(C/C++学习)10.C++文件流
说明:C++中的文件流分为三种:文件输入流、文件输出流、文件输入/输出流,其对应的类分别为 ifstream、ofstream 和 fstream 。由这三个类创建类对象,完成对文件的操作。其中文件的操作包括:打开、读写以及关闭。
注意:输入输出流中的输入与输出,是针对程序(也可以说是针对当前进程)来说的,文件的输入指将文件的内容输入到程序中,即读取文件;同理,输出即指将数据从程序中往文件中输出。
一.定义流对象
1 ifstream ifile; //定义一个文件输入流对象 2 ofstream ofile; //定义一个文件输出流对象 3 fstream iofile; //定义一个文件输出/输入流对象
二.文件的打开
1.定义了文件流对象后,就可以利用其成员函数 open()打开需要操作的文件,该成员函数的函数原型为:
1 void open(const unsigned char *filename,int mode,int access=filebuf:openprot);
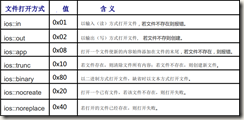
其中:filename 是一个字符型指针,指定了要打开的文件名;mode 指定了文件的打开方式,其值如下表所示;access 指定了文件的系统属性,取默认即可。
打开文件的方式:
在实际使用过程中,可以根据需要将以上打开文件的方式用“|”组合起来。如:
1 ios::in|ios::out|ios::binary 2 表示以二进制读/写方式打开文件
2) 如果未指明以二进制方式打开文件,则默认是以文本方式打开文件。
3) 对于 ifstream 流, mode 参数的默认值为 ios::in,对于 ofstream 流,mode 的默认值为 ios::out|ios::trunc, 对于 fstream 流, mode 的默认值为 ios::int|ios::out|ios::app。
4) 出错处理是通过对类对象进行判断的。若文件打开成功,返回 1,否则返回 0。
如下代码:往文件中写入用户输入的名字以及年纪
1 fstream of; 2 of.open("xxx.txt",ios::out|ios::trunc); 3 if(of == NULL) 4 return -1; 5 char buf[1024]; 6 cout<<"pls input name : "; 7 cin.getline(buf,20); 8 of<<buf<<'\n'; 9 cout<<"pls input age : "; 10 cin.getline(buf,1024); 11 of<<buf<<'\n';12 return 0;
而下面代码,将刚才写入文件的内容打印出来
1 char buf[1024]; 2 fstream ifp; 3 ifp.open("xxx.txt",ios::in); 4 if(ifp == NULL) 5 return -1; 6 while(ifp>>buf) 7 cout<<buf<<endl; 8 return 0;
注意:在用某个类创建其类对象的时候,需要包含其相应的头文件。
三.流文件的状态
系统为了标识当前文件操作的状态,提供了标识位和检查标识位的如下函数。
1.eof():如果读文件到达文件末尾,返回 true。
2.bad():如果在读写过程中出错,返回 true 。例如:当我们要对一个不是打开为写状态的文件进行写入时,或者我们要写入的设备没有剩余空间的时候。
3.fail():除了与 bad() 同样的情况下会返回 true 以外,加上格式错误时也返回 true ,例如当想要读入一个整数,而获得了一个字母的时候。或是遇到 eof。
4.good():这是最通用的:如果调用以上任何一个函数返回 true 的话,此函数返回 false 。
5.clear():标识位一旦被置位,这些标志将不会被改变,要想重置以上成员函数所检查的状态标志,你可以使用成员函数 clear(),没有参数。比如:通过函数移动文件指针,并不会使 eof 标志位自动重置。
测试代码:
1 int main() 2 { 3 int integerVal; 4 cout << "Before a bad input operation:" 5 << "\n cin.eof(): " <<cin.eof() 6 << "\n cin.fail(): " <<cin.fail() 7 << "\n cin.bad(): " <<cin.bad() 8 << "\n cin.good(): " <<cin.good()<<endl; 9 cin>>integerVal; // control + D/Z 10 cout << "After a bad input operation:" 11 << "\n cin.eof(): " <<cin.eof() 12 << "\n cin.fail(): " <<cin.fail() 13 << "\n cin.bad(): " <<cin.bad() 14 << "\n cin.good(): " <<cin.good()<<endl; 15 cin.clear(); 16 cout<< "\n cin.eof(): " <<cin.eof() 17 << "\n cin.fail(): " <<cin.fail() 18 << "\n cin.bad(): " <<cin.bad() 19 << "\n cin.good(): " <<cin.good()<<endl; 20 }
四.文件读写
1.文本文件的读出
1 operator>> 2 int get(); 3 istream& get(int); 4 istream & get(char*,int n, char deli ) 5 istream& getline(char * ,int n);
2.文本文件的写入
1 operator<< 2 ostream put(int)
示例代码:
1 fstream ifs; 2 fstream ofs; 3 ifs.open("xxx.txt",ios::in); 4 if(ifs == NULL) 5 return -1; 6 ofs.open("yyy.txt",ios::out|ios::trunc); 7 if(ofs == NULL) 8 return -1; 9 char ch; 10 while(ifs.get(ch)) 11 ofs.put(ch); 12 return 0;
3.二进制文件的读取
1 ostream & write(const char * buffer,int len); 2 istream & read(char * buff, int len);
示例代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<fstream> 3 #include<string.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 struct student 6 { 7 int num; 8 char name[20]; 9 float score; 10 }; 11 int main() 12 { 13 int i; 14 student stud[5] = { 15 1001 ,"xiaoli",67, 16 1002,"xiaoho",76, 17 1003,"xiaohua",89, 18 1004,"xiaoh",78, 19 1005,"fygh",89 20 }; 21 fstream fs("stu.dat",ios::in|ios::out|ios::binary|ios::trunc); 22 if(!fs) 23 cout<<"open error"; 24 for(i = 0;i<5;i++) 25 fs.write((char*)&stud[i],sizeof(stud[i])); 26 student stud1[5]; 27 for(i = 0;i < 5;i++) 28 { 29 fs.seekg(i*sizeof(stud[i]),ios::beg); 30 fs.read((char*)&stud1[i],sizeof(stud1[i])); 31 cout<<stud1[i].num<<'\t'<<stud1[i].name<<'\t'<<stud1[i].score<<endl; 32 } 33 cout<<"+++++++++++++++++++"<<endl; 34 stud[2].num = 1012; 35 strcpy(stud[2].name,"wulin"); 36 stud[2].score = 60; 37 fs.seekp(2*sizeof(stud[0]),ios::beg); 38 fs.write((char *)&stud[2],sizeof(stud[2])); 39 fs.seekg(0,ios::beg); 40 for(i = 0;i<5;i++) 41 { 42 fs.read((char*)&stud1[i],sizeof(stud1[i])); 43 cout<<stud1[i].num<<'\t'<<stud1[i].name<<'\t'<<stud1[i].score<<endl; 44 } 45 return 0; 46 } 47 48 49 50
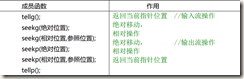
五.与文件指针相关的函数
注:g 是 get 的意思,代表用于输入的函数。p 代表 put 的意思,用于输出函数。如果是既可输入又可输出的文件,则任意使用。
而参照位置有三个:ios::beg = 0,相对于文件头;ios::cur = 1,相对于当前位置;ios::end = 2,相对于文件尾。
示例代码:
1 fstream ifs; 2 ifs.open("xxx.txt",ios::in); 3 if(ifs == NULL) 4 return -1; 5 cout<<ifs.tellg()<<endl; 6 ifs.seekg(10); 7 cout<<ifs.tellg()<<endl; 8 ifs.seekg(5,ios::beg); 9 cout<<ifs.tellg()<<endl; 10 return 0;
输出分别为:0,10,5.
6.文件的关闭
在文件操作结束(即读、写完毕)时应及时调用成员函数 close()来关闭文件。该函数比较简单,没有参数和返回值。