学习笔记——K-D tree
K-D tree学习笔记
0x00 前置知识
BST,最好学过替罪羊树
0x01 引入
看一道SB题:
给定一个\(n*n\)的二维数组,每个格子里有一个整数,初始时全部为0
现在有两种操作:
\(1\ x\ y\ A\)给a[x][y]加上A
\(2\ x1\ y1\ x2\ y2\) 求\((x1,y1)(x2,y2)\)这个矩阵的数字和
输入3终止输入
我:老师我会树套树!
老师:
空间限制\(20MB\)
我:……老师我会CDQ!
老师:
接下来每行一个操作。每条命令除第一个数字之外,均要异或上一次输出的答案\(lastans\),初始时\(lastans=0\)。
我:……老师我会暴力
老师:
\(1\leq N\leq 500000\),操作数不超过\(200000\)个
我:CNM
这种问题怎么解决?
答曰:K-D tree
0x02 思考
定义:有效点为矩阵中的非零点
容易发现,矩阵中的有效点十分稀少
因此,考虑用一个什么东西来维护这些点
老师!我会!BST!
如何比较两个点?
老师!我会!以x为关键字!
考虑这么一个东西:
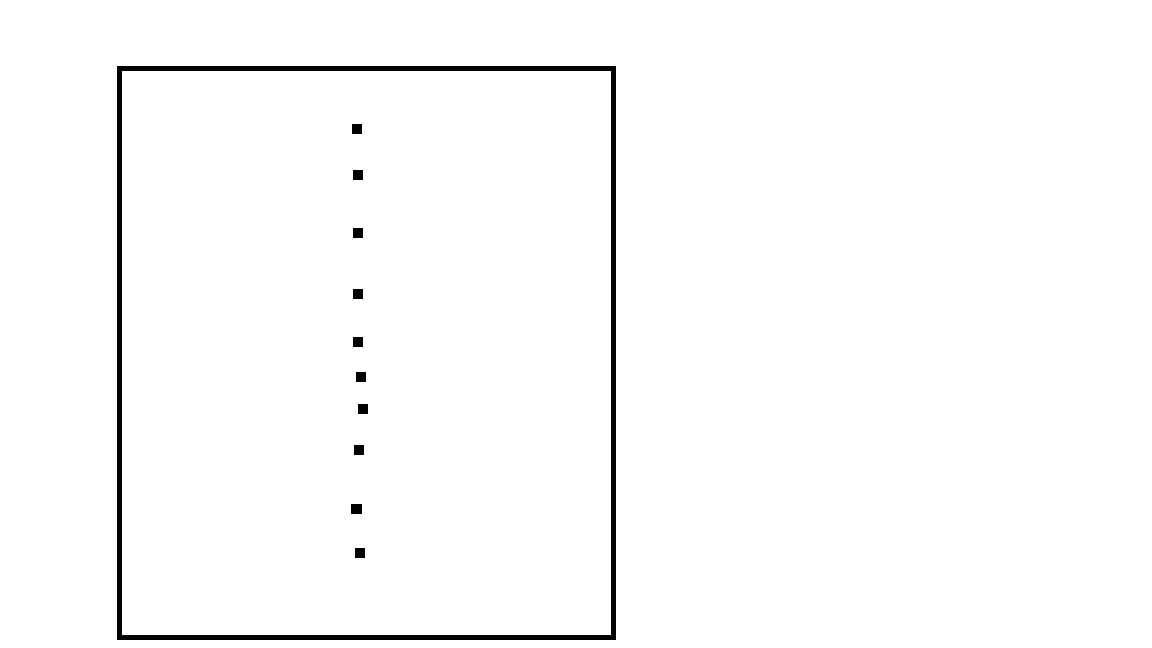
你发现他们的x都差不多,这时候一个个暴力找y就和暴力没有什么区别了
老师:你们想一想怎么办
我:(数十分钟的沉默)
老师:很简单的
我:(持续沉默)
老师:不要停留在一个维度上
懂了吗?
不一定要一定以某一个维度作为关键字,我们可以轮流来
这样子的话,直观感受下,分割大概是这个样子的:
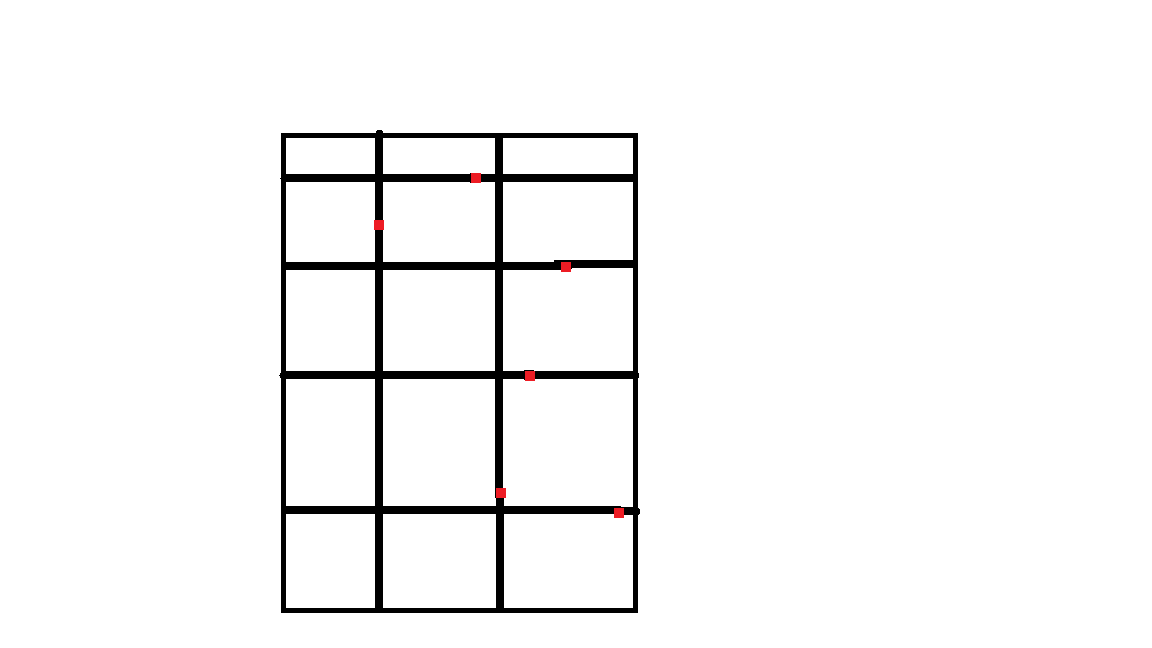
红色的点为有效点
这就似乎可以了?
思考怎么查询
这部分并不能讲清楚,所以直接放代码
inline bool in_range(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int a1,int b1,int a2,int b2) {
return (a1>=x1&&a2<=x2&&b1>=y1&&b2<=y2);
}
inline bool out_range(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int a1,int b1,int a2,int b2) {
return (a2<x1 || x2<a1 || b2<y1 || y2<b1);
}
int query(int o,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2) {
if (!o) {
return 0;
}
int r=0;
if (in_range(x1,y1,x2,y2,t[o].min_n[0],t[o].min_n[1],t[o].max_n[0],t[o].max_n[1])) {
return t[o].sum;
}
if (out_range(x1,y1,x2,y2,t[o].min_n[0],t[o].min_n[1],t[o].max_n[0],t[o].max_n[1])) {
return 0;
}
if (in_range(x1,y1,x2,y2,t[o].val.w[0],t[o].val.w[1],t[o].val.w[0],t[o].val.w[1])) {
r+=t[o].val.val;
}
r+=query(t[o].ch[0],x1,y1,x2,y2)+query(t[o].ch[1],x1,y1,x2,y2);
return r;
}
很好理解但说不出来,所以就这样吧
复杂度玄学,听说是\(O(nlogn)\)~\(O(n \sqrt{n})\)
0x03 (只有时间的)正确性保证
仅仅是轮换维度并不能保证复杂度就是正确的,仍然可以像卡BST一样去卡K-D tree
为了避免这种情况,我们想把BST换成平衡树
首先,每一层有一个唯一对应的维度,这直接决定了我们的query函数的正确定,而旋转会破坏这个性质
因此,我们选用的平衡树不能带旋转操作
于是:\(fhq\_treap\)和替罪羊树之间选一个吧
为了方便,肯定是替罪羊树啊!
我自己YY的解释:
因为fhq_treap需要大量的up和down操作(当然在K-D tree中并没有down),而K-D tree的up常数不是一般的大,加上fhq_treap本身的常数,很容易被卡常,因此选用替罪羊树
当然大部分题可以直接建出一颗平衡的树而之后再也没有修改操作于是BST就完事了
0x04 结束
就这样吧,建议在luogu上把那5道题做一下,你就成功地入门了!(实话
下面是例题的代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N=250010;
const int K=2;
const double alpha=0.75;
inline void read(int &x) {
x=0;
int f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {
if (ch=='-') {
f=-1;
}
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
x*=f;
}
struct point {
int w[K];
int val;
};
struct note {
int ch[2];
int max_n[K],min_n[K];
int sum;
int siz;
point val;
};
int rt;
point p[N];
note t[N];
int siz;
int WD;
queue<int> tra;
inline bool comp(const point &x,const point &y) {
return x.w[WD]<y.w[WD];
}
inline int new_node() {
if (!tra.empty()) {
int x=tra.front();
tra.pop();
return x;
}
return ++siz;
}
inline void up(int o) {
t[o].siz=t[t[o].ch[0]].siz+t[t[o].ch[1]].siz+1;
t[o].sum=t[t[o].ch[0]].sum+t[t[o].ch[1]].sum+t[o].val.val;
for(int i=0;i<K;i++) {
t[o].max_n[i]=t[o].min_n[i]=t[o].val.w[i];
for(int j=0;j<=1;j++) {
if (t[o].ch[j]) {
t[o].max_n[i]=max(t[o].max_n[i],t[t[o].ch[j]].max_n[i]);
t[o].min_n[i]=min(t[o].min_n[i],t[t[o].ch[j]].min_n[i]);
}
}
}
}
void build(int &o,int l,int r,int d) {
if (l>r) {
return;
}
o=new_node();
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
WD=d;
nth_element(p+l,p+mid,p+r+1,comp);
t[o].val=p[mid];
build(t[o].ch[0],l,mid-1,(d+1)%K);
build(t[o].ch[1],mid+1,r,(d+1)%K);
up(o);
}
void Beat_flat(int o,int &tot) {
if (t[o].ch[0]) {
Beat_flat(t[o].ch[0],tot);
}
p[++tot]=t[o].val;
if (t[o].ch[1]) {
Beat_flat(t[o].ch[1],tot);
}
}
inline void rebuild(int &o,int d) {
int tot=0;
Beat_flat(o,tot);
build(o,1,tot,d);
}
inline bool check(int o) {
if (t[o].siz*alpha<t[t[o].ch[0]].siz||t[o].siz*alpha<t[t[o].ch[1]].siz) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void insert(int &o,point val,int d) {
if (!o) {
o=new_node();
t[o].ch[0]=t[o].ch[1]=0;
t[o].val=val;
up(o);
return;
}
if (val.w[d]<=t[o].val.w[d]) {
insert(t[o].ch[0],val,(d+1)%K);
} else {
insert(t[o].ch[1],val,(d+1)%K);
}
up(o);
if (check(o)) {
rebuild(o,d);
}
}
inline bool in_range(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int a1,int b1,int a2,int b2) {
return (a1>=x1&&a2<=x2&&b1>=y1&&b2<=y2);
}
inline bool out_range(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int a1,int b1,int a2,int b2) {
return (a2<x1 || x2<a1 || b2<y1 || y2<b1);
}
int query(int o,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2) {
if (!o) {
return 0;
}
int r=0;
if (in_range(x1,y1,x2,y2,t[o].min_n[0],t[o].min_n[1],t[o].max_n[0],t[o].max_n[1])) {
return t[o].sum;
}
if (out_range(x1,y1,x2,y2,t[o].min_n[0],t[o].min_n[1],t[o].max_n[0],t[o].max_n[1])) {
return 0;
}
if (in_range(x1,y1,x2,y2,t[o].val.w[0],t[o].val.w[1],t[o].val.w[0],t[o].val.w[1])) {
r+=t[o].val.val;
}
r+=query(t[o].ch[0],x1,y1,x2,y2)+query(t[o].ch[1],x1,y1,x2,y2);
return r;
}
int n,m;
int last_ans;
inline void in(int &x) {
read(x);
x^=last_ans;
}
int main() {
read(n);
for(;;) {
int opx;
read(opx);
if (opx==1) {
int x,y,A;
in(x),in(y),in(A);
insert(rt,(point){{x,y},A},0);//加上一个数可以看做插入一个关键点
} else if (opx==2) {
int x1,y1,x2,y2;
in(x1),in(y1),in(x2),in(y2);
printf("%d\n",last_ans=query(rt,x1,y1,x2,y2));
} else {
break;
}
}
return 0;
}

