Codeforces Round #777(Div.2) [A~D]
链接:contest link
A.Modaka and Math Dad
题目
给定 \(n\) ,求不含 \(0\) 且相邻数位不相等的最大十进制数,且这个十进制数各数位上数字和为 \(n\)
分析
考虑如何产生最大的十进制数,必然要使位数尽可能多,而数位和为 \(n\) ,所以每个数位上的数字为 \(1\) 或 \(2\) 时位数最多。由于相邻数位不能相等,那么答案一定是 \(1212\cdots\) 或 \(2121\cdots\) ,所以答案中 \(1\) 的个数 \(x\) 和 \(2\) 的个数 \(y\) 只有三种情况:
-
\(x=y+1\)
\(\therefore n=x+2y=3y+1\Rightarrow n\bmod 3=1\)
进一步求出位数为 \(x+y=\frac{2(n-1)}{3}+1\) ,且首位为 \(1\)
-
\(x=y\)
\(\therefore n=x+2y=3y\Rightarrow n\bmod 3=0\)
位数为 \(x+y=\frac{2n}{3}\) ,且首位为 \(2\)
-
\(x=y-1\)
\(\therefore n=x+2y=3y-1\Rightarrow n\bmod 3=2\)
位数为 \(x+y=\frac{2(n+1)}{3}-1\) ,且首位为 \(2\)
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
if(n % 3 == 2) {
for(int i = 1; i <= (n + 1) * 2 / 3 - 1; i++)
cout << (i % 2 ? 2 : 1);
} else if(n % 3 == 1) {
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * (n - 1) / 3 + 1; i++)
cout << (i % 2 ? 1 : 2);
} else {
for(int i = 1; i <= n * 2 / 3; i++)
cout << (i % 2 ? 2 : 1);
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B.Madoka and the Elegant Gift
题目
给定一个由 \(n\) 行 \(m\) 列个方块组成的矩形表,每个方块上有一个数字,为 \(0\) 或 \(1\) ,有如下定义:
- 当所有在子矩形 \(A\) 中的方块都在子矩形 \(B\) 中时,\(A\) 包含于 \(B\)
- 两个子矩形的交集指的是同时在两个子矩形中的方块的集合
- 当一个子矩形中不存在数字为 \(0\) 的方块时我们称这个子矩形是 black 的
- 当一个子矩形是 black 的且它不包含于另一个 black 的子矩形时我们称这个子矩形是 nice 的
- 当一个矩形表中不存在两个 nice 且交集不为空的子矩形时我们称这个矩形表是 elegant 的
判断给定的矩形表是否是 elegant 的
分析
可以发现两个 nice 且交集不为空的子矩形形成的形状一定不是一个新的矩形(如下图),否则就违反了性质4
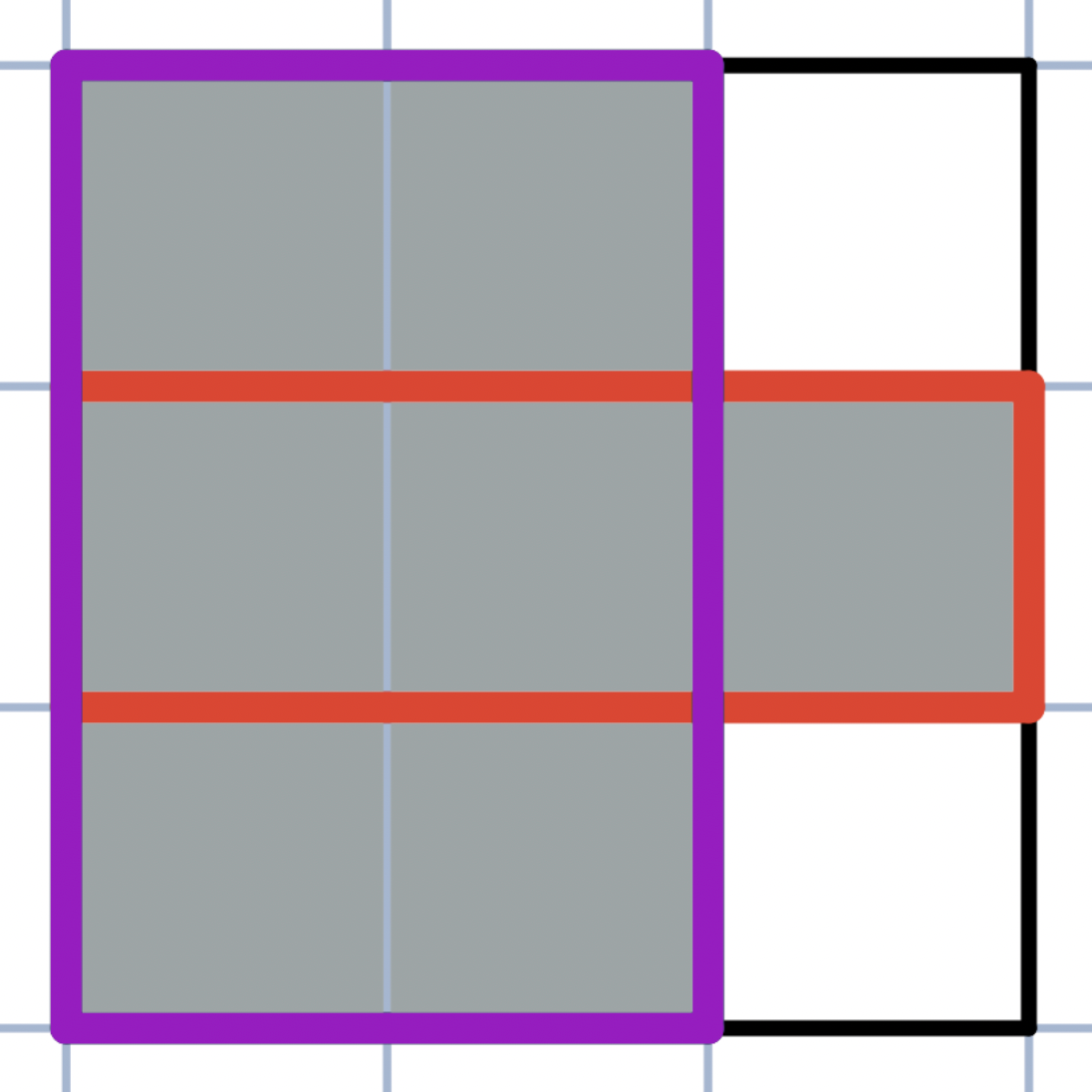
那么只需要用一个dfs用类似于求连通块的方法求出一整片数字为 \(1\) 的区域,并记录边界,例如上图的边界左上角就是 \((1,1)\) ,由于紫色矩形覆盖了第 \(3\) 行的部分区域,红色矩形覆盖了第 \(3\) 列的部分区域,所以边界右下角是 \((3,3)\)
求出边界后再遍历边界里的所有方块,如果存在为 \(0\) 的方块则这个区域一定是由两个 nice 且交集不为空的子矩形组成的
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool mat[100 + 5][100 + 5];
bool vis[100 + 5][100 + 5];
int n, m;
int dx[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int dy[] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
void dfs(int x, int y, int &x1, int &y1, int &x2, int &y2)
{
vis[x][y] = true;
x1 = min(x, x1);
x2 = max(x, x2);
y1 = min(y, y1);
y2 = max(y, y2);
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];
if(nx < 1 || nx > n || ny < 1 || ny > m || mat[nx][ny] != mat[x][y] || vis[nx][ny])
continue;
dfs(nx, ny, x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
}
bool check(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2)
{
for(int i = x1; i <= x2; i++)
for(int j = y1; j <= y2; j++)
if(!mat[i][j])
return false;
return true;
}
bool solve()
{
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
if(!vis[i][j] && mat[i][j]) {
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
x1 = x2 = i;
y1 = y2 = j;
dfs(i, j, x1, y1, x2, y2);
if(!check(x1, y1, x2, y2)) {
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--) {
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
string s;
cin >> s;
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
mat[i][j] = s[j - 1] - '0';
}
cout << (solve() ? "YES" : "NO") << endl;
}
return 0;
}
C.Madoka and Childish Pranks
题目
题意较复杂,参照原文:Problem C
代码
分析坐标为 \((x,y)\) 的方块
- 如果要使 \((x,y)\) 变为
1,那么当 \(x>1\) 时只要对 \((x-1,y),(x,y)\) 执行一次操作,当 \(y>1\) 时只要对 \((x,y-1),(x,y)\) 执行一次操作即可,当 \(x=y=1\) 时无法操作 - 如果要使其变为
0,直接对 \((x,y),(x,y)\) 执行一次操作即可
注意到每次操作只会影响左边或者上面的方块,所以我们从右到左,从下到上依次操作,这样可以确保当前的操作就不会影响之前已经处理好的方块,而处理一个方块要用的操作要么为 \(0\) 次要么为 \(1\) 次,所以 \(n\) 行 \(m\) 列的方块总操作数不超过 \(n\times m\) ,满足条件。当 \((1,1)\) 为 1 时无论什么操作都无法成功
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool mat1[100 + 5][100 + 5], mat2[100 + 5][100 + 5];
int n, m;
struct step {
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
} st[100000 + 5];
int cnt;
void solve()
{
if(mat1[1][1] == true) {
cnt = -1;
return;
}
cnt = 0;
memset(mat2, 0, sizeof(mat2));
for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
for(int j = m; j >= 1; j--) {
if(mat1[i][j] != mat2[i][j]) {
if(mat1[i][j]) {
if(j >= 2) {
mat2[i][j] = true;
mat2[i][j - 1] = false;
st[++cnt] = {i, j - 1, i, j};
} else {
mat2[i][j] = true;
mat2[i - 1][j] = false;
st[++cnt] = {i - 1, j, i, j};
}
} else {
mat2[i][j] = false;
st[++cnt] = {i, j, i, j};
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--) {
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
string s;
cin >> s;
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
mat1[i][j] = s[j - 1] - '0';
}
solve();
cout << cnt << endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
cout << st[i].x1 << ' ' << st[i].y1 << ' ' << st[i].x2 << ' ' << st[i].y2 << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
D.Madoka and the Best School in Russia
题目
给定整数 \(x,d\) ,有如下定义:
- 如果一个数是 \(d\) 的倍数则称它是好的
- 如果一个数是好的且它不能被表示为两个好数的乘积,那么称它是美的
判断是否存在两种或以上方法,将 \(x\) 分解为若干个美数的乘积
分析
设一个好数为 \(k_1d\) ,另一个好数为 \(k_2d\) ,那么 \(k_1k_2d^2\) 就不是美数,且 \(k_1k_2\) 可以取到任意整数,那么可以得出 \(n\) 为美数的充要条件是 \(d\mid n,d^2\not\mid n\)
设 \(x=d^p\times q\) 其中 \(d\not\mid q\)
-
若 \(p=0\) ,显然方案数为 \(0\)
-
若 \(p=1\) ,只有一种方案 \(x=x\)
-
若 \(p\geq 2\) ,可以发现其中一种方案为:\(x=d\cdot d\cdots(dq)\) ,另一种方案存在与否需要继续分类:
-
若 \(q\not\in \mathbb{P}\) ,设 \(q=ab\) 则有 \(x=(da)\cdot(db)\cdot d\cdots d\)
-
若 \(q\in\mathbb{P}\)
-
若 \(d\in \mathbb{P}\)
不存在其他方案
-
若 \(d\not\in\mathbb{P}\) ,设 \(d=mn\)
- \(p\geq 4\) 时 \(x=(dn)\cdot(dm)\cdot(dq)\cdot d\cdots d\)
- \(p=2\) 时不存在其他方案
- \(p=3\) 时
- 若 \(d\) 是 \(q\) 的幂次,设 \(d=q^k\)
- \(k=2\) 时不存在其他方案
- \(k\geq 3\) 时 \(x=(dq^{k-1})\cdot(dq^2)\)
- 若 \(d\) 不是 \(q\) 的幂次,则 \(d\) 存在与 \(q\) 互质的因子,设为 \(m\) ,因为 \(d=mn\) ,所以 \(qn\) 不是 \(d\) 的倍数,所以有 \(x=(dqn)\cdot(dm)\)
- 若 \(d\) 是 \(q\) 的幂次,设 \(d=q^k\)
-
-
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int prime(int x)
{
for (int i = 2; i * i <= x; ++i) {
if (x % i == 0)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void solve()
{
int x, d;
cin >> x >> d;
int cnt = 0;
while (x % d == 0) {
++cnt;
x /= d;
}
if (cnt == 1) {
cout << "NO\n";
return;
}
if (prime(x) != -1) {
cout << "YES\n";
return;
}
if (prime(d) != -1 && d == prime(d) * prime(d)) {
if (x == prime(d) && cnt == 3) {
cout << "NO\n";
return;
}
}
if (cnt > 2 && prime(d) != -1) {
cout << "YES\n";
return;
}
cout << "NO\n";
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号