C#线程同步自动重置事件——AutoResetEvent
AutoResetEvent对象用来进行线程同步操作,AutoResetEvent类继承waitHandle类。
AutoResetEvent对象有终止和非终止两种状态,终止状态是线程继续执行,非终止状态使线程阻塞,可以调用set和reset方法使对象进入终止和非终止状态。AutoResetEvent顾名思义,其对象在调用一次set之后会自动调用一次reset,进入非终止状态使调用了等待方法的线程进入阻塞状态。
waitHandle对象的waitone可以使当前线程进入阻塞状态,等待一个信号。直到当前 waitHandle对象收到信号,才会继续执行。
set可以发送一个信号,允许一个或多个因为调用waitone而等待线程继续执行,经实验,如果有多个等待的线程,一次set只能让一个线程继续执行。
reset可以使因为调用waitone而等待线程都进入阻塞状态。
下面的例子是启动了两个线程,用AutoResetEvent对象来让他们阻塞或者继续。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; namespace myTest { class Program { const int numIterations = 5; //initialState 若要一开始就是阻塞的,则设为false,一开始是非阻塞的,则设为true。 static AutoResetEvent myResetEvent = new AutoResetEvent(false); static int number=0; static void Main(string[] args) { Thread myReaderThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(MyReadThreadProc)); myReaderThread.Name = "ReaderThread"; myReaderThread.Start(); Thread myReaderThread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(MyReadThreadProc2)); myReaderThread2.Name = "ReaderThread2"; myReaderThread2.Start(); //myResetEvent.Reset(); // 设为终止状态,让 waitone的线程阻塞 for (int i = 1; i <= numIterations; i++) { Console.WriteLine("Writer thread writing value: {0}", i); number = i; //将事件状态设置为终止状态,允许一个或多个等待线程继续。 myResetEvent.Set(); Thread.Sleep(2000); myResetEvent.Set(); //休息一下,让线程1和2来得及执行 Thread.Sleep(2000); } myReaderThread.Abort(); Console.ReadLine(); } static void MyReadThreadProc() { while (true) { // 阻止当前线程,直到 Threading.waitHandler 收到一次信号 myResetEvent.WaitOne(); Console.WriteLine("Thread1: {0} reading value: {1}", Thread.CurrentThread.Name, number); } } static void MyReadThreadProc2() { while (true) { // 阻止当前线程,直到 Threading.waitHandler 收到一次信号 myResetEvent.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString()); Console.WriteLine("Thread2:{0} reading value: {1}", Thread.CurrentThread.Name, number); } } } }
执行结果:
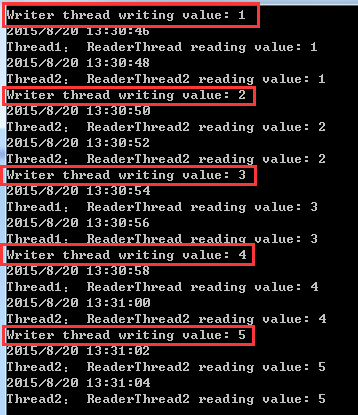
在结果中可以看到,如果有多个线程等待,每次set之后只有一个线程继续执行,且继续执行的线程是随机的。

