


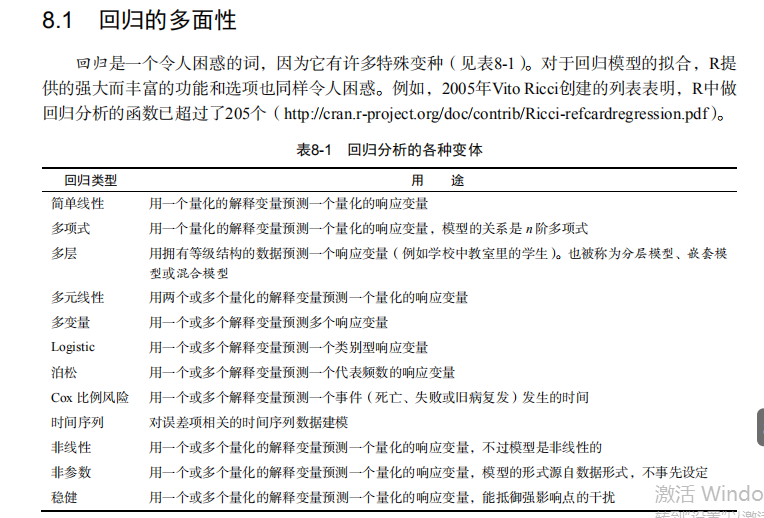






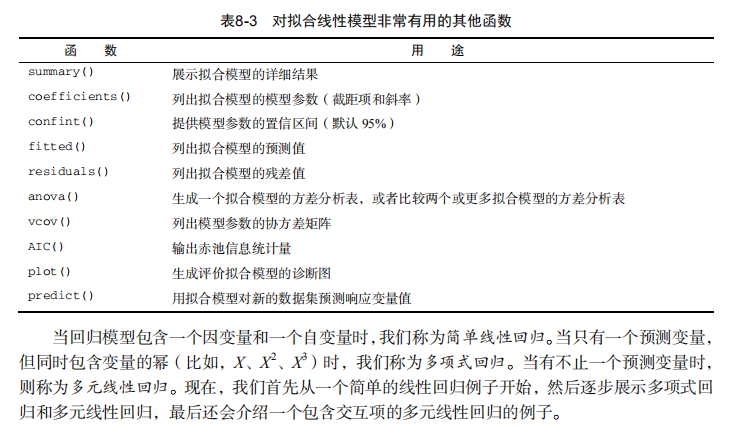
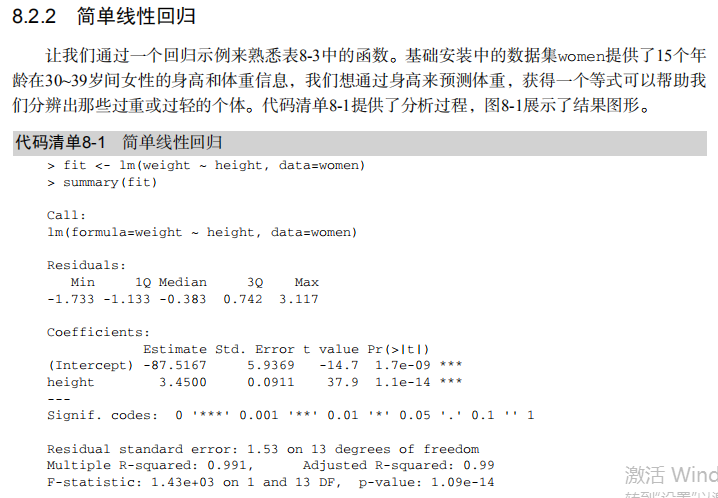

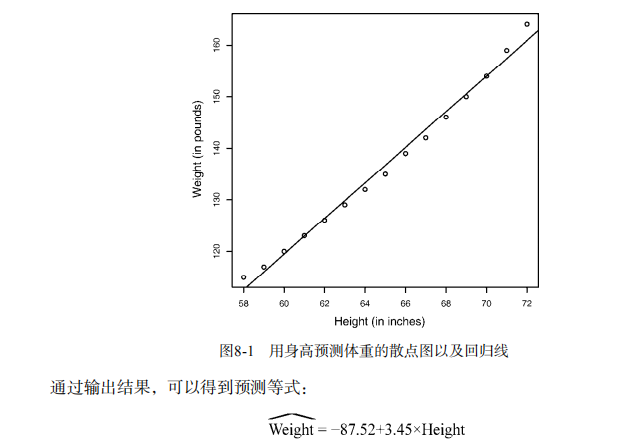

#------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 8 # # Regression # # requires packages car, gvlma, MASS, leaps to be installed # # install.packages(c("car", "gvlma", "MASS", "leaps")) # #------------------------------------------------------------# par(ask=TRUE) opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE) # Listing 8.1 - Simple linear regression fit <- lm(weight ~ height, data=women) summary(fit) women$weight fitted(fit) residuals(fit) plot(women$height,women$weight, main="Women Age 30-39", xlab="Height (in inches)", ylab="Weight (in pounds)") # add the line of best fit abline(fit) # Listing 8.2 - Polynomial regression fit2 <- lm(weight ~ height + I(height^2), data=women) summary(fit2) plot(women$height,women$weight, main="Women Age 30-39", xlab="Height (in inches)", ylab="Weight (in lbs)") lines(women$height,fitted(fit2)) # Enhanced scatterplot for women data library(car) library(car) scatterplot(weight ~ height, data=women, spread=FALSE, smoother.args=list(lty=2), pch=19, main="Women Age 30-39", xlab="Height (inches)", ylab="Weight (lbs.)") # Listing 8.3 - Examining bivariate relationships states <- as.data.frame(state.x77[,c("Murder", "Population", "Illiteracy", "Income", "Frost")]) cor(states) library(car) scatterplotMatrix(states, spread=FALSE, smoother.args=list(lty=2), main="Scatter Plot Matrix") # Listing 8.4 - Multiple linear regression states <- as.data.frame(state.x77[,c("Murder", "Population", "Illiteracy", "Income", "Frost")]) fit <- lm(Murder ~ Population + Illiteracy + Income + Frost, data=states) summary(fit) # Listing 8.5 - Mutiple linear regression with a significant interaction term fit <- lm(mpg ~ hp + wt + hp:wt, data=mtcars) summary(fit) library(effects) plot(effect("hp:wt", fit,, list(wt=c(2.2, 3.2, 4.2))), multiline=TRUE) # simple regression diagnostics fit <- lm(weight ~ height, data=women) par(mfrow=c(2,2)) plot(fit) newfit <- lm(weight ~ height + I(height^2), data=women) par(opar) par(mfrow=c(2,2)) plot(newfit) par(opar) # basic regression diagnostics for states data opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE) fit <- lm(weight ~ height, data=women) par(mfrow=c(2,2)) plot(fit) par(opar) fit2 <- lm(weight ~ height + I(height^2), data=women) opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE) par(mfrow=c(2,2)) plot(fit2) par(opar) # Assessing normality library(car) states <- as.data.frame(state.x77[,c("Murder", "Population", "Illiteracy", "Income", "Frost")]) fit <- lm(Murder ~ Population + Illiteracy + Income + Frost, data=states) qqPlot(fit, labels=row.names(states), id.method="identify", simulate=TRUE, main="Q-Q Plot") # Listing 8.6 - Function for plotting studentized residuals residplot <- function(fit, nbreaks=10) { z <- rstudent(fit) hist(z, breaks=nbreaks, freq=FALSE, xlab="Studentized Residual", main="Distribution of Errors") rug(jitter(z), col="brown") curve(dnorm(x, mean=mean(z), sd=sd(z)), add=TRUE, col="blue", lwd=2) lines(density(z)$x, density(z)$y, col="red", lwd=2, lty=2) legend("topright", legend = c( "Normal Curve", "Kernel Density Curve"), lty=1:2, col=c("blue","red"), cex=.7) } residplot(fit) # Assessing linearity library(car) crPlots(fit) # Listing 8.7 - Assessing homoscedasticity library(car) ncvTest(fit) spreadLevelPlot(fit) # Listing 8.8 - Global test of linear model assumptions library(gvlma) gvmodel <- gvlma(fit) summary(gvmodel) # Listing 8.9 - Evaluating multi-collinearity library(car) vif(fit) sqrt(vif(fit)) > 2 # problem? # Assessing outliers library(car) outlierTest(fit) # Identifying high leverage points hat.plot <- function(fit) { p <- length(coefficients(fit)) n <- length(fitted(fit)) plot(hatvalues(fit), main="Index Plot of Hat Values") abline(h=c(2,3)*p/n, col="red", lty=2) identify(1:n, hatvalues(fit), names(hatvalues(fit))) } hat.plot(fit) # Identifying influential observations # Cooks Distance D # identify D values > 4/(n-k-1) cutoff <- 4/(nrow(states)-length(fit$coefficients)-2) plot(fit, which=4, cook.levels=cutoff) abline(h=cutoff, lty=2, col="red") # Added variable plots # add id.method="identify" to interactively identify points library(car) avPlots(fit, ask=FALSE, id.method="identify") # Influence Plot library(car) influencePlot(fit, id.method="identify", main="Influence Plot", sub="Circle size is proportial to Cook's Distance" ) # Listing 8.10 - Box-Cox Transformation to normality library(car) summary(powerTransform(states$Murder)) # Box-Tidwell Transformations to linearity library(car) boxTidwell(Murder~Population+Illiteracy,data=states) # Listing 8.11 - Comparing nested models using the anova function states <- as.data.frame(state.x77[,c("Murder", "Population", "Illiteracy", "Income", "Frost")]) fit1 <- lm(Murder ~ Population + Illiteracy + Income + Frost, data=states) fit2 <- lm(Murder ~ Population + Illiteracy, data=states) anova(fit2, fit1) # Listing 8.12 - Comparing models with the AIC fit1 <- lm(Murder ~ Population + Illiteracy + Income + Frost, data=states) fit2 <- lm(Murder ~ Population + Illiteracy, data=states) AIC(fit1,fit2) # Listing 8.13 - Backward stepwise selection library(MASS) states <- as.data.frame(state.x77[,c("Murder", "Population", "Illiteracy", "Income", "Frost")]) fit <- lm(Murder ~ Population + Illiteracy + Income + Frost, data=states) stepAIC(fit, direction="backward") # Listing 8.14 - All subsets regression library(leaps) states <- as.data.frame(state.x77[,c("Murder", "Population", "Illiteracy", "Income", "Frost")]) leaps <-regsubsets(Murder ~ Population + Illiteracy + Income + Frost, data=states, nbest=4) plot(leaps, scale="adjr2") library(car) subsets(leaps, statistic="cp", main="Cp Plot for All Subsets Regression") abline(1,1,lty=2,col="red") # Listing 8.15 - Function for k-fold cross-validated R-square shrinkage <- function(fit,k=10){ require(bootstrap) # define functions theta.fit <- function(x,y){lsfit(x,y)} theta.predict <- function(fit,x){cbind(1,x)%*%fit$coef} # matrix of predictors x <- fit$model[,2:ncol(fit$model)] # vector of predicted values y <- fit$model[,1] results <- crossval(x,y,theta.fit,theta.predict,ngroup=k) r2 <- cor(y, fit$fitted.values)**2 # raw R2 r2cv <- cor(y,results$cv.fit)**2 # cross-validated R2 cat("Original R-square =", r2, "\n") cat(k, "Fold Cross-Validated R-square =", r2cv, "\n") cat("Change =", r2-r2cv, "\n") } # using it states <- as.data.frame(state.x77[,c("Murder", "Population", "Illiteracy", "Income", "Frost")]) fit <- lm(Murder ~ Population + Income + Illiteracy + Frost, data=states) shrinkage(fit) fit2 <- lm(Murder~Population+Illiteracy,data=states) shrinkage(fit2) # Calculating standardized regression coefficients states <- as.data.frame(state.x77[,c("Murder", "Population", "Illiteracy", "Income", "Frost")]) zstates <- as.data.frame(scale(states)) zfit <- lm(Murder~Population + Income + Illiteracy + Frost, data=zstates) coef(zfit) # Listing 8.16 rlweights function for clculating relative importance of predictors relweights <- function(fit,...){ R <- cor(fit$model) nvar <- ncol(R) rxx <- R[2:nvar, 2:nvar] rxy <- R[2:nvar, 1] svd <- eigen(rxx) evec <- svd$vectors ev <- svd$values delta <- diag(sqrt(ev)) lambda <- evec %*% delta %*% t(evec) lambdasq <- lambda ^ 2 beta <- solve(lambda) %*% rxy rsquare <- colSums(beta ^ 2) rawwgt <- lambdasq %*% beta ^ 2 import <- (rawwgt / rsquare) * 100 import <- as.data.frame(import) row.names(import) <- names(fit$model[2:nvar]) names(import) <- "Weights" import <- import[order(import),1, drop=FALSE] dotchart(import$Weights, labels=row.names(import), xlab="% of R-Square", pch=19, main="Relative Importance of Predictor Variables", sub=paste("Total R-Square=", round(rsquare, digits=3)), ...) return(import) } # Listing 8.17 - Applying the relweights function states <- as.data.frame(state.x77[,c("Murder", "Population", "Illiteracy", "Income", "Frost")]) fit <- lm(Murder ~ Population + Illiteracy + Income + Frost, data=states) relweights(fit, col="blue")



