计算器之策略模式
❶在WinForm里实现策略模式
一、代码实现
Form1代码
namespace szys { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } public static int right = 0; public static int Count = 0; private int t; string path = ".\text1.txt"; int a = 0; private void button5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Count++; StreamWriter baocun1 = File.AppendText("baocun1.txt"); baocun1.WriteLine(textBox1.Text); baocun1.Close(); StreamWriter baocun2 = File.AppendText("baocun2.txt"); baocun2.WriteLine(textBox4.Text); baocun2.Close(); StreamWriter baocun3 = File.AppendText("baocun3.txt"); baocun3.WriteLine(textBox2.Text); baocun3.Close(); richTextBox1.Text += textBox1.Text + textBox4.Text + textBox2.Text + label2.Text + textBox3.Text + "\n"; textBox1.Clear(); textBox4.Clear(); textBox2.Clear(); } private void btnsave_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)//保存已出试题; { SaveFileDialog TxtSaveDialog = new SaveFileDialog(); TxtSaveDialog.Filter = "文本文档(*.txt)|*.txt"; if (File.Exists(path)) { this.richTextBox1.LoadFile(path, RichTextBoxStreamType.PlainText); MessageBox.Show("保存成功", "提示信息", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Asterisk); this.richTextBox1.Clear(); btnsave.Enabled = false; } else { if (TxtSaveDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { this.richTextBox1.SaveFile(TxtSaveDialog.FileName, RichTextBoxStreamType.PlainText); MessageBox.Show("保存成功", "提示信息", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Asterisk); this.richTextBox1.Clear(); btnsave.Enabled = false; button1.Visible = true; } } } private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)//打开试题; { OpenFileDialog TxTOpenDialog = new OpenFileDialog(); TxTOpenDialog.Filter = "文本文档(*.txt)|*.txt"; if (TxTOpenDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { path = TxTOpenDialog.FileName; this.richTextBox2.LoadFile(TxTOpenDialog.FileName, RichTextBoxStreamType.PlainText); btnsave.Enabled = false; button1.Enabled = false; MessageBox.Show("打开成功", "提示信息", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Asterisk); } } private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)//添加算式题; { textBox1.Enabled = false; textBox2.Enabled = false; textBox4.Enabled = false; textBox1.BackColor = Color.Yellow; textBox4.BackColor = Color.Yellow; textBox2.BackColor = Color.Yellow; textBox3.BackColor = Color.Yellow; string[] m = new string[100]; m = File.ReadAllLines("baocun1.txt"); textBox1.Text = m[a]; string[] n = new string[100]; n = File.ReadAllLines("baocun2.txt"); textBox4.Text = n[a]; string[] v = new string[100]; v = File.ReadAllLines("baocun3.txt"); textBox2.Text = v[a]; a++; } private void textBox3_MouseClick(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)//计时; { label3.Text = t.ToString(); timer1.Enabled = true; timer1.Interval = 1000; timer1.Start(); } private void timer1_Tick(object sender, EventArgs e) { t = t + 1; label3.Text = t.ToString(); } private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { MessageBox.Show("一共用时" + label3.Text + "秒"); Form2 frm2 = new Form2(); frm2.ShowDialog(); } private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //调用; szys.celuemoshi.Sub.yunsuanfu clacuter = new szys.celuemoshi.Sub.yunsuanfu(textBox4.Text); int result = clacuter.Calculation(int.Parse(textBox1.Text), int.Parse(textBox2.Text)); if (textBox3.Text==result.ToString()) { MessageBox.Show("恭喜你,小朋友!回答正确!"); right++; Count++; } else { MessageBox.Show("回答错误,继续加油!小朋友"); Count++; } textBox1.Clear(); textBox2.Clear(); textBox3.Clear(); textBox4.Clear(); } } }
Form2代码
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Text; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace szys { public partial class Form2 : Form { public Form2() { InitializeComponent(); } private void Form2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { textBox1.Text = Form1.Count.ToString(); textBox2.Text = Form1.right.ToString(); textBox4.Text = ((Form1.right / (double)(Form1.Count)) * 100).ToString() + "%"; } } }
策略模式代码
namespace szys { class celuemoshi { interface Strategy //定义一个Strategy接口; { int calculate(int n1, int n2);//定义一个方法,用于计算; } class Add : Strategy //定义具体的算法类,实现Strategy接口 { public int calculate(int n1, int n2) { return n1 + n2;; } } class Sub : Strategy { public int calculate(int n1, int n2) { return n1 - n2; ; } class Mul : Strategy { public int calculate(int n1, int n2) { return n1 * n2; ; } } class Div : Strategy { public int calculate(int n1, int n2) { return n1 / n2; ; } } public class yunsuanfu { private Strategy type; public yunsuanfu(string a) { switch (a) { case "+": type = new Add(); break; case "-": type = new Sub(); break; case "*": type = new Mul(); break; case "/": type = new Div(); break; } } public int Calculation(int n1, int n2) { return type.calculate(n1, n2); } } } }
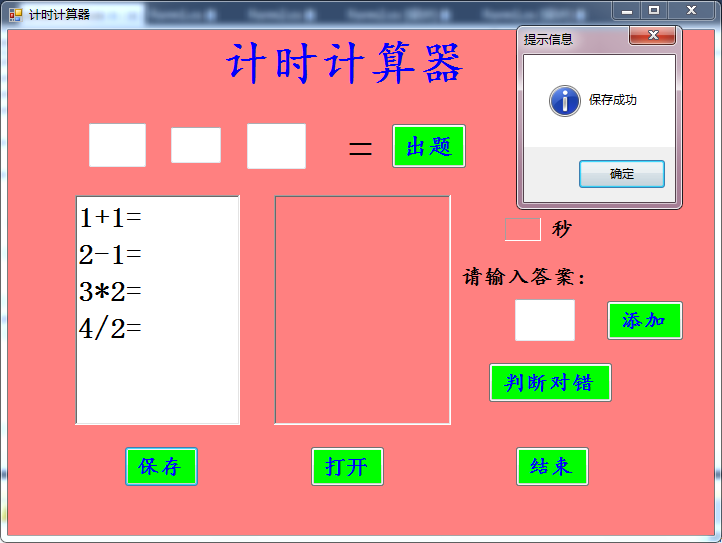
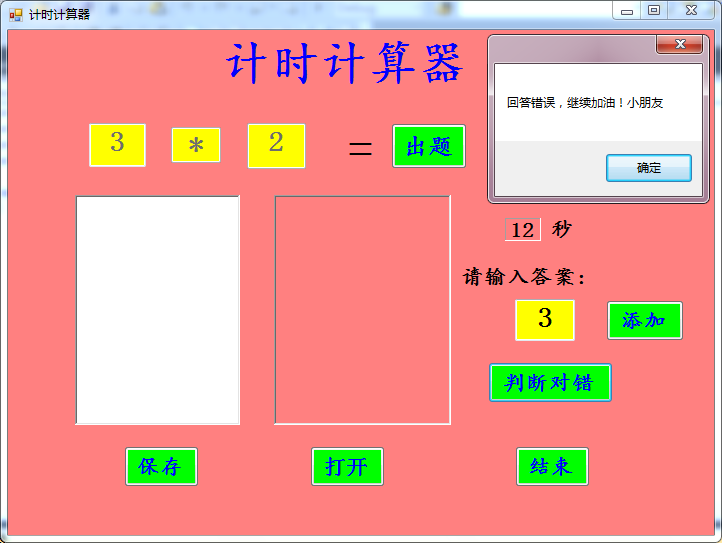
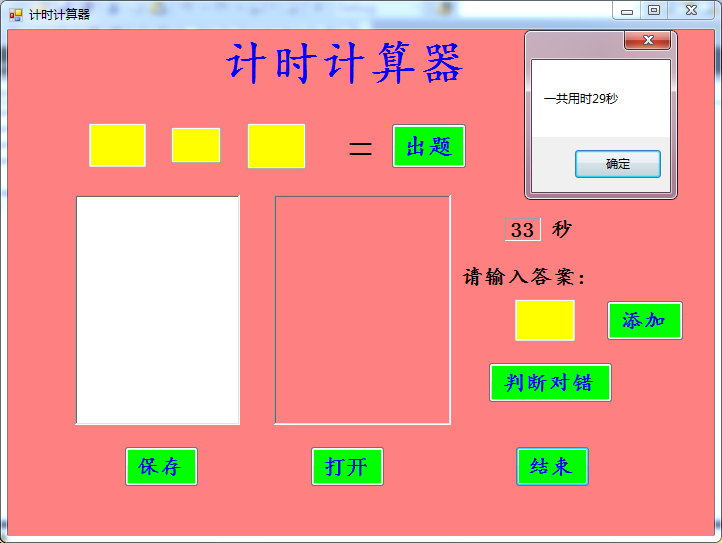
二、测试



❷在ASP.NET里实现策略模式
一、具体代码
策略模式代码
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Web; /// <summary> ///Class1 的摘要说明 /// </summary> public interface Calculator //定义一个接口 { int Cal(int n1, int n2);//定义一个方法,用于计算; } public class Add : Calculator //定义具体的算法类,实现Calculator接口 { public int Cal(int n1, int n2) { int result = 0; result = n1 + n2; return result; } } public class Sub : Calculator { public int Cal(int n1, int n2) { int result = 0; result = n1 - n2; return result; } } public class Mul : Calculator { public int Cal(int n1, int n2) { int result = 0; result = n1 * n2; return result; } } public class Div : Calculator { public int Cal(int n1, int n2) { int result = 0; result = n1 / n2; return result; } } public class Content { private Calculator calculate; public Content(Calculator calculate) { this.calculate = calculate; } public int Cal(int n1, int n2, String m) { return this.calculate.Cal(n1, n2); } }
Default2.aspx.cs代码
public partial class Chapter1_Default2 : System.Web.UI.Page { protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { } int a = 0; private int t; public static int Count=0; public static int right=0; protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Content content = null; int a = int.Parse(TextBox1.Text); int b = int.Parse(TextBox3.Text); string m = TextBox2.Text; switch (m) { case "+": content = new Content(new Add()); break; case "-": content = new Content(new Sub()); break; case "*": content = new Content(new Mul()); break; case "/": content = new Content(new Div()); break; default: break; } string answer = content.Cal(a, b, m).ToString(); if (TextBox4.Text == answer.ToString()) { Label1.Text = ("恭喜你,小朋友!回答正确!"); Label1.ForeColor = Color.Blue; right++; } else { Label1.Text = ("回答错误,继续加油!小朋友"); Label1.ForeColor = Color.Red; } } protected void Button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Count++; StreamWriter baocun1 = File.AppendText("C:\\baocun1.txt"); baocun1.WriteLine(TextBox1.Text); baocun1.Close(); StreamWriter baocun2 = File.AppendText("C:\\baocun2.txt"); baocun2.WriteLine(TextBox2.Text); baocun2.Close(); StreamWriter baocun3 = File.AppendText("C:\\baocun3.txt"); baocun3.WriteLine(TextBox3.Text); baocun3.Close(); ListBox1.Items.Add(TextBox1.Text + TextBox2.Text + TextBox3.Text + "="); TextBox1.Text = ""; TextBox2.Text = ""; TextBox3.Text = ""; } protected void Button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { TextBox1.BackColor = Color.Yellow; TextBox2.BackColor = Color.Yellow; TextBox3.BackColor = Color.Yellow; TextBox4.BackColor = Color.Yellow; TextBox1.Enabled = false; TextBox2.Enabled = false; TextBox3.Enabled = false; string[] m = new string[100]; m = File.ReadAllLines("C:\\baocun1.txt"); TextBox1.Text = m[a]; string[] n = new string[100]; n = File.ReadAllLines("C:\\baocun2.txt"); TextBox2.Text = n[a]; string[] v = new string[100]; v = File.ReadAllLines("C:\\baocun3.txt"); TextBox3.Text = v[a]; a++; } protected void Button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { TextBox1.Text = ""; TextBox2.Text = ""; TextBox3.Text = ""; TextBox4.Text = ""; Label1.Text = ""; } protected void Button5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Label6.Text = "总计"; Label7.Text = "正确"; Label8.Text = "正确率"; Label3.Text = Count.ToString(); Label4.Text = right.ToString(); Label5.Text = ((right / (double)(Count)) * 100).ToString() + "%"; } }
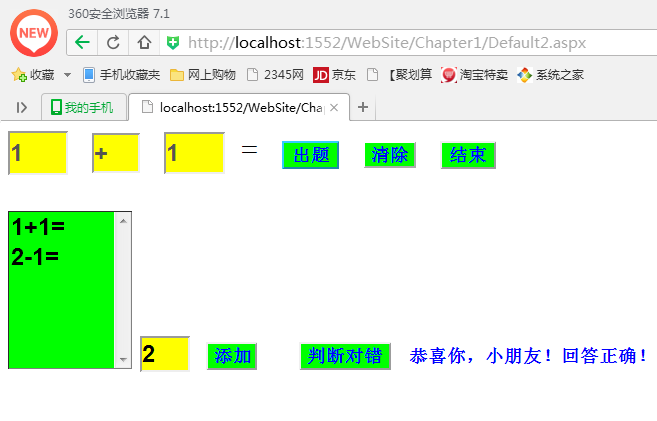
二、测试


三、总结
上课老师给我们讲过策略模式,但还是半懂不懂的,当用策略模式做这个计算器的时候,上网查了很多资料,也看了同学的博客,才对策略模式有了概念:它就是定义了一系列的算法,并将每一个算法封装起来,而且使它们还可以相互替换。它让算法的变化不会影响到使用算法的客户。
首先定义一个Strategy接口,其中定义一个方法,用于计算。
public interface Strategy { public int calculate(int a, int b); }
定义具体的算法类,实现Strategy接口
public class Add: Strategy { public int calculate(int a, int b) { return a + b; } }
定义具体上下文环境,维护Strategy引用
public class Context { private Strategystrategy; public Context(Strategy strategy) { this.strategy = strategy; } public void contextInterface() { strategy.algorithmInterface(); } }
客户端代码.
Context context; context = new Context(new Add()); context.contextInterface(); context = new Context(new Sub()); context.contextInterface(); context = new Context(new Mul()); context.contextInterface(); context = new Context(new Div()); context.contextInterface();
策略模式由下面几项的组成
(1)抽象策略角色: 策略类,通常由一个接口或者抽象类实现。
(2)具体策略角色:包装了相关的算法和行为。
(3)环境角色:持有一个策略类的引用,最终给客户端调用。
使用策略模式的好处就是它简化了单元测试,因为每个算法都有自己的类,可以通过自己的接口单独测试。还避免了程序中使用多重条件语句,使系统更灵活,并易于扩展。




