super详解
1.super和this的区别
super调用的是父类的属性或方法,this是调用当前类的属性或者方法。 (1)super和this关于属性的调用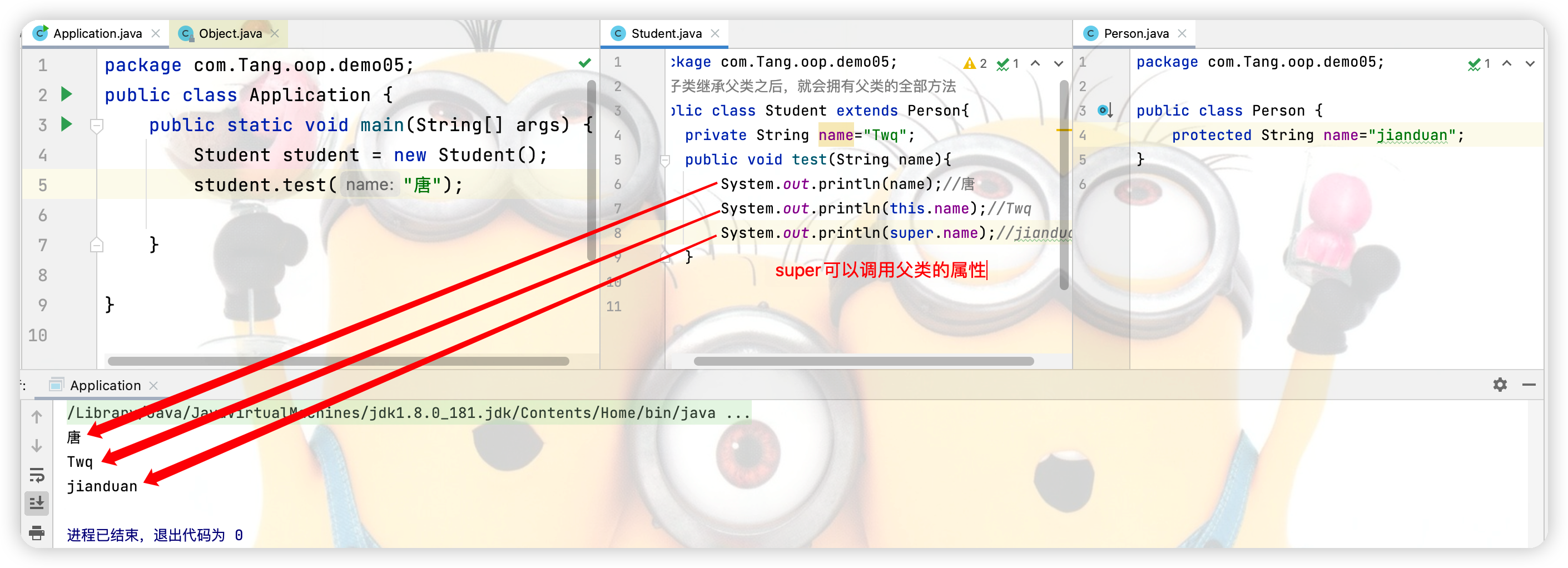
(2)super和this关于方法的调用
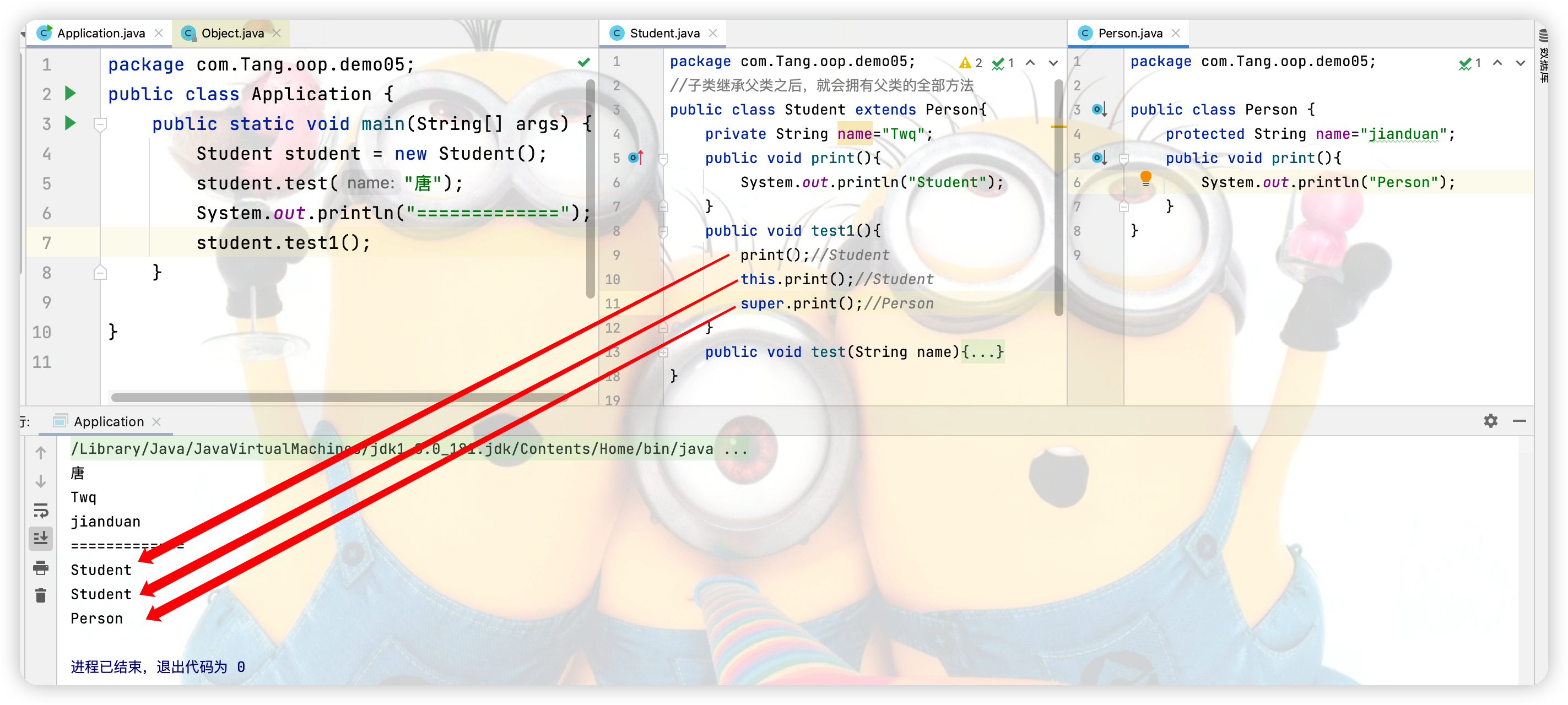
(3)代表的对象不同:
this:代表本身调用者这个对象
super:代表父类对象的引用
(4)使用前提条件不同:
this:在没有继承关系中也可以使用
super:只能在继承条件下才可以使用
(5)构造方法:
this:默认调用本类的构造器
super:默认调用的是父类的构造器
2.构造器在继承中的调用顺序
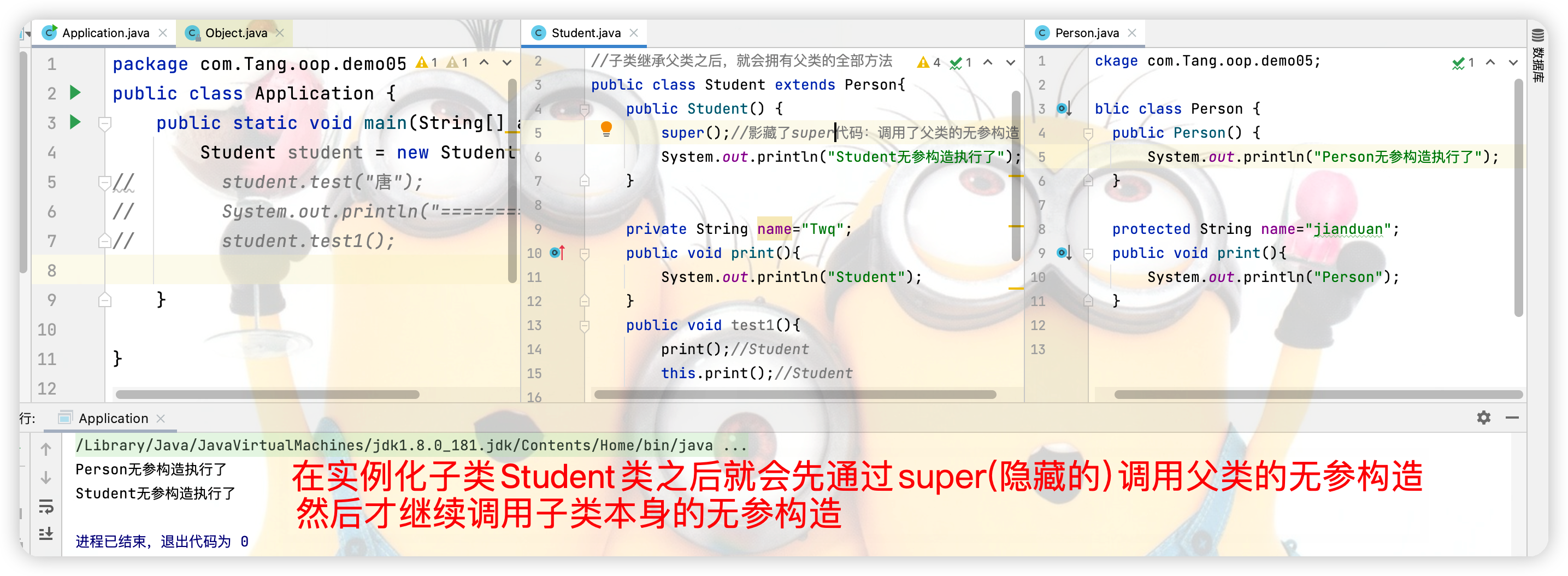
3.有参无参在继承中的注意点
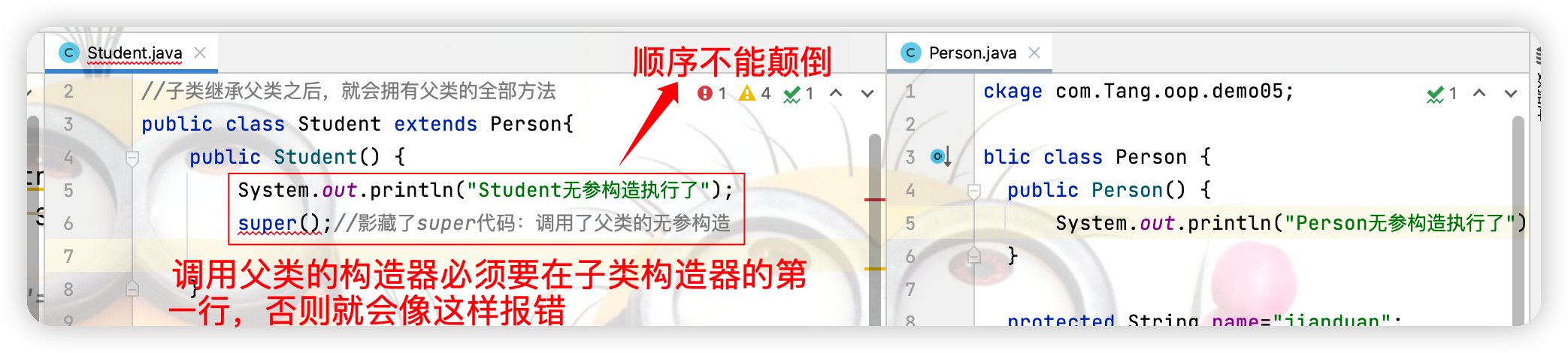
下图子类无参构造报错的原因是:当父类写了有参构造器而没有显示定义无参构造器,则父类的有参构造器会自动干掉其无参构造器,而子类无参构造器在使用前会先调用父类的无参构造器,父类的无参被有参干掉,导致子类也无法使用无参构造器。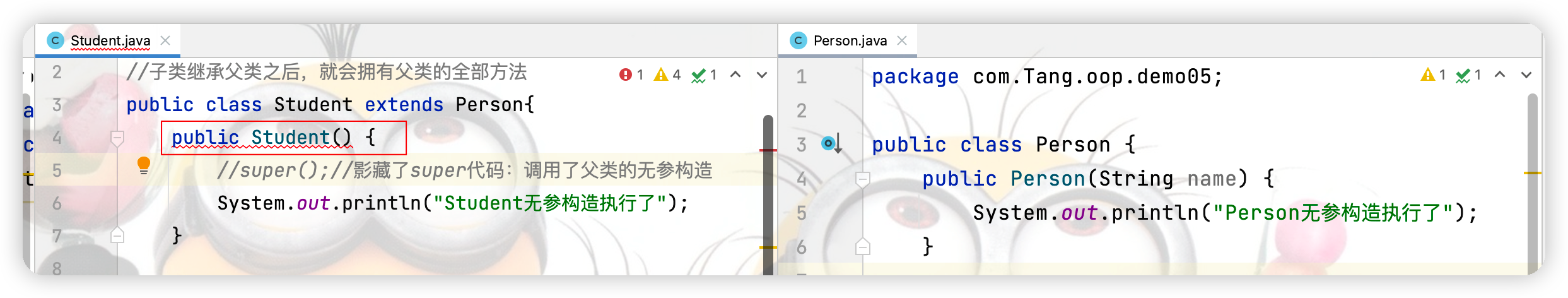
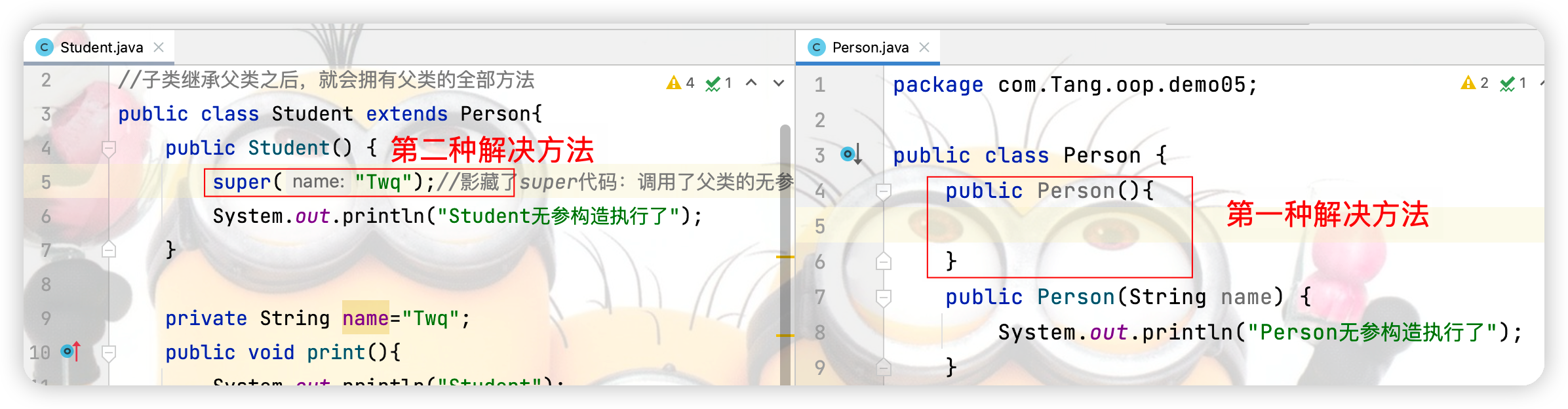
以上错误有两种解决方法:
(1)父类中重写了有参构造器之后,显示定义无参构造器
(2)在子类中调用父类的有参构造即可。如下图:
注:若在子类中不显示写super则默认调用的是无参构造,在父类重写有参构造器的前提下,想要不报错,父类中必须显示定义无参构造器
4.super在使用时的注意点
(1)当super调用父类的构造方法时必须在子类构造方法的第一行。 (2)super只能出现在子类的方法或构造方法中。 (3)super和this不能同时调用构造方法,因为这两都必须要在构造方法的第一行,因此不能同时在构造方法中使用。点击查看代码
package com.Tang.oop.demo05;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
student.test("唐");
System.out.println("=============");
student.test1();
}
}
package com.Tang.oop.demo05;
//子类继承父类之后,就会拥有父类的全部方法
public class Student extends Person{
public Student() {
super("Twq");//影藏了super代码:调用了父类的无参构造
System.out.println("Student无参构造执行了");
}
private String name="Twq";
public void print(){
System.out.println("Student");
}
public void test1(){
print();//Student
this.print();//Student
super.print();//Person
}
public void test(String name){
System.out.println(name);//唐
System.out.println(this.name);//Twq
System.out.println(super.name);//jianduan
}
}
package com.Tang.oop.demo05;
public class Person {
public Person(){
}
public Person(String name) {
System.out.println("Person无参构造执行了");
}
protected String name="jianduan";
public void print(){
System.out.println("Person");
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号