【题解】【UVA】UVA10181 15-Puzzle Problem
题外话:
老师:这些题都不难,都只是搜索+剪枝
我:不会……
题面
十五数码问题 保证45步内有解
题解
IDA*入门题目,和八数码问题没差多少
↑抱着天真想法的我
事实上,这题比八数码难了不少……
首先,先像八数码一样把IDA*敲好
然后?
然后你发现样例你都T了
WDNMD
——发现自己样例TLE之后的我
冷静分析一波

首先我们从开始条件入手:
- 如果一开始就符合,那就不用搜了,直接输出空行
- 如果无解,也不用搜了,直接输出“This puzzle is not solvable.”
似乎很科学
问题是怎么判断无解呢
直接上结论,证明在此
先将表格平铺,然后计算N=逆序数对之和,e=空白所在的行数。若N+e为偶数,则有解,反之无解
如此,我们可以减掉很多的无解情况
然后你满心欢喜地交上去
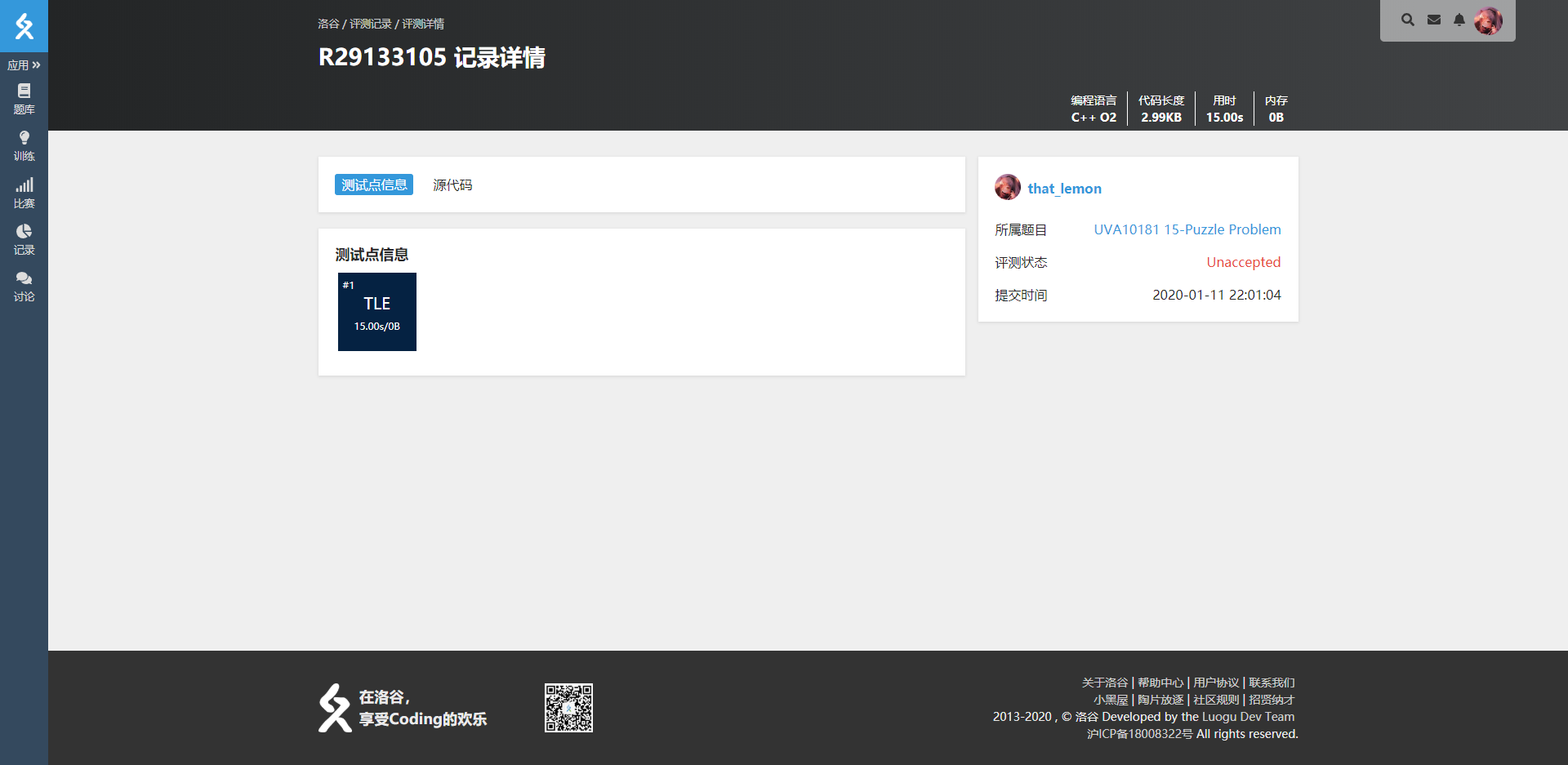
WDNMD*2
我们还要继续剪枝
我们知道,IDA*的效率很大程度上建立在估价函数的好坏上
然后我们看下我这种菜鸡写出来的估价函数\(g(x)\):
inline int count() {
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<4;j++) {
if (a[i][j]!=ans[i][j]) {
cnt++;
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
发现了吗?它给出的下界太松了
考虑这样一个事实:
我们要让一个元素归位,最理想的情况是一路畅通无阻地换过去,没有任何浪费的步数
所以,让一个元素归为的最小代价是这个元素当前位置和目标位置的曼哈顿距离
根据上一个结论,我们可以打出这个估价函数:
inline int count() {
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<4;j++) {
if (!a[i][j]) {
continue;
}
int goal_x=(a[i][j]-1)/4;
int goal_y=(a[i][j]-1)%4;
cnt+=abs(goal_x-i)+abs(goal_y-j);
}
}
return cnt;
}
完美~
交上去,过啦!
再不过就没有天理了
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int d[4][2]={{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
const int ans[4][4]={{1,2,3,4},
{5,6,7,8},
{9,10,11,12},
{13,14,15,0}};
const char mp[4]={'D','R','L','U'};
inline void read(int &x) {
x=0;
int f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {
if (ch=='-') {
f=-1;
}
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
x*=f;
}
int a[4][4];
inline int check() {
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<4;j++) {
if (a[i][j]!=ans[i][j]) {
return 0;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
int found;
inline int count() {
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<4;j++) {
if (!a[i][j]) {
continue;
}
int goal_x=(a[i][j]-1)/4;
int goal_y=(a[i][j]-1)%4;
cnt+=abs(goal_x-i)+abs(goal_y-j);
}
}
return cnt;
}
char sol[50];
void Astar(int step,int x,int y,int max_step,int last_step) {
if (step==max_step) {
if (check()) {
found=1;
}
return;
}
if (found) {
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) {
int x1=x+d[i][0],y1=y+d[i][1];
if (i+last_step==3) {
continue;
}
if (x1<0||x1>3||y1<0||y1>3) {
continue;
}
swap(a[x][y],a[x1][y1]);
if (!(count()+step>max_step)&&!found) {
sol[step+1]=mp[i];
Astar(step+1,x1,y1,max_step,i);
}
swap(a[x][y],a[x1][y1]);
}
}
int p[20];
inline int solveable() {
int cnt=0,con=0;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<4;j++) {
p[con++]=a[i][j];
}
}
for(int i=0;i<16;i++) {
if (p[i]==0) {
cnt+=3-(i/4);
} else {
for(int j=0;j<i;j++) {
if (p[j]&&p[j]>p[i]) {
cnt++;
}
}
}
}
return !(cnt&1);
}
int main() {
int t;
read(t);
while(t--) {
int sx,sy;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<4;j++) {
read(a[i][j]);
if (a[i][j]==0) {
sx=i;
sy=j;
}
}
}
if (check()) {
printf("\n");
continue;
}
if (!solveable()) {
printf("This puzzle is not solvable.\n");
continue;
}
int max_step=1;
for(;;max_step++) {
Astar(0,sx,sy,max_step,-1);
if (found) {
break;
}
}
if (found) {
for(int i=1;i<=max_step;i++) {
putchar(sol[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
found=0;
}
return 0;
}

