Django项目:CMDB(服务器硬件资产自动采集系统)--06--06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令01
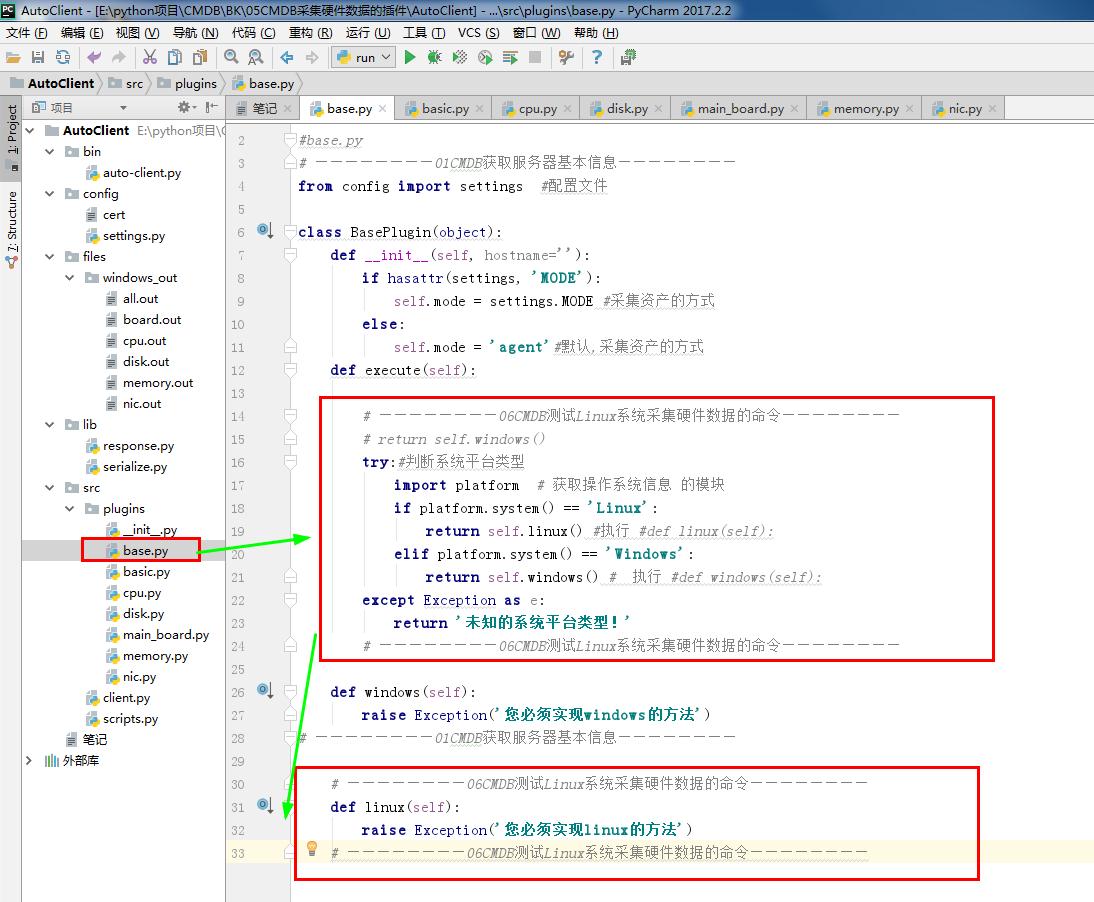

1 #base.py 2 # ————————01CMDB获取服务器基本信息———————— 3 from config import settings #配置文件 4 5 class BasePlugin(object): 6 def __init__(self, hostname=''): 7 if hasattr(settings, 'MODE'): 8 self.mode = settings.MODE #采集资产的方式 9 else: 10 self.mode = 'agent'#默认,采集资产的方式 11 def execute(self): 12 13 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 14 # return self.windows() 15 try:#判断系统平台类型 16 import platform # 获取操作系统信息 的模块 17 if platform.system() == 'Linux': 18 return self.linux() #执行 #def linux(self): 19 elif platform.system() == 'Windows': 20 return self.windows() # 执行 #def windows(self): 21 except Exception as e: 22 return '未知的系统平台类型!' 23 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 24 25 def windows(self): 26 raise Exception('您必须实现windows的方法') 27 # ————————01CMDB获取服务器基本信息———————— 28 29 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 30 def linux(self): 31 raise Exception('您必须实现linux的方法') 32 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令————————

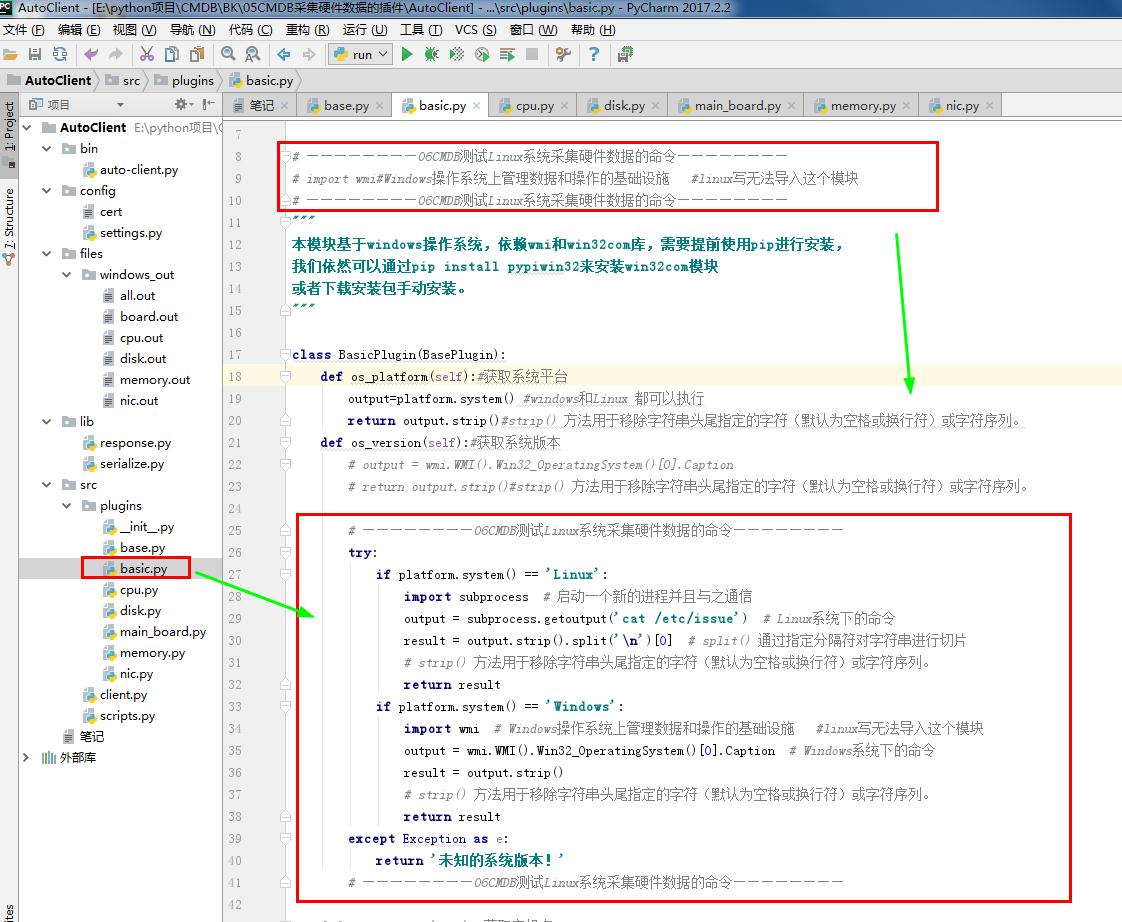


1 # basic.py 2 # ————————01CMDB获取服务器基本信息———————— 3 from .base import BasePlugin #采集资产的方式 4 from lib.response import BaseResponse #提交数据的类型 5 import platform #platform模块给我们提供了很多方法去获取操作系统的信息 6 7 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 8 # import wmi#Windows操作系统上管理数据和操作的基础设施 #linux写无法导入这个模块 9 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 10 """ 11 本模块基于windows操作系统,依赖wmi和win32com库,需要提前使用pip进行安装, 12 我们依然可以通过pip install pypiwin32来安装win32com模块 13 或者下载安装包手动安装。 14 """ 15 16 class BasicPlugin(BasePlugin): 17 def os_platform(self):#获取系统平台 18 output=platform.system() #windows和Linux 都可以执行 19 return output.strip()#strip() 方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列。 20 def os_version(self):#获取系统版本 21 # output = wmi.WMI().Win32_OperatingSystem()[0].Caption 22 # return output.strip()#strip() 方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列。 23 24 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 25 try: 26 if platform.system() == 'Linux': 27 import subprocess # 启动一个新的进程并且与之通信 28 output = subprocess.getoutput('cat /etc/issue') # Linux系统下的命令 29 result = output.strip().split('\n')[0] # split() 通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 30 # strip() 方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列。 31 return result 32 if platform.system() == 'Windows': 33 import wmi # Windows操作系统上管理数据和操作的基础设施 #linux写无法导入这个模块 34 output = wmi.WMI().Win32_OperatingSystem()[0].Caption # Windows系统下的命令 35 result = output.strip() 36 # strip() 方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列。 37 return result 38 except Exception as e: 39 return '未知的系统版本!' 40 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 41 42 def os_hostname(self):#获取主机名 43 # output = wmi.WMI().Win32_OperatingSystem()[0].CSName 44 # return output.strip()#strip() 方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列。 45 46 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 47 try: 48 if platform.system() == 'Linux': 49 import subprocess # 启动一个新的进程并且与之通信 50 output = subprocess.getoutput('hostname') # Linux系统下的命令 51 return output.strip() # strip() 方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列。 52 elif platform.system() == 'Windows': 53 import wmi # Windows操作系统上管理数据和操作的基础设施 #linux写无法导入这个模块 54 output = wmi.WMI().Win32_OperatingSystem()[0].CSName # Windows系统下的命令 55 return output.strip() # strip() 方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列。 56 except Exception as e: 57 return '未知的主机名!' 58 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 59 60 def windows(self): 61 response = BaseResponse()#提交数据的类型 62 try: 63 ret = { 64 'os_platform': self.os_platform(),#系统平台 65 'os_version': self.os_version(),#系统版本 66 'hostname': self.os_hostname(),#主机名 67 } 68 response.data = ret #字典形式 69 print('windows服务器基本信息:',response.data) 70 except Exception as e: 71 response.status = False#获取信息时出现错误 72 return response 73 """ 74 class BaseResponse(object): #提交数据的类型 75 def __init__(self): 76 self.status = True #状态 77 self.message = None #消息 78 self.data = None #数据内容 79 self.error = None #错误信息 80 81 """ 82 # ————————01CMDB获取服务器基本信息———————— 83 84 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 85 def linux(self): 86 response = self.windows() #因为执行同样的方法,所以,就不重复写。 87 print('linux服务器基本信息:', response.data) 88 return response 89 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令————————

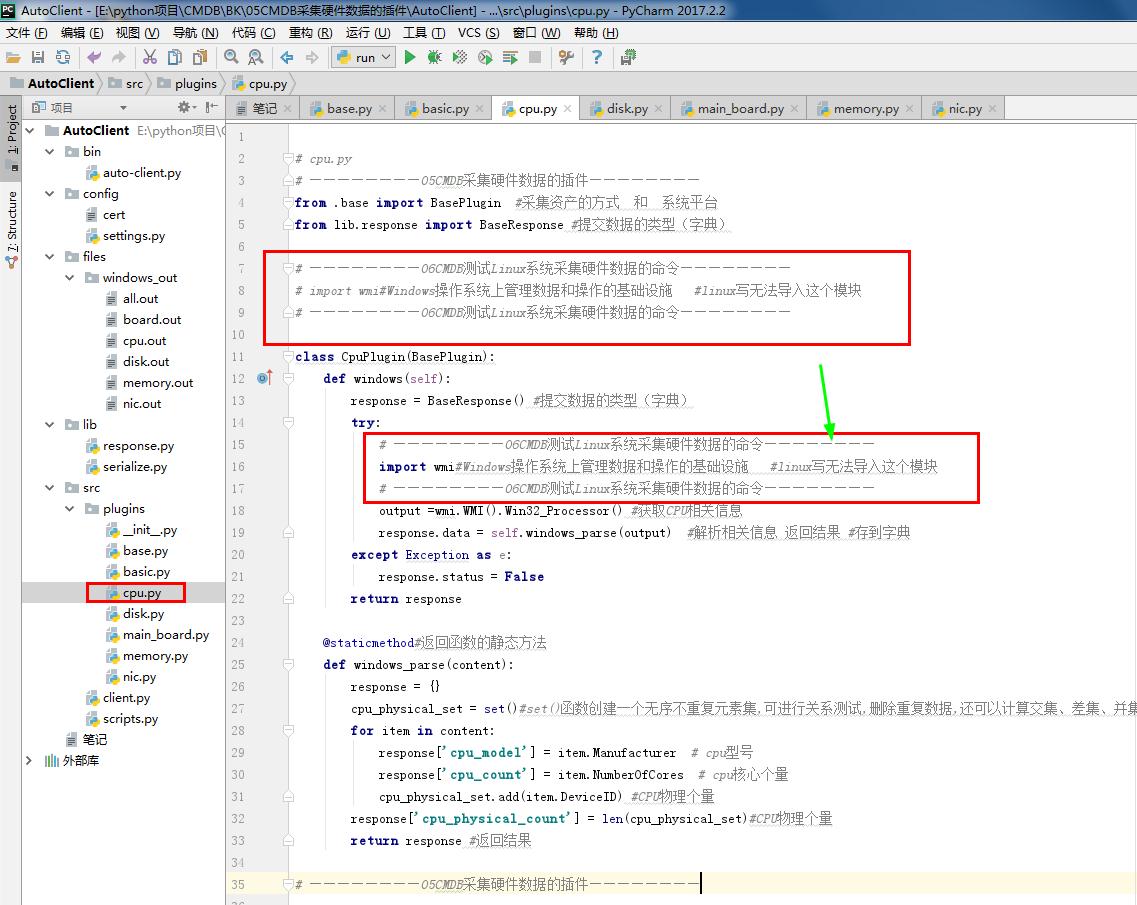

1 # cpu.py 2 # ————————05CMDB采集硬件数据的插件———————— 3 from .base import BasePlugin #采集资产的方式 和 系统平台 4 from lib.response import BaseResponse #提交数据的类型(字典) 5 6 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 7 # import wmi#Windows操作系统上管理数据和操作的基础设施 #linux写无法导入这个模块 8 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 9 10 class CpuPlugin(BasePlugin): 11 def windows(self): 12 response = BaseResponse() #提交数据的类型(字典) 13 try: 14 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 15 import wmi#Windows操作系统上管理数据和操作的基础设施 #linux写无法导入这个模块 16 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 17 output =wmi.WMI().Win32_Processor() #获取CPU相关信息 18 response.data = self.windows_parse(output) #解析相关信息 返回结果 #存到字典 19 except Exception as e: 20 response.status = False 21 return response 22 23 @staticmethod#返回函数的静态方法 24 def windows_parse(content): 25 response = {} 26 cpu_physical_set = set()#set()函数创建一个无序不重复元素集,可进行关系测试,删除重复数据,还可以计算交集、差集、并集等。 27 for item in content: 28 response['cpu_model'] = item.Manufacturer # cpu型号 29 response['cpu_count'] = item.NumberOfCores # cpu核心个量 30 cpu_physical_set.add(item.DeviceID) #CPU物理个量 31 response['cpu_physical_count'] = len(cpu_physical_set)#CPU物理个量 32 return response #返回结果 33 34 # ————————05CMDB采集硬件数据的插件———————— 35 36 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 37 def linux(self): 38 response = BaseResponse() # 提交数据的类型(字典) 39 try: 40 import subprocess # 启动一个新的进程并且与之通信 41 shell_command = "cat /proc/cpuinfo" # 定义命令 lscpu 42 output = subprocess.getoutput(shell_command) # linux系统上执行的命令 43 response.data = self.linux_parse(output) # 解析shell命令返回结果 44 except Exception as e: 45 response.status = False 46 return response 47 48 @staticmethod # 返回函数的静态方法 49 def linux_parse(content): # 解析shell命令返回结果 50 response = {'cpu_count': 0, 'cpu_physical_count': 0, 'cpu_model': ''} 51 cpu_physical_set = set() # set()函数创建一个无序不重复元素集,可进行关系测试,删除重复数据,还可以计算交集、差集、并集等。 52 content = content.strip() # strip()方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列 53 for item in content.split('\n\n'): # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 54 for row_line in item.split('\n'): 55 key, value = row_line.split(':') 56 key = key.strip() 57 if key == 'processor': 58 response['cpu_count'] += 1 # cpu核心个量 59 elif key == 'physical id': 60 cpu_physical_set.add(value) # CPU物理个量 61 elif key == 'model name': 62 if not response['cpu_model']: 63 response['cpu_model'] = value # cpu型号 64 response['cpu_physical_count'] = len(cpu_physical_set) # CPU物理个量 65 return response 66 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令————————
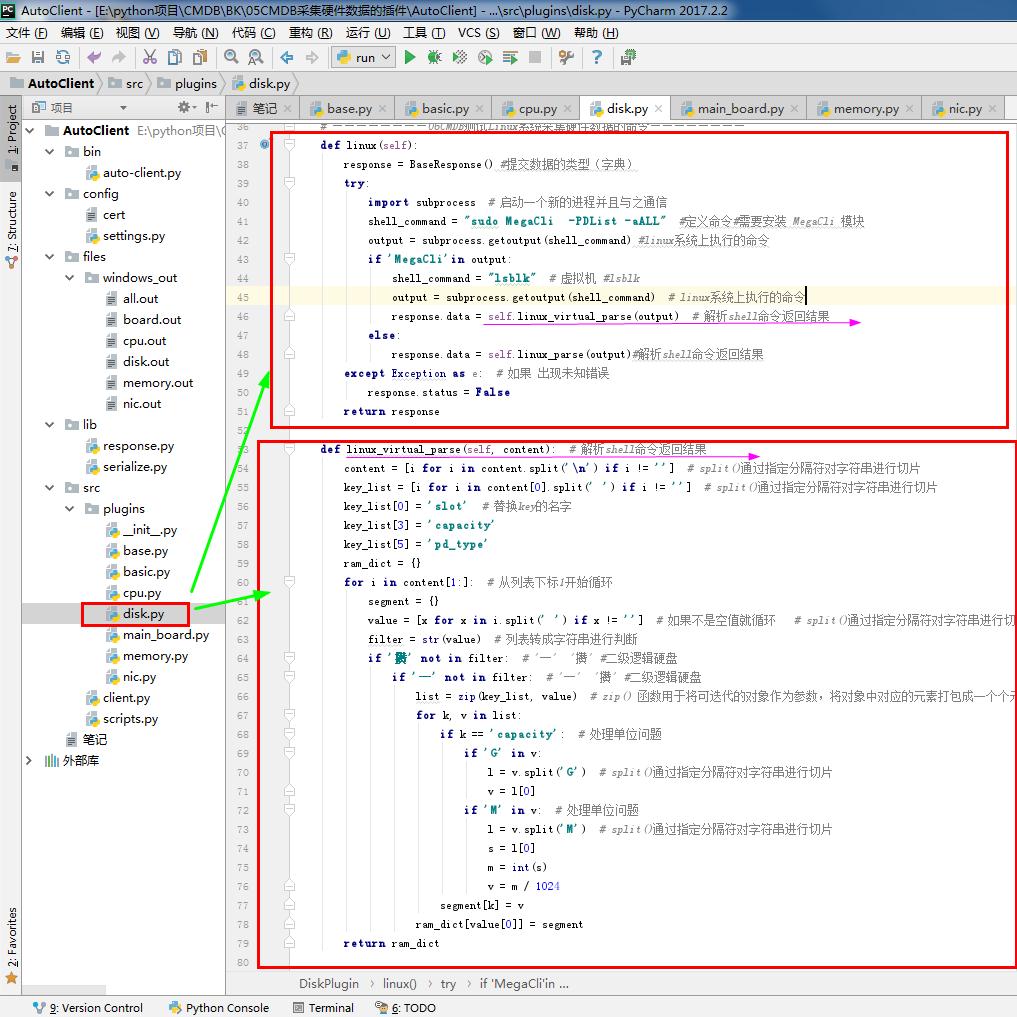
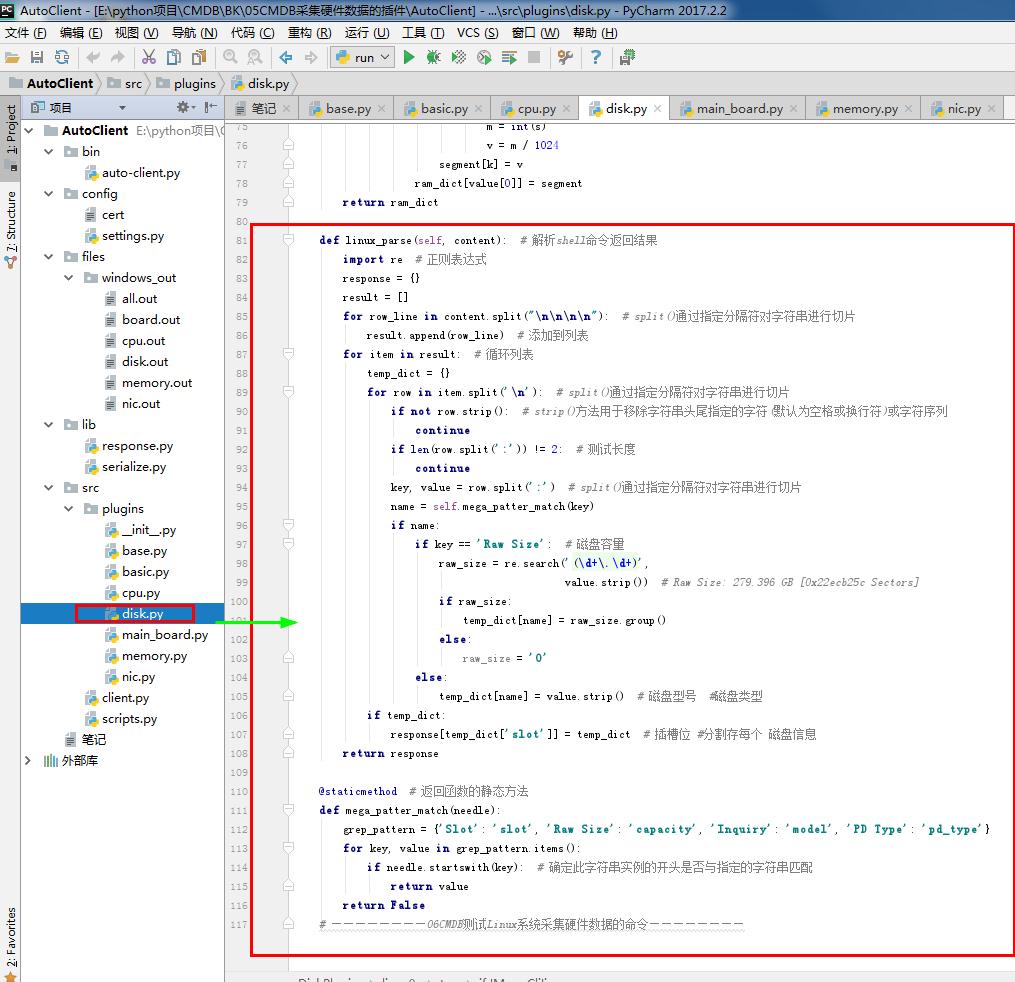
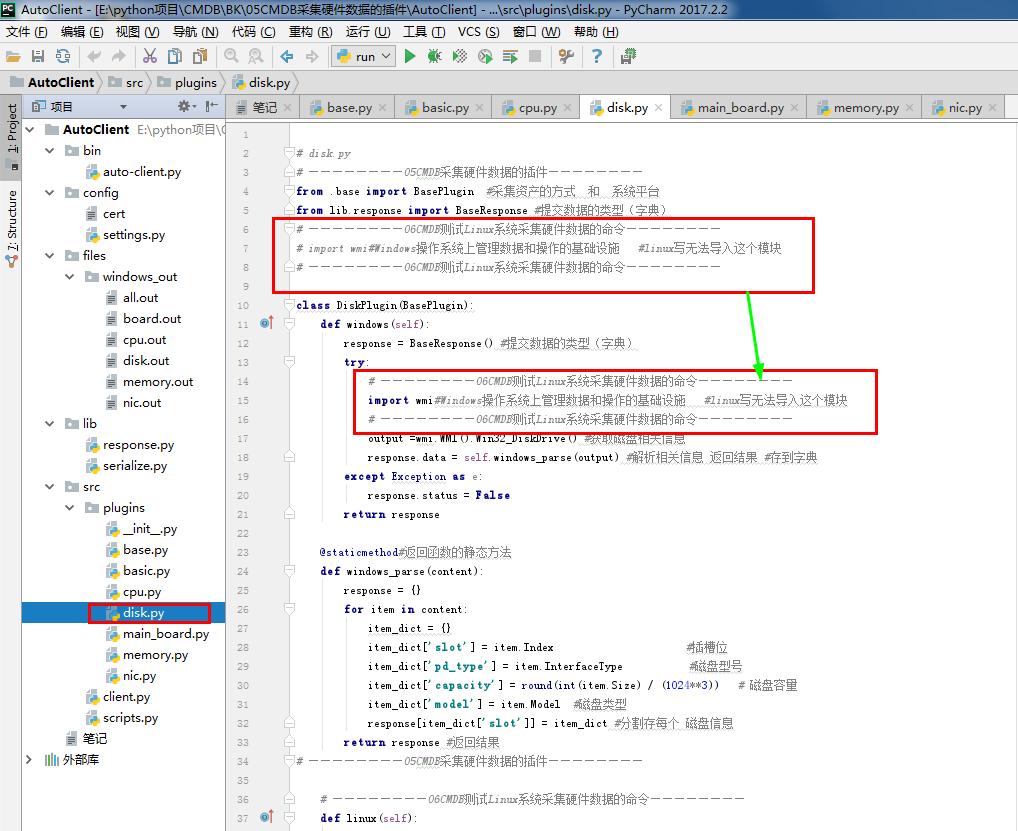

1 # disk.py 2 # ————————05CMDB采集硬件数据的插件———————— 3 from .base import BasePlugin #采集资产的方式 和 系统平台 4 from lib.response import BaseResponse #提交数据的类型(字典) 5 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 6 # import wmi#Windows操作系统上管理数据和操作的基础设施 #linux写无法导入这个模块 7 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 8 9 class DiskPlugin(BasePlugin): 10 def windows(self): 11 response = BaseResponse() #提交数据的类型(字典) 12 try: 13 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 14 import wmi#Windows操作系统上管理数据和操作的基础设施 #linux写无法导入这个模块 15 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 16 output =wmi.WMI().Win32_DiskDrive() #获取磁盘相关信息 17 response.data = self.windows_parse(output) #解析相关信息 返回结果 #存到字典 18 except Exception as e: 19 response.status = False 20 return response 21 22 @staticmethod#返回函数的静态方法 23 def windows_parse(content): 24 response = {} 25 for item in content: 26 item_dict = {} 27 item_dict['slot'] = item.Index #插槽位 28 item_dict['pd_type'] = item.InterfaceType #磁盘型号 29 item_dict['capacity'] = round(int(item.Size) / (1024**3)) # 磁盘容量 30 item_dict['model'] = item.Model #磁盘类型 31 response[item_dict['slot']] = item_dict #分割存每个 磁盘信息 32 return response #返回结果 33 # ————————05CMDB采集硬件数据的插件———————— 34 35 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 36 def linux(self): 37 response = BaseResponse() #提交数据的类型(字典) 38 try: 39 import subprocess # 启动一个新的进程并且与之通信 40 shell_command = "sudo MegaCli -PDList -aALL" #定义命令#需要安装 MegaCli 模块 41 output = subprocess.getoutput(shell_command) #linux系统上执行的命令 42 if 'MegaCli'in output: 43 shell_command = "lsblk" # 虚拟机 #lsblk 44 output = subprocess.getoutput(shell_command) # linux系统上执行的命令 45 response.data = self.linux_virtual_parse(output) # 解析shell命令返回结果 46 else: 47 response.data = self.linux_parse(output)#解析shell命令返回结果 48 except Exception as e: # 如果 出现未知错误 49 response.status = False 50 return response 51 52 def linux_virtual_parse(self, content): # 解析shell命令返回结果 53 content = [i for i in content.split('\n') if i != ''] # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 54 key_list = [i for i in content[0].split(' ') if i != ''] # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 55 key_list[0] = 'slot' # 替换key的名字 56 key_list[3] = 'capacity' 57 key_list[5] = 'pd_type' 58 ram_dict = {} 59 for i in content[1:]: # 从列表下标1开始循环 60 segment = {} 61 value = [x for x in i.split(' ') if x != ''] # 如果不是空值就循环 # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 62 filter = str(value) # 列表转成字符串进行判断 63 if '攢' not in filter: # '─' '攢' #二级逻辑硬盘 64 if '─' not in filter: # '─' '攢' #二级逻辑硬盘 65 list = zip(key_list, value) # zip() 函数用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表。 66 for k, v in list: 67 if k == 'capacity': # 处理单位问题 68 if 'G' in v: 69 l = v.split('G') # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 70 v = l[0] 71 if 'M' in v: # 处理单位问题 72 l = v.split('M') # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 73 s = l[0] 74 m = int(s) 75 v = m / 1024 76 segment[k] = v 77 ram_dict[value[0]] = segment 78 return ram_dict 79 80 def linux_parse(self, content): # 解析shell命令返回结果 81 import re # 正则表达式 82 response = {} 83 result = [] 84 for row_line in content.split("\n\n\n\n"): # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 85 result.append(row_line) # 添加到列表 86 for item in result: # 循环列表 87 temp_dict = {} 88 for row in item.split('\n'): # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 89 if not row.strip(): # strip()方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列 90 continue 91 if len(row.split(':')) != 2: # 测试长度 92 continue 93 key, value = row.split(':') # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 94 name = self.mega_patter_match(key) 95 if name: 96 if key == 'Raw Size': # 磁盘容量 97 raw_size = re.search('(\d+\.\d+)', 98 value.strip()) # Raw Size: 279.396 GB [0x22ecb25c Sectors] 99 if raw_size: 100 temp_dict[name] = raw_size.group() 101 else: 102 raw_size = '0' 103 else: 104 temp_dict[name] = value.strip() # 磁盘型号 #磁盘类型 105 if temp_dict: 106 response[temp_dict['slot']] = temp_dict # 插槽位 #分割存每个 磁盘信息 107 return response 108 109 @staticmethod # 返回函数的静态方法 110 def mega_patter_match(needle): 111 grep_pattern = {'Slot': 'slot', 'Raw Size': 'capacity', 'Inquiry': 'model', 'PD Type': 'pd_type'} 112 for key, value in grep_pattern.items(): 113 if needle.startswith(key): # 确定此字符串实例的开头是否与指定的字符串匹配 114 return value 115 return False 116 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令————————

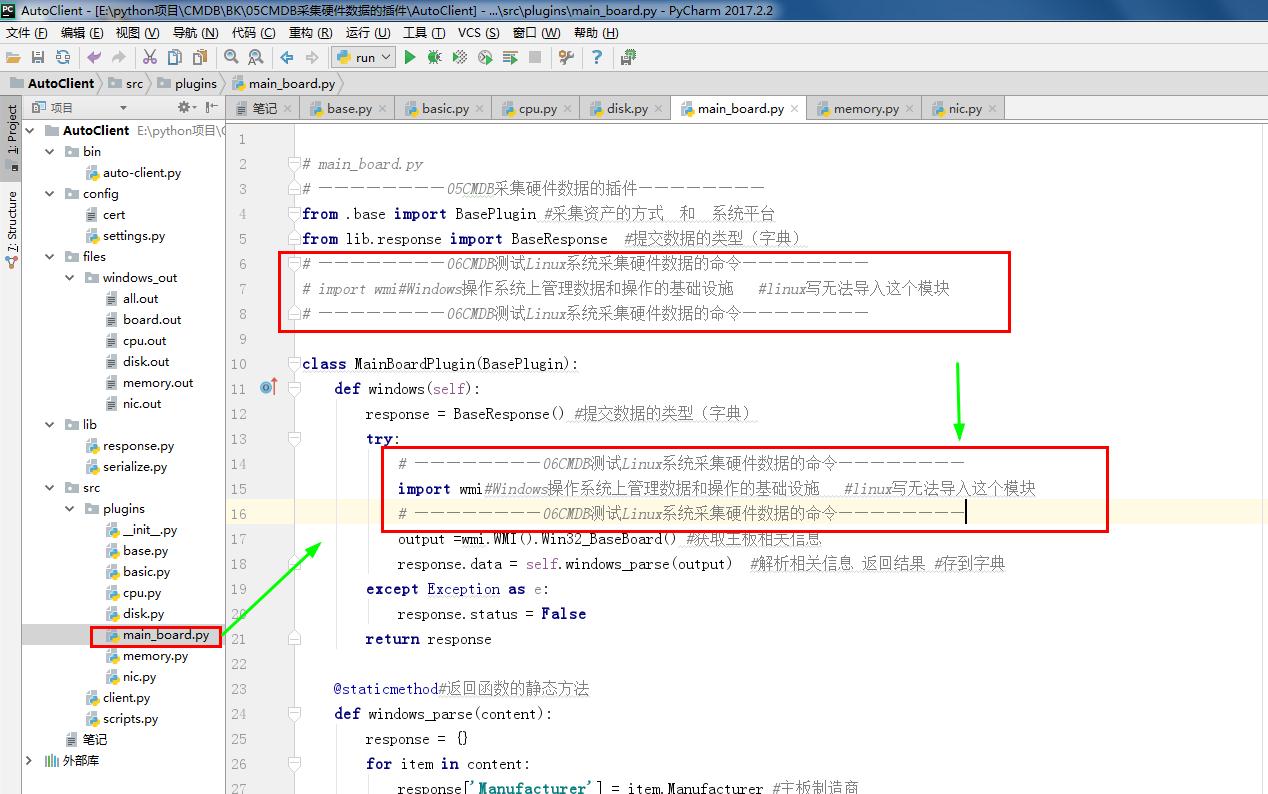

1 # main_board.py 2 # ————————05CMDB采集硬件数据的插件———————— 3 from .base import BasePlugin #采集资产的方式 和 系统平台 4 from lib.response import BaseResponse #提交数据的类型(字典) 5 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 6 # import wmi#Windows操作系统上管理数据和操作的基础设施 #linux写无法导入这个模块 7 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 8 9 class MainBoardPlugin(BasePlugin): 10 def windows(self): 11 response = BaseResponse() #提交数据的类型(字典) 12 try: 13 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 14 import wmi#Windows操作系统上管理数据和操作的基础设施 #linux写无法导入这个模块 15 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 16 output =wmi.WMI().Win32_BaseBoard() #获取主板相关信息 17 response.data = self.windows_parse(output) #解析相关信息 返回结果 #存到字典 18 except Exception as e: 19 response.status = False 20 return response 21 22 @staticmethod#返回函数的静态方法 23 def windows_parse(content): 24 response = {} 25 for item in content: 26 response['Manufacturer'] = item.Manufacturer #主板制造商 27 response['model'] = item.Name #主板型号 28 response['sn'] = item.SerialNumber #主板SN号 29 return response #返回结果 30 # ————————05CMDB采集硬件数据的插件———————— 31 32 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 33 def linux(self): 34 response = BaseResponse() #提交数据的类型(字典) 35 try: 36 import subprocess # 启动一个新的进程并且与之通信 37 shell_command = "sudo dmidecode -t1" #定义命令 38 output =subprocess.getoutput(shell_command) #linux系统上执行的命令 39 response.data = self.linux_parse(output) #解析shell命令返回结果 40 except Exception as e: 41 response.status = False 42 return response 43 44 def linux_parse(self, content):#解析shell命令返回结果 45 result = {} 46 key_map = {'Manufacturer': 'manufacturer', 'Product Name': 'model','Serial Number': 'sn',} 47 for item in content.split('\n'): #split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 48 row_data = item.strip().split(':') #strip()方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列 49 if len(row_data) == 2: 50 if row_data[0] in key_map:#如果在需要的字典里 51 result[key_map[row_data[0]]] = row_data[1].strip() if row_data[1] else row_data[1] 52 return result 53 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令————————
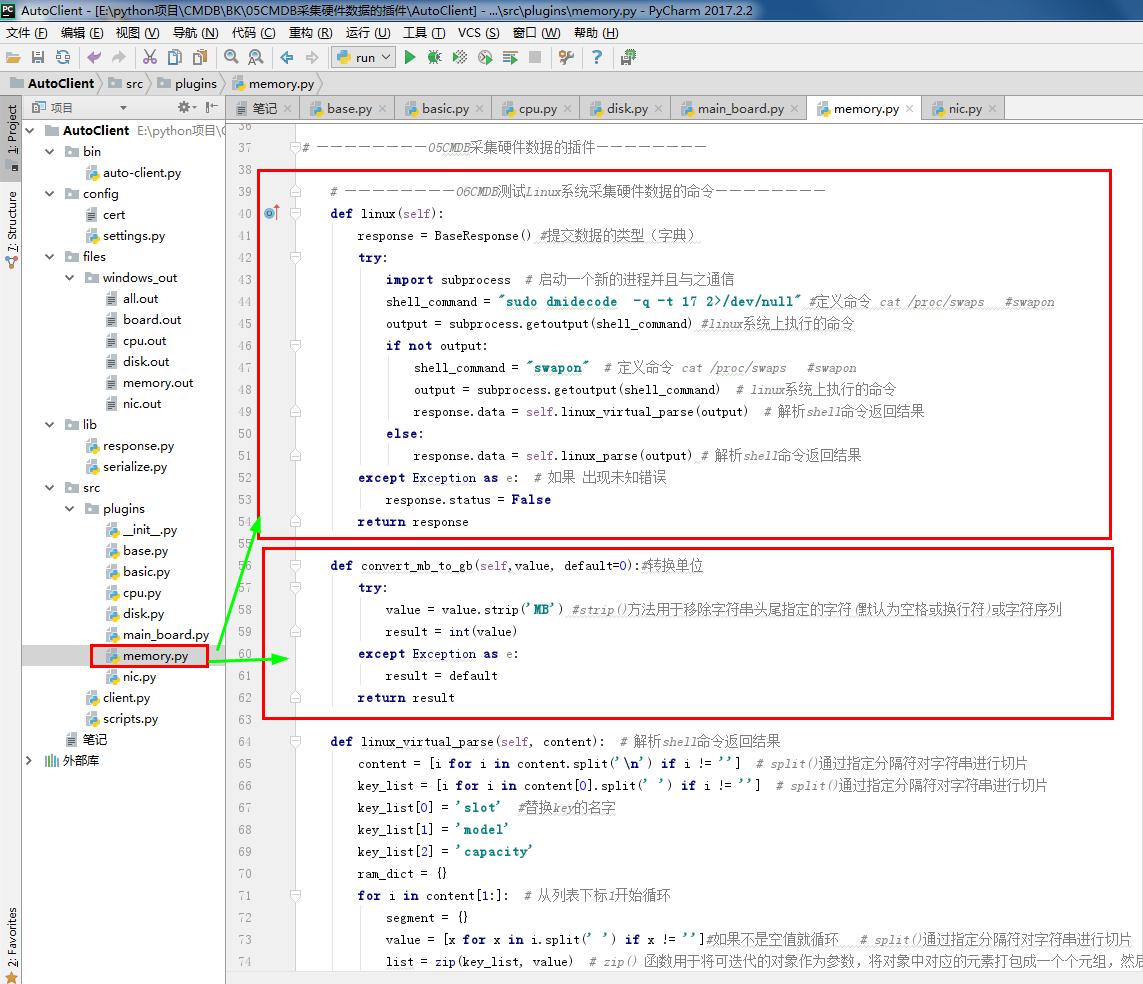
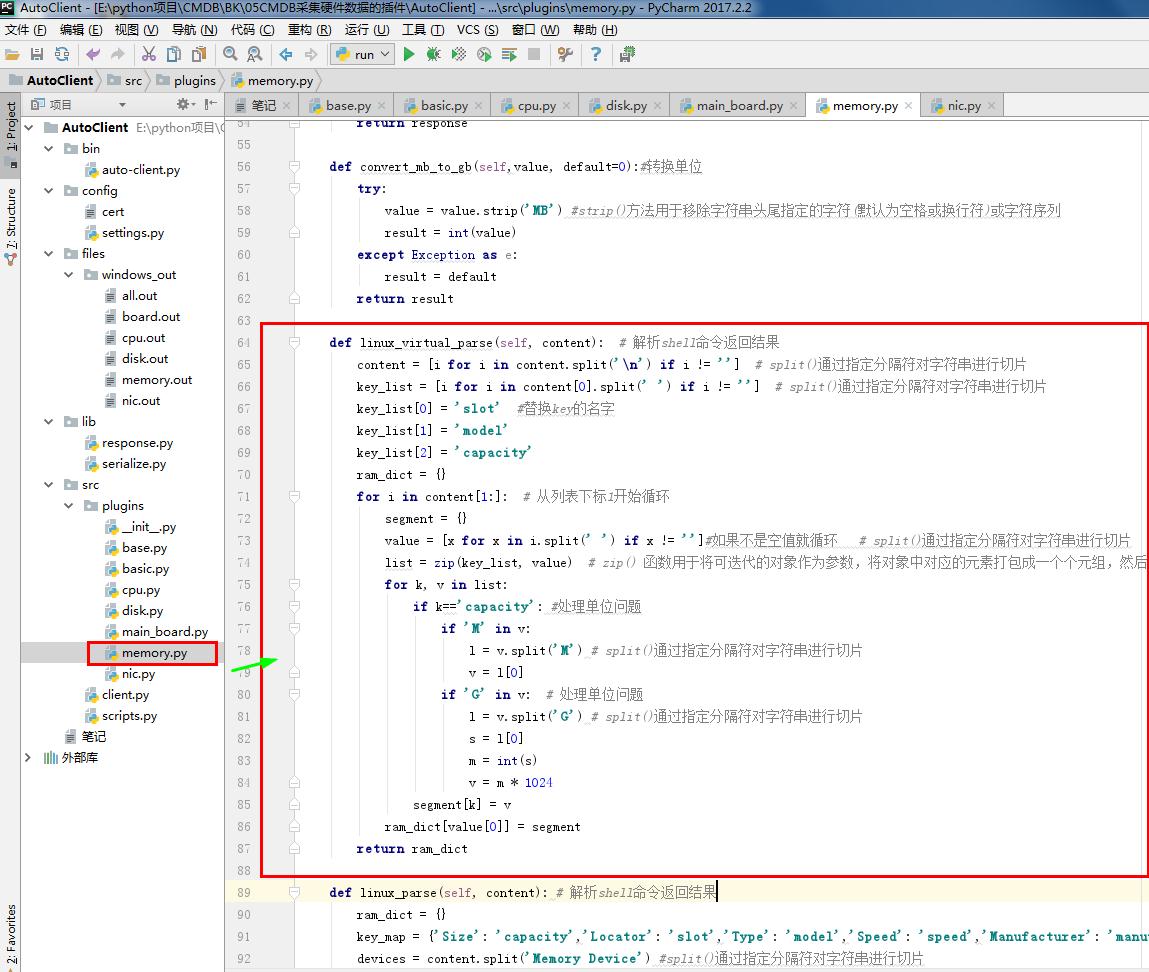
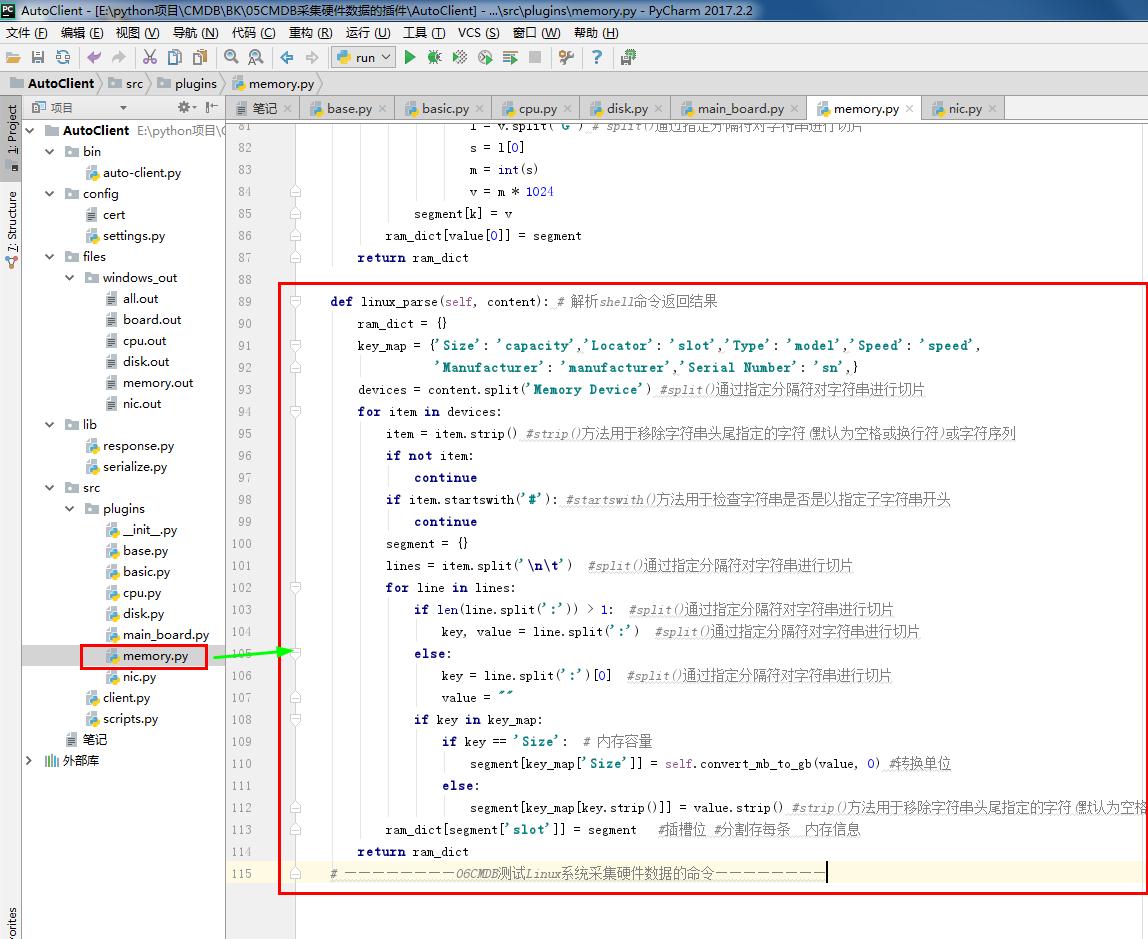


1 # memory.py 2 # ————————05CMDB采集硬件数据的插件———————— 3 from .base import BasePlugin #采集资产的方式 和 系统平台 4 from lib.response import BaseResponse #提交数据的类型(字典) 5 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 6 # import wmi#Windows操作系统上管理数据和操作的基础设施 #linux写无法导入这个模块 7 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 8 9 class MemoryPlugin(BasePlugin): 10 def windows(self): 11 response = BaseResponse() #提交数据的类型(字典) 12 try: 13 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 14 import wmi#Windows操作系统上管理数据和操作的基础设施 #linux写无法导入这个模块 15 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 16 output =wmi.WMI().Win32_PhysicalMemory() #获取内存相关信息 17 response.data = self.windows_parse(output) 18 except Exception as e: 19 response.status = False 20 return response 21 22 @staticmethod#返回函数的静态方法 23 def windows_parse(content): 24 response={} 25 for item in content: 26 item_dict = {} 27 item_dict['slot'] = item.DeviceLocator #插槽位 28 item_dict['manufacturer'] = item.Manufacturer # 内存制造商 29 item_dict['model'] =item.FormFactor # 内存型号 30 item_dict['Capacity'] = round(int(item.Capacity) / (1024**3)) # 内存容量 31 item_dict['sn'] = item.SerialNumber #内存SN号 32 item_dict['speed'] = item.Speed #内存速度 33 response[item_dict['slot']] = item_dict #分割存每条 内存信息 34 return response 35 36 # ————————05CMDB采集硬件数据的插件———————— 37 38 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 39 def linux(self): 40 response = BaseResponse() #提交数据的类型(字典) 41 try: 42 import subprocess # 启动一个新的进程并且与之通信 43 shell_command = "sudo dmidecode -q -t 17 2>/dev/null" #定义命令 cat /proc/swaps #swapon 44 output = subprocess.getoutput(shell_command) #linux系统上执行的命令 45 if not output: 46 shell_command = "swapon" # 定义命令 cat /proc/swaps #swapon 47 output = subprocess.getoutput(shell_command) # linux系统上执行的命令 48 response.data = self.linux_virtual_parse(output) # 解析shell命令返回结果 49 else: 50 response.data = self.linux_parse(output) # 解析shell命令返回结果 51 except Exception as e: # 如果 出现未知错误 52 response.status = False 53 return response 54 55 def convert_mb_to_gb(self,value, default=0):#转换单位 56 try: 57 value = value.strip('MB') #strip()方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列 58 result = int(value) 59 except Exception as e: 60 result = default 61 return result 62 63 def linux_virtual_parse(self, content): # 解析shell命令返回结果 64 content = [i for i in content.split('\n') if i != ''] # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 65 key_list = [i for i in content[0].split(' ') if i != ''] # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 66 key_list[0] = 'slot' #替换key的名字 67 key_list[1] = 'model' 68 key_list[2] = 'capacity' 69 ram_dict = {} 70 for i in content[1:]: # 从列表下标1开始循环 71 segment = {} 72 value = [x for x in i.split(' ') if x != '']#如果不是空值就循环 # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 73 list = zip(key_list, value) # zip() 函数用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表。 74 for k, v in list: 75 if k=='capacity': #处理单位问题 76 if 'M' in v: 77 l = v.split('M') # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 78 v = l[0] 79 if 'G' in v: # 处理单位问题 80 l = v.split('G') # split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 81 s = l[0] 82 m = int(s) 83 v = m * 1024 84 segment[k] = v 85 ram_dict[value[0]] = segment 86 return ram_dict 87 88 def linux_parse(self, content): # 解析shell命令返回结果 89 ram_dict = {} 90 key_map = {'Size': 'capacity','Locator': 'slot','Type': 'model','Speed': 'speed', 91 'Manufacturer': 'manufacturer','Serial Number': 'sn',} 92 devices = content.split('Memory Device') #split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 93 for item in devices: 94 item = item.strip() #strip()方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列 95 if not item: 96 continue 97 if item.startswith('#'): #startswith()方法用于检查字符串是否是以指定子字符串开头 98 continue 99 segment = {} 100 lines = item.split('\n\t') #split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 101 for line in lines: 102 if len(line.split(':')) > 1: #split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 103 key, value = line.split(':') #split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 104 else: 105 key = line.split(':')[0] #split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 106 value = "" 107 if key in key_map: 108 if key == 'Size': # 内存容量 109 segment[key_map['Size']] = self.convert_mb_to_gb(value, 0) #转换单位 110 else: 111 segment[key_map[key.strip()]] = value.strip() #strip()方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列 112 ram_dict[segment['slot']] = segment #插槽位 #分割存每条 内存信息 113 return ram_dict 114 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令————————
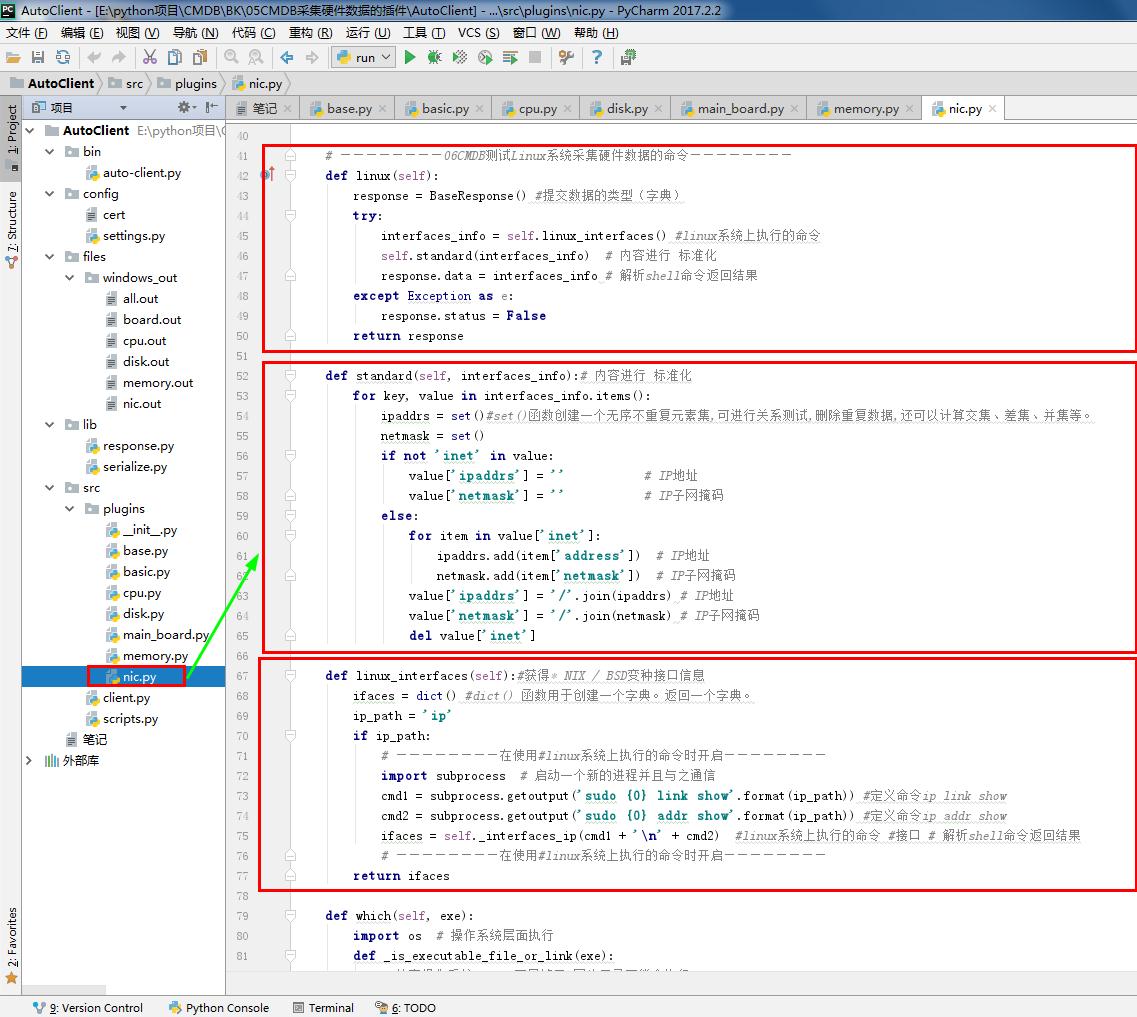
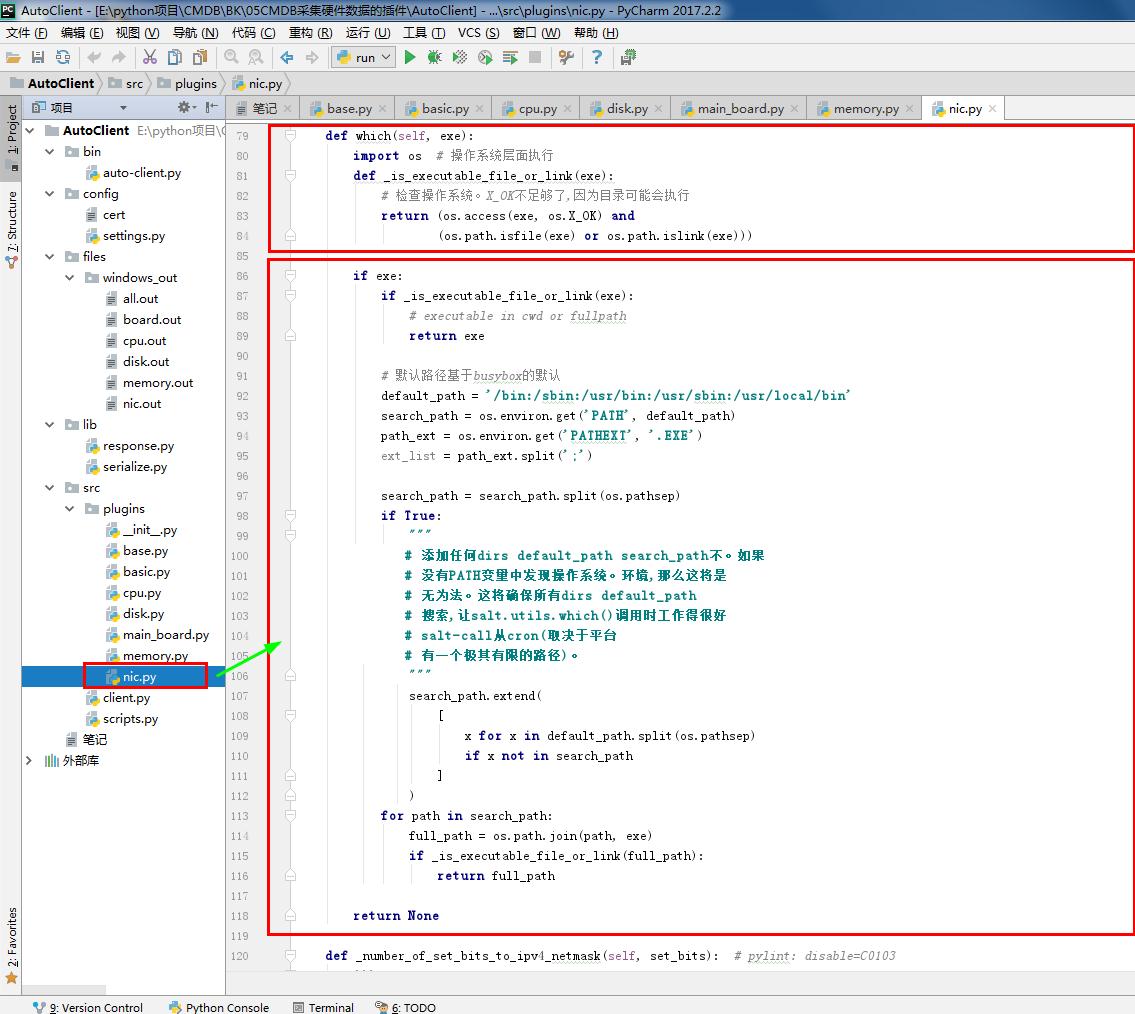
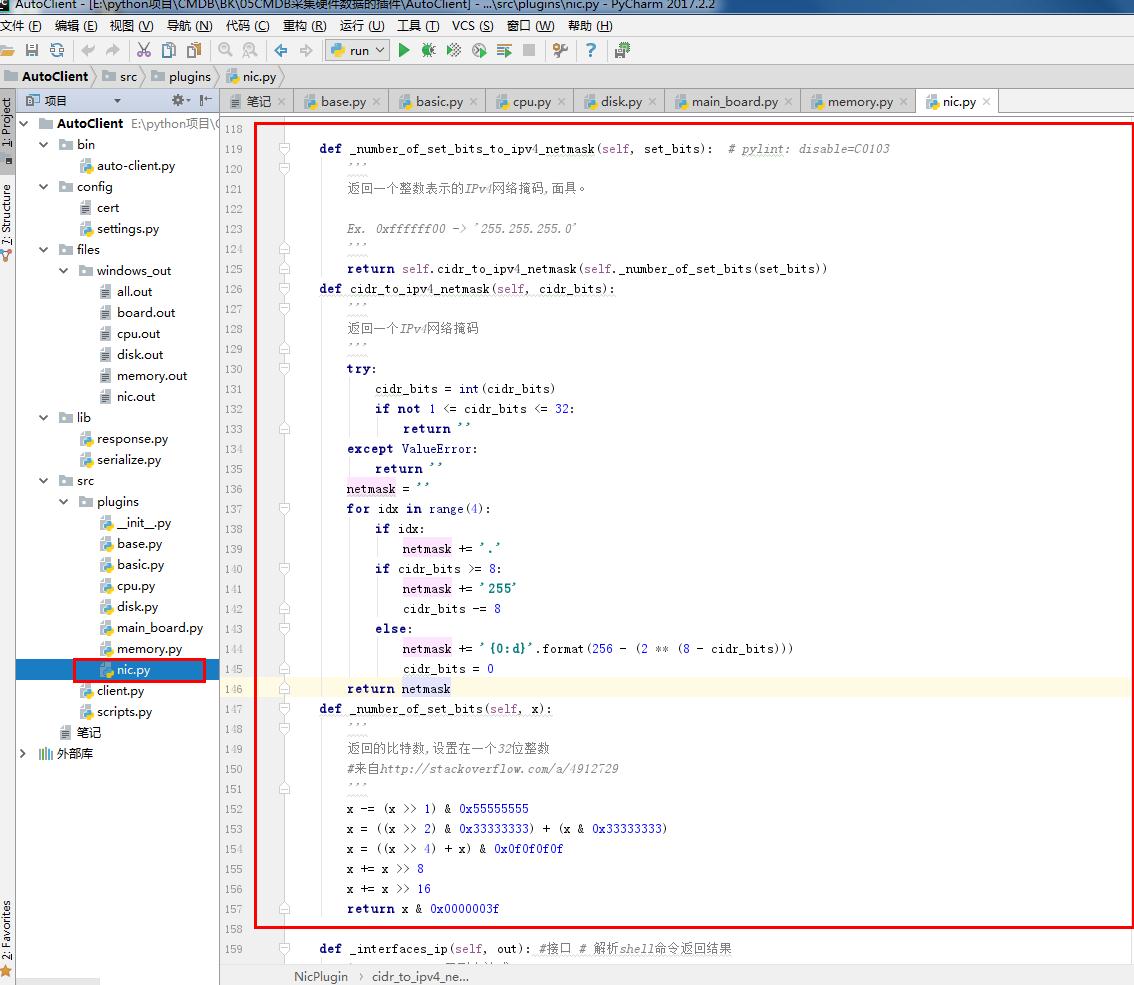
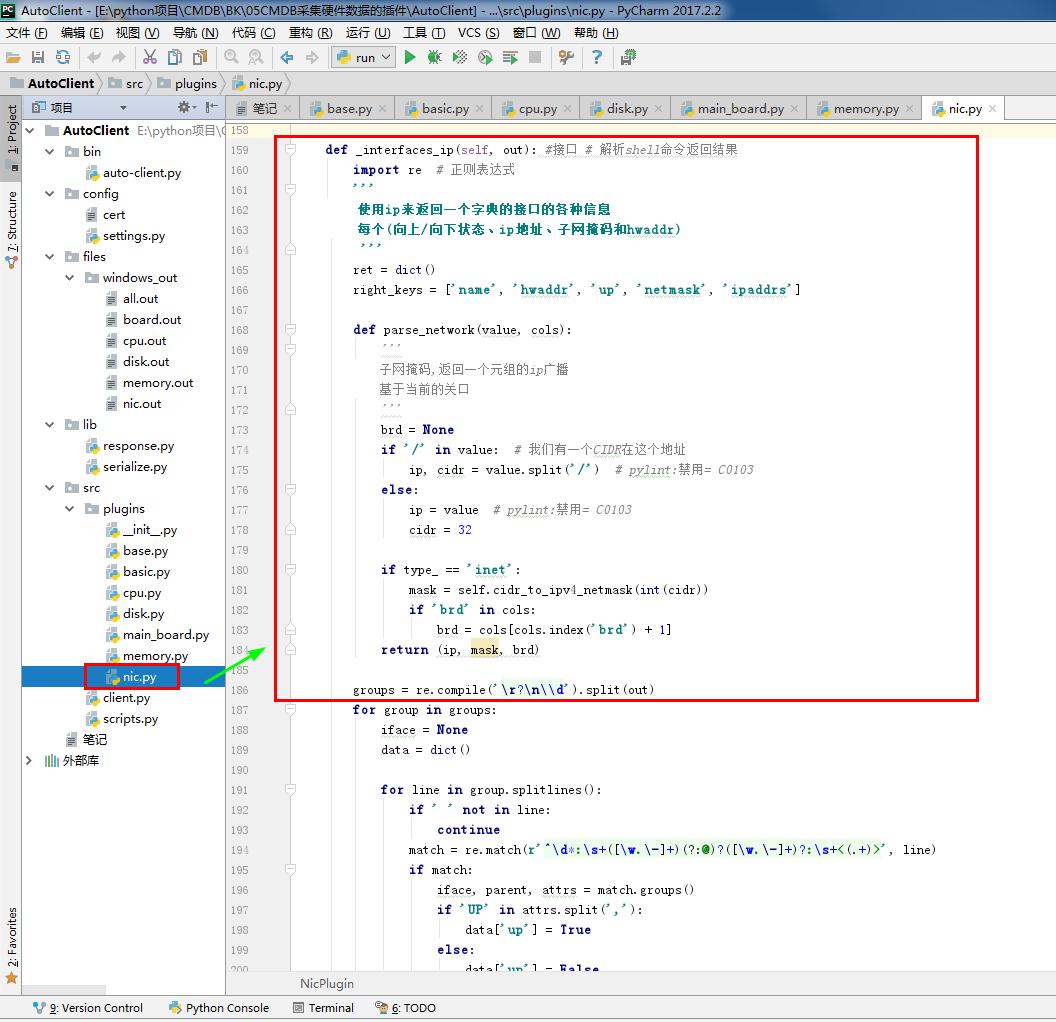
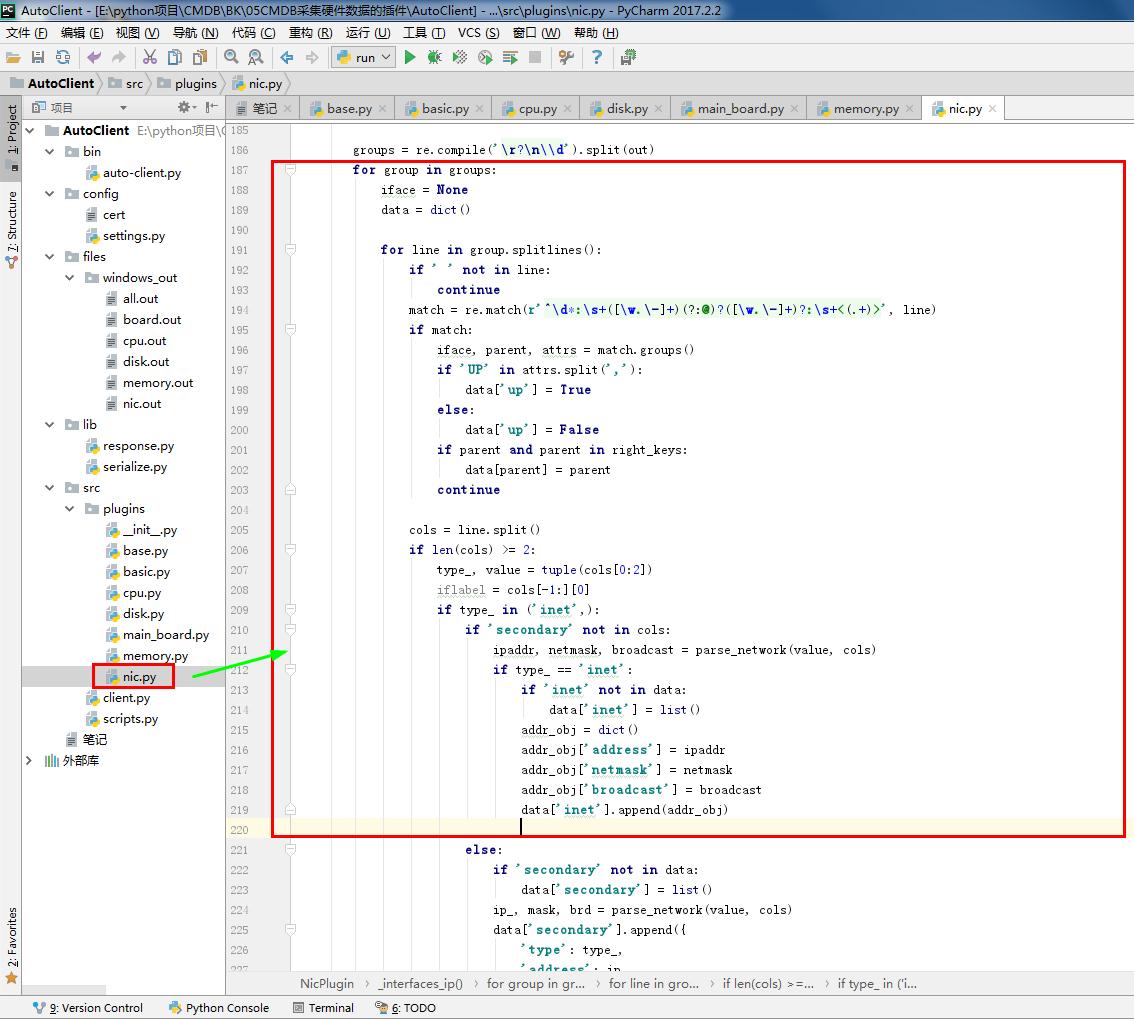
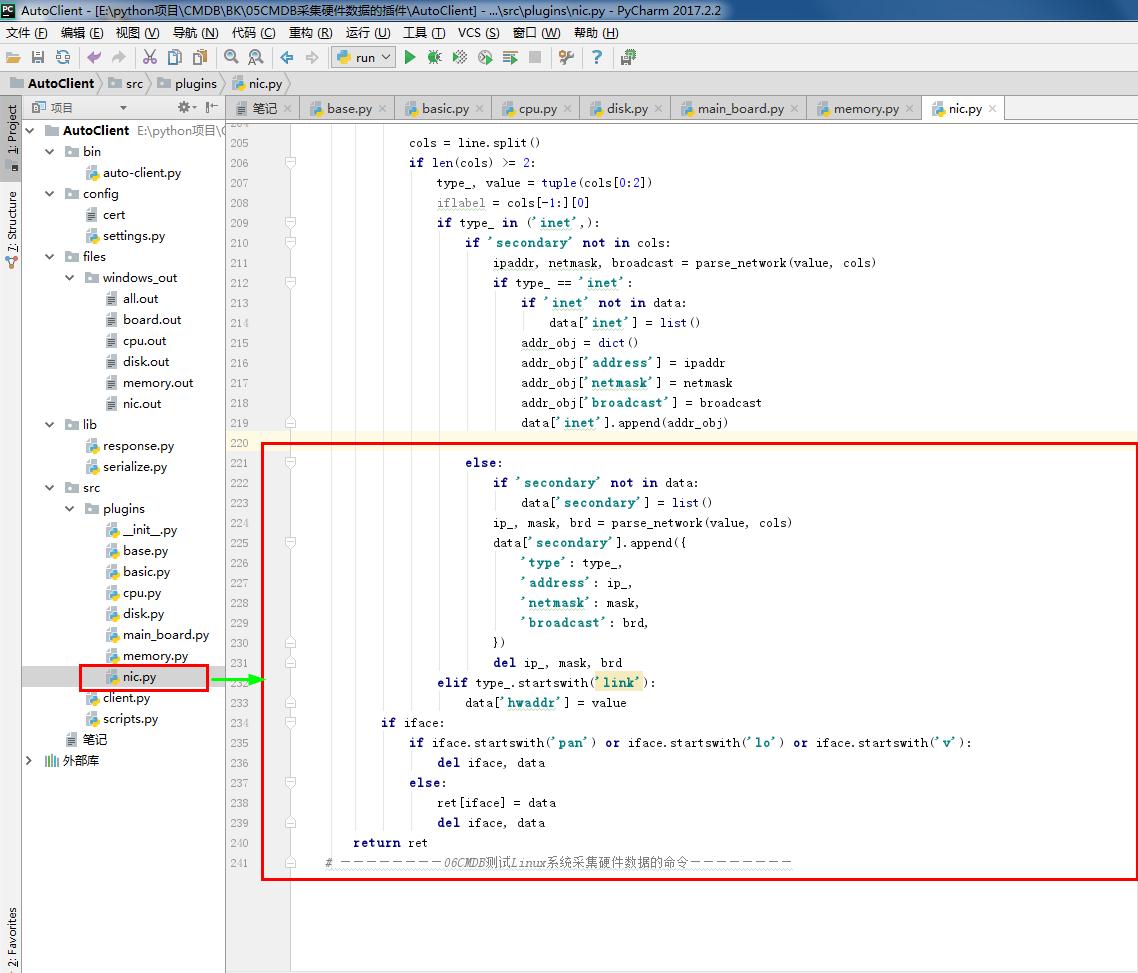

1 # nic.py 2 # ————————05CMDB采集硬件数据的插件———————— 3 from .base import BasePlugin #采集资产的方式 和 系统平台 4 from lib.response import BaseResponse #提交数据的类型(字典) 5 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 6 # import wmi#Windows操作系统上管理数据和操作的基础设施 #linux写无法导入这个模块 7 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 8 9 class NicPlugin(BasePlugin): 10 def windows(self): 11 response = BaseResponse() #提交数据的类型(字典) 12 try: 13 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 14 import wmi#Windows操作系统上管理数据和操作的基础设施 #linux写无法导入这个模块 15 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 16 output =wmi.WMI().Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration() #获取网卡相关信息 17 response.data = self.windows_parse(output) #解析相关信息 返回结果 #存到字典 18 except Exception as e: 19 response.status = False 20 return response 21 22 @staticmethod#返回函数的静态方法 23 def windows_parse(content): 24 response={} 25 IPCM = 0 # 权重 26 for item in content: 27 if item.IPConnectionMetric: # 权重 28 if item.IPConnectionMetric > IPCM: # 权重 #防止虚拟网卡 29 item_dict = {} 30 name=item.ServiceName # 网卡名称 31 item_dict['hwaddr'] = item.MACAddress # 网卡MAC地址 32 item_dict['ipaddrs'] = item.IPAddress[0] # IP地址 33 item_dict['netmask'] = item.IPSubnet[0] # IP子网掩码 34 item_dict['up'] = item.IPEnabled #是否有启用 35 response[name] = item_dict 36 IPCM = item.IPConnectionMetric # 权重 37 return response 38 # ————————05CMDB采集硬件数据的插件———————— 39 40 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 41 def linux(self): 42 response = BaseResponse() #提交数据的类型(字典) 43 try: 44 interfaces_info = self.linux_interfaces() #linux系统上执行的命令 45 self.standard(interfaces_info) # 内容进行 标准化 46 response.data = interfaces_info # 解析shell命令返回结果 47 except Exception as e: 48 response.status = False 49 return response 50 51 def standard(self, interfaces_info):# 内容进行 标准化 52 for key, value in interfaces_info.items(): 53 ipaddrs = set()#set()函数创建一个无序不重复元素集,可进行关系测试,删除重复数据,还可以计算交集、差集、并集等。 54 netmask = set() 55 if not 'inet' in value: 56 value['ipaddrs'] = '' # IP地址 57 value['netmask'] = '' # IP子网掩码 58 else: 59 for item in value['inet']: 60 ipaddrs.add(item['address']) # IP地址 61 netmask.add(item['netmask']) # IP子网掩码 62 value['ipaddrs'] = '/'.join(ipaddrs) # IP地址 63 value['netmask'] = '/'.join(netmask) # IP子网掩码 64 del value['inet'] 65 66 def linux_interfaces(self):#获得* NIX / BSD变种接口信息 67 ifaces = dict() #dict() 函数用于创建一个字典。返回一个字典。 68 ip_path = 'ip' 69 if ip_path: 70 # ————————在使用#linux系统上执行的命令时开启———————— 71 import subprocess # 启动一个新的进程并且与之通信 72 cmd1 = subprocess.getoutput('sudo {0} link show'.format(ip_path)) #定义命令ip link show 73 cmd2 = subprocess.getoutput('sudo {0} addr show'.format(ip_path)) #定义命令ip addr show 74 ifaces = self._interfaces_ip(cmd1 + '\n' + cmd2) #linux系统上执行的命令 #接口 # 解析shell命令返回结果 75 # ————————在使用#linux系统上执行的命令时开启———————— 76 return ifaces 77 78 def which(self, exe): 79 import os # 操作系统层面执行 80 def _is_executable_file_or_link(exe): 81 # 检查操作系统。X_OK不足够了,因为目录可能会执行 82 return (os.access(exe, os.X_OK) and 83 (os.path.isfile(exe) or os.path.islink(exe))) 84 85 if exe: 86 if _is_executable_file_or_link(exe): 87 # executable in cwd or fullpath 88 return exe 89 90 # 默认路径基于busybox的默认 91 default_path = '/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/local/bin' 92 search_path = os.environ.get('PATH', default_path) 93 path_ext = os.environ.get('PATHEXT', '.EXE') 94 ext_list = path_ext.split(';') 95 96 search_path = search_path.split(os.pathsep) 97 if True: 98 """ 99 # 添加任何dirs default_path search_path不。如果 100 # 没有PATH变量中发现操作系统。环境,那么这将是 101 # 无为法。这将确保所有dirs default_path 102 # 搜索,让salt.utils.which()调用时工作得很好 103 # salt-call从cron(取决于平台 104 # 有一个极其有限的路径)。 105 """ 106 search_path.extend( 107 [ 108 x for x in default_path.split(os.pathsep) 109 if x not in search_path 110 ] 111 ) 112 for path in search_path: 113 full_path = os.path.join(path, exe) 114 if _is_executable_file_or_link(full_path): 115 return full_path 116 return None 117 118 def _number_of_set_bits_to_ipv4_netmask(self, set_bits): # pylint: disable=C0103 119 ''' 120 返回一个整数表示的IPv4网络掩码,面具。 121 122 Ex. 0xffffff00 -> '255.255.255.0' 123 ''' 124 return self.cidr_to_ipv4_netmask(self._number_of_set_bits(set_bits)) 125 def cidr_to_ipv4_netmask(self, cidr_bits): 126 ''' 127 返回一个IPv4网络掩码 128 ''' 129 try: 130 cidr_bits = int(cidr_bits) 131 if not 1 <= cidr_bits <= 32: 132 return '' 133 except ValueError: 134 return '' 135 netmask = '' 136 for idx in range(4): 137 if idx: 138 netmask += '.' 139 if cidr_bits >= 8: 140 netmask += '255' 141 cidr_bits -= 8 142 else: 143 netmask += '{0:d}'.format(256 - (2 ** (8 - cidr_bits))) 144 cidr_bits = 0 145 return netmask 146 def _number_of_set_bits(self, x): 147 ''' 148 返回的比特数,设置在一个32位整数 149 #来自http://stackoverflow.com/a/4912729 150 ''' 151 x -= (x >> 1) & 0x55555555 152 x = ((x >> 2) & 0x33333333) + (x & 0x33333333) 153 x = ((x >> 4) + x) & 0x0f0f0f0f 154 x += x >> 8 155 x += x >> 16 156 return x & 0x0000003f 157 158 def _interfaces_ip(self, out): #接口 # 解析shell命令返回结果 159 import re # 正则表达式 160 ''' 161 使用ip来返回一个字典的接口的各种信息 162 每个(向上/向下状态、ip地址、子网掩码和hwaddr) 163 ''' 164 ret = dict() 165 right_keys = ['name', 'hwaddr', 'up', 'netmask', 'ipaddrs'] 166 167 def parse_network(value, cols): 168 ''' 169 子网掩码,返回一个元组的ip广播 170 基于当前的关口 171 ''' 172 brd = None 173 if '/' in value: # 我们有一个CIDR在这个地址 174 ip, cidr = value.split('/') # pylint:禁用= C0103 175 else: 176 ip = value # pylint:禁用= C0103 177 cidr = 32 178 179 if type_ == 'inet': 180 mask = self.cidr_to_ipv4_netmask(int(cidr)) 181 if 'brd' in cols: 182 brd = cols[cols.index('brd') + 1] 183 return (ip, mask, brd) 184 185 groups = re.compile('\r?\n\\d').split(out) 186 for group in groups: 187 iface = None 188 data = dict() 189 190 for line in group.splitlines(): 191 if ' ' not in line: 192 continue 193 match = re.match(r'^\d*:\s+([\w.\-]+)(?:@)?([\w.\-]+)?:\s+<(.+)>', line) 194 if match: 195 iface, parent, attrs = match.groups() 196 if 'UP' in attrs.split(','): 197 data['up'] = True 198 else: 199 data['up'] = False 200 if parent and parent in right_keys: 201 data[parent] = parent 202 continue 203 204 cols = line.split() 205 if len(cols) >= 2: 206 type_, value = tuple(cols[0:2]) 207 iflabel = cols[-1:][0] 208 if type_ in ('inet',): 209 if 'secondary' not in cols: 210 ipaddr, netmask, broadcast = parse_network(value, cols) 211 if type_ == 'inet': 212 if 'inet' not in data: 213 data['inet'] = list() 214 addr_obj = dict() 215 addr_obj['address'] = ipaddr 216 addr_obj['netmask'] = netmask 217 addr_obj['broadcast'] = broadcast 218 data['inet'].append(addr_obj) 219 220 else: 221 if 'secondary' not in data: 222 data['secondary'] = list() 223 ip_, mask, brd = parse_network(value, cols) 224 data['secondary'].append({ 225 'type': type_, 226 'address': ip_, 227 'netmask': mask, 228 'broadcast': brd, 229 }) 230 del ip_, mask, brd 231 elif type_.startswith('link'): 232 data['hwaddr'] = value 233 if iface: 234 if iface.startswith('pan') or iface.startswith('lo') or iface.startswith('v'): 235 del iface, data 236 else: 237 ret[iface] = data 238 del iface, data 239 return ret 240 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令————————

1 #auto-client.py 2 # ————————01CMDB获取服务器基本信息———————— 3 import os 4 BASEDIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))#当前路径 5 print('当前路径:',type(BASEDIR),BASEDIR) 6 os.path.join(BASEDIR)# Join(转成字符串) 7 8 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 9 import sys 10 sys.path.append(BASEDIR)# 设置工作目录,使得包和模块能够正常导入 11 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 12 13 from src.scripts import client 14 if __name__ == '__main__':#让你写的脚本模块既可以导入到别的模块中用,另外该模块自己也可执行 15 client() 16 # ————————01CMDB获取服务器基本信息————————

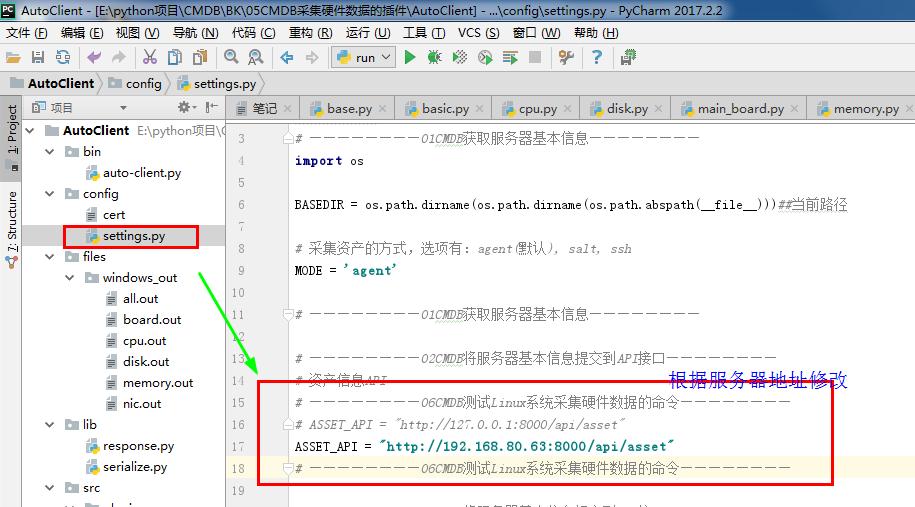

1 #settings.py 2 # ————————01CMDB获取服务器基本信息———————— 3 import os 4 5 BASEDIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))##当前路径 6 7 # 采集资产的方式,选项有:agent(默认), salt, ssh 8 MODE = 'agent' 9 10 # ————————01CMDB获取服务器基本信息———————— 11 12 # ————————02CMDB将服务器基本信息提交到API接口———————— 13 # 资产信息API 14 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 15 # ASSET_API = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/asset" 16 ASSET_API = "http://192.168.80.63:8000/api/asset" 17 # ————————06CMDB测试Linux系统采集硬件数据的命令———————— 18 19 # ————————02CMDB将服务器基本信息提交到API接口———————— 20 21 # ————————03CMDB信息安全API接口交互认证———————— 22 # 用于API认证的KEY 23 KEY = '299095cc-1330-11e5-b06a-a45e60bec08b' #认证的密码 24 # 用于API认证的请求头 25 AUTH_KEY_NAME = 'auth-key' 26 # ————————03CMDB信息安全API接口交互认证———————— 27 28 29 # ————————04CMDB本地(Agent)模式客户端唯一标识(ID)———————— 30 # Agent模式保存服务器唯一ID的文件 31 CERT_FILE_PATH = os.path.join(BASEDIR, 'config', 'cert') #文件路径 32 # ————————04CMDB本地(Agent)模式客户端唯一标识(ID)———————— 33 34 # ————————05CMDB采集硬件数据的插件———————— 35 # 采集硬件数据的插件 36 PLUGINS_DICT = { 37 'cpu': 'src.plugins.cpu.CpuPlugin', 38 'disk': 'src.plugins.disk.DiskPlugin', 39 'main_board': 'src.plugins.main_board.MainBoardPlugin', 40 'memory': 'src.plugins.memory.MemoryPlugin', 41 'nic': 'src.plugins.nic.NicPlugin', 42 } 43 # ————————05CMDB采集硬件数据的插件————————



