupKey = "", commandKey = "", threadPoolKey = "")
关于请求缓存
工作流程图
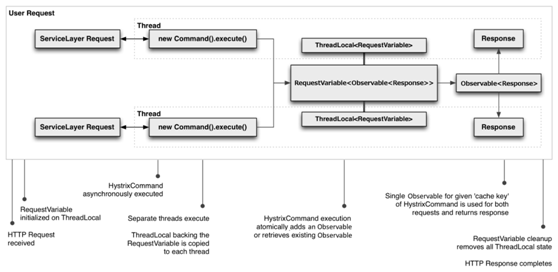
优势
·复用性
这里的复用性指的是代码复用性
·一致性
也就是常说的幂等性,不管请求几次,得到的结果应该都是一样的
·减少重复工作
由于请求缓存是在HystrixCommand的construct()或run()运行之前运行,所有可以有效减少线程的使用
适用场景
请求缓存的优势显而易见,但是也不是银弹。
在读少写多的场景就显得不太合适,对于读的请求,需要add缓存。对于增删改的请求,需要把缓存remove。在增加系统资源开销的同时,又很鸡肋。
所以一般适合读多写少的场景。似乎所有缓存机制都有这个局限性吧
Coding
原生模式
继承HystrixCommand后,重写getCacheKey()方法,该方法默认返回的是null,也就是不使用请求缓存功能。相同key的请求会使用相同的缓存。
注解模式
在方法名上增加,并添加与cacheKeyMethod字符串相同的方法。两者共用入参。
@CacheResult(cacheKeyMethod = "getCacheKey") public String post2AnotherService(String seed){ } public String getCacheKey(String seed){ return seed; }
初始化HystrixRequestContext
还有关键的一步,在调用HystrixCommand之前初始化HystrixRequestContext,其实就是创建一个ThreadLocal的副本,共享请求缓存就是通过ThreadLocal来实现的。
HystrixRequestContext context=HystrixRequestContext.initializeContext();
操作完成后context.shutdown();
一般情况可以在过滤器中控制是初始化和关闭整个生命周期
//启动HystrixRequestContext HystrixRequestContext context = HystrixRequestContext.initializeContext(); try { chain.doFilter(req, res); } finally { //关闭HystrixRequestContext context.shutdown(); }
关于请求合并(Requst Collapsing)
工作流程图
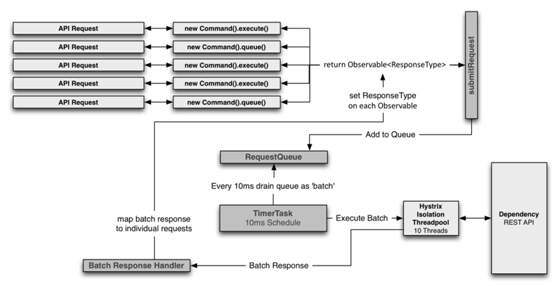
上半部分是模拟请求,下半部分是该请求的依赖设置,时间窗口默认是10ms,在这个时间窗口内,所有对于该接口的请求都会被加入队列,然后进行批处理。这样的好处在于,如果短时间内对于某个接口有大量请求,那么可以只处理一次就完成所有响应。
优势
全局线程合并
在tomcat容器中,所有请求共用一个进程,也就是一个JVM容器,在并发场景下会派生出许多线程,collapsing可以合并整个JVM中的请求线程,这样可以解决不同使用者同时请求的大量并发问题。
局部线程合并
可以合并单个tomcat请求线程,比如在10ms内有10个请求被同一线程处理(这不是像往常一样请求->处理,而是请求->加入请求队列,所有可以快速收集请求),那这些请求可以被合并。
对象建模和代码复杂度
在实际场景下,调用接口取数据的复杂度往往高于数据的复杂度,通俗来说就是取数据可以千变万化的取,而数据就那么几个接口。
collapsing可以帮助你更好的实现你的业务,比如多次请求合并结果后再广播出去。
适用场景
·并发量大接口
当并发量小,一个时间窗口内只有几个或没有请求,那么就白白浪费了请求合并的资源。
·请求耗时接口
时间窗口是固定的,假如一个请求实际耗时10ms,加上固定的时间窗口,最大延迟达到20ms,延迟被提高了100%。若一个请求实际耗时有1s,那么时间窗口的延迟就可以被忽略不计。
Coding
原生模式
/** * 批量返回值类型 * 返回值类型 * 请求参数类型 */ public class CommandCollapserGetValueForKey extends HystrixCollapser<List<String>, String, Integer> { private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CommandCollapserGetValueForKey.class); private final Integer key; public CommandCollapserGetValueForKey(Integer key) { this.key = key; } /** *获取请求参数 */ public Integer getRequestArgument() { return key; } /** *合并请求产生批量命令的具体实现 */ protected HystrixCommand<List<String>> createCommand(final Collection<CollapsedRequest<String, Integer>> requests) { return new BatchCommand(requests); } /** *批量命令结果返回后的处理,需要实现将批量结果拆分并传递给合并前的各原子请求命令的逻辑中 */ protected void mapResponseToRequests(List<String> batchResponse, Collection<CollapsedRequest<String, Integer>> requests) { int count = 0; //请求响应一一对应 for (CollapsedRequest<String, Integer> request : requests) { request.setResponse(batchResponse.get(count++)); } } private static final class BatchCommand extends HystrixCommand<List<String>> { private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CommandCollapserGetValueForKey.BatchCommand.class); private final Collection<CollapsedRequest<String, Integer>> requests; private BatchCommand(Collection<CollapsedRequest<String, Integer>> requests) { super(Setter.withGroupKey(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ExampleGroup")) .andCommandKey(HystrixCommandKey.Factory.asKey("GetValueForKey"))); this.requests = requests; } @Override protected List<String> run() { ArrayList<String> response = new ArrayList<String>(); // 处理每个请求,返回结果 for (CollapsedRequest<String, Integer> request : requests) { logger.info("request.getArgument()={}",request.getArgument()); // artificial response for each argument received in the batch response.add("ValueForKey: " + request.getArgument()); } return response; } } }
调用的时候只需要new CommandCollapserGetValueForKey(1).queue()
在同一个时间窗口内,批处理的函数调用顺序为
getRequestArgument()->createCommand()->mapResponseToRequests()
关于配置
所有的配置在HystrixCommandProperties类中
每种配置都有4种优先级,以下为优先级从低到高的解释
1.基于代码的全局缺省值
2.基于properties配置表的全局配置
3.基于代码对配置更改
4.基于代码对配置动态更改
注:同一个配置,采用不同方法更改,那么配置的key会有不同
|
默认配置key |
代码更改key |
默认值 |
解释 |
|
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.strategy |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.execution.isolation.strategy |
THREAD |
可选择的参数有THREAD, SEMAPHORE,表示隔离类型 |
|
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds |
1000 |
降级的超时时间,单位ms |
|
hystrix.command.default.execution.timeout.enabled |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.execution.timeout.enabled |
true |
针对HystrixCommand.run() 是否使用超时降级策略 |
|
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.thread.interruptOnTimeout |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.execution.isolation.thread.interruptOnTimeout |
true |
HystrixCommand.run() 超时后是否应该中断 |
|
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.thread.interruptOnCancel |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.execution.isolation.thread.interruptOnCancel |
false |
HystrixCommand.run() 当发生cancel事件后是否应该取中断 |
|
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.semaphore.maxConcurrentRequests |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.execution.isolation.semaphore.maxConcurrentRequests |
10 |
当使用信号量隔离的时候,此配置有效。 官方给出5000请求只需要2个 |
|
hystrix.command.default.fallback.isolation.semaphore.maxConcurrentRequests |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.fallback.isolation.semaphore.maxConcurrentRequests |
10 |
HystrixCommand.getFallback() 最大并发数,超过此并发则拒绝请求 |
|
hystrix.command.default.fallback.enabled |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.fallback.enabled |
true |
是否打开快速失败 |
|
hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.enabled |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.circuitBreaker.enabled |
true |
是否打开熔断器 |
|
hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold |
20 |
时间窗口内最小请求数,当小于这个请求数,即使全部失败也不会熔断 |
|
hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds |
5000 |
熔断后,请求retry的时间间隔 |
|
hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage |
50 |
失败率阈值,超过这个失败率就会熔断 |
|
hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.forceOpen |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.circuitBreaker.forceOpen |
false |
是否强制开启熔断,这样会导致拒绝所有请求 |
|
hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.forceClosed |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.circuitBreaker.forceClosed |
false |
是否强制关闭熔断,这样任何原因都无法触发熔断 注:优先级小于强制开启 |
|
hystrix.command.default.requestCache.enabled |
hystrix.command.HystrixCommandKey.requestCache.enabled |
true |
是否打开请求缓存功能 |
|
|
|
true |
|
|
hystrix.collapser.default.maxRequestsInBatch |
hystrix.collapser.HystrixCollapserKey.maxRequestsInBatch |
Integer.MAX_VALUE |
|
|
hystrix.collapser.default.timerDelayInMilliseconds |
hystrix.collapser.HystrixCollapserKey.timerDelayInMilliseconds |
10 |
|
|
hystrix.collapser.default.requestCache.enabled |
hystrix.collapser.HystrixCollapserKey.requestCache.enabled |
true |
|
|
hystrix.threadpool.default.coreSize |
hystrix.threadpool.HystrixThreadPoolKey.coreSize |
10 |
requests per second at peak when healthy × 99th percentile latency in seconds + some breathing room 例如: 30rps * 0.2s + breathing
room = 10 |
|
hystrix.threadpool.default.maximumSize |
hystrix.threadpool.HystrixThreadPoolKey.maximumSize |
10 |
|
|
hystrix.threadpool.default.maxQueueSize |
hystrix.threadpool.HystrixThreadPoolKey.maxQueueSize |
-1 |
|
|
hystrix.threadpool.default.queueSizeRejectionThreshold |
hystrix.threadpool.HystrixThreadPoolKey.queueSizeRejectionThreshold |
5 |
|
|
hystrix.threadpool.default.keepAliveTimeMinutes |
hystrix.threadpool.HystrixThreadPoolKey.keepAliveTimeMinutes |
1 |
|
|
hystrix.threadpool.default.allowMaximumSizeToDivergeFromCoreSize |
hystrix.threadpool.HystrixThreadPoolKey.allowMaximumSizeToDivergeFromCoreSize |
false |
|
|
hystrix.threadpool.default.metrics.rollingStats.timeInMilliseconds |
hystrix.threadpool.HystrixThreadPoolKey.metrics.rollingStats.timeInMilliseconds |
10000 |
|
|
hystrix.threadpool.default.metrics.rollingStats.numBuckets |
hystrix.threadpool.HystrixThreadPoolProperties.metrics.rollingStats.numBuckets |
10 |
metrics.rollingStats.timeInMilliseconds %
metrics.rollingStats.numBuckets == 0 |
//官方配置文档
https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/wiki/Configuration#circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds



