堆排序、冒泡、选择、插入、归并、希尔等排序算法的Python实现
先引用这哥们的博客:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41239584/article/details/82193879
一,冒泡排序
时间复杂度:O(n2)
稳定性:稳定
冒泡排序我就不多讲了,大体上就是比较相邻的两个数,每次把较大的数沉底。流程图大致上如下:
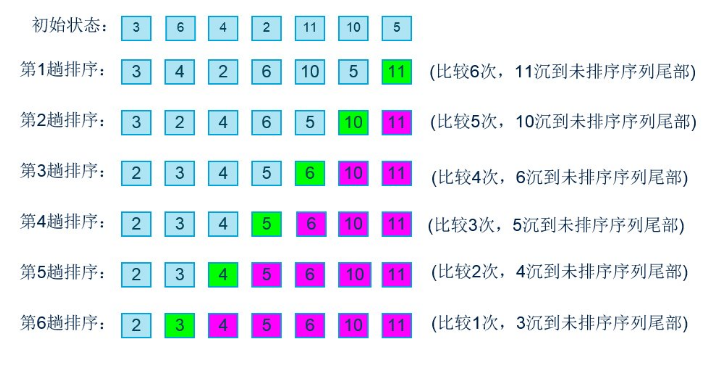
图是截得别人的,只是说明一下,代码没有参看别人的,写的不好,有更好的写法可以一起探讨。下面是代码:
1 def bubble(list): 2 #print(list) 3 for index in range(1,len(list)): #比较6趟 4 print(" index: %d" %index) 5 for index2 in range(len(list)-1,0,-1): 6 print("index2 = %d:" %index2) 7 if list[len(list) - index2-1] > list[len(list) - index2]: 8 temp = list[len(list) - index2-1] 9 list[len(list) - index2 - 1] = list[len(list) - index2] 10 list[len(list) - index2] = temp 11 print(list) 12 list = [3, 6, 4, 2, 11, 10, 5,12,1,7,10] 13 bubble(list)
这里添加了新的解法(2019.6.25):
''' 若list长度为n则迭代n-1次,每次迭代只要有前面大于后面便交换 ''' def buble_sort(list): n = 1 while len(list)-n: for i in range(len(list)-1): if list[i] > list[i+1]: list[i],list[i+1] = list[i+1],list[i] n +=1 print(n-1,":",list) l = [3,6,4,2,11,10,5,1] buble_sort(l)
=================再精简一下===================
def bubble(list):
for i in range(len(list)-1):
for j in range(len(list)-1):
if list[j] > list[j+1]:
list[j + 1],list[j] =list[j], list[j + 1]
print(list)
bubble([3, 6, 4, 2, 11, 10, 5,20])
二,选择排序
时间复杂度:O(n2)
稳定性:不稳定
如:8,9,8,6,7中第四个数6位最小的,将与第一个8交换,这时候第一个8就变为了第二个了,因此不稳定。
选择排序大体上就是每次在列表中找出最小的数,拿出来,然后再把拿出最小值后的列表在找最小数,就是这个思路。如图:

1 def xuanze(list): 2 list2 = [] 3 for index in range(1,len(list)): 4 print("第 %d 次排序list,list2分别为:" %index) 5 min = list[0] #最小值 6 for i in list: #这里的i是里面的数值,而不是序号,print(i)可验证 7 #print(i) 8 if i < min: 9 min = i 10 #print(list.index(min)) #知道值求位置 11 locate = list.index(min) #最小值的序号 12 temp = list[0] #以下三行是交换 13 list[0] = list[locate] 14 list[locate] = temp 15 16 print(list) 17 list2.append(list[0]) 18 list.remove(list[0]) 19 '''当交换位置后的list第一个值被remove出去后, 20 此时的list是[56,80,91,20]了,依此类推,这里是 21 本算法利用list最好玩的地方,可以少写一个for''' 22 print(list2) 23 24 print("最终的list2:") 25 list2.append(list[0]) 26 print(list2) 27 if __name__ == '__main__': 28 list = [56,12,80,91,20,33,89,99] 29 xuanze(list)
17:06:26 2018-05-24
这里添加了新的解法(2019.6.25):
def selection_sort(list): new_list = [] while len(list): min = list[0] for i in range(0,len(list)): if list[i] < min: min= list[i] new_list.append(min) list.remove(min) print(new_list) l = [10,6,7,11,8,3] selection_sort(l)
三,插入排序
时间复杂度:O(n2)
稳定性:稳定
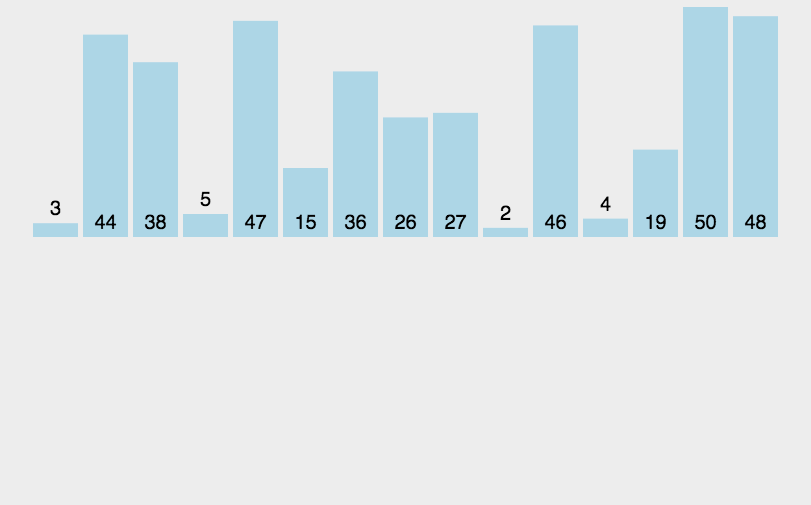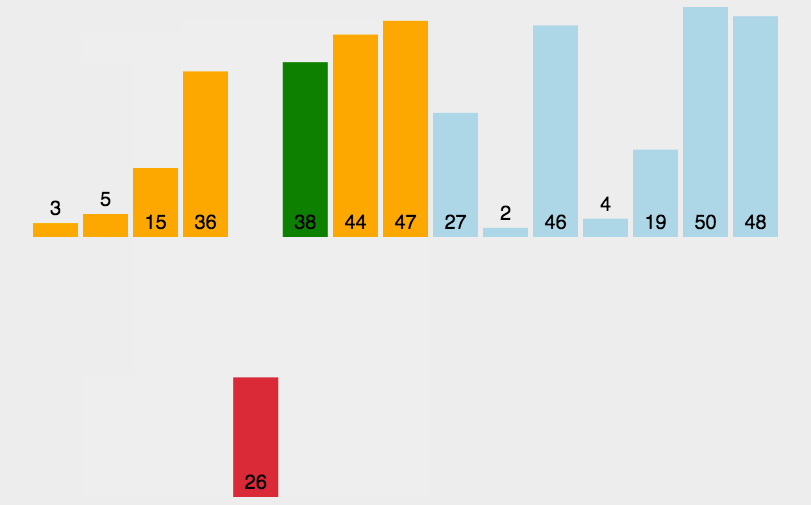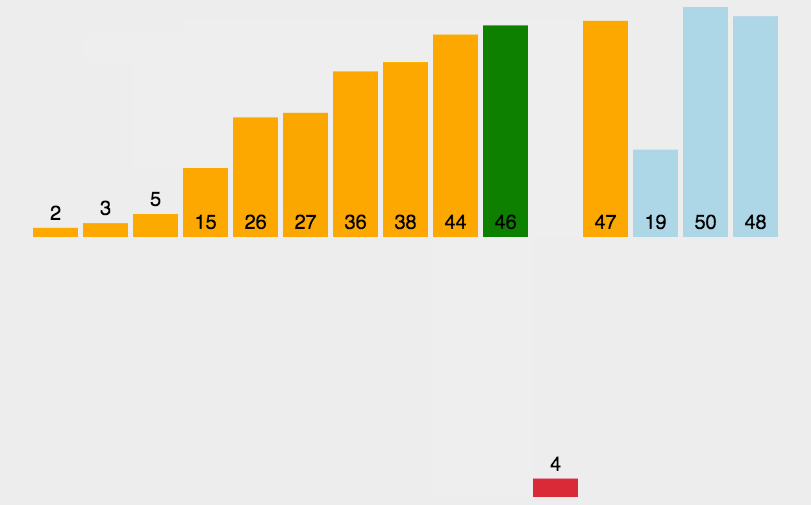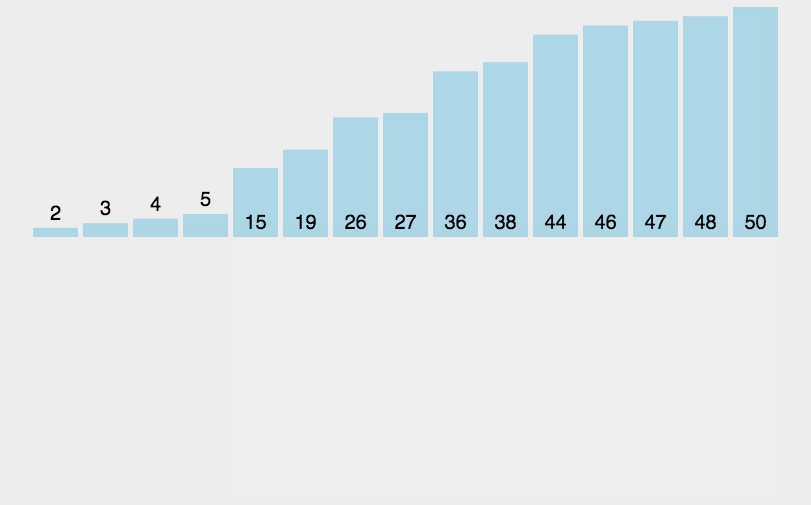
基本就是这个样子吧,看示意图能看明白,不再赘述。代码如下:
1 def charu(list): 2 num = len(list) 3 for i in range(1,num): 4 for j in range(0,i): 5 print("i=",i,"j=",j," list[i]=",list[i],"list[j]=",list[j]) 6 if list[i] < list[j]: 7 temp = list[i] 8 list.remove(list[i]) 9 list.insert(j,temp) 10 print(list) 11 break 12 list = [3,44,39,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48] #13个数 13 charu(list)
这里添加了新的解法(2019.6.26):
def insertion_sort(list): for i in range(1,len(list)): for j in range(0,i): temp = list[i] if temp < list[j]: list.pop(i) list.insert(j,temp) return list l = [3,44,39,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48] insertion_sort(l)
四,归并排序
O(n*logn),稳定
归并用到了分治的思想。
def merge_sort(list): if len(list) == 1: return list else: mid = len(list)//2 #地板除 left = list[:mid] right = list[mid:] return merge(left,right) #合并两个排好的list def merge(left,right): left.extend(right) sort_list = sorted(left) return sort_list result = merge_sort([9,1,7,3,4,8,2,6]) print(result)
五,快速排序
O(n*logn) 不稳定
引用:https://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/6684558
''' 基本思想: 1.先从数列中取出一个数作为基准数。 2.分区过程,将比这个数大的数全放到它的右边,小于或等于它的数全放到它的左边。 3.再对左右区间重复第二步,直到各区间只有一个数。 ''' def quick_sort(list): if len(list) == 1: return list else: base = list[0] left = [] right = [] for i in list: if i>=base: right.append(i) else: left.append(i) return combine(left,right) #合并两个排好的list def combine(left,right): left.extend(right) sort_list = sorted(left) return sort_list l = [5,1,7,3,4,45,0,2,6] result = quick_sort(l) print(result)
====================================
def quicksort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
pivot = arr[len(arr) // 2]
left = [x for x in arr if x < pivot]
middle = [x for x in arr if x == pivot]
right = [x for x in arr if x > pivot]
return quicksort(left) + middle + quicksort(right)
print(quicksort([3,6,8,10,1,2,1]))
六,希尔排序
不稳定
def shell_sort(list,gap):
#导入的list的长度
length = len(list)
#gap为0则停止,不为0则继续迭代
if gap == 0:
return list
else:
#list_container用于装按照gap打散(分组)后的列表
list_container = []
for i in range(0,gap):
temp_list = []
for j in range(i,length,gap):
temp_list.append(list[j])
# print(temp_list)
list_sep = sort(temp_list)
list_container.append(list_sep)
print("按照对应gap划分出的列表:",list_container)
sorted_list = sort_all_list(list_container, length, gap)
print("调用sort_all_list后:",sorted_list)
#gap减小以达到最终迭代终止条件
gap = gap//2
#最后调用自己以迭代
return shell_sort(sorted_list, gap)
def sort(list1):
return sorted(list1)
#把按照gap打散(分组)后的列表排到一个理好顺序的list中
def sort_all_list(list2,length,gap):
new_list = []
for mm in range(length):
new_list.append(0)
#把l2每个数组按照每隔gap组成一个new_list
for list in list2:
N = list2.index(list)
for i in range(N,length,gap):
num = int((i-N)/gap)
new_list[i] = list[num]
# print("sort_all_list:",new_list)
return new_list
l = [9,1,3,6,87,12,64,9,11,65,7]
#初始gap
if len(l) % 2 == 0:
gap = int(len(l) / 2)
else:
gap = int((len(l) - 1) / 2)
shell_sort(l,gap)
七,堆排序
堆排序是不稳定的,因为建堆后的堆顶要和最后一个数交换。但我这里的稳定性这里是稳定的,因为第我没用这个方法,而是在42pop出最大值,然后再把pop后的list进行建堆,再pop,所以不用交换。后期我会改进。
1 def adjuste_tree(non_leaf,list): 2 #先验证non_leaf是否有右子节点。若相等则有右子树,否则没有。 还得分大于3和小于等于3. 3 if list[non_leaf] < list[2 * non_leaf + 1] or list[non_leaf] < list[2 * non_leaf + 2]: 4 if (list[2 * non_leaf + 1] > list[2 * non_leaf + 2]): 5 list[non_leaf], list[2 * non_leaf + 1] = list[2 * non_leaf + 1], list[non_leaf] 6 # print("Left:", list[non_leaf], [2 * non_leaf + 1], [2 * non_leaf + 2]) 7 elif (list[2 * non_leaf + 1] < list[2 * non_leaf + 2]): 8 list[non_leaf], list[2 * non_leaf + 2] = list[2 * non_leaf + 2], list[non_leaf] 9 # print("Right:",list[non_leaf],[2 * non_leaf + 1],[2 * non_leaf + 2]) 10 return list 11 12 def Heap_sort(list): 13 #1,建堆,以找出最大值(因为不管怎样都能找出最大根,即使下面排的不对) 14 #第一个非叶子节点为len/2-1 15 n = int(len(list) / 2 - 1) 16 for non_leaf in range(n,-1,-1): 17 #若节点小于他的子节点。 18 adjuste_tree(non_leaf, list) 19 20 #2,取出根再调整堆 21 22 #3,重复2直到只剩下一个数 23 24 list =[4,1,3,2,16,9,10,14,8,7] 25 Heap_sort(list)
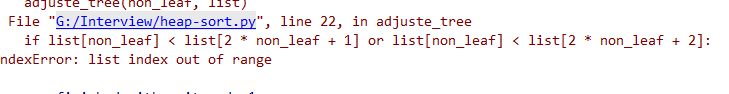
这里的错误是因为在第3行没有管它有没右子树,所以我们要加上这一步。
现在,我们吧24行的list随便加一个数使他除叶子节点外都有右节点,经过多次验证,发现得出的结果没问题,因此我们字需要关注他‘第一个非叶子结点’没有右子节点时候的情形:
1 def adjuste_tree(non_leaf, list): 2 # 先验证最后一个非叶子节点是否有右子节点。 3 # 若相等则有右子树,否则没有。 4 # 还得分大于3和小于等于3. 5 6 if non_leaf == int(len(list)/2-1): #是否是最后一个非叶子节点 7 if 2*non_leaf+2 == len(list)-1: #这个最后一个非叶子节点是否有右子节点 8 if list[non_leaf] < list[2 * non_leaf + 1] or list[non_leaf] < list[2 * non_leaf + 2]: 9 if (list[2 * non_leaf + 1] > list[2 * non_leaf + 2]): 10 list[non_leaf], list[2 * non_leaf + 1] = list[2 * non_leaf + 1], list[non_leaf] 11 # print("Left:", list[non_leaf], [2 * non_leaf + 1], [2 * non_leaf + 2]) 12 elif (list[2 * non_leaf + 1] < list[2 * non_leaf + 2]): 13 list[non_leaf], list[2 * non_leaf + 2] = list[2 * non_leaf + 2], list[non_leaf] 14 # print("Right:",list[non_leaf],[2 * non_leaf + 1],[2 * non_leaf + 2]) 15 else: #进入这里证明没有右子节点 16 if list[non_leaf] < list[2*non_leaf+1]: #这个最后一个非叶子节点是否比它的左子节点大 17 list[2 * non_leaf + 1], list[non_leaf] = list[non_leaf], list[2 * non_leaf + 1] 18 else: 19 if list[non_leaf] < list[2 * non_leaf + 1] or list[non_leaf] < list[2 * non_leaf + 2]: 20 if (list[2 * non_leaf + 1] > list[2 * non_leaf + 2]): 21 list[non_leaf], list[2 * non_leaf + 1] = list[2 * non_leaf + 1], list[non_leaf] 22 # print("Left:", list[non_leaf], [2 * non_leaf + 1], [2 * non_leaf + 2]) 23 elif (list[2 * non_leaf + 1] < list[2 * non_leaf + 2]): 24 list[non_leaf], list[2 * non_leaf + 2] = list[2 * non_leaf + 2], list[non_leaf] 25 # print("Right:",list[non_leaf],[2 * non_leaf + 1],[2 * non_leaf + 2]) 26 print(non_leaf,list) 27 28 def Heap_sort(list): 29 #1,建堆,以找出最大值(因为不管怎样都能找出最大根,即使下面排的不对) 30 #第一个非叶子节点为len/2-1 31 n = int(len(list) / 2 - 1) 32 for non_leaf in range(n,-1,-1): 33 #若节点小于他的子节点。 34 adjuste_tree(non_leaf, list) 35 36 #2,取出根再调整堆 37 38 #3,重复2直到只剩下一个数 39 40 list = [4,1,3,2,16,9,10,14,8,7] 41 Heap_sort(list)
这样一次建堆就一定能把最大值找出来,但是上层改变之后下层还是没变,不影响最后结果。
最后结果:
1 #调整树的三个节点,不能调整调整后的下层节点,但不影响结果 2 def adjuste_tree(non_leaf, list): 3 # 一定注意得先验证最后一个非叶子节点是否有右子节点。 4 if len(list) == 1 or len(list) == 0: 5 return list 6 else: 7 if non_leaf == int(len(list)/2-1): #是否是最后一个非叶子节点 8 if 2*non_leaf+2 == len(list)-1: #这个最后一个非叶子节点是否有右子节点 9 if list[non_leaf] < list[2 * non_leaf + 1] or list[non_leaf] < list[2 * non_leaf + 2]: 10 if (list[2 * non_leaf + 1] > list[2 * non_leaf + 2]): 11 list[non_leaf], list[2 * non_leaf + 1] = list[2 * non_leaf + 1], list[non_leaf] 12 # print("Left:", list[non_leaf], [2 * non_leaf + 1], [2 * non_leaf + 2]) 13 elif (list[2 * non_leaf + 1] < list[2 * non_leaf + 2]): 14 list[non_leaf], list[2 * non_leaf + 2] = list[2 * non_leaf + 2], list[non_leaf] 15 # print("Right:",list[non_leaf],[2 * non_leaf + 1],[2 * non_leaf + 2]) 16 else: #进入这里证明没有右子节点 17 if list[non_leaf] < list[2*non_leaf+1]: #这个最后一个非叶子节点是否比它的左子节点大 18 list[2 * non_leaf + 1], list[non_leaf] = list[non_leaf], list[2 * non_leaf + 1] 19 else: 20 if list[non_leaf] < list[2 * non_leaf + 1] or list[non_leaf] < list[2 * non_leaf + 2]: 21 if (list[2 * non_leaf + 1] > list[2 * non_leaf + 2]): 22 list[non_leaf], list[2 * non_leaf + 1] = list[2 * non_leaf + 1], list[non_leaf] 23 elif (list[2 * non_leaf + 1] < list[2 * non_leaf + 2]): 24 list[non_leaf], list[2 * non_leaf + 2] = list[2 * non_leaf + 2], list[non_leaf] 25 26 def Heap_sort(list): 27 #1,建堆,以找出最大值 28 #第一个非叶子节点为len/2-1 29 n = int(len(list) / 2 - 1) 30 for non_leaf in range(n,-1,-1): #根节点序号为0时也要排序 31 #若节点小于他的子节点。 32 adjuste_tree(non_leaf, list) 33 34 if __name__ == '__main__': 35 list = [4, 1, 3, 2, 16, 9, 10, 14, 8, 7] 36 soted_heap_list = [] 37 38 #2,取出根再调整堆 39 #3,重复2直到只剩下一个数 40 while(len(list)): 41 Heap_sort(list) 42 soted_heap_list.append(list.pop(0)) 43 print(soted_heap_list)
昨天太晚了,没做改进,今天上午来进行了修改,把调整树函数变为递归形式,使他能在换位后改变子节点的位置。
1 #调整树的三个节点,调整调整后的下层节点。 2 def adjuste_tree(heap,root): 3 HeapSize = len(heap) 4 #有右子节点 且 (左节点 > 根 or 右节点 > 根) 5 if 2*root+2 <= len(heap)-1 and (heap[2*root+2] > heap[root] or heap[2*root+1] > heap[root]): 6 if heap[2*root+1] > heap[2*root+2]: 7 heap[2 * root + 1], heap[root] = heap[root], heap[2 * root + 1] 8 adjuste_tree(heap, 2 * root + 1) 9 else: 10 heap[2 * root + 2], heap[root] = heap[root], heap[2 * root + 2] 11 adjuste_tree(heap, 2 * root + 2) 12 # 无右子节点 且 (左节点 > 根) 13 if 2*root+2 <= len(heap) and (heap[2*root+1] > heap[root]): 14 heap[2 * root + 1],heap[root] = heap[root],heap[2 * root + 1] 15 adjuste_tree(heap, 2 * root + 1) 16 17 def Heap_sort(list): 18 #1,建堆,以找出最大值 19 #第一个非叶子节点为len/2-1 20 n = int(len(list) / 2 - 1) 21 for non_leaf in range(n,-1,-1): #根节点序号为0时也要排序 22 #若节点小于他的子节点。 23 adjuste_tree(list,non_leaf) 24 25 if __name__ == '__main__': 26 list = [4, 1, 3, 2, 16, 9, 10, 14, 8, 7] 27 soted_heap_list = [] 28 29 #2,取出根再调整堆 30 #3,重复2直到只剩下一个数 31 while(len(list)): 32 Heap_sort(list) 33 soted_heap_list.append(list.pop(0)) 34 print(soted_heap_list)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号