代码随想录算法训练营第十三天 | 第六章二叉树-理论基础,递归遍历,迭代遍历,统一迭代
一、参考资料
二叉树理论基础
文章讲解:https://programmercarl.com/%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html
递归遍历
题目链接/文章讲解/视频讲解:https://programmercarl.com/%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E9%80%92%E5%BD%92%E9%81%8D%E5%8E%86.html
迭代遍历
题目链接/文章讲解/视频讲解:https://programmercarl.com/%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E8%BF%AD%E4%BB%A3%E9%81%8D%E5%8E%86.html
统一迭代
二、二叉树理论基础
https://programmercarl.com/%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html

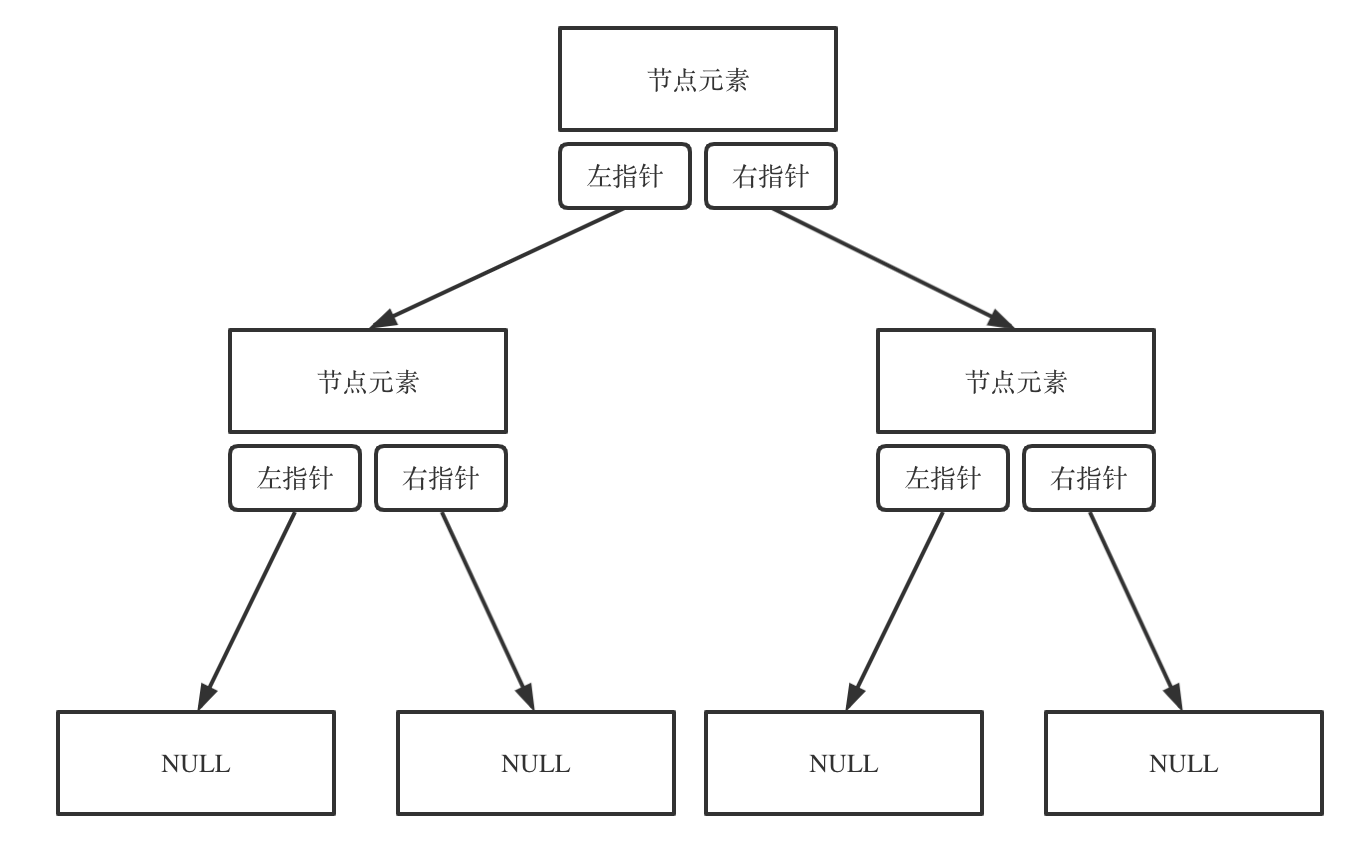
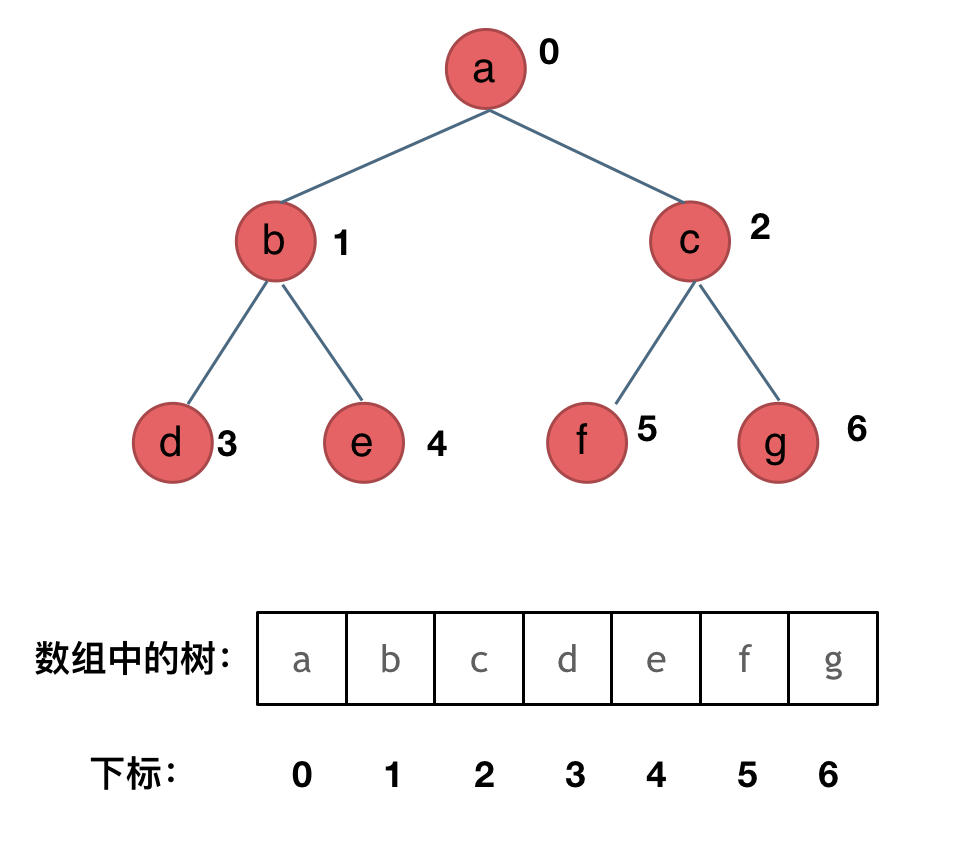
二叉树的存储方式:链式存储和顺序存储。
二叉树主要有两种遍历方式:
深度优先遍历:先往深走,遇到叶子节点再往回走。
广度优先遍历:一层一层的去遍历。
深度优先遍历
前序遍历(递归法,迭代法) 中左右
中序遍历(递归法,迭代法) 左中右
后序遍历(递归法,迭代法) 左右中
广度优先遍历
层次遍历(迭代法)
三、递归遍历
递归算法的三个要素:
1. 确定递归函数的参数和返回值: 确定哪些参数是递归的过程中需要处理的,那么就在递归函数里加上这个参数, 并且还要明确每次递归的返回值是什么进而确定递归函数的返回类型。
2. 确定终止条件: 写完了递归算法, 运行的时候,经常会遇到栈溢出的错误,就是没写终止条件或者终止条件写的不对,操作系统也是用一个栈的结构来保存每一层递归的信息,如果递归没有终止,操作系统的内存栈必然就会溢出。
3. 确定单层递归的逻辑: 确定每一层递归需要处理的信息。在这里也就会重复调用自己来实现递归的过程。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
// version_1:递归方式,声明数组引用,在方法内部进行调用
class Solution {
public:
// 二叉树的前序遍历
void traversal (TreeNode *cur, vector<int> &res) {
// 第一步,确定递归函数的参数和返回值
// 第二步,确定终止条件
// 第三步,确定单层递归的逻辑
if (cur == NULL) return;
res.push_back(cur->val); // 中
traversal(cur->left, res); // 左
traversal(cur->right, res);// 右
}
// 主函数调用前序遍历函数,返回前序遍历的结果数组
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
traversal(root, res);
return res;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
// version_2:递归方式,声明全局数组
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> res;
public:
// 二叉树的前序遍历
void traversal (TreeNode *cur) {
// 第一步,确定递归函数的参数和返回值
// 第二步,确定终止条件
// 第三步,确定单层递归的逻辑
if (cur == NULL) return;
res.push_back(cur->val); // 中
traversal(cur->left); // 左
traversal(cur->right);// 右
}
// 主函数调用前序遍历函数,返回前序遍历的结果数组
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
traversal(root);
return res;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void traversal (TreeNode *cur, vector<int> &res) {
if (cur == NULL) return;
traversal(cur->left, res);
traversal(cur->right, res);
res.push_back(cur->val);
}
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
traversal(root, res);
return res;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void traversal(TreeNode *cur, vector<int> &res) {
if (cur == NULL) return ;
traversal(cur->left, res);
res.push_back(cur->val);
traversal(cur->right, res);
}
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
traversal(root, res);
return res;
}
};四、迭代遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
// version_3:非递归方式
class Solution {
public:
// 注意代码中空节点不入栈
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> result;
if (root == NULL) return result;
st.push(root);
while(!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top(); //中
st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); //右
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); //左
}
return result;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> res;
if(root == NULL) return res;
st.push(root);
while(!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
st.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left) st.push(node->left);
if (node->right) st.push(node->right);
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void swap(int &a, int &b) {
int tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
// 手动实现数组反转
vector<int> reverse(vector<int> res) {
int i = 0;
int j = res.size() - 1;
while (i < j) {
swap(res[i], res[j]);
i++;
j--;
}
return res;
}
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> res;
if(root == NULL) return res;
st.push(root);
while(!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
st.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left) st.push(node->left);
if (node->right) st.push(node->right);
}
// reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
res = reverse(res);
return res;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
// 中序遍历是左中右,先访问的是二叉树顶部的节点,然后一层一层向下访问,直到到达树左面的最底部,再开始处理节点(也就是在把节点的数值放进result数组中),这就造成了处理顺序和访问顺序是不一致的。那么在使用迭代法写中序遍历,就需要借用指针的遍历来帮助访问节点,栈则用来处理节点上的元素。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur != NULL || !st.empty()) {
if (cur != NULL) { // 指针来访问节点,访问到最底层
st.push(cur); // 将访问的节点放进栈
cur = cur->left; // 左
} else {
cur = st.top(); // 从栈里弹出的数据,就是要处理的数据(放进result数组里的数据)
st.pop();
result.push_back(cur->val); // 中
cur = cur->right; // 右
}
}
return result;
}
};五、统一迭代
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
// version_4:非递归方式 —— 统一迭代法
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> res;
if (root != NULL) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop();
if (node->right) st.push(node->right);
if (node->left) st.push(node->left);
st.push(node);
st.push(NULL);
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
}
}
return res;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
// version_4:非递归方式 —— 统一迭代法
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root != NULL) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop(); // 将该节点弹出,避免重复操作,下面再将右中左节点添加到栈中
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 添加右节点(空节点不入栈)
st.push(node); // 添加中节点
st.push(NULL); // 中节点访问过,但是还没有处理,加入空节点做为标记。
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 添加左节点(空节点不入栈)
} else { // 只有遇到空节点的时候,才将下一个节点放进结果集
st.pop(); // 将空节点弹出
node = st.top(); // 重新取出栈中元素
st.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
}
}
return res;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur != NULL || !st.empty()) {
if (cur != NULL) {
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
} else {
cur = st.top();
st.pop();
res.push_back(cur->val);
cur = cur->right;
}
}
return res;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> res;
if (root != NULL) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop();
st.push(node);
st.push(NULL);
if (node->right) st.push(node->right);
if (node->left) st.push(node->left);
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
}
}
return res;
}
};补博客!
刷题加油鸭~~






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 29 期(2025年3.1-3.9)
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异