C#-多态(十二)
继承概念
多态:即一个接口,多个功能
同一种操作作用于不同的对象,可以有不同的解释,产生不同的执行结果
多态性可以是静态的或动态的。在静态多态性中,函数的响应是在编译时发生的。在动态多态性中,函数的响应是在运行时发生的
静态多态性
在静态多态性中,函数的响应是在编译时发生的
父类中如果有方法需要子类重写,可以将该方法标记为虚方法
虚方法必须在父类中有实现,空实现也可以
虚方法子类可以重写,也可以不重写
实现静态多态性有两种方法;
函数重载
运算符重载
函数重载
即在同一范围中对同一函数名的多重定义
通过定义函数的传参的不同类型或数量进行区分
在调用函数时,根据传的参数类型和数量判断调用名字相同的那个方法
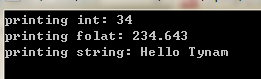
1 using System; 2 3 namespace 函数重载 4 { 5 class printdata 6 { 7 void print(int i) 8 { 9 Console.WriteLine("printing int: {0}", i); 10 } 11 12 void print(double f) 13 { 14 Console.WriteLine("printing folat: {0}", f); 15 } 16 17 void print(string s) 18 { 19 Console.WriteLine("printing string: {0}", s); 20 } 21 22 static void Main(string[] args) 23 { 24 printdata p = new printdata(); 25 26 // 调用 print 来打印整数 27 p.print(34); 28 29 // 调用 print 来打印浮点数 30 p.print(234.643); 31 32 // 调用 print 来打印字符串 33 p.print("Hello Tynam"); 34 35 Console.ReadKey(); 36 37 } 38 } 39 }
运行结果
· 
运算符重载
重定义或重载C#中内置的运算符
通过关键字operator加运算符的符号来定义
与其他函数一样,重载运算符有返回类型和参数列表
1 using System; 2 3 namespace 运算符重载 4 { 5 class Complex 6 { 7 public int x; 8 public int y; 9 public int z; 10 public Complex(int x, int y, int z) 11 { 12 this.x = x; 13 this.y = y; 14 this.z = z; 15 } 16 17 public static Complex operator+(Complex v1,Complex v2) 18 { 19 return new Complex(v1.x + v2.x,v1.y + v2.y,v1.z + v2.z); 20 } 21 22 public static Complex operator /(Complex v1, Complex v2) 23 { 24 return new Complex(v1.x / v2.x, v1.y / v2.y, v1.z / v2.z); 25 } 26 } 27 28 class Program 29 { 30 static void Main(string[] args) 31 { 32 Complex v1 = new Complex(1,20,31); 33 Complex v2 = new Complex(5,6,7); 34 Complex v3 = v1 + v2; 35 Complex v4 = v1 / v2; 36 Console.WriteLine("x is {0} ; y is {1} ; z is {2}", v3.x, v3.y, v3.z); 37 Console.WriteLine("x is {0} ; y is {1} ; z is {2}", v4.x, v4.y, v4.z); 38 Console.ReadKey(); 39 } 40 } 41 }
运行结果
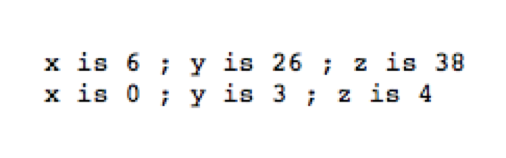
可重载和不可重载运算符
可以被重载的一元运算符:+、 -、 !、~、++、--
可以被重载的二元运算符:+、 -、 *、 /、 %
可以被重载的比较运算符:==、!=、<、>、<=、>=
不能被直接重载的条件逻辑运算符:&&、||
不能被重载的赋值运算符:+=、-=、*=、/=、 %=
不能被重载的其他运算符:=、 .、 ?:, ->、 new、 is、sizeof、typeof
动态多态性
在动态多态性中,函数的响应是在运行时发生的
使用关键字abstract创建抽象类,用于提供接口的部分类的实现
当一个派生类继承自该抽象类时,实现即完成
抽象类包含抽象方法,抽象方法可被派生类实现
抽象方法不允许有方法体的
当一个子类继承抽象类时,必须把父类的所有抽象成员都重写;若子类也是一个抽象类,可以不写
子类重写父类的方法,参数和返回值必须跟父类一样
抽象方法不能用static修饰
抽象类是有构造函数的,虽然不能被实例化
抽象类标记abstract,不能有任何实现,不能有方法体
1 using System; 2 3 namespace 动态多态性 4 { 5 abstract class Shape 6 { 7 public abstract int area(); 8 } 9 10 class Rectangle : Shape 11 { 12 private int length; 13 private int width; 14 15 public Rectangle(int a = 0, int b = 0) 16 { 17 length = a; 18 width = b; 19 } 20 21 public override int area() 22 { 23 return (width * length); 24 } 25 } 26 27 class RectangleTester 28 { 29 static void Main(string[] args) 30 { 31 Rectangle r = new Rectangle(2, 4); 32 double a = r.area(); 33 Console.WriteLine("RectangleArea is: {0}",a); 34 Console.ReadKey(); 35 } 36 } 37 38 }
运行结果
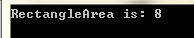


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号