数据库编程是互联网编程的基础,Spring框架为开发者提供了JDBC模板模式,即jdbcTemplate,它可以简化许多代码,但在实际应用中jdbcTemplate并不常用。工作更多的时候,用的是Hibernate框架和MyBatis框架进行数据库编程。
package entity; public class MyUser { private Integer uid; private String uname; private String usex; public Integer getUid() { return uid; } public void setUid(Integer uid) { this.uid = uid; } public String getUname() { return uname; } public void setUname(String uname) { this.uname = uname; } public String getUsex() { return usex; } public void setUsex(String usex) { this.usex = usex; } public String toString() { return "myUser [uid=" + uid + ", uname=" + uname + ", usex=" + usex + "]"; } }
package dao; import java.util.List; import entity.MyUser; public interface TestDao { public int update(String sql, Object[] param); public List<MyUser> query(String sql, Object[] param); }
package dao; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import entity.MyUser; @Repository public class TestDaoImpl implements TestDao { @Autowired // 使用配置类中的JDBC模板 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; /** * 更新方法,包括添加、修改、删除 param为sql中的参数,如通配符? */ @Override public int update(String sql, Object[] param) { return jdbcTemplate.update(sql, param); } /** * 查询方法 param为sql中的参数,如通配符? */ @Override public List<MyUser> query(String sql, Object[] param) { RowMapper<MyUser> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<MyUser>(MyUser.class); return jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rowMapper); } }
package service; public interface TestService { public void testJDBC(); }
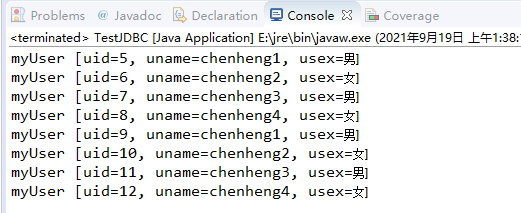
package service; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import dao.TestDao; import entity.MyUser; @Service @Transactional public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService { @Autowired public TestDao testDao; @Override public void testJDBC() { String insertSql = "insert into user values(null,?,?)"; // 数组param的值与insertSql语句中?一一对应 Object param1[] = { "chenheng1", "男" }; Object param2[] = { "chenheng2", "女" }; Object param3[] = { "chenheng3", "男" }; Object param4[] = { "chenheng4", "女" }; String insertSql1 = "insert into user values(?,?,?)"; Object param5[] = { 1, "chenheng5", "女" }; Object param6[] = { 1, "chenheng6", "女" }; // 添加用户 testDao.update(insertSql, param1); testDao.update(insertSql, param2); testDao.update(insertSql, param3); testDao.update(insertSql, param4); // 添加两个ID相同的用户,出现唯一性约束异常,使事物回滚。 //testDao.update(insertSql1, param5); //testDao.update(insertSql1, param6); // 查询用户 String selectSql = "select * from user"; List<MyUser> list = testDao.query(selectSql, null); for (MyUser mu : list) { System.out.println(mu); } } }
package config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; @Configuration // 通过该注解来表明该类是一个Spring的配置,相当于一个xml文件 @ComponentScan(basePackages = { "dao", "service" }) // 配置扫描包 //配置多个配置文件value={"classpath:jdbc.properties","xx","xxx"} @PropertySource(value = { "classpath:jdbc.properties" }, ignoreResourceNotFound = true) @EnableTransactionManagement // 开启声明式事务的支持 public class SpringJDBCConfig { @Value("${jdbc.url}") // 注入属性文件jdbc.properties中的jdbc.url private String jdbcUrl; @Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}") private String jdbcDriverClassName; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String jdbcUsername; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String jdbcPassword; /** * 配置数据源 */ @Bean public DriverManagerDataSource dataSource() { System.out.println(this.jdbcUrl); System.out.println(this.jdbcDriverClassName); System.out.println(this.jdbcUsername); System.out.println(this.jdbcPassword); DriverManagerDataSource myDataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource(); // 数据库驱动 myDataSource.setDriverClassName(this.jdbcDriverClassName); // 相应驱动的jdbcUrl myDataSource.setUrl(this.jdbcUrl); // 数据库的用户名 myDataSource.setUsername(this.jdbcUsername); // 数据库的密码 myDataSource.setPassword(this.jdbcPassword); return myDataSource; } /** * 配置JdbcTemplate */ @Bean(value = "jdbcTemplate") public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate() { return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource()); } /** * 为数据源添加事务管理器 */ @Bean public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager() { DataSourceTransactionManager dt = new DataSourceTransactionManager(); dt.setDataSource(dataSource()); return dt; } }
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springtest?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=admin
package config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import service.TestService; public class TestJDBC { public static void main(String[] args) { // 初始化Spring容器ApplicationContext AnnotationConfigApplicationContext appCon = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringJDBCConfig.class); TestService ts = appCon.getBean(TestService.class); ts.testJDBC(); appCon.close(); } }
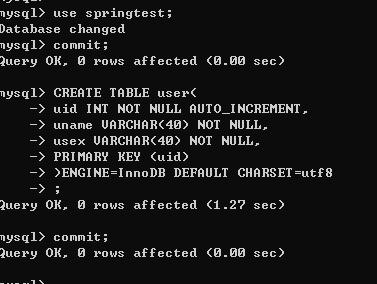
CREATE DATABASE springtest; commit; use springtest; commit; CREATE TABLE user( uid INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, uname VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL, usex VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (uid) )ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ; commit;