Django的一些操作与视图函数
一 . Django的安装
pip install django==1.14.6 # 后面的数字是django的版本
二 . 通过命令行(cmd)来创建Django项目
1. 切换到保存项目的文件夹下 # cd 空格 文件夹名 2. django-admin startproject 项目名称 # 创建一个新项目 3. python manage.py runserver 127.0.0.1:8000 # 启动django项目, 后面的ip地址和端口 4. django-admin startapp app名字 # 创建App, 可以创建多个
添加完App后,需要在settings文件里面的INSTALLED_APPS后面加上一句话.

如果有多个App 为了避免URL都写在一起看着太乱,需要把各个需要的urls.py文件写到自己的App文件下.
此时在主urls.py文件里面写内容就要有一些变化了.
from django.conf.urls import url,include
from django.contrib import admin
from App01 import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls,),
url(r'^login/', views.login, name='login'),
url(r'^App01/', include('App01.urls')), # 凡是以App01开头的请求,都去App01.urls里面找.
]
# 但是此时的搜索路径需要以App01开头了, 比如原来搜索127.0.0.1:8000/login就能找到login页面,
但是如果这个login的url在App01的文件里 就需要写成 127.0.0.1:8000/App01/login 这样才能找到login页面
URL的别名应用

# 上述操作是在HTML文件中进行的,a标签也是这样做的, 但是在视图(views)里面的渲染就不一样啦.
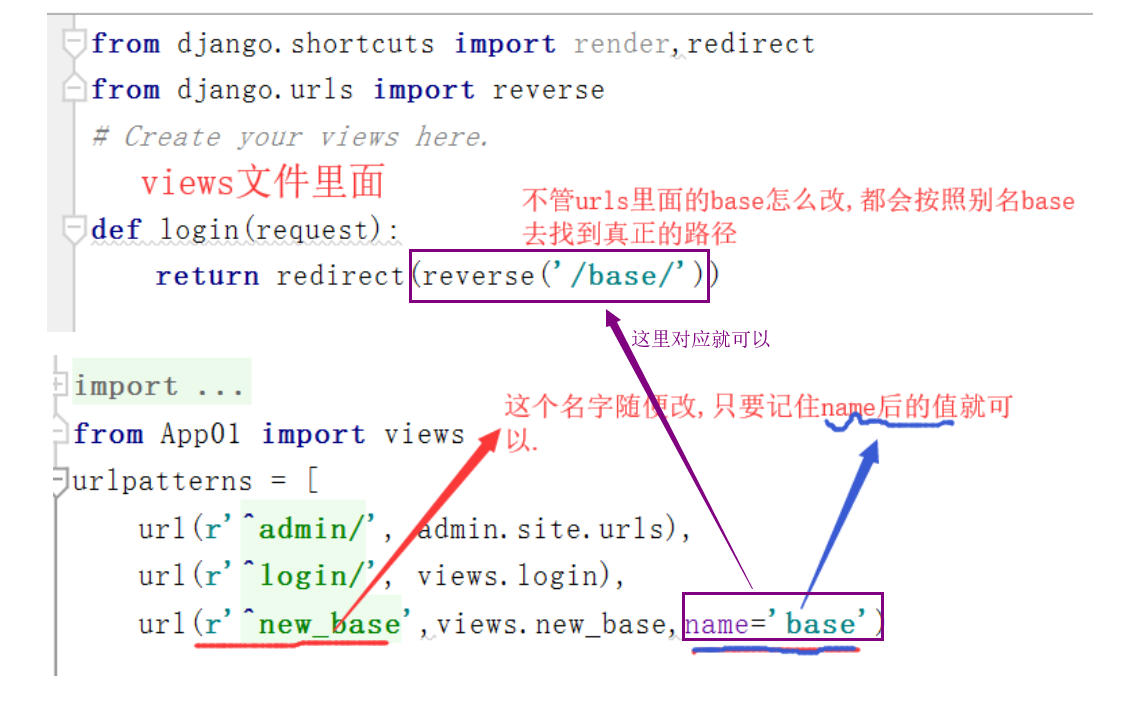
namespace的用法

crm里面url的写法
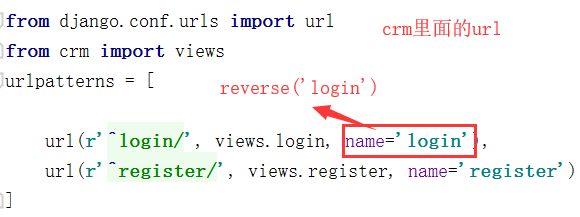
app01里面url的写法
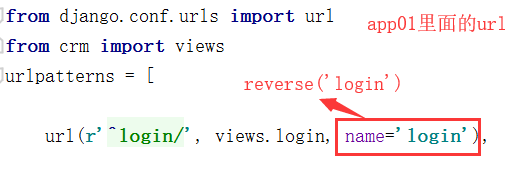
crm视图函数

三 . 通过pycharm来创建django项目
打开pycharm-->File-->NewProject-->Django
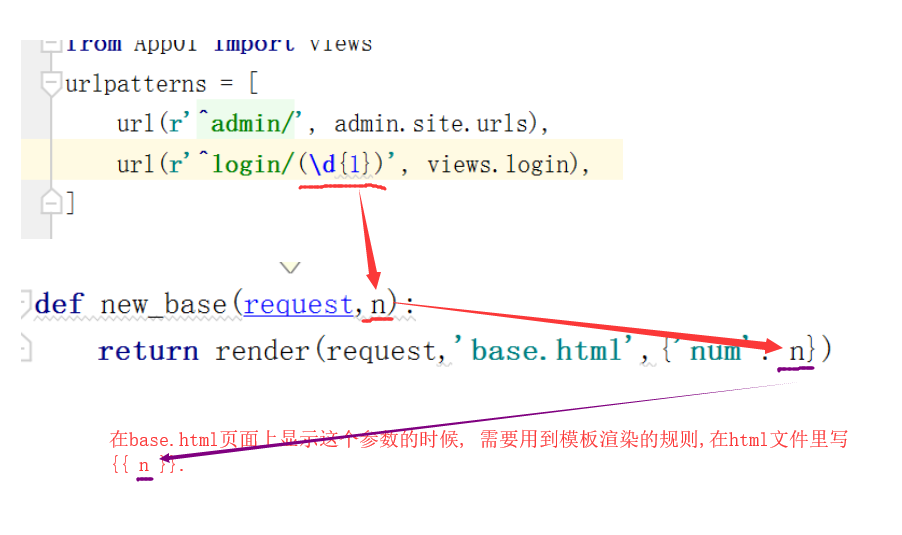
四 . 传参方式
# login后面用括号括起来的是是参数,而且必须用括号括起来,
在视图里面的函数必须用一个形参来接收
五 . CBV与FBV
FBV(function base views) 在视图里面写函数就是FBV(常用的)
CBV(class base views) 在视图里面写类, 同时urls.py里面也和FBV不一样(基本用不到)
CBV 的本质也是FBV 先实例化,然后赋值self.request,然后执行里面的dispatch方法,dispatch方法通过反射可以拿到get或者post然后去执行函数
# path拿到的是不带参数的路径, get_full_path拿到的是带参数的路径 request.path 拿到的路径是/index/ request.get_full_path() 拿到的路径是 /index/?page=1
# 写在视图里面的
class Myd(View):
def get(self,request,*args, **kwargs):
print('get方法执行了')
return render(request,'cvpost.html',{'name':self.name})
def post(self,request,n):
print('post方法被执行了')
return HttpResponse('post')
# urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url
from myapp.views import MyView #引入我们在views.py里面创建的类
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^index/$', MyView.as_view()), # as_view()这个方法拿到的是view函数然后去u执行
]
# 传参
url(r'^cv/(\d{2})/', views.Myd.as_view(),name='cv'),
CBV加装饰器
我们在给类方法加装饰器的时候,他不同于函数直接写在上面就可以,我们要先将其转化为方法装饰器.
Django中提供了method_decorator装饰器用于函数装饰器转化为方法装饰器
from django.views import View
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator
class AddClass(View):
@method_decorator(wrapper) #这个wrapper就是定义的装饰器
def get(self, request):
return render(request, "add_class.html")
def post(self, request):
class_name = request.POST.get("class_name")
models.Classes.objects.create(name=class_name)
return redirect("/class_list/")
给CBV加装饰器的方法有三种
# 第一种方法
class AddClass(View):
@method_decorator(wrapper)
def get(self, request):
return render(request, "add_class.html")
# 直接写在方法上面
# 第二种方法,写在类上面,但是需要指定给谁加 name=谁
@method_decorator(wrapper, name='get')
class AddClass(View):
def get(self, request):
return render(request, "add_class.html")
# 第三种方法, dispatch方法 from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator @method_decorator(wrapper) def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return super().dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs) # 自己定义一个dispatch方法,这个方法是无论get还是post方法都被加上装饰器
六 . 浏览器的八种请求方式
http_method_names = ['get', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'delete', 'head', 'options', 'trace']
七 . request后面的属性与方法
request.POST/GET/method/COOKIES/session/FILES/path/get_full_path/META/body




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号