MySQL_python操作MySQL
概要
1 python操作MySQL
2 SQL注入问题及解决办法
3 python中实现MySQL的"增 删 改 查"<最完整链接配置>
4 mysql 连接池
详细
1 python操作MySQL
1-1 安装pymysql
查看有没有装过pymysql模块
若,没有
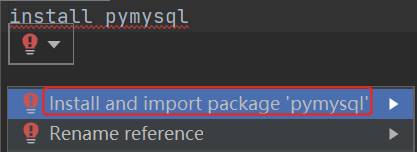
在py文件中直接写 install pymysql,点击出现的红色小灯泡,然后选安装即可,如下图
1-2 获取数据库中表数据及控制光标移动

import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect( host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='1', charset='utf8', # 千万不要加- # 指定要操作哪个库 database='db3' ) # 链接数据库 # 产生一个游标对象(类似在cmd中登陆mysql客户端后的哪个等待你输命令的闪烁的短下划线) """ 将查询的结果以字典的形式返回 """ cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) sql = 'select * from dep' res = cursor.execute(sql) # print(res) # 5 表示:表dep中有5条数据 # ---用法1: 获取数据--- # print(cursor.fetchone()) # 只获取一条数据 # print(cursor.fetchmany(2)) # 获取指定条数据 # print(cursor.fetchall()) # 获取'光标后的'所有的数据 (使用较多) # # 用法1.1 # print(cursor.fetchone()) # 只获取一条数据 # # {'id': 1, 'name': '教师部'} # # 用法1.2 # # 拿到了所有的数据 # print(cursor.fetchall()) # # [{'id': 1, 'name': '教师部'}, {'id': 2, 'name': '后勤部'}, # # {'id': 3, 'name': '财务部'}, {'id': 4, 'name': '人事部'}, {'id': 5, 'name': '行政部'}] # 用法1.3 # 获取指定条数据 # print(cursor.fetchmany(2)) # 结果: [{'id': 1, 'name': '教师部'}, {'id': 2, 'name': '后勤部'}] # ---用法2: 控制光标移动--- # # 2.1 未控制前 # print(cursor.fetchone()) # print(cursor.fetchone()) # print(cursor.fetchall()) """ {'id': 1, 'name': '教师部'} {'id': 2, 'name': '后勤部'} [{'id': 3, 'name': '财务部'}, {'id': 4, 'name': '人事部'}, {'id': 5, 'name': '行政部'}] """ # 2.1 控制后 # # 2.11 # print(cursor.fetchone()) # print(cursor.fetchone()) # cursor.scroll(2, 'relative') # 光标相对于当前位置往后移几位 # print(cursor.fetchall()) """ {'id': 1, 'name': '教师部'} {'id': 2, 'name': '后勤部'} [{'id': 5, 'name': '行政部'}] """ # 2.12 print(cursor.fetchone()) print(cursor.fetchone()) cursor.scroll(3, 'absolute') # 光标相对于起始位置往后移几位 print(cursor.fetchall()) """ {'id': 1, 'name': '教师部'} {'id': 2, 'name': '后勤部'} [{'id': 5, 'name': '行政部'}] """
2 SQL注入问题及解决办法
2-1 SQL注入问题
-
利用MySQL的注释语法,钻空子实现常规操作才能操作的功能
案例: 结合MySQL实现用户的登陆

import pymysql # 链接数据库 conn = pymysql.connect( host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='1', charset='utf8', database='db6' ) # 产生一个游标对象 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) username = input('请输入用户名>>>:').strip() password = input('请输入密码>>>:').strip() sql = "select * from user where name='%s' and password='%s'" % (username, password) print(sql) res_sql = cursor.execute(sql) # 若输入正确 if res_sql: print('登陆成功') # 获取数据 print(cursor.fetchall()) else: print('登陆失败')
现象1: 无需用户名即可登陆
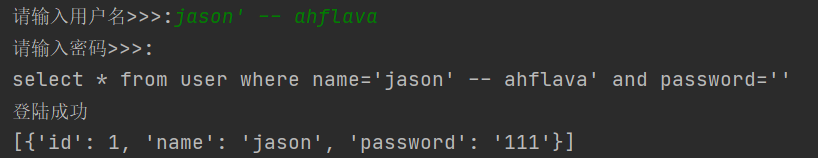
现象2: 无需密码可登陆
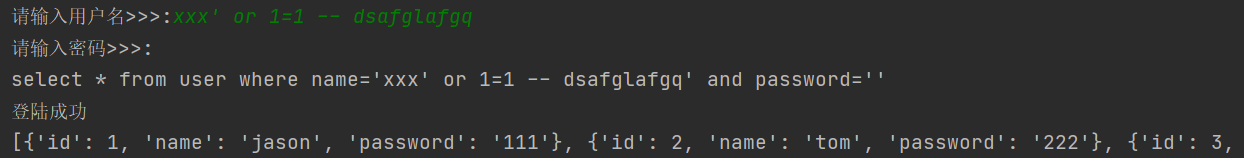
2-2 解决

import pymysql # 链接数据库 conn = pymysql.connect( host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='1', charset='utf8', database='db6' ) # 产生一个游标对象 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) username = input('请输入用户名>>>:').strip() password = input('请输入密码>>>:').strip() sql = "select * from user where name=%s and password=%s" """ 办法: 不手动拼接敏感数据,先用%s占位,之后将需要拼接的数据交给execute方法 """ print(sql) """ 将要拼接的数据用元组的形式组合起来,execute 会自动识别%s,过滤特殊符号,并用元组里的数据替换%s """ res_sql = cursor.execute(sql, (username,password)) # 若输入正确 if res_sql: print('登陆成功') # 获取数据 print(cursor.fetchall()) else: print('登陆失败')
3 python中实现MySQL的"增 删 改 查"<最完整链接配置>

import pymysql # 链接数据库<最完整配置!!!> conn = pymysql.connect( host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='1', charset='utf8', database='db6', # 确认修改数据的语句 autocommit=True ) # 产生一个游标对象 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # sql = "select * from user where name=%s and password=%s" # 增 sql = "insert into user(name, password) values(%s, %s)" # 增加单条数据 # res_sql = cursor.execute(sql, ('hhh', 1111)) # print(res_sql) # 如何增加多条数据<!!!> # 1) cursor.executemany() # 2) 用列表套元组的形式 res_sql = cursor.executemany(sql, [('aaa', 1), ('bbb', '2'), ('ccc', 3)]) print(res_sql) # # 删除 # # sql = "delete from user where id=4" # res_sql = cursor.execute(sql) # print(res_sql) # # 修改 # # sql = "update user set name = 'yyy' where id=1" # # res_sql = cursor.execute(sql) # print(res_sql) # # 查 # sql = "select * from user " # cursor.execute(sql) # print(cursor.fetchall())
4 mysql 连接池(是否有问题,还需要实际案例验证)
├─database
│ │ db_config.py
│ │ db_handler.py
│ │ example.py
│ │ __init__.py
1) db_config.py
# db_config.py import pymysql mysql_config = { 'host': 'localhost', 'port': 3306, 'user': 'root', 'password': '123', 'database': 't_celery2', 'charset': 'utf8mb4', 'cursorclass': pymysql.cursors.DictCursor, # 'autocommit': True }
2) db_handler.py
# db_handler.py import pymysql import threading import traceback from contextlib import contextmanager from database.db_config import mysql_config class MySQLConnectionPool: _instance = None _lock = threading.Lock() def __new__(cls, db_config, max_connections=10): with cls._lock: if not cls._instance: cls._instance = super().__new__(cls) cls._instance.db_config = db_config cls._instance.max_connections = max_connections cls._instance.connections = [] cls._instance._initialize_connections() return cls._instance def _initialize_connections(self): for _ in range(self.max_connections): conn = self._create_connection() self.connections.append(conn) def acquire_connection(self): if not self.connections: raise Exception('No available connections in the pool') return self.connections.pop() def return_connection(self, conn): self.connections.append(conn) def _create_connection(self): return pymysql.connect(**self.db_config) # 创建MySQL数据库连接 @contextmanager def get_connection(): pool = MySQLConnectionPool(mysql_config) conn = pool.acquire_connection() try: yield conn except Exception as e: err_msg = f"Error executing SQL query\nTraceback:\n{traceback.format_exc()}" # 把err_msg加入日志中 if conn: conn.rollback() raise e finally: if conn: pool.return_connection(conn) def execute_sql_query(sql, *args): with get_connection() as conn: cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(sql, args) results = cursor.fetchall() return results
3) example.py
# example.py --- 其他py文件使用示例 # from database.queries import execute_sql_query from database.db_handler import execute_sql_query # 示例用法 sql1 = 'SELECT * FROM app01_student WHERE name = %s AND age = %s' results = execute_sql_query(sql1, 'lll', 20) print(f'Results: {results}')




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号