浅谈深度学习
浅谈深度学习
这里有几个原因:
深度学习,确实需要一定的数学基础,但真的那么难么?这个,还真没有。不信?听我来给你侃侃。看完,你也会觉得没那么难了。
《1天搞懂深度学习》,300多页的ppt,台湾李宏毅教授写的,非常棒。
不夸张地说,是我看过最系统,也最通俗易懂的,关于深度学习的文章。
Deep Learning是机器学习中一个非常接近AI的领域,其动机在于建立、模拟人脑进行分析学习的神经网络,最近研究了机器学习中一些深度学习的相关知识,本文给出一些很有用的资料和心得。
Key Words:有监督学习与无监督学习,分类、回归,密度估计、聚类,深度学习,Sparse DBN,
1. 有监督学习和无监督学习
给定一组数据(input,target)为Z=(X,Y)。
有监督学习:最常见的是regression & classification。
regression:Y是实数vector。回归问题,就是拟合(X,Y)的一条曲线,使得下式cost function L最小。

classification:Y是一个finite number,可以看做类标号。分类问题需要首先给定有label的数据训练分类器,故属于有监督学习过程。分类问题中,cost function L(X,Y)是X属于类Y的概率的负对数。
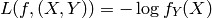 ,其中fi(X)=P(Y=i | X);
,其中fi(X)=P(Y=i | X);
无监督学习:无监督学习的目的是学习一个function f,使它可以描述给定数据的位置分布P(Z)。 包括两种:density estimation & clustering.
density estimation就是密度估计,估计该数据在任意位置的分布密度
clustering就是聚类,将Z聚集几类(如K-Means),或者给出一个样本属于每一类的概率。由于不需要事先根据训练数据去train聚类器,故属于无监督学习。
PCA和很多deep learning算法都属于无监督学习。
Depth 概念:depth: the length of the longest path from an input to an output.
Deep Architecture 的三个特点:深度不足会出现问题;人脑具有一个深度结构(每深入一层进行一次abstraction,由lower-layer的features描述而成的feature构成,就是上篇中提到的feature hierarchy问题,而且该hierarchy是一个稀疏矩阵);认知过程逐层进行,逐步抽象
3篇文章介绍Deep Belief Networks,作为DBN的breakthrough
3.Deep Learning Algorithm 的核心思想:
把learning hierarchy 看做一个network,则
①无监督学习用于每一层网络的pre-train;
②每次用无监督学习只训练一层,将其训练结果作为其higher一层的输入;
③用监督学习去调整所有层
这里不负责任地理解下,举个例子在Autoencoder中,无监督学习学的是feature,有监督学习用在fine-tuning. 比如每一个neural network 学出的hidden layer就是feature,作为下一次神经网络无监督学习的input……这样一次次就学出了一个deep的网络,每一层都是上一次学习的hidden layer。再用softmax classifier去fine-tuning这个deep network的系数。
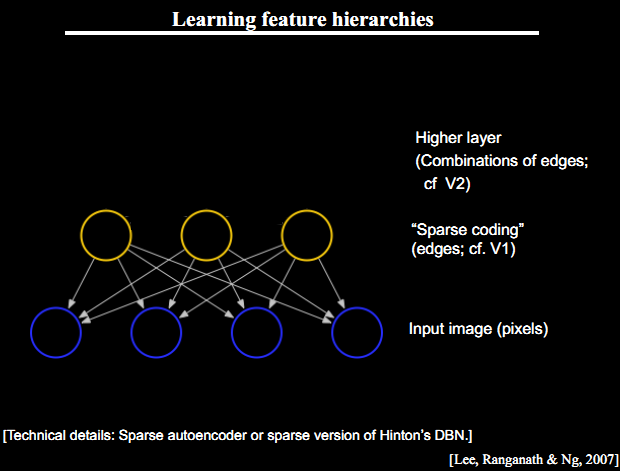
这三个点是Deep Learning Algorithm的精髓,我在上一篇文章中也有讲到,其中第三部分:Learning Features Hierachy & Sparse DBN就讲了如何运用Sparse DBN进行feature学习。
4. Deep Learning 经典阅读材料:
- The monograph or review paper Learning Deep Architectures for AI (Foundations & Trends in Machine Learning, 2009).
- The ICML 2009 Workshop on Learning Feature Hierarchies webpage has a list of references.
- The LISA public wiki has a reading list and a bibliography.
- Geoff Hinton has readings from last year’s NIPS tutorial.
阐述Deep learning主要思想的三篇文章:
- Hinton, G. E., Osindero, S. and Teh, Y., A fast learning algorithm for deep belief netsNeural Computation 18:1527-1554, 2006
- Yoshua Bengio, Pascal Lamblin, Dan Popovici and Hugo Larochelle, Greedy Layer-Wise Training of Deep Networks, in J. Platt et al. (Eds), Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 19 (NIPS 2006), pp. 153-160, MIT Press, 2007<比较了RBM和Auto-encoder>
- Marc’Aurelio Ranzato, Christopher Poultney, Sumit Chopra and Yann LeCun Efficient Learning of Sparse Representations with an Energy-Based Model, in J. Platt et al. (Eds), Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2006), MIT Press, 2007<将稀疏自编码用于回旋结构(convolutional architecture)>
06年后,大批deep learning文章涌现,感兴趣的可以看下大牛Yoshua Bengio的综述Learning deep architectures for {AI},不过本文很长,很长……
5. Deep Learning工具—— Theano
Theano是deep learning的Python库,要求首先熟悉Python语言和numpy,建议读者先看Theano basic tutorial,然后按照Getting Started 下载相关数据并用gradient descent的方法进行学习。
学习了Theano的基本方法后,可以练习写以下几个算法:
有监督学习:
- Logistic Regression - using Theano for something simple
- Multilayer perceptron - introduction to layers
- Deep Convolutional Network - a simplified version of LeNet5
无监督学习:
- Auto Encoders, Denoising Autoencoders - description of autoencoders
- Stacked Denoising Auto-Encoders - easy steps into unsupervised pre-training for deep nets
- Restricted Boltzmann Machines - single layer generative RBM model
- Deep Belief Networks - unsupervised generative pre-training of stacked RBMs followed by supervised fine-tuning
最后呢,推荐给大家基本ML的书籍:
- Chris Bishop, “Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning”, 2007
- Simon Haykin, “Neural Networks: a Comprehensive Foundation”, 2009 (3rd edition)
- Richard O. Duda, Peter E. Hart and David G. Stork, “Pattern Classification”, 2001 (2nd edition)
关于Machine Learning更多的学习资料将继续更新,敬请关注本博客和新浪微博Sophia_qing。
References:
1. Brief Introduction to ML for AI
3.A tutorial on deep learning - Video
参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7826917/


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号