第7章 异常处理
| 7、异常及处理 | |
| 7.1 异常概述与异常体系结构 | 1课时 |
| 7.2 常见异常 | 1课时 |
| 7.3 异常处理机制一:try-catch-finally | 1课时 |
| 7.4 异常处理机制二:throws | 1课时 |
| 7.5 手动抛出异常:throw | 1课时 |
| 7.6 用户自定义异常类 | 1课时 |
- 空指针访问
- 试图读取不存在的文件
- 网络连接中断
案例
/**
* Error:Java虚拟机无法解决的严重问题。如:JVM系统内部错误、资源耗尽等严重情况。
* 比如:StackOverflowError和OOM。一般不编写针对性的代码进行处理。
*
* 对Error的处理:一般不编写针对性的代码进行处理。
*/
public class Error {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.java.lang.StackOverflowError
// main(args);
//2.OutOfMemoryError
// Integer[] arr = new Integer[1024 * 1024 * 1024];
}
}
/** * @author Heaton * @email tzy70416450@163.com * @date 2018/9/28 0028 11:21 * @describe 异常体系结构: * java.lang.Throwable * 1|----Error:错误。不编写针对性的代码进行处理。 * 1.1|----StackOverflowError * 1.2|----OOM * 2|----Exception:异常:可以编写针对性的代码进行处理。 * 2.1|----编译时异常:编译时就会不通过,报出来的异常(IDEA会提示) * 2.1.1|----FileNotFoundException * 2.2|----运行时异常(RuntimeException):编译通过,运行时不通过,报出来的异常(控制台) * 2.2.1|----ArithmeticException 算数异常 * 2.2.2|----ClassCastException 类型转换错误 * 2.2.3|----ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 数组下标越界异常 * 2.2.4|----NullPointerException 空指针异常 * 2.2.5|----InputMismatchException 输入不匹配异常 * |----。。。。 * * 面试题:常见的异常,手写5个 */ public class ExceptionTest {
//5.FileNotFoundException:文件找不到异常,编译时异常,必须用代码进行处理
@Test
public void tste6() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:\\day17\\source\\hello.txt");
//java.io.FileNotFoundException
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int value = fis.read();
while (value != -1) {
System.out.print((char) value);
value = fis.read();
}
fis.close();
}
//5.java.util.InputMismatchException:输入不匹配异常
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("有种你输入S");
int i = s.nextInt();
}
//4.java.lang.NullPointerException:空指针异常
@Test
public void tste4() {
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.charAt(2));
}
//3.java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 10:数组下标越界异常
@Test
public void tste3() {
int[] arr = new int[10];
System.out.println(arr[10]);
}
//2.java.lang.ClassCastException: java.util.Date cannot be cast to java.lang.String:类型转换错误
@Test
public void tste2() {
Object obj = new Date();
String str = (String) obj;
}
//1.java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero算数异常
@Test
public void tste1() {
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 0;
System.out.println(num1 / num2);
}
}
Java异常(3)
- 对于这些错误,一般有两种解决方法:一是遇到错误就终止程序的运行。另一种方法是由程序员在编写程序时,就考虑到错误的检测、错误消息的提示,以及错误的处理。
- 捕获错误最理想的是在编译期间
,但有的错误只有在运行时才会发生。比如:除数为0,数组下标越界等- 分类:编译时异常和运行时异常

Java异常(4)
1.运行时异常
- 是指编译器不要求强制处置的异常。一般是指编程时的逻辑错误,是程序员应该积极避免其出现的异常。
java.lang.RuntimeException类及它的子类都是运行时异常。
2.编译时异常
- 是指编译器要求必须处置的异常。即程序在运行时由于外界因素造成的一般性异常。编译器要求java程序必须捕获或声明所有编译时异常。
- 对于这类异常,如果程序不处理,可能会带来意想不到的结果。
7-2 常见异常
- java.lang.RuntimeException
- ClassCastException
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
- NullPointerException
- ArithmeticException
- ...
- java.io.IOExeption
- FileNotFoundException
- EOFException
- java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
- java.lang.InterruptedException
- java.io.FileNotFoundException
- java.sql.SQLException
Java异常举例(1)
public class Test7_1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String friends[]={"lisa","bily","kessy"};
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
System.out.println(friends[i]); //friends[4]?
}
System.out.println("\nthis is the end");
}
}
程序Test7_ 1编译正确,运行结果:java Test7_1
lisa
bily
kessy
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
at Test7_1.main(Test7_1.java:5)
Exception in thread "main"
Java异常举例(2)
public class NullRef{
int i=1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
NullRef t=new NullRef();
t=null;
System.out.println(t.i);
}
}
程序NullRef.java编译正确,运行结果:java NullRef
java.lang.NullPointerException
at NullRef.main(NullRef.java:6)
Exception in thread "main"
Java异常举例(3)
public class DivideZero{
int x;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int y;
DivideZero c=new DivideZero();
y=3/c.x;
System.out.println(“program ends ok!”);
}
}
程序DivideZero.java编译正确,运行结果:java DivideZero
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at DivideZero.main(DivideZero.java:6)
Exception in thread "main"
Java异常举例(4)
class Person {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object obj = new Date();
Person person;
person = (Person)obj;
System.out.println(person);
}
}
程序Person.java编译正确,运行结果:java Person
java.lang. java.lang.ClassCastException
at Person.main(Person.java:5)
Exception in thread "main"
7-3 异常处理机制一
异常处理机制(1)
在编写程序时,经常要在可能出现错误的地方加上检测的代码,如进行x/y运算时,要检测分母为0,数据为空,输入的不是数据而是字符等。过多的分支会导致程序的代码加长,可读性差。因此采用异常机制。
Java异常处理
Java采用异常处理机制,将异常处理的程序代码集中在一起,与正常的程序代码分开,使得程序简洁,并易于维护。
案例
/**
* @author Heaton
* @email tzy70416450@163.com
* @date 2018/9/28 0028 11:49
* @describe 如何处理异常(Exception)
* java提供了异常处理的:抓抛模型
* 1.过程一:抛:程序在正常的执行过程中,一旦出现了异常,就会在相应的代码处生成相应的异常类的对象,并将此对象抛出
* >异常出现位置后面的代码就不在执行
* >异常对象产生的方式:(1.自动抛出,2手动抛出,在方法()后,使用throws + 异常类对象)---抛异常参考--->异常处理的方式二
*
* 2.过程二:“抓”:看出是异常的处理方式:try-catch-finally (thorws XxxxException,XxxxException...)
* try{
* //可能会出现异常的代码
* }catch(Exception1 e){
* //处理该异常的方式
* }catch(Exception2 e){
* //处理该异常的方式
* }
* ......
* finally{
* //一定会执行的操作
* }
*
* 说明:
* 1.finally是可选的。
* 2.在执行try中的语句时,一旦出现异常,就会抛出相应异常的对象,此对象会在如下的catch中进行类型匹配,一旦
* 匹配成功,就进入相应的catch的代码块中进行相应的异常的处理。一旦处理完成,就跳出整个try-catch结构。
* 不再执行其后的catch语句。
* 3.多个catch语句中的异常类型说明:子类异常必须声明在父类异常的上面。否则编译不通过。
* 如果多个异常类型没有子父类关系,则声明没有顺序要求。
* 4.执行完catch语句以后,如果其结构后还有操作,则可以正常执行。
* 5.在try中定义的变量,其作用域仅限于try声明的一对{},出了此{},不可再被调用
* 6.catch中常见的异常处理方法:① getMessage()返回一个String变量
* ② printStackTrace():打印异常产生的堆栈信息
* 7.try-catch-finally结构可以嵌套
*
* 总结:对于运行时异常,我们可以不使用try-catch-finaly的方式进行处理。
* 对于编译时异常,我们一定要进行异常的处理,否则编译不通过!
* --->实际上,通过try-catch-finally的方式,将编译时异常延迟到运行时才可能出现的异常了。
*/
public class ExceptionTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
int num1 = 0;
try {
num1 = 10;
//情况3
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.charAt(2));
//情况2
String c = "cc";
num1 = Integer.parseInt(c);
//情况1
int num2 = 0;
System.out.println(num1 / num2);
System.out.println("抛出异常后我会执行么?");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("出现了数学算数异常");
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("出现了数值格式化异常");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("出现了异常");
//e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("成都");
System.out.println(num1);
}
@Test
public void tste4() {
try {
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.charAt(2));
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void test3() {
try {
Object obj = new Date();
String s = (String) obj;
System.out.println(s);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void test4() {
try {
File file = new File("D:\\day17\\source\\hello.txt");
//java.io.FileNotFoundException
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int value = fis.read();
while (value != -1) {
System.out.print((char) value);
value = fis.read();
}
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
finally的使用说明
/**
* @author Heaton
* @email tzy70416450@163.com
* @date 2018/9/28 0028 13:55
* @describe 关于try-catch-finally结构中finally的使用
* 1.finally是可以选择使用的
* 2.即使在catch中出现异常;try中有return;catch中有return;三种情况,finally中的代码也一定会被执行!
* 3.开始种的应用:IO流资源、网络Socket、数据库连接等。JVM不会自动进行资源的关闭和流垃圾的回收,需要我们
* 手动的去释放资源。所以此操作必须声明在finally中。
*/
public class FinallyTest {
//具体应用
@Test
public void test1() {
try {
Object obj = new Date();
String s = (String) obj;
System.out.println(s);
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("Hello!");
}
}
public int method() {
try {
System.out.println("hello!");
System.out.println(10 / 0);
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 2;
}finally {
System.out.println("haha!@");
return 3;
}
}
@Test
public void test2() {
int num = method();
System.out.println(num);
}
@Test
public void test3() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
File file = new File("D:\\day17\\source\\hello.txt");
//java.io.FileNotFoundException
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int value = fis.read();
while (value != -1) {
System.out.print((char) value);
value = fis.read();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//常用来关闭资源
try {
if(fis!=null){
fis.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
案例
/**
* @author Heaton
* @email tzy70416450@163.com
* @date 2018/9/28 0028 14:09
* @describe 异常处理的方式二:
* 使用"throws+异常类型",表示:一旦方法执行过程中,出现异常,将此异常对象抛出
* 1.上述出现的异常对象,会抛给方法的调用者。比如:method1()在method2()调用,如果method1()出现异常,
* 则将此异常抛给了method2()。
* 2.体会:try-catch-finally:真正的处理异常,一旦处理完,就不会影响后续代码的执行。
* throws:并没有真正的处理掉此异常。
* 3.总结:在开发中如何选择使用哪种处理方式呢?
* 3.1 如果父类被重写的方法没有throws的方式处理异常,则子类重写的方法也不能throws的方式去处理异常,只能使用try-catch-finally
* 3.2 在一个方法A中,调用另外的3个方法,此3个方法通常都是递进关系的,
* 一般情况下,此3个方法中如果出现异常,通常使用throws的方式来处理。然后统一在一个方法A中使用try-catch-finally进行处理
*/
public class ExceptionTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExceptionTest2 ex = new ExceptionTest2();
ex.method3();
}
public void method3() {
try {
method2();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void method2() throws IOException {
method1();
}
public void method1() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
File file = new File("D:\\day17\\source\\hello.txt");
//java.io.FileNotFoundException
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int value = fis.read();
while (value != -1) {
System.out.print((char) value);
value = fis.read();
}
fis.close();
}
}
异常处理机制(2)
- Java提供的是异常处理的抓抛模型。
- Java程序的执行过程中如出现异常,会生成一个异常类对象,该异常对象将被提交给Java运行时系统,这个过程称为抛出(throw)异常。
- 异常对象的生成
- 由虚拟机自动生成:程序运行过程中,虚拟机检测到程序发生了问题,如果在当前代码中没有找到相应的处理程序,就会在后台自动创建一个对应异常类的实例对象并抛出——自动抛出。
- 由开发人员手动创建:Exception exception = new ClassCastException();——创建好的异常对象不抛出对程序没有任何影响,和创建一个普通对象一样。
异常的抛出机制

为保证程序正常执行,代码必须对可能出现的异常进行处理。
异常处理机制(3)
- 如果一个方法内抛出异常,该异常对象会被抛给调用者方法中处理。如果异常没有在调用者方法中处理,它继续被抛给这个调用方法的上层方法。这个过程将一直继续下去,直到异常被处理。这一过程称为捕获(catch)异常。
- 如果一个异常回到main()方法,并且main()也不处理,则程序运行终止。
- 程序员通常只能处理Exception,而对Error无能为力。
异常处理机制(4)
异常处理是通过try-catch-finally语句实现的。
try{
...... //可能产生异常的代码
}
catch( ExceptionName1 e ){
...... //当产生ExceptionName1型异常时的处置措施
}
catch( ExceptionName2 e ){
...... //当产生ExceptionName2型异常时的处置措施
}
[ finally{
...... //无论是否发生异常,都无条件执行的语句
} ]
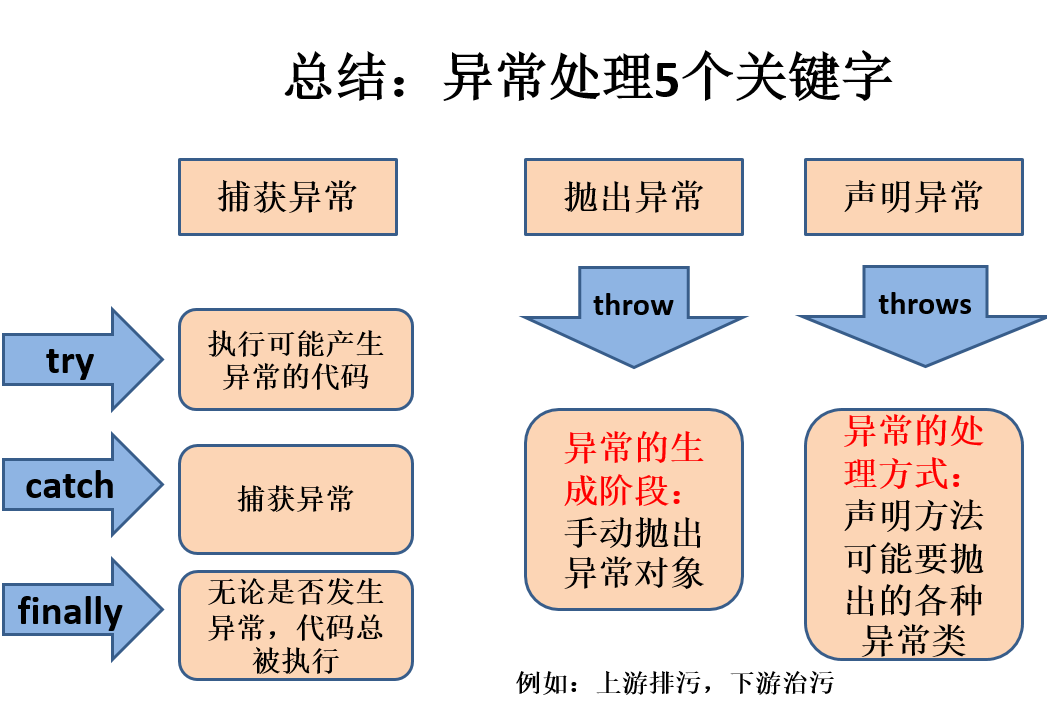
捕获异常(1)
-
try
捕获异常的第一步是用try{…}语句块选定捕获异常的范围,将可能出现异常的代码放在try语句块中。
-
catch (Exceptiontype e)
在catch语句块中是对异常对象进行处理的代码。每个try语句块可以伴随一个或多个catch语句,用于处理可能产生的不同类型的异常对象。
如果明确知道产生的是何种异常,可以用该异常类作为catch的参数;也可以用其父类作为catch的参数。比如:可以用ArithmeticException类作为参数的地方,就可以用RuntimeException类作为参数,或者用所有异常的父类Exception类作为参数。但不能是与ArithmeticException类无关的异常,如NullPointerException(catch中的语句将不会执行)。
捕获异常(2)
- 捕获异常的有关信息:与其它对象一样,可以访问一个异常对象的成员变量或调用它的方法。
- getMessage() 获取异常信息,返回字符串
- printStackTrace() 获取异常类名和异常信息,以及异常出现在程序中的位置。返回值void。
![]()
捕获异常(3)
- finally
- 捕获异常的最后一步是通过finally语句为异常处理提供一个统一的出口,使得在控制流转到程序的其它部分以前,能够对程序的状态作统一的管理。
- 不论在try代码块中是否发生了异常事件,catch语句是否执行,catch语句是否有异常,catch语句中是否有return,finally块中的语句都会被执行。
- finally语句和catch语句是任选的
捕获异常(4)
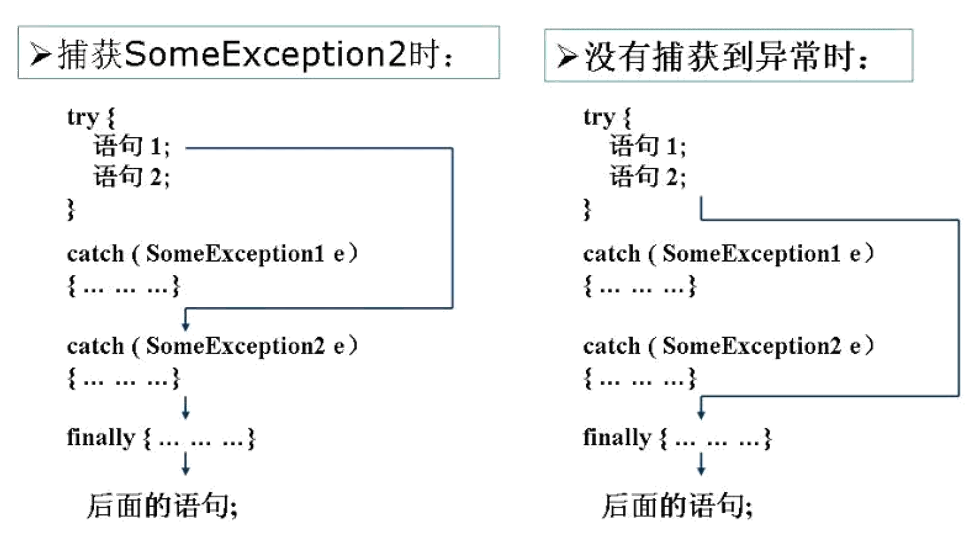








7-4 异常处理机制二

子父类涉及方法重写时throws异常的规定
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
//规定:子类重写的方法抛出的异常类型不能大于父类被重写的方法抛出的异常。
public class MethodOverrideTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SuperClass s = new SubClass();
try {
s.method();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class SuperClass{
public void method() throws IOException{
}
public void method1(){
}
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass{
public void method() throws FileNotFoundException{
}
@Override
public void method1() {
// File file = new File("hello.txt");
// FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//
// int value = fis.read();
// while(value != -1){
// System.out.print((char)value);
// value = fis.read();
// }
//
// fis.close();
}
}



7-5 手动抛出异常

案例
//手动抛出一个异常类的对象:在方法内,使用throw + 异常类的对象
//面试题:throws , throw 区别?
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu = new Student();
try {
stu.regist(-1001);
System.out.println(stu);
} catch (Exception e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
class Student{
int id;
public void regist(int id) throws Exception {
if(id <= 0){
// throw new Exception("传入的数据为非正数!非法!");
throw new MyException("传入的数据为非正数!非法!");
// throw new String("传入的数据为非正数!非法!");//错误的
}
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + "]";
}
}
/** * 如何自定义异常类? * 1.继承于现有的异常类。(一般情况下,继承于Exception/RuntimeException) * 2.提供重载的构造器 * 3.提供全局常量:serialVersionUID * */ public class MyException extends Exception{
/**
* 序列版本号唯一的标识当前类
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6650357798030558092L;
public MyException(){}
public MyException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}
7-6 用户自定义异常类



课后练习,运行结果是什么
public class ReturnExceptionDemo {
static void methodA() {
try {
System.out.println("进入方法A");
throw new RuntimeException("制造异常");
} finally {
System.out.println("用A方法的finally");
}
}
static void methodB() {
try {
System.out.println("进入方法B");
return;
} finally {
System.out.println("调用B方法的finally");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
methodA();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
methodB();
}
}
答案:
进入方法A
用A方法的finally
制造异常
进入方法B
调用B方法的finally
课后练习
/*
* 编写应用程序EcmDef.java,接收命令行的两个参数,要求不能输入负数,计算两数相除。
对数据类型不一致(NumberFormatException)、缺少命令行参数(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException、
除0(ArithmeticException)及输入负数(EcDef 自定义的异常)进行异常处理。
提示:
(1)在主类(EcmDef)中定义异常方法(ecm)完成两数相除功能。
(2)在main()方法中使用异常处理语句进行异常处理。
(3)在程序中,自定义对应输入负数的异常类(EcDef)。
(4)运行时接受参数 java EcmDef 20 10
//args[0]=“20” args[1]=“10”
(5)Interger类的static方法parseInt(String s)将s转换成对应的int值。如int a=Interger.parseInt(“314”); //a=314;
*/
public class EcmDef {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
int result = ecm(num1,num2);
}catch (EcDef e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}catch(NumberFormatException e){
System.out.println("输入的数据类型不一致的异常");
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("缺少命令行参数的异常");
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("除0的异常");
}
}
public static int ecm(int i,int j) throws EcDef{
if(i < 0 || j < 0){
throw new EcDef("非法传入负数了!");
}
return i / j;
}
}
public class EcDef extends Exception{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7330126729521530121L;
public EcDef(){}
public EcDef(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}

您的资助是我最大的动力!
金额随意,欢迎来赏!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号