vue_02_重学Vue
重学_vue_01
基础
创建 VUE 实例的几种方式
创建组件实例有两个方法:1.通过 new Vue()、2. 通过 new 构造器()
挂载到容器上也有两个方法:1. 通过mount
-
Vue 实例 new Vue()
- 可以通过自身 components 引用 vue.extend 构造,通过自身 data 向构造传参
- 可以通过自身 component 引用组件模版,通过自身 data 向组件传参
-
Vue 组件 Vue.Component()
Vue.Component('name', options) 用来创建全局组件
options 可以是 Vue.extend 或 {}- 可通过自身初始化组件结构
- 可通过引入 vue.extend 初始化组件结构
- 可通过第三方模版 temple.html 初始化组件结构
- 使用范围: 任何已被 vue 初始化的元素内
-
Vue 构造 Vue.extend( options )
参数 options 是一个包含组件选项的对象,data 比较特殊必须是一个方法
vue.extend 创建了一个 vue 组件的子类但是没有实例化这个子类,可以挂载在组件是使用- 只能通过自身初始化结构 使用范围
- 挂载在某元素下
- 被 vue 实例的 components 引用
- Vue.component 组件引用
-
new vue,vue.extend,vue.component 的区别
关系:vue 构造--->vue 组件---->vue 实例
不同的组件可以共用同一个 vue 构造,不同的 vue 实例可以共用一个 vue 组件
// Vue 构造
const extend1 = Vue.extend({
template: `<div>{{text}}</div>`,
props: ['T'],
data: function() {
return {
text: "这里是构造器"
}
}
})
const extend2 = {
template: `<div>{{text}}</div>`,
props: ['T'],
data: function() {
return {
text: "其中也可以不使用 extend 方法,而直接定义对象。"
}
}
}
// Vue 组件
Vue.component("name1", extend1); // 可以是 Vue.extend
Vue.component("name2", extend2); // 也可以直接是个对象
// Vue 实例
// 当要在页面展示时,需要用到组件实例,需要将要展示的组件实例和容器绑定起来。
// 创建组件实例有两个方法:1. 通过new Vue(); 2.通过new 构造器()。
// 挂载到容器上也有两个方法:1. 通过$el;2. 通过$mount
// 通过new Vue()
new Vue {
el: "#app",
data: function() {
return {
}
}
}
const app = new Vue {
data: function() {
return {}
}
}
app.$mount('#app');
const componentA = { /* ... */};
new Vue {
components: {
'component-a': componentA,
}
}
// 通过new 构造器()
new extend1({
el: "#app",
propsData: {
T: "可以通过xxx创建xxx"
}
})
new extend2().$mount('#app');
// 组件的渲染方式也有两种,普通的就是通过字符串模板,即HTML,在通过component。
// 还可以通过渲染函数——render。
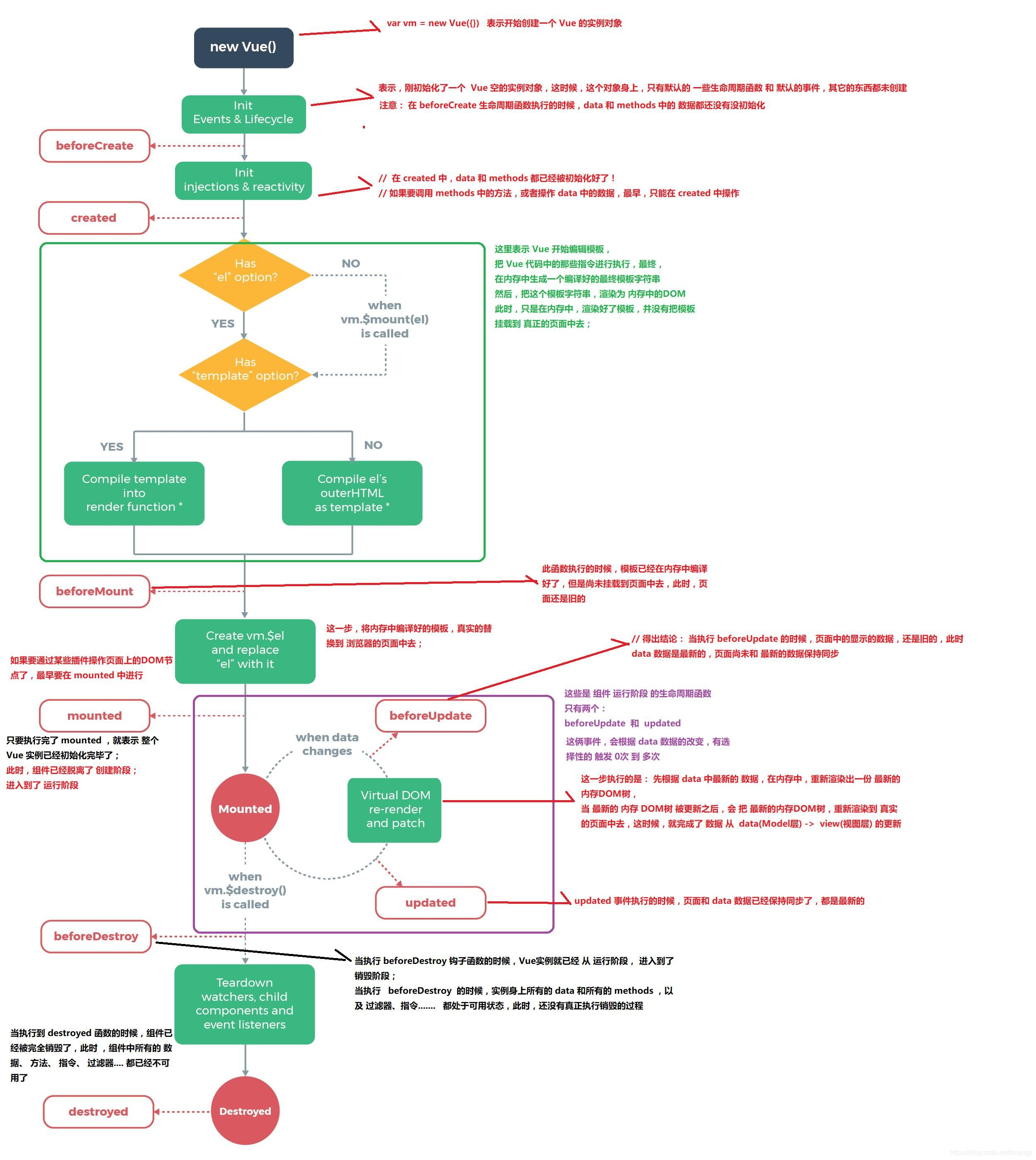
VUE 的生命周期
1. 生命周期
Vue是一个构造函数,当执行执行这个函数时,相当于初始化vue实例在创建实例过程中,需要设置数据监听,编译模板,将实例挂载到DOM上,数据更新能够让DOM也更新,在这个初始化,又会不同阶段默认调用一些函数执行,这些函数就是生命周期的钩子函数
- beforeCreate // vue 实例 创建前
- created // 创建实例成功(一般此处请求实现数据的异步请求)
- beforeMount // 第一次渲染前
- mounted // 渲染成功
- beforeUpdate // 更新前
- updated // 更新完成
- beforeDestroy // 销毁前
- destroyed // 销毁完成
注:创建前后 可以获取数据及方法 渲染前后可以获取到真实的 DOM 更新前后能数据更新执行 销毁前后 销毁实例、数据不在双向绑定
2.其它三个钩子函数
生命周期钩子函数,让开发者在初始化实例时,添加自己的代码; 生命周期的钩子函数中的this,会默认指向vue的实例;
component 内置组件,用 is 属性来判断组件; is 属性的属性值和组件名称一直
keep-alive 内置组件 用于缓存组件
- activated // 当缓存组件有被显示出来时,会触发这个钩子函数
- deactivated // 当缓存的组件隐藏时,会触发这个钩子函数;
- errorCaptured // 当子孙组件出错时,会调用这个钩子函数
const html1 = `<div>模板1</div>`;
const html2 = `<div>模板2</div>`;
const html3 = `<div>模板3</div>`;
const template = `
<keep-alive>
<component :is="element"></component>
</keep-alive>
`;
const app = new Vue({
template: template,
data: function() {
return data {
element: 'html1',
}
},
components: {
html1: html1,
html2: html2,
html3: html3
},
beforeCreate() {
console.log("vue 实例化之前");
},
created() {
console.log("创建后");
},
beforeMount() {
console.log("渲染前");
},
mounted() {
console.log("渲染后");
},
beforeUpdate() {
console.log("更新前");
},
updated() {
console.log("更新后");
},
beforeDestroy() {
console.log("销毁前");
},
destroyed() {
console.log("销毁后");
},
activated() {
console.log("缓存的组件显示出来了");
},
deactivated() {
console.log("缓存的组件被隐藏了");
},
errorCaptured(a,b,c) {
// 当捕获一个来自子孙组件的错误时被调用。
// 此钩子会收到三个参数:错误对象、发生错误的组件实例以及一个包含错误来源信息的字符串。
// 此钩子可以返回 false 以阻止该错误继续向上传播。
console.log("子组件报错");
},
methods: {
fn() {
const ary = ['html1', 'html2', 'html3'];
let fi = ary.indexOf(this.element);
if(fi<2) {
this.element = ary[fi+1];
} else {
this.element = ary[0];
}
}
}
});
数据、方法
Vue实现使用new Vue函数创建,当一个 Vue 实例被创建时,它向 Vue 的响应式系统中加入了其 data 对象中能找到的所有的属性,当这些属性的值发生改变时,视图将会产生“响应”,即匹配更新为新的值
- 一般用 {{...}} 来引用属性
- vue 中使属性双向绑定,需要将属性写在data中
- 可用 Object.freeze() 阻止修改现有属性
new Vue({
template:
`<div id="app">
<input :value="data"/>
</div>`,
data() {
return {
data: "",
}
},
created() {
this.closeData = ""; // 此处会挂载在 当前实例上 但是无法双向绑定
},
update() {
this.getData();
},
methods: {
getData() {
console.log("data", data); // data
}
}
})
计算属性和侦听器
- 计算属性在依赖的响应式属性改变之前会一直返回之前计算好的值`
- 侦听属性监听的属性必须是data中声明过或props中的数据,当数据发送变化的时候触发其它操作`
- 侦听属性对对象或数组进行监听的时候可以设置
deep:true开启深度监听 也可以通过 计算属性+侦听属性的方式监听对象属性的改变 设置immediate: true可以让侦听属性在页面开始时便开始监听`
new Vue({
template: `<div>{{fullName}} || {{fullName('123456')}}</div>`,
data() {
return {
name: "",
obj: {
name: ''
}
}
},
computed: { // 计算属性
fullName: {
set: (newValue)=>{
this.name = "xxxxxxxxx"+newValue;
},
get: ()=>{
return this.name + 'xxxxxxxxx';
}
}
},
watch: {
name: (newValue, oldValue)=>{
this.name = newValue + oldValue;
},
'obj.name': {
handler: (newValue, oldValue) => {
},
deep:true, // 深度监听
immediate:true ,// 是否在页面开始的时候运行
}
}
})
混入
多个组件都需要同样的方法和变量等的时候可以用 混入 提高复用性
- 混入的钩子函数在本组件同名钩子函数之前调用,且同名钩子函数会合并
- 混入和组件,属性或方法名冲突时,取组件的对象和方法
- 全局混入会影响之后创建的所有vue实例(在main.js中用
Vue.mixin())
let mixin = {
data () {
return {
name: '混入XXXX'
}
},
methods: {
getName () {
console.log(this.name)
}
}
}
new Vue({
mixins: [mixin],
data () {
return {
sex: "男",
}
},
methods: {
getName () {
console.log('name', this.name, 'sex:', this.sex)
}
}
})
指令
1. 指令的本质:语法糖,标志位。在编译阶段 render 函数里,会把指令编译成 JavaScript 代码。
2. 不推荐同时使用 v-if 和 v-for 应为 v-for的执行优先比v-if要高 会造成多次 判断
3. 给 v-for 设置key 的原因是 高效的更新虚拟dom
4. v-model text 和 textarea 元素使用 value 属性和 input 事件
5. v-model checkbox 和 radio 使用 checked property 和 change 事件
6. v-model select 字段将 value 作为 prop 并将 change 作为事件
- v-text 插入文本
- v-html 插入html
- v-show true 显示 false 隐藏 类似于display: none;
- v-if / v-else-if / v-else true 显示 false 隐藏 false时删除节点
- v-for 循环 使用的元素需要添加 key 属性
- v-on 简写 @ 绑定 事件
- v-bind 简写 : 动态地绑定一个或多个属性
- v-model 双向绑定的语法糖
- v-slot 简写 # 插槽
- v-pre 跳过这个元素和它的子元素的编译过程
- v-once 只渲染元素和组件一次
- v-cloak 保持在元素上直到关联实例结束编译(先隐藏等编译完成显示) 需配合css
<template>
<div
v-html="html"
v-show="false"
v-once
v-cloak
>
名称:{{name}}
</div>
<div>
<div v-if="false">
<input :value="name" @input="input"/>
<input v-model="name"/>
<!-- .lazy 在 change 时而非 input 时更新 -->
<input v-model.lazy="name" />
<!-- .number 将输入 string 变成 number -->
<input v-model.number="name" type="text" />
<!-- .trim 去除前后空格 -->
<input
v-model.trim="name" />
</div>
<div v-else>
<span v-for="i in 10" :key="'sp_'+i" v-text="i"></span>
</div>
<div v-pre>
{{name}}
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
name: "指令",
html: `<span style="color: red;">xxxx</span>`
}
},
methods: {
input(e) {
this.name = e.target.value;
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
[v-cloak] {
display: none;
}
</style>
自定义指令
- 全局自定义指令 Vue.directive('指令名', {})
- 局部自定义指令 directive: { '指令名':
- 生命周期:
a. bind 指令第一次绑定到元素时调用,只调用一次
b. inserted 被绑定元素插入父节点时调用
c. update 所在组件的 VNode 更新时调用,但是可能发生在其子 VNode 更新之前
d. componentUpdated 指令所在组件的 VNode 及其子 VNode 全部更新后调用
e. unbind 指令与元素解绑时调用
Vue.directive('v-custom',{
bind(el, binding, vnode){
// el: 绑定元素的 dom
// binding: 指令相关的集合
// vnode: Vue 编译生成的虚拟节点
// oldVnode:上一个虚拟节点 只有 update 和 componentUpdated 可用
},
inserted(el, binding, vnode) {
},
update(el, binding, vnode, oldVnode) {
},
componentUpdated(el, binding, vnode, oldVnode) {
},
unbind(el, binding, vnode, prevVno) {
}
})
条件、列表渲染
- v-if / v-else-if / v-else
- v-show
- v-for
- 想要 v-if 和 v-for 的元素节点不渲染后不包含 所在节点可用使用 template
- 用 key 管理可复用的元素 ( vue 一般情况下会复用已有元素 )
- v-if 与 v-show 的区别: v-show 只是隐藏元素 无论是否显示都渲染 v-if 是移除元素
- v-if 与 v-for 不一起使用 因为 v-for 优先级高于 v-if 会造成多次判断
过滤器
- 属性 | 过滤器 | 过滤器 在 {{}} 和 v-bind 中可用使用
- 全局过滤器 Vue.filters({})
<template >
<div>
{{'aaa' | filters('name', 1)}}
</div>
</template>
Vue.filters({
filterValue: (value, name, slice)=>{
return (value+name).slice(0,-2);
}
})
渲染函数和 JSX
<template>里面所使用模板HTML语法组建页面的,vue 中都会编译成 render 函数,因为vue 中采用的是 虚拟DOM 所以拿到template模板时也要转译成 VNode(virtual node 虚拟节点) 函数- render 有一个参数 createElement
a. createElement('标签名', { '/*样式,属性,传的组件的参数,需要绑定的事件 */' }, ['设置分发的内容,如新增的其他组件 内如 ,子节点 createElement'])
// VNode属性
// {
// class: { // 与 `v-bind:class`
// foo: true,
// bar: false
// },
// style: { // 与 `v-bind:style`
// color: 'red',
// fontSize: '14px'
// },
// attrs: { // 普通的 HTML attribute 也可以用于传参到 props
// id: 'foo'
// },
// domProps: { // DOM property
// innerHTML: 'baz'
// },
// // 事件监听器在 `on` 内,
// // 但不再支持如 `v-on:keyup.enter` 这样的修饰器。
// // 需要在处理函数中手动检查 keyCode。
// on: {
// },
// // 仅用于组件,用于监听原生事件,而不是组件内部使用
// // `vm.$emit` 触发的事件。
// nativeOn: {
// },
// // 自定义指令。注意,你无法对 `binding` 中的 `oldValue`
// // 赋值,因为 Vue 已经自动为你进行了同步。
// directives: [
// {
// name: 'my-custom-directive',
// value: '2',
// expression: '1 + 1',
// arg: 'foo',
// modifiers: {
// bar: true
// }
// }
// ],
// // 作用域插槽的格式为
// // { name: props => VNode | Array<VNode> }
// scopedSlots: {
// default: props => createElement('span', props.text)
// },
// // 如果组件是其它组件的子组件,需为插槽指定名称
// slot: 'name-of-slot',
// // 其它特殊顶层 property
// key: 'myKey',
// ref: 'myRef',
// // 如果你在渲染函数中给多个元素都应用了相同的 ref 名,
// // 那么 `$refs.myRef` 会变成一个数组。
// refInFor: true
// }
// 只 创建
let render_1 = {
// render 和 template 不可共存 render 返回的就是一个node 节点
// render 会传递一个参数 createElement
render(createElement) {
return createElement(
"div",
{
style: { color: "red" },
domProps: {
// 此处会覆盖掉 第三个参数中的内容
innerHTML: "此处可以插入值"
}
},
[ `createElement('name', VNode属性, children) `
`createElement('标签名', { /*样式,属性,传的组件的参数,需要绑定的事件*/ },[ '子元素' ])`
]
);
}
}
new Vue ({
el: "#app",
mixins: [render_1]
})
// render 组件和插槽
let render_2 = {
props: {
tag: String,
data: Array
},
data () {
return {
name: "此处是xxxx"
}
},
render(c) {
let elem = this.data.map(item=> c('div', { style: { color: 'red'} },item.toString()))
return c(
this.tag,
{
on: {
click: (e)=>{
console.log("点击事件xxxx",e);
}
},
},
[
c('header', this.$slots.header&&this.$scopedSlots.header({ user: 'header' }) || '头部插槽默认内容'),
c('main', [this.$scopedSlots.default({ content: this.name }) || elem]),
c('footer', [this.$slots.footer&&this.$scopedSlots.footer({ footer: this.name })]),
]
)
}
}
new Vue ({
el: "#app",
components: {render_2},
render: c=>c(
render_2,
{
props: {
tag: 'div',
data: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
},
scopedSlots: {
default: prop => {
console.log("prop",prop);
return prop.user
},
footer: prop => { // 作用域插槽
// 这两的返回值会覆盖掉 children 中的值
return prop.footer + 'U盾四安徽'
}
}
},
[
'使用默认插槽 可以不写插槽名称',
c('div', { slot: 'footer' }, '使用底部插槽')
]
)
})




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】