实验4 类的组合、继承、模板类、标准库
实验任务2

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <numeric> 6 #include <iomanip> 7 8 using std::vector; 9 using std::string; 10 using std::cin; 11 using std::cout; 12 using std::endl; 13 14 class GradeCalc: public vector<int> { 15 public: 16 GradeCalc(const string &cname, int size); 17 void input(); // 录入成绩 18 void output() const; // 输出成绩 19 void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序) 20 int min() const; // 返回最低分 21 int max() const; // 返回最高分 22 float average() const; // 返回平均分 23 void info(); // 输出课程成绩信息 24 25 private: 26 void compute(); // 成绩统计 27 28 private: 29 string course_name; // 课程名 30 int n; // 课程人数 31 vector<int> counts = vector<int>(5, 0); // 保存各分数段人数([0, 60), [60, 70), [70, 80), [80, 90), [90, 100] 32 vector<double> rates = vector<double>(5, 0); // 保存各分数段比例 33 }; 34 35 GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const string &cname, int size): course_name{cname}, n{size} {} 36 37 void GradeCalc::input() { 38 int grade; 39 40 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 41 cin >> grade; 42 this->push_back(grade); 43 } 44 } 45 46 void GradeCalc::output() const { 47 for(auto ptr = this->begin(); ptr != this->end(); ++ptr) 48 cout << *ptr << " "; 49 cout << endl; 50 } 51 52 void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) { 53 if(ascending) 54 std::sort(this->begin(), this->end()); 55 else 56 std::sort(this->begin(), this->end(), std::greater<int>()); 57 } 58 59 int GradeCalc::min() const { 60 return *std::min_element(this->begin(), this->end()); 61 } 62 63 int GradeCalc::max() const { 64 return *std::max_element(this->begin(), this->end()); 65 } 66 67 float GradeCalc::average() const { 68 return std::accumulate(this->begin(), this->end(), 0) * 1.0 / n; 69 } 70 71 void GradeCalc::compute() { 72 for(int grade: *this) { 73 if(grade < 60) 74 counts.at(0)++; 75 else if(grade >= 60 && grade < 70) 76 counts.at(1)++; 77 else if(grade >= 70 && grade < 80) 78 counts.at(2)++; 79 else if(grade >= 80 && grade < 90) 80 counts.at(3)++; 81 else if(grade >= 90) 82 counts.at(4)++; 83 } 84 85 for(int i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i) 86 rates.at(i) = counts.at(i) * 1.0 / n; 87 } 88 89 void GradeCalc::info() { 90 cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << endl; 91 cout << "排序后成绩: \t"; 92 sort(); output(); 93 cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << endl; 94 cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << endl; 95 cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << endl; 96 97 compute(); // 统计各分数段人数、比例 98 99 vector<string> tmp{"[0, 60) ", "[60, 70)", "[70, 80)","[80, 90)", "[90, 100]"}; 100 for(int i = tmp.size()-1; i >= 0; --i) 101 cout << tmp[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t" 102 << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i]*100 << "%" << endl; 103 }

1 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 2 #include <iomanip> 3 4 void test() { 5 int n; 6 cout << "输入班级人数: "; 7 cin >> n; 8 9 GradeCalc c1("OOP", n); 10 11 cout << "录入成绩: " << endl;; 12 c1.input(); 13 cout << "输出成绩: " << endl; 14 c1.output(); 15 16 cout << string(20, '*') + "课程成绩信息" + string(20, '*') << endl; 17 c1.info(); 18 } 19 20 int main() { 21 test(); 22 }
运行测试截图
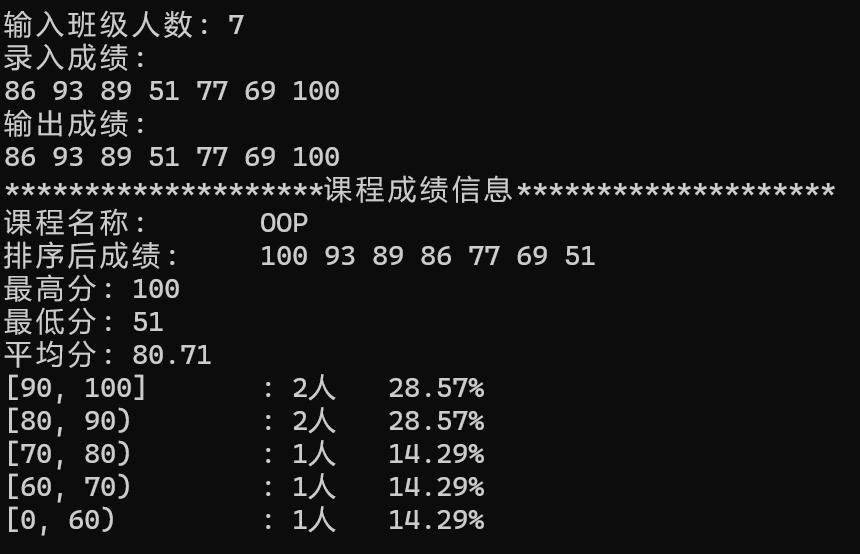
问题1
在 GradeCalc 类中,成绩存储在其基类 vector<int> 的实例中。由于 GradeCalc 继承自 vector<int>,因此它继承了 vector 的所有方法和属性,包括用于存储元素的内部数组。
访问成绩:sort, min, max, average, output 方法通过 this->begin(), this->end() 等接口访问成绩。这些方法利用了 vector 提供的迭代器接口。
存储数据:input 方法通过 this->push_back(grade) 接口将成绩存入对象。push_back 是 vector 类的一个成员函数,用于在容器的末尾添加一个新元素。
问题2
分母的功能:在 average 方法中,分母 n 的功能是计算平均成绩时所需的成绩总数。它确保计算的是所有成绩的平均值。
去掉乘以1.0的影响:如果去掉乘以1.0的代码,即直接使用 std::accumulate(this->begin(), this->end(), 0) / n,结果将是整数除法,这将导致结果向下取整,而不是计算平均值的浮点结果。
乘以1.0的原因:乘以1.0是为了确保进行的是浮点除法而不是整数除法。这保证了平均成绩能够保留小数部分,从而提供更精确的结果。
问题3
从真实应用场景角度考虑,GradeCalc 类在设计及代码实现细节上可能需要以下迭代和完善:
数据验证:在 input 方法中,应添加对输入成绩的验证,确保输入的是有效的整数,并且可能需要在一定范围内(如0到100)。
异常处理:在处理输入和计算时,应添加异常处理机制,以处理可能的错误情况,如输入非数字字符、空输入等。
代码重构:继承 vector<int> 可能不是最佳设计选择,因为 GradeCalc 类不仅包含成绩列表,还包含其他与课程相关的属性(如课程名)。使用组合而不是继承可能是一个更好的选择,即 GradeCalc 类内部包含一个 vector<int> 成员变量来存储成绩。
可扩展性和灵活性:当前的 compute 方法硬编码了分数段的划分。可以考虑提供一个方法来允许用户自定义分数段。可以添加更多的统计信息,如中位数、众数等。
实验任务3

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <numeric> 6 #include <iomanip> 7 8 using std::vector; 9 using std::string; 10 using std::cin; 11 using std::cout; 12 using std::endl; 13 14 class GradeCalc { 15 public: 16 GradeCalc(const string &cname, int size); 17 void input(); // 录入成绩 18 void output() const; // 输出成绩 19 void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序) 20 int min() const; // 返回最低分 21 int max() const; // 返回最高分 22 float average() const; // 返回平均分 23 void info(); // 输出课程成绩信息 24 25 private: 26 void compute(); // 成绩统计 27 28 private: 29 string course_name; // 课程名 30 int n; // 课程人数 31 vector<int> grades; // 课程成绩 32 vector<int> counts = vector<int>(5, 0); // 保存各分数段人数([0, 60), [60, 70), [70, 80), [80, 90), [90, 100] 33 vector<double> rates = vector<double>(5, 0); // 保存各分数段比例 34 }; 35 36 GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const string &cname, int size): course_name{cname}, n{size} {} 37 38 void GradeCalc::input() { 39 int grade; 40 41 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 42 cin >> grade; 43 grades.push_back(grade); 44 } 45 } 46 47 void GradeCalc::output() const { 48 for(int grade: grades) 49 cout << grade << " "; 50 cout << endl; 51 } 52 53 void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) { 54 if(ascending) 55 std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end()); 56 else 57 std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end(), std::greater<int>()); 58 59 } 60 61 int GradeCalc::min() const { 62 return *std::min_element(grades.begin(), grades.end()); 63 } 64 65 int GradeCalc::max() const { 66 return *std::max_element(grades.begin(), grades.end()); 67 } 68 69 float GradeCalc::average() const { 70 return std::accumulate(grades.begin(), grades.end(), 0) * 1.0 / n; 71 } 72 73 void GradeCalc::compute() { 74 for(int grade: grades) { 75 if(grade < 60) 76 counts.at(0)++; 77 else if(grade >= 60 && grade < 70) 78 counts.at(1)++; 79 else if(grade >= 70 && grade < 80) 80 counts.at(2)++; 81 else if(grade >= 80 && grade < 90) 82 counts.at(3)++; 83 else if(grade >= 90) 84 counts.at(4)++; 85 } 86 87 for(int i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i) 88 rates.at(i) = counts.at(i) *1.0 / n; 89 } 90 91 void GradeCalc::info() { 92 cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << endl; 93 cout << "排序后成绩: \t"; 94 sort(); output(); 95 cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << endl; 96 cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << endl; 97 cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << endl; 98 99 compute(); // 统计各分数段人数、比例 100 101 vector<string> tmp{"[0, 60) ", "[60, 70)", "[70, 80)","[80, 90)", "[90, 100]"}; 102 for(int i = tmp.size()-1; i >= 0; --i) 103 cout << tmp[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t" 104 << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i]*100 << "%" << endl; 105 }

1 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 2 #include <iomanip> 3 4 void test() { 5 int n; 6 cout << "输入班级人数: "; 7 cin >> n; 8 9 GradeCalc c1("OOP", n); 10 11 cout << "录入成绩: " << endl;; 12 c1.input(); 13 cout << "输出成绩: " << endl; 14 c1.output(); 15 16 cout << string(20, '*') + "课程成绩信息" + string(20, '*') << endl; 17 c1.info(); 18 } 19 20 int main() { 21 test(); 22 }
运行测试截图
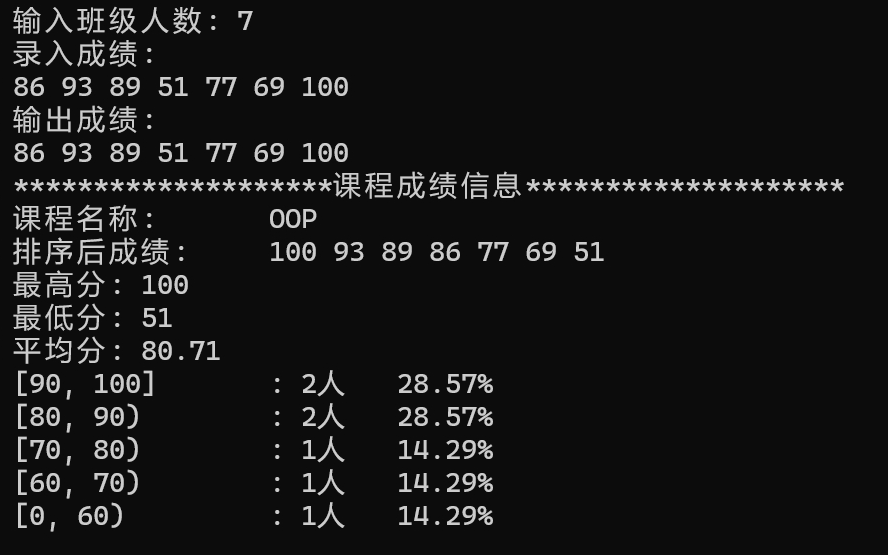
问题1
在实验任务3代码中,组合类 GradeCalc 的成绩存储在私有成员变量 grades 中,这是一个 vector<int> 类型的变量,专门用于存储课程成绩。
组合类 GradeCalc 的方法 sort, min, max, average, output 需要访问这些成绩时,通过 grades 成员变量的接口进行访问。
具体来说,这些方法使用了 grades.begin(), grades.end(), 以及范围基于的for循环(for(int grade: grades))来遍历或操作成绩数据。
与实验任务2相比,实验任务3在代码写法细节上的主要差别在于:
实验任务2中,GradeCalc 类继承自 vector<int>,因此成绩直接存储在继承的 vector 中。
而实验任务3中,GradeCalc 类包含一个 vector<int> 类型的私有成员变量 grades,用于存储成绩,这是一种组合关系而非继承关系。
由于这种设计变化,实验任务3中的方法访问成绩时,需要使用 grades 成员变量及其方法,而不是直接使用 this-> 指针。
问题2
对比实验任务2和实验任务3,虽然主体代码逻辑和类 GradeCalc 的接口没有变更,但类 GradeCalc 的设计及接口内部实现细节发生了显著变化。
这种变化让我对面向对象编程有了更深入的理解和领悟:
继承与组合的选择:
继承是面向对象编程中的一种强大工具,但它应该谨慎使用。当子类确实需要复用父类的行为和属性时,继承是合适的。然而,如果子类只是需要使用父类的某些功能,而不需要成为父类的一种特殊类型,那么组合可能是一个更好的选择。实验任务3通过组合而非继承来实现 GradeCalc 类,避免了潜在的继承问题(如脆弱的基类问题),并使类的职责更加清晰。
封装与数据隐藏:
在面向对象编程中,封装和数据隐藏是非常重要的原则。它们有助于保护对象的状态,防止外部代码直接访问和修改对象的内部数据。实验任务3通过私有成员变量 grades 实现了更好的封装和数据隐藏,而实验任务2则由于继承关系而暴露了更多的内部细节。
灵活性和可维护性:
组合通常比继承更具灵活性和可维护性。通过组合,可以更容易地替换或扩展类的部分功能,而不需要修改整个类的继承结构。实验任务3的设计使得未来对 GradeCalc 类的修改和扩展更加容易,例如添加新的统计方法或更改成绩存储方式。
遵循单一职责原则:
单一职责原则指出,一个类应该只有一个引起它变化的原因,即一个类应该只有一个职责。实验任务3通过将成绩存储和成绩计算分离到不同的成员变量和方法中,更好地遵循了这一原则。这使得类的每个部分都更加清晰和易于理解。
综上所述,实验任务3通过采用组合而非继承、实现更好的封装和数据隐藏、提高灵活性和可维护性,以及遵循单一职责原则,展示了面向对象编程中的一些重要原则和最佳实践。
实验任务4

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <limits> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 void test1() { 8 string s1, s2; 9 cin >> s1 >> s2; // cin: 从输入流读取字符串, 碰到空白符(空格/回车/Tab)即结束 10 cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl; 11 cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl; 12 } 13 14 void test2() { 15 string s1, s2; 16 getline(cin, s1); // getline(): 从输入流中提取字符串,直到遇到换行符 17 getline(cin, s2); 18 cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl; 19 cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl; 20 } 21 22 void test3() { 23 string s1, s2; 24 getline(cin, s1, ' '); //从输入流中提取字符串,直到遇到指定分隔符 25 getline(cin, s2); 26 cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl; 27 cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl; 28 } 29 30 int main() { 31 cout << "测试1: 使用标准输入流对象cin输入字符串" << endl; 32 test1(); 33 cout << endl; 34 35 cin.ignore(numeric_limits<streamsize>::max(), '\n'); 36 37 cout << "测试2: 使用函数getline()输入字符串" << endl; 38 test2(); 39 cout << endl; 40 41 cout << "测试3: 使用函数getline()输入字符串, 指定字符串分隔符" << endl; 42 test3(); 43 }
运行测试截图

问题一
运行测试截图
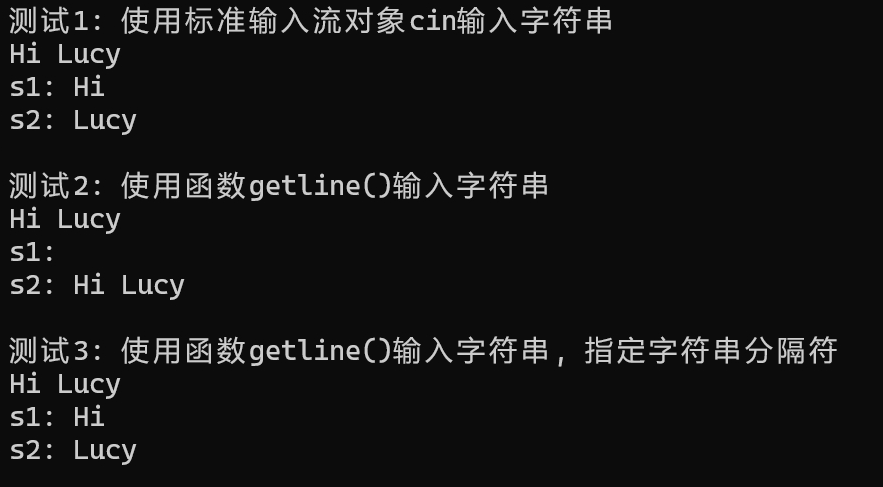
这行代码的用途是清除(忽略)输入缓冲区中直到下一个换行符(\n)之前的所有字符。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <limits> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 void output(const vector<string> &v) { 9 for(auto &s: v) 10 cout << s << endl; 11 } 12 13 void test() { 14 int n; 15 while(cout << "Enter n: ", cin >> n) { 16 vector<string> v1; 17 18 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 19 string s; 20 cin >> s; 21 v1.push_back(s); 22 } 23 24 cout << "output v1: " << endl; 25 output(v1); 26 cout << endl; 27 } 28 } 29 30 int main() { 31 cout << "测试: 使用cin多组输入字符串" << endl; 32 test(); 33 }
运行测试截图


1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <limits> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 void output(const vector<string> &v) { 9 for(auto &s: v) 10 cout << s << endl; 11 } 12 13 void test() { 14 int n; 15 while(cout << "Enter n: ", cin >> n) { 16 cin.ignore(numeric_limits<streamsize>::max(), '\n'); 17 18 vector<string> v2; 19 20 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 21 string s; 22 getline(cin, s); 23 v2.push_back(s); 24 } 25 cout << "output v2: " << endl; 26 output(v2); 27 cout << endl; 28 } 29 } 30 31 int main() { 32 cout << "测试: 使用函数getline()多组输入字符串" << endl; 33 test(); 34 }
运行测试截图

问题2
运行测试截图
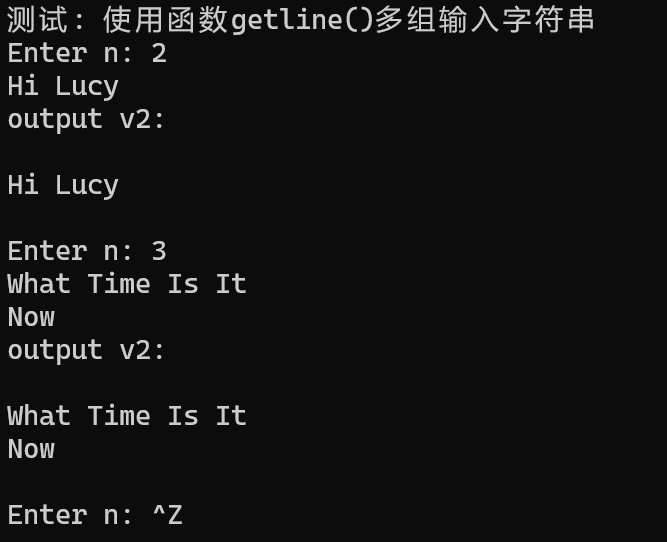
cin.ignore(numeric_limits<streamsize>::max(), '\n'); 的用途是为了清除(忽略)输入缓冲区中直到下一个换行符(\n)为止的所有字符。
实验任务5

1 #ifndef GRM_HPP 2 #define GRM_HPP 3 4 template <typename T> 5 class GameResourceManager { 6 private: 7 T resource; 8 9 public: 10 // 带参数的构造函数,初始化当前资源数量 11 GameResourceManager(T initial_resource) : resource(initial_resource) {} 12 13 // 获取当前的资源数量 14 T get() const { 15 return resource; 16 } 17 18 // 更新当前的资源数量(增加、减少),当资源数量减少到<0时,则归0 19 void update(T delta) { 20 resource += delta; 21 if (resource < 0) { 22 resource = 0; 23 } 24 } 25 }; 26 27 #endif // GRM_HPP

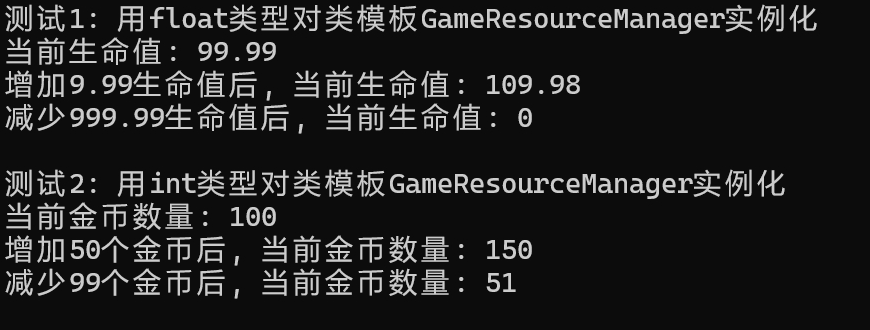
1 #include "grm.hpp" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 7 void test1() { 8 GameResourceManager<float> HP_manager(99.99); 9 cout << "当前生命值: " << HP_manager.get() << endl; 10 HP_manager.update(9.99); 11 cout << "增加9.99生命值后, 当前生命值: " << HP_manager.get() << endl; 12 HP_manager.update(-999.99); 13 cout <<"减少999.99生命值后, 当前生命值: " << HP_manager.get() << endl; 14 } 15 16 void test2() { 17 GameResourceManager<int> Gold_manager(100); 18 cout << "当前金币数量: " << Gold_manager.get() << endl; 19 Gold_manager.update(50); 20 cout << "增加50个金币后, 当前金币数量: " << Gold_manager.get() << endl; 21 Gold_manager.update(-99); 22 cout <<"减少99个金币后, 当前金币数量: " << Gold_manager.get() << endl; 23 } 24 25 26 int main() { 27 cout << "测试1: 用float类型对类模板GameResourceManager实例化" << endl; 28 test1(); 29 cout << endl; 30 31 cout << "测试2: 用int类型对类模板GameResourceManager实例化" << endl; 32 test2(); 33 }
运行测试截图
实验任务6

1 #ifndef INFO_HPP 2 #define INFO_HPP 3 4 #include <string> 5 #include <iostream> 6 7 class Info { 8 private: 9 std::string nickname; 10 std::string contact; 11 std::string city; 12 int n; // 预定参加人数 13 14 public: 15 // 带参数的构造函数 16 Info(const std::string& nick, const std::string& cont, const std::string& cit, int num) 17 : nickname(nick), contact(cont), city(cit), n(num) {} 18 19 // 显示信息 20 void display() const { 21 std::cout << "昵称: " << nickname << "\n" 22 << "联系方式: " << contact << "\n" 23 << "所在城市: " << city << "\n" 24 << "预定参加人数: " << n << "\n"; 25 } 26 27 // 获取预定参加人数 28 int getNumber() const { 29 return n; 30 } 31 }; 32 33 #endif // INFO_HPP

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <sstream> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include "info.hpp" 6 7 int main() { 8 const int capacity = 100; // 设定场地容纳人数的上限 9 std::vector<Info> audienceList; // 用于存储所有听众信息的容器 10 int filledCapacity = 0; // 记录已填充的容量 11 12 std::cout << "录入用户预约信息:\n"; 13 std::cout << "昵称 联系方式(email或手机号) 所在城市 预定参加人数:\n"; 14 15 std::string inputLine; 16 while (std::getline(std::cin, inputLine)) { 17 18 if (std::cin.eof() && inputLine.empty()) { 19 break; 20 } 21 22 23 if (inputLine.empty()) { 24 continue; // 跳过空行,重新请求输入 25 } 26 27 std::istringstream iss(inputLine); 28 std::string nickname, contact, city; 29 int numberOfPeople; 30 31 // 解析用户输入 32 if (!(iss >> nickname >> contact >> city >> numberOfPeople) || numberOfPeople < 0) { 33 // 注意:这里我们不再将numberOfPeople < 0作为结束输入的条件,而是作为无效输入处理 34 std::cout << "无效输入,请按照格式重新输入:\n"; 35 std::cout << "昵称 联系方式(email或手机号) 所在城市 预定参加人数:\n"; 36 continue; // 跳过当前循环,重新请求输入 37 } 38 39 // 检查预定人数是否超过剩余容量 40 if (numberOfPeople > (capacity - filledCapacity)) { 41 std::string choice; 42 std::cout << "预定人数超过剩余容量,请输入'q'退出预定,或输入'u'更新预定信息:"; 43 std::cin >> choice; 44 if (choice == "q") { 45 break; // 退出预定循环 46 } else if (choice == "u") { 47 continue; // 重新请求输入更新后的预定信息 48 } else { 49 std::cout << "无效选择,请输入'q'退出或'u'更新。\n"; 50 continue; // 无效选择,重新请求输入 51 } 52 } 53 54 // 创建Info对象并添加到列表中 55 audienceList.emplace_back(nickname, contact, city, numberOfPeople); 56 filledCapacity += numberOfPeople; // 更新已填充的容量 57 58 // 检查是否已经达到容量上限 59 if (filledCapacity >= capacity) { 60 break; // 达到上限,退出循环 61 } 62 } 63 64 // 打印所有预约的听众信息 65 std::cout << "\n截止目前,一共有" << filledCapacity << "位听众预约,预约听众信息如下:\n"; 66 for (const auto& info : audienceList) { 67 info.display(); 68 std::cout << "\n"; 69 } 70 71 return 0; 72 }
运行测试截图


实验任务7

1 #ifndef __DATE_H__ 2 #define __DATE_H__ 3 class Date { 4 private: 5 int year; 6 int month; 7 int day; 8 int totalDays; 9 public: 10 Date(int year, int month, int day); 11 int getYear() const { return year; } 12 int getMonth() const { return month; } 13 int getDay() const { return day; } 14 int getMaxDay() const; 15 bool isLeapYear() const { 16 return year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0; 17 } 18 void show() const; 19 20 int distance(const Date& date) const { 21 return totalDays - date.totalDays; 22 } 23 }; 24 #endif //__DATE_H__

1 #include "date.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 using namespace std; 5 namespace { 6 const int DAYS_BEFORE_MONTH[] = { 0, 31, 59, 90, 120, 151, 181, 212, 243, 273, 304, 334, 365 }; 7 } 8 Date::Date(int year, int month, int day) : year(year), month(month), day(day) { 9 if (day <= 0 || day > getMaxDay()) { 10 cout << "Invalid date: "; 11 show(); 12 cout << endl; 13 exit(1); 14 } 15 int years = year - 1; 16 totalDays = years * 365 + years / 4 - years / 100 + years / 400 17 + DAYS_BEFORE_MONTH[month - 1] + day; 18 if (isLeapYear() && month > 2) totalDays++; 19 } 20 int Date::getMaxDay() const { 21 if (isLeapYear() && month == 2) 22 return 29; 23 else 24 return DAYS_BEFORE_MONTH[month]- DAYS_BEFORE_MONTH[month - 1]; 25 } 26 void Date::show() const { 27 cout << getYear() << "-" << getMonth() << "-" << getDay(); 28 }

1 #ifndef __ACCUMULATOR_H__ 2 #define __ACCUMULATOR_H__ 3 #include "date.h" 4 class Accumulator { 5 private: 6 Date lastDate; 7 double value; 8 double sum; 9 public: 10 11 Accumulator(const Date &date, double value) 12 : lastDate(date), value(value), sum(0) { } 13 14 double getSum(const Date &date) const { 15 return sum + value * date.distance(lastDate); 16 } 17 18 void change(const Date &date, double value) { 19 sum = getSum(date); 20 lastDate = date; this->value = value; 21 } 22 23 void reset(const Date &date, double value) { 24 lastDate = date; this->value = value; sum = 0; 25 } 26 }; 27 #endif //__ACCUMULATOR_H__

1 #ifndef __ACCOUNT_H__ 2 #define __ACCOUNT_H__ 3 #include "date.h" 4 #include "accumulator.h" 5 #include <string> 6 class Account { 7 private: 8 std::string id; 9 double balance; 10 static double total; 11 protected: 12 13 Account(const Date &date, const std::string &id); 14 15 void record(const Date &date, double amount, const std::string &desc); 16 17 void error(const std::string &msg) const; 18 public: 19 const std::string &getId() const { return id; } 20 double getBalance() const { return balance; } 21 static double getTotal() { return total; } 22 23 void show() const; 24 }; 25 class SavingsAccount : public Account { 26 private: 27 Accumulator acc; 28 double rate; 29 public: 30 31 SavingsAccount(const Date &date, const std::string &id, double rate); 32 double getRate() const { return rate; } 33 34 void deposit(const Date &date, double amount, const std::string &desc); 35 36 void withdraw(const Date &date, double amount, const std::string &desc); 37 void settle(const Date &date); 38 }; 39 class CreditAccount : public Account { 40 private: 41 Accumulator acc; 42 double credit; 43 double rate; 44 double fee; 45 double getDebt() const { 46 double balance = getBalance(); 47 return (balance < 0 ? balance : 0); 48 } 49 public: 50 51 CreditAccount(const Date &date, const std::string &id, double credit, double rate, double fee); 52 double getCredit() const { return credit; } 53 double getRate() const { return rate; } 54 double getFee() const { return fee; } 55 double getAvailableCredit() const { 56 if (getBalance() < 0) 57 return credit + getBalance(); 58 else 59 return credit; 60 } 61 //瀛樺叆鐜伴噾 62 void deposit(const Date &date, double amount, const std::string &desc); 63 //鍙栧嚭鐜伴噾 64 void withdraw(const Date &date, double amount, const std::string &desc); 65 void settle(const Date &date); //缁撶畻鍒╂伅鍜屽勾璐癸紝姣忔湀1鏃ヨ皟鐢ㄤ竴娆¤鍑芥暟 66 void show() const; 67 }; 68 #endif //__ACCOUNT_H__

1 #include "account.h" 2 #include <cmath> 3 #include <iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 double Account::total = 0; 6 7 Account::Account(const Date &date, const string &id) 8 : id(id), balance(0) { 9 date.show(); cout << "\t#" << id << " created" << endl; 10 } 11 void Account::record(const Date &date, double amount, const string &desc) { 12 amount = floor(amount * 100 + 0.5) / 100; 13 balance += amount; total += amount; 14 date.show(); 15 cout << "\t#" << id << "\t" << amount << "\t" << balance << "\t" << desc << endl; 16 } 17 void Account::show() const { cout << id << "\tBalance: " << balance; } 18 void Account::error(const string &msg) const { 19 cout << "Error(#" << id << "): " << msg << endl; 20 } 21 22 SavingsAccount::SavingsAccount(const Date &date, const string &id, double rate) 23 : Account(date, id), rate(rate), acc(date, 0) { } 24 void SavingsAccount::deposit(const Date &date, double amount, const string &desc) { 25 record(date, amount, desc); 26 acc.change(date, getBalance()); 27 } 28 void SavingsAccount::withdraw(const Date &date, double amount, const string &desc) { 29 if (amount > getBalance()) { 30 error("not enough money"); 31 } else { 32 record(date, -amount, desc); 33 acc.change(date, getBalance()); 34 } 35 } 36 void SavingsAccount::settle(const Date &date) { 37 double interest = acc.getSum(date) * rate 38 / date.distance(Date(date.getYear() - 1, 1, 1)); 39 if (interest != 0) record(date, interest, "interest"); 40 acc.reset(date, getBalance()); 41 } 42 43 CreditAccount::CreditAccount(const Date& date, const string& id, double credit, double rate, double fee) 44 : Account(date, id), credit(credit), rate(rate), fee(fee), acc(date, 0) { } 45 void CreditAccount::deposit(const Date &date, double amount, const string &desc) { 46 record(date, amount, desc); 47 acc.change(date, getDebt()); 48 } 49 void CreditAccount::withdraw(const Date &date, double amount, const string &desc) { 50 if (amount - getBalance() > credit) { 51 error("not enough credit"); 52 } else { 53 record(date, -amount, desc); 54 acc.change(date, getDebt()); 55 } 56 } 57 void CreditAccount::settle(const Date &date) { 58 double interest = acc.getSum(date) * rate; 59 if (interest != 0) record(date, interest, "interest"); 60 if (date.getMonth() == 1) 61 record(date, -fee, "annual fee"); 62 acc.reset(date, getDebt()); 63 } 64 void CreditAccount::show() const { 65 Account::show(); 66 cout << "\tAvailable credit:" << getAvailableCredit(); 67 }

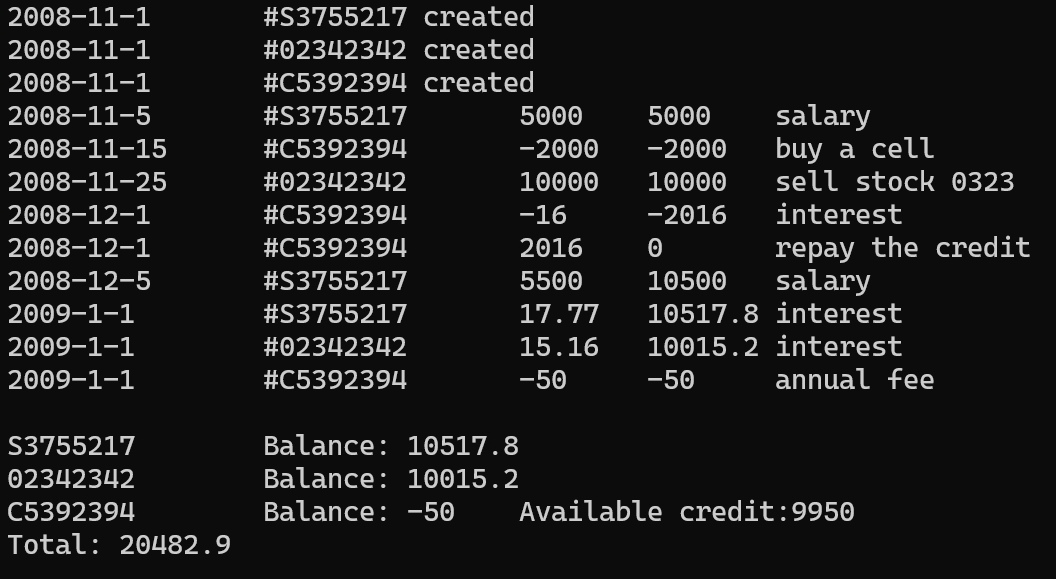
1 #include "account.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() { 5 Date date(2008, 11, 1); 6 7 SavingsAccount sa1(date, "S3755217", 0.015); 8 SavingsAccount sa2(date, "02342342", 0.015); 9 CreditAccount ca(date, "C5392394", 10000, 0.0005, 50); 10 11 sa1.deposit(Date(2008, 11, 5), 5000, "salary"); 12 ca.withdraw(Date(2008, 11, 15), 2000, "buy a cell"); 13 sa2.deposit(Date(2008, 11, 25), 10000, "sell stock 0323"); 14 15 ca.settle(Date(2008, 12, 1)); 16 17 ca.deposit(Date(2008, 12, 1), 2016, "repay the credit"); 18 sa1.deposit(Date(2008, 12, 5), 5500, "salary"); 19 20 sa1.settle(Date(2009, 1, 1)); 21 sa2.settle(Date(2009, 1, 1)); 22 ca.settle(Date(2009, 1, 1)); 23 24 cout << endl; 25 sa1.show(); cout << endl; 26 sa2.show(); cout << endl; 27 ca.show(); cout << endl; 28 cout << "Total: " << Account::getTotal() << endl; 29 return 0; 30 }
运行测试截图




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号