Scala篇:Scala语言基础
Scala语言基础

1 语言介绍
- 他已经出生15年了,就像明星一样,谁都不可能一开始就人气爆棚粉丝无数,得慢慢混。
- 成功原因:完全兼容java代码。
- 身世介绍
- Scala在2004年正式问世,他的爸爸是Martin Odersky,这位老头同时也是Genenric Java的爸爸。神不神奇!Scala和Genenric Java居然是亲兄弟。
- Scala的全称叫scalable,可伸缩的意思。说白了就是可以简单又可以复杂。scala是个纯正的面向对象语言,并且具备函数式编程特性,这也是他最吸引人的地方。
- Scala之所以这么受欢迎还有一个原因,那就是Spark。专为大规模数据处理而设计的快速通用的计算引擎,这正是spark的最好诠释,关于spark的更多信息请百度。spark就是Scala编写的,所以想了解spark的优越性能及应用就必须得学习Scala。
- 学语言很枯燥,案例走一遍,有个印象,做demo用到回来看看就可以了,不要太在意,熟能生巧。
2 变量和数据类型
2.1 注释
- 单行注释
//这是单行注释
- 多行注释
/*
这是多行注释
*/
- 文档注释
/**
这是文档注释
*/
2.2 变量
2.2.1 变量声明
变量声明:var 变量名:类型 = 初始值
常量声明:var 变量名:类型 = 初始值
Scala中可以不写 ; --->一般情况我们都不写,因为;本来就对代码没有什么意义;
Scala中有自动类型推断,所以一般情况都可以省略,故可以写成如下方式。
变量声明:var 变量名 = 初始值
常量声明:var 变量名 = 初始值
在函数式编程中,能用常量就用常量,因为多线程中变量会引起线程安全问题。
2.2.2 数据类型
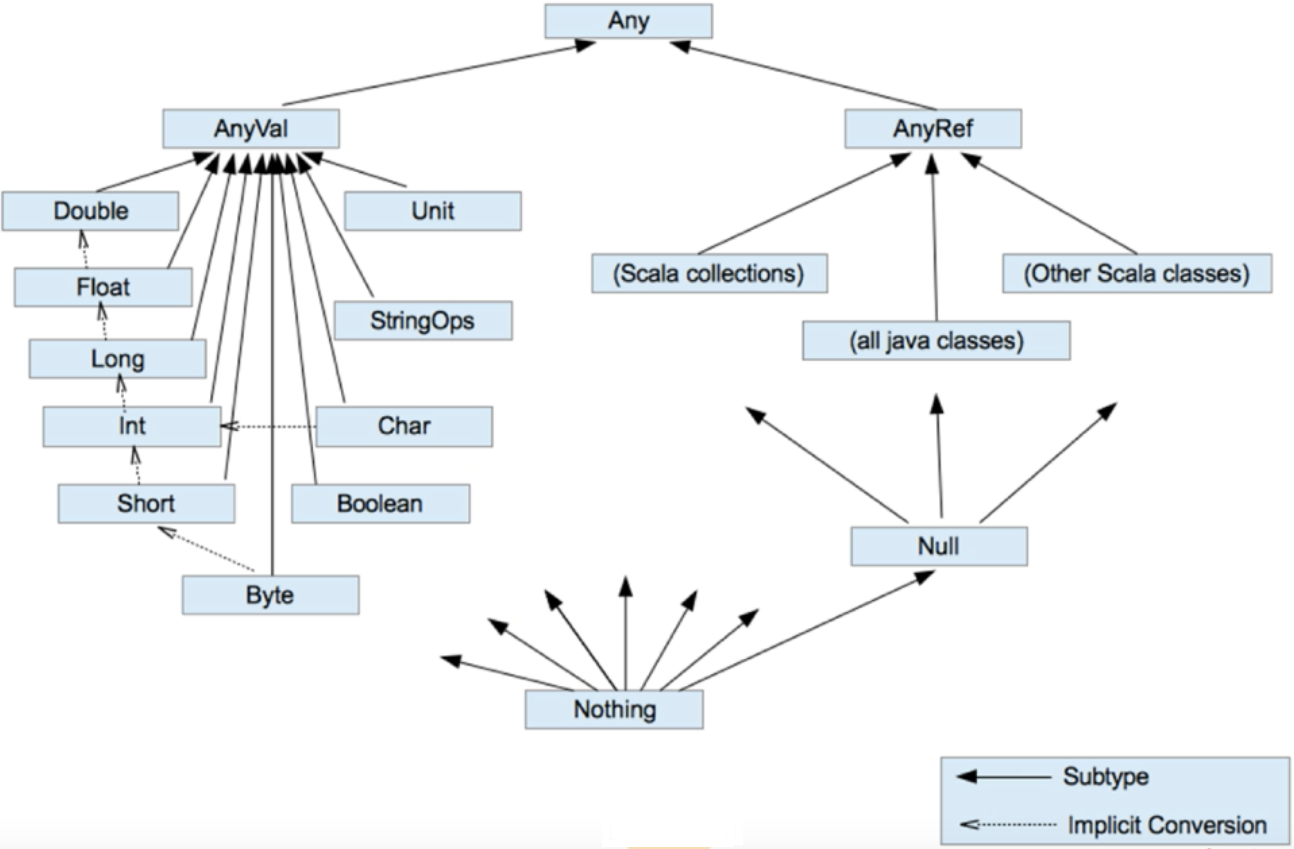
- Any:所以类的父类
- AnyVal:值类型->类似Java中的基本类型
- 在Java中基本类型int,对应Scala中的Int,注意不是包装类,在Scala中认为都是对象,故首字母都是大写
- StringOps:在Java中String是引用类型,在Scala中是值类型,这个类对String进行了拓展,也可以直接使用Java的String类
- Unit:对应Java中的Void,但是Void没有返回值,而Unit有返回值:
()
- AnyRef:引用类型
- Null:所有引用类型的子类,值为
null
- Null:所有引用类型的子类,值为
- AnyVal:值类型->类似Java中的基本类型
- Nothing:所有类的子类
- 如果需要使用值类型的初始值,需要使用 _ 如:var name:String = _
2.2.3 类型转换
和Java一样,Scala也分自动类型转换和强制类型转换
自动类型转换规则和Java一样,都是从范围小类型转换到范围大类型
强制类型转换和Java不一样,Scala是调用方法的方式来完成转换
- 强制类型转换和自动类型转换
object Demo {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//强制类型转换
val a = 10
println(a.toDouble)//10.0
/**
*自动类型转换
* byte->short->int->long->float->double
* char->int->long->float->double
*/
val b:Double = 10
println(b)//10.0
// 如下这种自动类型转换会失败,因为不能自动类型转换不能大转小
// val c:Int = 10.0
}
}
3 字符串转换
object Demo1 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//name = zhangsan,age = 10 sal = 50.56
printf("name = %s,age = %d sal = %.2f", "zhangsan", 10, 50.55555)
//name = lisi,age = 30
val name = "lisi"
val age = 20
println(s"name = ${name},age = ${age + 10}")
/**
* a
* b
* c
*/
val s =
"""
|a
|b
|c
""".stripMargin
println(s)
}
}
4 If Else
Scala中没有三元运算符,只能使用If Else来实现其功能,写法和Java一样
Scala中没有switch
Scala中,任何语法结构都有类型和值,返回最后一行代码的值。如If Else,赋值语句,代码块等等
Scala中 == 等价于Java中的equals()方法,eq 等价于Java中的 ==
object Demo2 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
var i = 1
if (true) {
i = 2
} else {
i = 0
}
//2
println(i)
}
}
object Demo3 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val func = if (true) {
1
2
} else {
0
}
//2
println(func)
}
}
object Demo4 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val func = if (true) {
}
//()
println(func)
}
}
5 循环
while和do while和Java一样
for不像Java,其实是一种遍历
5.1 while
object Demo5 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
var i = 1
while (i < 5) {
println(i)
i += 1
}
}
}
5.2 do while
object Demo6 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
var i = 1
do {
println(i)
i -= 1
} while (i > 1)
}
}
5.3 for
object Demo7 extends App {
//遍历序列
for (x <- "123456") {
println(x)
}
//间隔,反转:打印10到1,并且间隔2个打印
for (y <- 1.to(10, 2).reverse) {
println(y)
}
//循环守卫:打印1到10的偶数
for (z <- 1.to(10) if z % 2 == 0) {
println(z)
}
//for推到:使循环可以返回最后的值,如下1到10的平方
val a = for (z <- 1.to(10)) yield z * z
println(a)
}
import scala.util.control.Breaks._
object Demo8 extends App {
//退出循环
breakable(
for (x <- 1.to(10)) {
if (x == 5) break()
println(x)
}
)
}
6 Lambda及函数
函数式编程强调执行的结果而非执行过程,倡导利用若干简单的单元让计算结果不断演进,逐层推到复杂运算,而不是设计一个复杂的运算过程。
在Scala中,函数也是一个对象,会有返回值,可以作为值传递给另外的函数。
函数的定义: def 函数名(参数1:参数1类型,参数2:参数2类型):函数返回值 = { 代码块 }
函数返回值是可以自动推到的: def 函数名(参数1:参数1类型,参数2:参数2类型)= { 代码块 }
函数形参都是val常量
-
纯函数
-
不能产生副作用
- 函数不会产生副作用,除了返回值外,不修改程序的外部状态(如修改全局变量,入参等)
- 常见副作用:改变外部变量的值、向磁盘写入数据、将页面的一个按钮设置为能否点击
-
引用透明
- 函数的运行不依赖于外部的变量或状态,简单的理解为多次调用,不会因为外部值而改变返回结果。
- 天然适合并编程,因为调用函数的结果具有一致性,所以根本不需要加锁,也不存在死锁
-
//纯函数
def add(a: Int, b: Int): Unit = {
a + b
}
//纯非函数
def add1(a: Int, b: Int): Unit = {
//破坏了纯函数,产生副作用
println("打印功能")
a + b
}
//纯非函数
var x = 0;
def add2(a: Int, b: Int): Unit = {
//破坏了纯函数,产生副作用
x = 100
a + b
}
var x = 1;
def add(a: Int, b: Int)= {
//破坏了纯函数
a + b + x
}
println(add(1, 2)) //4
x = 10
println(add(1, 2)) //13
- 可变形参函数
参数类型*为可变形参,传入一个序列中的每个元素。
def add(a: Int*) = {
a.sum
}
println(add(1, 2, 3)) //6
def add(a: Int*) = {
a.sum
}
val arr: Range.Inclusive = 1.to(3)
println(add(arr: _*)) //6 序列展开需要使用: _*
- 函数参数默认值
def myconcat(x: String, pre: String = "<html>", suf: String = "</html>") = {
pre + x + suf
}
//<html>abc</html>
println(myconcat("abc", "<html>", "</html>"))
println(myconcat("abc"))
println(myconcat("abc", suf = "</html>"))
7 异常
同Java处理方式,有点小不同
import java.io.{FileInputStream, FileNotFoundException}
object Demo9 extends App {
//在Java中FileNotFoundException属于编译时异常,必须处理,而Scala可以不处理,发生直接抛
//new FileInputStream("")
//java.io.FileNotFoundException:
//处理完毕
try {
new FileInputStream("")
} catch {
case e: FileNotFoundException => println(e)
}finally {
println("处理完毕")
}
}
8 对象
-
Scala object相当于java中的单例,object中定义的全是静态的,相当于java中的工具类,Object默认不可以传参,对象要传参,使用apply方法。
-
Scala类中可以传参,传参一定要指定类型,有了参数就有了默认了构造。类中的属性默认有getter和setter方法
-
类中重载构造时,构造中第一行必须先调用默认的构造 。def this(....)
-
在同一个scala文件中,class名称和Object名称一样时,这个类叫做个对象的伴生类,这个对象叫做这个类的伴生对象,他们之间可以互相访问私有变量。
8.1 主构造器
object Demo10 extends App {
val user1 = new User("zhangsan", 15, "man")
val user = new User( age=15, sex="man")
/*set*/
user.name = "lisi"
//报错 user.age=12
//报错 user.sex="女"
/*get*/
println(user.name)
println(user.age)
//报错 println(user.sex)
}
class User(var name: String = "aa", val age: Int, sex: String) {
/**
* 构造函数及get set方法都自动生成了
* var 变量 会在有参数的构造器中,get set方法都有
* val 常量 会在有参数的构造器中,只有get方法
* 无变量修饰符 会在有参数的构造器中,无get set方法
* 可以传递默认值,由指定参数创建
* 参数都是私有的属性
* 类自身就是public的,而且不限个数
**/
//主构造器,这里面写的代码,都会在对象创建的时候进行
println("我生成了")
}
8.2 辅助构造器
object Demo11 extends App {
val user = new User(15)
println(user.name)
println(user.age)
}
class User(var name: String = "aa", val age: Int, sex: String) {
//辅助构造器,可以定义很多,类似于java的重载
def this(username: String) = {
//辅助构造器参数只能在当前辅助构造函数内当做普通的常量使用
//第一个辅助构造的首行必须是调用主构造
this(username, 10, "男")
}
def this(age: Int) {
//可以调用前面的辅助构造器
//this(name, age, "男")
this("lisi")
}
}
8.3 继承
object Demo12 extends App {
val zhangsan = new Son("zhangsan", 12)
println(zhangsan.name)
println(zhangsan.add(1, 2))
}
class Father(val name: String, val age: Int) {
def add(a: Int, b: Int): Int = {
a + b
}
}
/**
* 属性复写:
* 如果子类属性名和父类属性名一样,主类属性被隐藏
* 可以选择override复写主类属性
* 被复写的属性只能是val的
* 未指定val,var的属性,本身就是私有的,和继承无关
* 方法复写:
* 使用override关键字
**/
class Son(override val name: String, override val age: Int) extends Father(name, age) {
override def add(a: Int, b: Int): Int = {
a + b + 1
}
}
8.4 抽象类
object Demo13 extends App {
val son = new Son()
println(son.a)
println(son.add(1, 2))
//多态,强转
val father: Father = new Son
if (father.isInstanceOf[Son]) {
val s: Son = father.asInstanceOf[Son]
println(s.a)
}
//匿名内部类
println(new Father {
override var a: Int = 1
override def add(a: Int, b: Int): Int = {
1
}
}.a)
}
/**
* 抽象类:
* 使用abstract关键字
**/
abstract class Father() {
//抽象字段
var a: Int
//抽象方法
def add(a: Int, b: Int): Int
}
class Son extends Father {
override var a: Int = _
override def add(a: Int, b: Int): Int = {
a + b
}
}
8.5 伴生类和伴生对象
object Demo14 extends App {
//使用new关键字,直接走类的构造器
val zhangsan = new Father("zhangsan", 12)
//不适用new关键字,走伴生对象的apply()方法
val lisi = Father("lisi", 20) //进入apply()方法
println(zhangsan) //name:zhangsan,age:12
println(lisi) //name:lisi,age:20
}
//Father对象的伴生类
class Father(val name: String, val age: Int) {
override def toString: String = s"name:${name},age:${age}"
}
//Father类的伴生对象
object Father {
//伴生对象中使用apply()方法,创建该对象的时候会调用该方法
def apply(name: String, age: Int): Father = {
println("进入apply()方法")
new Father(name, age)
}
}
8.6 特质Trait
Scala中的trait非常类似于Java中的interface,主要为了解决单继承的问题。
一个类实现多个trait时,第一个关键字使用 extends,之后使用with
object Demo15 extends App {
val son = new Son
son.walk() //走路
son.eat() //吃饭
}
trait Features {
def walk()
}
trait Hobby {
def eat()
}
class Son extends Features with Hobby {
override def walk(): Unit = {
println("走路")
}
override def eat(): Unit = {
println("吃饭")
}
}
8.7 隐式转换
隐式转换是在Scala编译器进行类型匹配时,如果找不到合适的类型,那么隐式转换会让编译器在作用范围内自动推导出来合适的类型,简单的说就是:把任何东西,转换成我们需要的格式。
- 隐式函数
名字无所谓,作用域范围有效,在使用到相关功能的时候,找到是否有相关的隐式函数,有就直接使用。
注意:隐式转换函数只与函数的参数类型和返回类型有关,与函数名称无关,所以作用域内不能有相同的参数类型和返回类型的不同名称隐式转换函数。
object Demo16 extends App {
implicit def double2Double(num: Double): Int = num.toInt
var a: Int = 10.1
println(a) //10
implicit def father2Son(father: Father): Son = father.toSon
var son: Son = new Father
son.speakDad //Dad
}
class Father {
def toSon: Son = {
new Son
}
}
class Son {
def speakDad {
println("Dad")
}
}
- 隐式值与隐式参数
隐式值是指在定义参数时前面加上implicit。隐式参数是指在定义方法时,方法中的部分参数是由implicit修饰【必须使用柯里化的方式,将隐式参数写在后面的括号中】。隐式转换作用就是:当调用方法时,不必手动传入方法中的隐式参数,Scala会自动在作用域范围内寻找隐式值自动传入。
隐式值和隐式参数注意:
隐式值和隐式参数一起使用
同类型的参数的隐式值只能在作用域内出现一次,同一个作用域内不能定义多个类型一样的隐式值。
implicit 关键字必须放在隐式参数定义的开头
一个方法只有一个参数是隐式转换参数时,那么可以直接定义implicit关键字修饰的参数,调用时直接创建类型不传入参数即可。
一个方法如果有多个参数,要实现部分参数的隐式转换,必须使用柯里化这种方式,隐式关键字出现在后面,只能出现一次
object Demo17 extends App {
implicit val zs: String = "zhangsan"
implicit val sr: Int = 100
def printStudent(age: Int)(implicit name: String, score: Int) = {
println(s"student :$name ,age = $age ,score = $score")
}
def printTeacher(implicit name: String) = {
println(s"teacher name is = $name")
}
printStudent(18) //student :zhangsan ,age = 18 ,score = 100
printTeacher //teacher name is = zhangsan
printTeacher("lisi") //teacher name is = lisi
}
- 隐式类
使用implicit关键字修饰的类就是隐式类。若一个变量A没有某些方法或者某些变量时,而这个变量A可以调用某些方法或者某些变量时,可以定义一个隐式类,隐式类中定义这些方法或者变量,隐式类中传入A即可。
隐式类注意:
- 隐式类必须定义在类,包对象,伴生对象中。(必须是内部的)
- 隐式类的构造必须只有一个参数,同一个类,包对象,伴生对象中不能出现同类型构造的隐式类。
object Demo18 extends App {
implicit class Father(son: Son) {
def speak() = {
println(son.name + " You Are Excellent...")
}
}
val f: Father = new Son("lisi")
f.speak() //lisi You Are Excellent...
}
class Son(val s: String) {
var name = s
}
9 集合
Scala中支持不可变集合和可变集合,不可变集合可以安全的并发访问
可变集合:scala.collection.mutable 更改原集合
不可变集合:scala.collection.immutable 不会更改原集合,只会返回一个新集合
Scala默认采用不可变集合
9.1 数组
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| def apply( x: T, xs: T* ): Array[T] | 创建指定对象 T 的数组, T 的值可以是 Unit, Double, Float, Long, Int, Char, Short, Byte, Boolean。 |
| def concat[T]( xss: Array[T]* ): Array[T] | 合并数组 |
| def copy( src: AnyRef, srcPos: Int, dest: AnyRef, destPos: Int, length: Int ): Unit | 复制一个数组到另一个数组上。相等于 Java's System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length)。 |
| def empty[T]: Array[T] | 返回长度为 0 的数组 |
| def iterate[T]( start: T, len: Int )( f: (T) => T ): Array[T] | 返回指定长度数组,每个数组元素为指定函数的返回值。 |
| def fill[T]( n: Int )(elem: => T): Array[T] | 返回数组,长度为第一个参数指定,同时每个元素使用第二个参数进行填充。 |
| def fill[T]( n1: Int, n2: Int )( elem: => T ): Array[Array[T]] | 返回二数组,长度为第一个参数指定,同时每个元素使用第二个参数进行填充。 |
| def ofDim[T]( n1: Int ): Array[T] | 创建指定长度的数组 |
| def ofDim[T]( n1: Int, n2: Int ): Array[Array[T]] | 创建二维数组 |
| def ofDim[T]( n1: Int, n2: Int, n3: Int ): Array[Array[Array[T]]] | 创建三维数组 |
| def range( start: Int, end: Int, step: Int ): Array[Int] | 创建指定区间内的数组,step 为每个元素间的步长 |
| def range( start: Int, end: Int ): Array[Int] | 创建指定区间内的数组 |
| def tabulate[T]( n: Int )(f: (Int)=> T): Array[T] | 返回指定长度数组,每个数组元素为指定函数的返回值,默认从 0 开始。 |
| def tabulate[T]( n1: Int, n2: Int )( f: (Int, Int ) => T): Array[Array[T]] | 返回指定长度的二维数组,每个数组元素为指定函数的返回值,默认从 0 开始。 |
- 定长数组
object Demo19 extends App {
//第一种方式
val arr: Array[Int] = Array(10, 20, 30, 40)
println(arr(0)) //10
println(arr.mkString(",")) //10,20,30,40
//10 20 30 40
for (i <- arr) {
print(i + "\t")
}
println()
//10 20 30 40
arr.foreach(x => print(x + "\t"))
println()
//第二种方式
val arr2: Array[Int] = new Array(3)
for (i <- 1.to(arr2.length)) {
arr2(i-1) = i * i
}
println(arr2.mkString(",")) //1,4,9
}
- 可变长度数组
import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer
object Demo20 extends App {
val arr = ArrayBuffer[String]("a", "b", "c")
arr.append("hello", "scala") //在元素末尾追加多个元素
arr.+=("end1", "end2") //在元素末尾追加多个元素
arr.+=:("start") //在开头添加元素
println(arr.mkString(",")) //start,a,b,c,hello,scala,end1,end2
}
另外还有++=(合并),--=(差集)
9.2 列表
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| def +(elem: A): List[A] | 前置一个元素列表 |
| def ::(x: A): List[A] | 在这个列表的开头添加的元素。 |
| def :::(prefix: List[A]): List[A] | 增加了一个给定列表中该列表前面的元素。 |
| def ::(x: A): List[A] | 增加了一个元素x在列表的开头 |
| def addString(b: StringBuilder): StringBuilder | 追加列表的一个字符串生成器的所有元素。 |
| def addString(b: StringBuilder, sep: String): StringBuilder | 追加列表的使用分隔字符串一个字符串生成器的所有元素。 |
| def apply(n: Int): A | 选择通过其在列表中索引的元素 |
| def contains(elem: Any): Boolean | 测试该列表中是否包含一个给定值作为元素。 |
| def copyToArray(xs: Array[A], start: Int, len: Int): Unit | 列表的副本元件阵列。填充给定的数组xs与此列表中最多len个元素,在位置开始。 |
| def distinct: List[A] | 建立从列表中没有任何重复的元素的新列表。 |
| def drop(n: Int): List[A] | 返回除了第n个的所有元素。 |
| def dropRight(n: Int): List[A] | 返回除了最后的n个的元素 |
| def dropWhile(p: (A) => Boolean): List[A] | 丢弃满足谓词的元素最长前缀。 |
| def endsWith[B](that: Seq[B]): Boolean | 测试列表是否使用给定序列结束。 |
| def equals(that: Any): Boolean | equals方法的任意序列。比较该序列到某些其他对象。 |
| def exists(p: (A) => Boolean): Boolean | 测试谓词是否持有一些列表的元素。 |
| def filter(p: (A) => Boolean): List[A] | 返回列表满足谓词的所有元素。 |
| def forall(p: (A) => Boolean): Boolean | 测试谓词是否持有该列表中的所有元素。 |
| def foreach(f: (A) => Unit): Unit | 应用一个函数f以列表的所有元素。 |
| def head: A | 选择列表的第一个元素 |
| def indexOf(elem: A, from: Int): Int | 经过或在某些起始索引查找列表中的一些值第一次出现的索引。 |
| def init: List[A] | 返回除了最后的所有元素 |
| def intersect(that: Seq[A]): List[A] | 计算列表和另一序列之间的多重集交集。 |
| def isEmpty: Boolean | 测试列表是否为空 |
| def iterator: Iterator[A] | 创建一个新的迭代器中包含的可迭代对象中的所有元素 |
| def last: A | 返回最后一个元素 |
| def lastIndexOf(elem: A, end: Int): Int | 之前或在一个给定的最终指数查找的列表中的一些值最后一次出现的索引 |
| def length: Int | 返回列表的长度 |
| def map[B](f: (A) => B): List[B] | 通过应用函数以g这个列表中的所有元素构建一个新的集合 |
| def max: A | 查找最大的元素 |
| def min: A | 查找最小元素 |
| def mkString: String | 显示列表的字符串中的所有元素 |
| def mkString(sep: String): String | 显示的列表中的字符串中使用分隔串的所有元素 |
| def reverse: List[A] | 返回新列表,在相反的顺序元素 |
| def sorted[B >: A]: List[A] | 根据排序对列表进行排序 |
| def startsWith[B](that: Seq[B], offset: Int): Boolean | 测试该列表中是否包含给定的索引处的给定的序列 |
| def sum: A | 概括这个集合的元素 |
| def tail: List[A] | 返回除了第一的所有元素 |
| def take(n: Int): List[A] | 返回前n个元素 |
| def takeRight(n: Int): List[A] | 返回最后n个元素 |
| def toArray: Array[A] | 列表以一个数组变换 |
| def toBuffer[B >: A]: Buffer[B] | 列表以一个可变缓冲器转换 |
| def toMap[T, U]: Map[T, U] | 此列表的映射转换 |
| def toSeq: Seq[A] | 列表的序列转换 |
| def toSet[B >: A]: Set[B] | 列表到集合变换 |
| def toString(): String | 列表转换为字符串 |
- 不可变列表
object Demo21 extends App {
val list = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
println(list(0)) //1
//filter过滤
val list1 = list.filter { x => x >= 3 }
println(list1.mkString(",")) //3,4,5
//count统计个数
val value = list.count(x => x > 3)
println("count统计结果:" + value) //count统计结果:2
}
- 可变数组
import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer
object Demo22 extends App {
val listBuffer: ListBuffer[Int] = ListBuffer[Int](1,2,3,4,5)
listBuffer.append(6,7,8,9)//末尾追加元素
listBuffer.+=(10)//末尾追加元素
listBuffer.+=:(100)//在开头加入元素
listBuffer.foreach(x => print(x.toString + "\t"))
}
9.3 集合
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| def +(elem: A): Set[A] | 为集合添加新元素,x并创建一个新的集合,除非元素已存在 |
| def -(elem: A): Set[A] | 移除集合中的元素,并创建一个新的集合 |
| def contains(elem: A): Boolean | 如果元素在集合中存在,返回 true,否则返回 false。 |
| def &(that: Set[A]): Set[A] | 返回两个集合的交集 |
| def &~(that: Set[A]): Set[A] | 返回两个集合的差集 |
| def +(elem1: A, elem2: A, elems: A*): Set[A] | 通过添加传入指定集合的元素创建一个新的不可变集合 |
| def ++(elems: A): Set[A] | 合并两个集合 |
| def -(elem1: A, elem2: A, elems: A*): Set[A] | 通过移除传入指定集合的元素创建一个新的不可变集合 |
| def addString(b: StringBuilder): StringBuilder | 将不可变集合的所有元素添加到字符串缓冲区 |
| def addString(b: StringBuilder, sep: String): StringBuilder | 将不可变集合的所有元素添加到字符串缓冲区,并使用指定的分隔符 |
| def apply(elem: A) | 检测集合中是否包含指定元素 |
| def count(p: (A) => Boolean): Int | 计算满足指定条件的集合元素个数 |
| def copyToArray(xs: Array[A], start: Int, len: Int): Unit | 复制不可变集合元素到数组 |
| def diff(that: Set[A]): Set[A] | 比较两个集合的差集 |
| def drop(n: Int): Set[A]] | 返回丢弃前n个元素新集合 |
| def dropRight(n: Int): Set[A] | 返回丢弃最后n个元素新集合 |
| def dropWhile(p: (A) => Boolean): Set[A] | 从左向右丢弃元素,直到条件p不成立 |
| def equals(that: Any): Boolean | equals 方法可用于任意序列。用于比较系列是否相等。 |
| def exists(p: (A) => Boolean): Boolean | 判断不可变集合中指定条件的元素是否存在。 |
| def filter(p: (A) => Boolean): Set[A] | 输出符合指定条件的所有不可变集合元素。 |
| def find(p: (A) => Boolean): Option[A] | 查找不可变集合中满足指定条件的第一个元素 |
| def forall(p: (A) => Boolean): Boolean | 查找不可变集合中满足指定条件的所有元素 |
| def foreach(f: (A) => Unit): Unit | 将函数应用到不可变集合的所有元素 |
| def head: A | 获取不可变集合的第一个元素 |
| def init: Set[A] | 返回所有元素,除了最后一个 |
| def intersect(that: Set[A]): Set[A] | 计算两个集合的交集 |
| def isEmpty: Boolean | 判断集合是否为空 |
| def iterator: Iterator[A] | 创建一个新的迭代器来迭代元素 |
| def last: A | 返回最后一个元素 |
| def map[B](f: (A) => B): immutable.Set[B] | 通过给定的方法将所有元素重新计算 |
| def max: A | 查找最大元素 |
| def min: A | 查找最小元素 |
| def mkString: String | 集合所有元素作为字符串显示 |
| def mkString(sep: String): String | 使用分隔符将集合所有元素作为字符串显示 |
| def product: A | 返回不可变集合中数字元素的积。 |
| def size: Int | 返回不可变集合元素的数量 |
| def splitAt(n: Int): (Set[A], Set[A]) | 把不可变集合拆分为两个容器,第一个由前 n 个元素组成,第二个由剩下的元素组成 |
| def subsetOf(that: Set[A]): Boolean | 如果集合A中含有子集B返回 true,否则返回false |
| def sum: A | 返回不可变集合中所有数字元素之和 |
| def tail: Set[A] | 返回一个不可变集合中除了第一元素之外的其他元素 |
| def take(n: Int): Set[A] | 返回前 n 个元素 |
| def takeRight(n: Int):Set[A] | 返回后 n 个元素 |
| def toArray: Array[A] | 将集合转换为数组 |
| def toBuffer[B >: A]: Buffer[B] | 返回缓冲区,包含了不可变集合的所有元素 |
| def toList: List[A] | 返回 List,包含了不可变集合的所有元素 |
| def toMap[T, U]: Map[T, U] | 返回 Map,包含了不可变集合的所有元素 |
| def toSeq: Seq[A] | 返回 Seq,包含了不可变集合的所有元素 |
| def toString(): String | 返回一个字符串,以对象来表示 |
- 不可变集合
object Demo23 extends App {
val set1 = Set(1, 2, 3, 4, 4)
set1.foreach(x => print(x + "\t"))//1 2 3 4
println()
//1 2 3 4
for (s <- set1) {
print(s + "\t")
}
}
- 可变集合
import scala.collection.mutable.Set
object Demo24 extends App {
val set1 = Set[Int](1,2,3,4,5)
set1.add(100)
set1.+=(1,210,300)
set1.foreach(x=>print(x+"\t"))//1 300 100 5 2 3 210 4
}
9.4 Map
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| def ++(xs: Map[(A, B)]): Map[A, B] | 返回一个新的 Map,新的 Map xs 组成 |
| def -(elem1: A, elem2: A, elems: A*): Map[A, B] | 返回一个新的 Map, 移除 key 为 elem1, elem2 或其他 elems。 |
| def --(xs: GTO[A]): Map[A, B] | 返回一个新的 Map, 移除 xs 对象中对应的 key |
| def get(key: A): Option[B] | 返回指定 key 的值 |
| def iterator: Iterator[(A, B)] | 创建新的迭代器,并输出 key/value 对 |
| def addString(b: StringBuilder): StringBuilder | 将 Map 中的所有元素附加到StringBuilder,可加入分隔符 |
| def addString(b: StringBuilder, sep: String): StringBuilder | 将 Map 中的所有元素附加到StringBuilder,可加入分隔符 |
| def apply(key: A): B | 返回指定键的值,如果不存在返回 Map 的默认方法 |
| def clone(): Map[A, B] | 从一个 Map 复制到另一个 Map |
| def contains(key: A): Boolean | 如果 Map 中存在指定 key,返回 true,否则返回 false。 |
| def copyToArray(xs: Array[(A, B)]): Unit | 复制集合到数组 |
| def count(p: ((A, B)) => Boolean): Int | 计算满足指定条件的集合元素数量 |
| def default(key: A): B | 定义 Map 的默认值,在 key 不存在时返回。 |
| def drop(n: Int): Map[A, B] | 返回丢弃前n个元素新集合 |
| def dropRight(n: Int): Map[A, B] | 返回丢弃最后n个元素新集合 |
| def dropWhile(p: ((A, B)) => Boolean): Map[A, B] | 从左向右丢弃元素,直到条件p不成立 |
| def empty: Map[A, B] | 返回相同类型的空 Map |
| def equals(that: Any): Boolean | 如果两个 Map 相等(key/value 均相等),返回true,否则返回false |
| def exists(p: ((A, B)) => Boolean): Boolean | 判断集合中指定条件的元素是否存在 |
| def filter(p: ((A, B))=> Boolean): Map[A, B] | 返回满足指定条件的所有集合 |
| def filterKeys(p: (A) => Boolean): Map[A, B] | 返回符合指定条件的的不可变 Map |
| def find(p: ((A, B)) => Boolean): Option[(A, B)] | 查找集合中满足指定条件的第一个元素 |
| def foreach(f: ((A, B)) => Unit): Unit | 将函数应用到集合的所有元素 |
| def init: Map[A, B] | 返回所有元素,除了最后一个 |
| def isEmpty: Boolean | 检测 Map 是否为空 |
| def keys: Iterable[A] | 返回所有的key/p> |
| def last: (A, B) | 返回最后一个元素 |
| def max: (A, B) | 查找最大元素 |
| def min: (A, B) | 查找最小元素 |
| def mkString: String | 集合所有元素作为字符串显示 |
| def product: (A, B) | 返回集合中数字元素的积。 |
| def remove(key: A): Option[B] | 移除指定 key |
| def retain(p: (A, B) => Boolean): Map.this.type | 如果符合满足条件的返回 true |
| def size: Int | 返回 Map 元素的个数 |
| def sum: (A, B) | 返回集合中所有数字元素之和 |
| def tail: Map[A, B] | 返回一个集合中除了第一元素之外的其他元素 |
| def take(n: Int): Map[A, B] | 返回前 n 个元素 |
| def takeRight(n: Int): Map[A, B] | 返回后 n 个元素 |
| def takeWhile(p: ((A, B)) => Boolean): Map[A, B] | 返回满足指定条件的元素 |
| def toArray: Array[(A, B)] | 集合转数组 |
| def toBuffer[B >: A]: Buffer[B] | 返回缓冲区,包含了 Map 的所有元素 |
| def toList: List[A] | 返回 List,包含了 Map 的所有元素 |
| def toSeq: Seq[A] | 返回 Seq,包含了 Map 的所有元素 |
| def toSet: Set[A] | 返回 Set,包含了 Map 的所有元素 |
| def toString(): String | 返回字符串对象 |
- 不可变Map
object Demo25 extends App {
val map = Map[String, Int]("a" -> 100, "b" -> 200, ("c", 300), ("c", 400))
val option1: Option[Int] = map.get("a")
val option2: Option[Int] = map.get("aa")
println("从map中取键为a的值\t"+option1) //从map中取键为a的值 Some(100)
println("从map中取键为a的值\t"+option1.get) //从map中取键为a的值 100
println("从map中取键为aa的值\t"+option2) //从map中取键为aa的值 None
println("从map中取键为aa的值\t"+option2.getOrElse("no value")) //从map中取键为aa的值 no value
println(map) //Map(a -> 100, b -> 200, c -> 400)
//(a,100) (b,200) (c,400)
for (elem <- map) {
print(elem + "\t")
}
println()
val keys: Iterable[String] = map.keys
//key = a ,value = 100 key = b ,value = 200 key = c ,value = 400
keys.foreach(key => {
val value = map.get(key).get
print(s"key = $key ,value = $value\t")
})
println()
val values: Iterable[Int] = map.values
values.foreach(x => print(x + "\t")) //100 200 400
println()
}
- 可变Map
import scala.collection.mutable.Map
object Demo26 extends App {
val map2 = Map[String, Int]()
map2.put("hello", 100)
map2.put("world", 200)
map2.put("hadoop", 200)
println(map2.mkString("\t")) //hadoop -> 200 world -> 200 hello -> 100
//count
val countResult = map2.count(x => {
x._1.equals("hadoop") && x._2 == 200
})
println(s"键为hadoop值为200的元素有 $countResult 个") //键为hadoop值为200的元素有 1 个
//filter
map2.filter(_._1 == "world").foreach(x => println((x._1, x._2))) //(world,200)
//contains
println("是否有键为hello的元素", map2.contains("hello")) //(是否有键为hello的元素,true)
//exist
println("符合条件的元素存在么", map2.exists(x => {
x._1.equals("hadoop")
})) //(符合条件的元素存在么,true)
}
9.5 元组
object Demo27 extends App {
val tuple1: Tuple1[String] = new Tuple1("hello")
val tuple2: (String, Int) = new Tuple2("a", 100)
val tuple3: (Int, Boolean, Char) = new Tuple3(1, true, 'C')
val tuple4: (Int, Double, String, Boolean) = Tuple4(1, 3.4, "abc", false)
val tuple6: (Int, Int, Int, Int, Int, String) = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, "abc")
val tuple22 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, "abc", 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22)
println("取值:" + tuple22._13) //取值:abc
println("输出整个元组:" + tuple4) //输出整个元组:(1,3.4,abc,false)
val iter: Iterator[Any] = tuple6.productIterator
//1 2 3 4 5 abc
while (iter.hasNext) {
print(iter.next() + "\t")
}
println()
//1 2 3 4 5 abc
tuple6.productIterator.foreach(x => print(x + "\t"))
}
10 Scala高级
10.1 高阶函数
能够接收函数作为参数的函数,或者返回值是函数的函数,就是高阶函数
object Demo28 extends App {
def sumNum(num1: Int, num2: Int)(f: (Int, Int) => Int): Unit = {
println(f(num1, num2))
}
sumNum(1, 2)(_ + _) //3
}
10.2 部分引用函数
在Scala中_充当占位符
object Demo29 extends App {
def add(num1: Int, num2: Int): Int = {
num1 + num2
}
val intAdd: Int => Int = add(1,_)
println(intAdd(1)) //2
println(intAdd(2)) //3
println(intAdd(3)) //4
}
10.3 柯里化
从单个参数列表,换成多个参数列表,简化了函数的调用,主要配合隐式值使用。
object Demo30 extends App {
def add(x: Int)(y: Int) = x + y
println(add(1)(2)) //3
implicit val a: Int = 10
def implicitAdd(x: Int)(implicit y: Int) = x + y
println(implicitAdd(1)) //11
}
10.4 Map映射
主要用来转化结构
object Demo31 extends App {
//val seq: IndexedSeq[String] = 1.to(10).map(x => x + "->")
val seq: IndexedSeq[String] = 1.to(10).map(_ + "->")
println(seq) //Vector(1->, 2->, 3->, 4->, 5->, 6->, 7->, 8->, 9->, 10->)
}
10.5 Filter过滤
object Demo32 extends App {
val list = List(10, 20, 30, 40)
val filterList: List[Int] = list.filter(_ > 10)
println(filterList.mkString(",")) //20,30,40
}
10.6 FlatMap平面化
object Demo33 extends App {
val list: List[List[Int]] = List(List(1, 2), List(3, 4), List(5, 6))
val fList: List[Int] = list.flatMap(list => list.map(_ * 2))
println(fList) //List(2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12)
}
10.7 Reduce聚合
object Demo34 extends App {
val list = List(1, 2, 3, 4)
val result: Int = list.reduce(_ + _)
println(result) //10
}
10.8 FoldLeft左折叠
Reduce加强版,如下wordCount案例
import scala.collection.mutable.Map
object Demo35 extends App {
val list = List("a", "b", "c", "d", "a", "b", "c", "a", "b", "a")
//写法一
val metaMap1: Map[String, Int] = Map[String, Int]()
val foldMap1: Map[String, Int] = list.foldLeft(metaMap1)((mp, listElement) => {
mp(listElement) = mp.getOrElse(listElement, 0) + 1
mp
})
println(foldMap1) //Map(b -> 3, d -> 1, a -> 4, c -> 2)
//写法二
val metaMap2: Map[String, Int] = Map[String, Int]()
val foldMap2: Map[String, Int] = (metaMap2 /: list) ((mp, listElement) => {
mp(listElement) = mp.getOrElse(listElement, 0) + 1
mp
})
println(foldMap2) //Map(b -> 3, d -> 1, a -> 4, c -> 2)
}
10.9 Scan扫描
保存折叠过程中的结果
object Demo36 extends App {
val list: List[Int] = 1.to(10).toList
val result: List[Int] = list.scan(0)(_ + _)
println(result) //List(0, 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, 28, 36, 45, 55)
}
10.10 拉链
object Demo37 extends App {
val list1: List[Int] = 1.to(10).toList
val list2: List[Int] = 11.to(19).toList
val tuples1: List[(Int, Int)] = list1.zip(list2)
val tuples2: List[(Int, Int)] = list1.zipAll(list2, 100, 200)
//如果数量不等,多的丢弃
println(tuples1) //List((1,11), (2,12), (3,13), (4,14), (5,15), (6,16), (7,17), (8,18), (9,19))
//如果数量不等,使用默认值补齐
println(tuples2) //List((1,11), (2,12), (3,13), (4,14), (5,15), (6,16), (7,17), (8,18), (9,19), (10,200))
val unzip: (List[Int], List[Int]) = tuples1.unzip
println(unzip) //(List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),List(11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19))
}
spark中数量不等,会抛异常
10.11 分组
object Demo38 extends App {
val list = List("a", "b", "c", "d", "a", "b", "c", "a", "b", "a")
val map: Map[String, List[String]] = list.groupBy(ele => ele)
println(map) //Map(b -> List(b, b, b), d -> List(d), a -> List(a, a, a, a), c -> List(c, c))
val result: Map[String, Int] = map.map(kv => (kv._1, kv._2.length))
println(result) //Map(b -> 3, d -> 1, a -> 4, c -> 2)
}
10.12 排序
object Demo39 extends App {
val list = List(1, 5, 8, 2, 3, 6)
//sorted排序
val slist1: List[Int] = list.sorted
println(slist1) //List(1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8)
val slist2: List[Int] = list.sorted(Ordering.Int.reverse)
println(slist2) //List(8, 6, 5, 3, 2, 1)
val sonList = List(Son("zhangsan", 10), Son("lisi", 5), Son("wangwu", 15))
implicit val sonOrdering = new Ordering[Son] {
override def compare(x: Son, y: Son): Int = {
x.age - y.age
}
}
println(sonList.sorted) //List(name:lisi,age:5, name:zhangsan,age:10, name:wangwu,age:15)
println(sonList.sorted(sonOrdering.reverse)) //List(name:wangwu,age:15, name:zhangsan,age:10, name:lisi,age:5)
//sortWith排序
val sortWithList: List[Int] = list.sortWith((x, y) => x < y)
println(sortWithList) //List(1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8)
val sortWithSon: List[Son] = sonList.sortWith((x, y) => x.age > y.age)
println(sortWithSon) //List(name:wangwu,age:15, name:zhangsan,age:10, name:lisi,age:5)
//sortBy
val sons1: List[Son] = sonList.sortBy(son=>(son.name.length))(Ordering.Int.reverse)
println(sons1) //List(name:zhangsan,age:10, name:wangwu,age:15, name:lisi,age:5)
val sons2: List[Son] = sonList.sortBy(son=>(son.name,son.age))(Ordering.Tuple2(Ordering.String.reverse,Ordering.Int.reverse))
println(sons2) //List(name:zhangsan,age:10, name:wangwu,age:15, name:lisi,age:5)
}
class Son(val name: String, val age: Int) {
override def toString: String = s"name:${name},age:${age}"
}
object Son {
def apply(name: String, age: Int): Son = new Son(name, age)
}
10.13 Stream
object Demo40 extends App {
val list = List(1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8)
val stream: Stream[Int] = list.toStream
println(stream.head) //1
println(stream.tail) //Stream(2, ?)
stream.tail.foreach(x => print(s"$x\t")) //2 3 5 6 8
println()
stream.take(3).foreach(x => print(s"$x\t")) //1 2 3
}
10.14 View
object Demo41 extends App {
val list = List(1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8)
val view = list.view
println(view.head) //1
view.tail.foreach(x => print(s"$x\t")) //2 3 5 6 8
}
10.15 切片
object Demo42 extends App {
val list = 1.to(10).toList
val slice1: List[Int] = list.slice(0, list.length - 1)
val slice2: List[Int] = list.slice(1, list.length)
val tuples: List[(Int, Int)] = slice1.zip(slice2)
println(tuples) //List((1,2), (2,3), (3,4), (4,5), (5,6), (6,7), (7,8), (8,9), (9,10))
val result: List[String] = tuples.map(tuples => tuples._1 + "->" + tuples._2)
println(result) //List(1->2, 2->3, 3->4, 4->5, 5->6, 6->7, 7->8, 8->9, 9->10)
}
10.16 模式匹配
10.16.1 基础模式匹配
object Demo43 extends App {
def operator(x: Int, y: Int, opt: String): Any = {
opt match {
case "+" => x + y
case "-" => x - y
case "*" => x * y
case "/" => x.toDouble / y.toDouble
case _ =>
}
}
println(operator(3, 2, "+")) //5
println(operator(3, 2, "-")) //1
println(operator(3, 2, "*")) //6
println(operator(3, 2, "/")) //1.5
println(operator(3, 2, "xxx")) //()
}
10.16.2 守卫模式匹配
object Demo44 extends App {
def operator(x: Char, y: Char, opt: String): Any = {
opt match {
case "+" => x + y
case "-" => x - y
case "*" => x * y
case "/" => x.toDouble / y.toDouble
case _ if (!Character.isDigit(x) || !Character.isDigit(y)) => "数字传递错误" //模式匹配守卫
case _ => "error"
}
}
println(operator('3', '2', "+")) //5
println(operator('3', '2', "-")) //1
println(operator('3', '2', "*")) //6
println(operator('3', '2', "/")) //1.5
println(operator('3', 'x', "xxx")) //数字传递错误
println(operator('3', '2', "xxx")) //error
}
10.16.3 变量作用域
object Demo45 extends App {
//z... ch在自己的作用域中,当做变量来处理,那么就可以匹配任意值,并赋值给ch
val ch = 'a'
'z' match {
case 'a' => println("a...")
case ch => println(ch + "...")
case _ => println("_...")
}
//_... 当首字母大写时,当做常量来处理,正常匹配流程
val Ch = 'a'
'z' match {
case 'a' => println("a...")
case Ch => println(Ch + "...")
case _ => println("_...")
}
}
10.16.4 类型匹配
object Demo46 extends App {
/**
* 20
* a
* 30
* b
* 40
* c
*/
val list = List(10, "a", 20, "b", 30, "c")
for (elem <- list) {
elem match {
case n: Int => println(n + 10)
case s: String => println(s)
case _ =>
}
}
//int array
val arr: Array[_] = Array[Int]()
arr match {
case arr: Array[String] => println("string array")
case arr: Array[Int] => println("int array")
}
}
10.17 样例类
使用了case关键字的类定义就是样例类(case classes),样例类是种特殊的类。实现了类构造参数的getter方法(构造参数默认被声明为val),当构造参数是声明为var类型的,它将帮你实现setter和getter方法。
样例类默认帮你实现了apply,toString,equals,copy和hashCode等方法。
样例类可以new, 也可以不用new
和模式匹配兼容性很好
object Demo47 extends App {
val p1 = Father("lisi", 20)
val p2 = Son("wangwu", 30)
/**
* father->name:lisi,age:20
* son->name:wangwu,age:30
*/
val list = List(p1, p2)
list.foreach(x => {
x match {
case Father(name,age) => println(s"father->name:$name,age:$age")
case Son(name,age) => println(s"son->name:$name,age:$age")
case _ => println("no match")
}
})
}
abstract class Person()
case class Father(name: String, age: Int)extends Person
case class Son(name: String, age: Int) extends Person
10.18 偏函数
如果一个方法中没有match 只有case,这个函数可以定义成PartialFunction偏函数。偏函数定义时,不能使用括号传参,默认定义PartialFunction中传入一个值,匹配上了对应的case,返回一个值。
只会出现满足的case,类似filter+map效果
object demo48 extends App {
def inc: PartialFunction[Any, Int] = {
case i: Int => i + 1
case _ => 0
}
val list = List(1, 3, 5, "seven") collect inc
println(list) //List(2, 4, 6, 0)
}
10.19 名调用
函数传名调用
Scala的解释器在解析函数参数(function arguments)时有两种方式:
- 传值调用(call-by-value):先计算参数表达式的值,再应用到函数内部;
- 传名调用(call-by-name):将未计算的参数表达式直接应用到函数内部
在进入函数内部前,传值调用方式就已经将参数表达式的值计算完毕,而传名调用是在函数内部进行参数表达式的值计算的。
这就造成了一种现象,每次使用传名调用时,解释器都会计算一次表达式的值。
object demo49 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val fun = add(println("abc"))
println(fun)
/**
* 结果为:
* abc
* ()
* abc
* ()
* 1
*
* 因为println返回值为(),add函数内调用函数a,属于名调用,在调用之前,a函数会被执行,每调用一次,解析执行一次
* */
}
def add(a: => Unit): Int = {
println(a)
println(a)
1
}
}
11 Actor
- Actor Model是用来编写并行计算或分布式系统的高层次抽象(类似java中的Thread)让程序员不必为多线程模式下共享锁而烦恼,被用在Erlang 语言上, 高可用性99.9999999 % 一年只有31ms 宕机Actors将状态和行为封装在一个轻量的进程/线程中,但是不和其他Actors分享状态,每个Actors有自己的世界观,当需要和其他Actors交互时,通过发送事件和消息,发送是异步的,非堵塞的(fire-andforget),发送消息后不必等另外Actors回复,也不必暂停,每个Actors有自己的消息队列,进来的消息按先来后到排列,这就有很好的并发策略和可伸缩性,可以建立性能很好的事件驱动系统。
- Actor的特征:
- ActorModel是消息传递模型,基本特征就是消息传递
- 消息发送是异步的,非阻塞的
- 消息一旦发送成功,不能修改
- Actor之间传递时,自己决定决定去检查消息,而不是一直等待,是异步非阻塞的
- 什么是Akka
- Akka 是一个用 Scala 编写的库,用于简化编写容错的、高可伸缩性的 Java 和Scala 的 Actor 模型应用,底层实现就是Actor,Akka是一个开发库和运行环境,可以用于构建高并发、分布式、可容错、事件驱动的基于JVM的应用。使构建高并发的分布式应用更加容易。
- spark1.6版本之前,spark分布式节点之间的消息传递使用的就是Akka,底层也就是actor实现的。1.6之后使用的netty传输。
- 案例一
import scala.actors.Actor
object Demo50 extends App {
//创建actor的消息接收和传递
val actor = new myActor()
//启动
actor.start()
//发送消息写法
/**
* get String =i love you !
* get Int
* get default
* */
actor ! "i love you !"
actor ! 500
actor ! true
}
class myActor extends Actor {
def act() {
while (true) {
receive {
case x: String => println("get String =" + x)
case x: Int => println("get Int")
case _ => println("get default")
}
}
}
}
- 案例2
import scala.actors.Actor
object Demo51 extends App {
val actor1 = new Actor1()
actor1.start()
val actor2 = new Actor2(actor1)
actor2.start()
/**
* i sava msg! = i love you !
* i love you too !
* could we have a date !
* */
}
case class Message(actor: Actor, msg: Any)
class Actor1 extends Actor {
def act() {
while (true) {
receive {
case msg: Message => {
println("i sava msg! = " + msg.msg)
msg.actor ! "i love you too !"
}
case msg: String => println(msg)
case _ => println("default msg!")
}
}
}
}
class Actor2(actor: Actor) extends Actor {
actor ! Message(this, "i love you !")
def act() {
while (true) {
receive {
case msg: String => {
if (msg.equals("i love you too !")) {
println(msg)
actor ! "could we have a date !"
}
}
case _ => println("default msg!")
}
}
}
}

您的资助是我最大的动力!
金额随意,欢迎来赏!

