常见的hash数据结构
遍历
hash表是一种比较简单和直观的数据结构,在查找时也有很好的性能。但是hash表不能提供有序遍历,这个是其特性决定,所以不足为奇。但是,更为实际的一个问题是如果遍历整个hash表中的所有元素?
直观上讲,可以遍历一个hash的所有桶(bucket),但是这样明显效率偏低,特别是如果hash表为了提高性能,桶的数量很多,整个结构的有效负载率不高,这种遍历方法就更加低效了。
STL的实现
stl中的hash表主要数据结构如下图所示,可以看到,实现遍历的关键是_M_before_begin指针,这个指针指指向桶的第一个元素(而不是最后插入的元素)。因为这个链表中同一个桶中的所有元素必须在链表内连续分布,在这种情况下,如果在下图中的第三个bucket中插入新元素,就没有办法知道bucket3子链表在整个链表中的起始位置(当然,这种说法并不严谨:也可以从_M_before_begin开始遍历并计算hash值,直到找到一个和当前hash不同的元素就知道当前链表的结尾了,不过这种效率看起来不太高)。
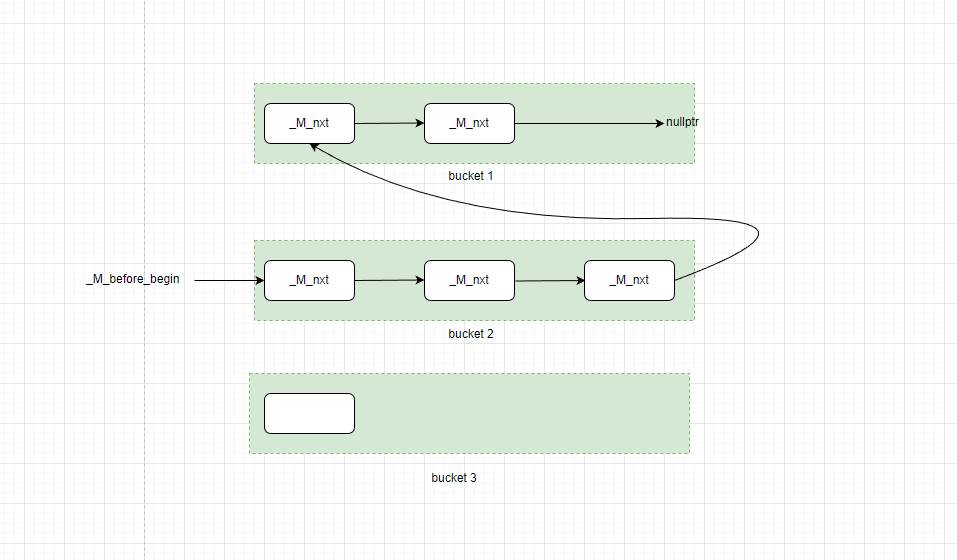
下面是库代码在桶头插入新元素的代码流程
///libstdc++-v3\include\bits\hashtable.h
template<typename _Key, typename _Value,
typename _Alloc, typename _ExtractKey, typename _Equal,
typename _H1, typename _H2, typename _Hash, typename _RehashPolicy,
typename _Traits>
void
_Hashtable<_Key, _Value, _Alloc, _ExtractKey, _Equal,
_H1, _H2, _Hash, _RehashPolicy, _Traits>::
_M_insert_bucket_begin(size_type __bkt, __node_type* __node)
{
if (_M_buckets[__bkt])
{
// Bucket is not empty, we just need to insert the new node
// after the bucket before begin.
__node->_M_nxt = _M_buckets[__bkt]->_M_nxt;
_M_buckets[__bkt]->_M_nxt = __node;
}
else
{
// The bucket is empty, the new node is inserted at the
// beginning of the singly-linked list and the bucket will
// contain _M_before_begin pointer.
__node->_M_nxt = _M_before_begin._M_nxt;
_M_before_begin._M_nxt = __node;
if (__node->_M_nxt)
// We must update former begin bucket that is pointing to
// _M_before_begin.
_M_buckets[_M_bucket_index(__node->_M_next())] = __node;
_M_buckets[__bkt] = &_M_before_begin;
}
}
特定键值的查找
由于链表没有边界,所以是通过计算节点键值的键值,进而根据键值获得bucket下标是否和当前查找节点的下标相同(_M_bucket_index(__p->_M_next()) != __n)来判断的。
// Find the node whose key compares equal to k in the bucket n.
// Return nullptr if no node is found.
template<typename _Key, typename _Value,
typename _Alloc, typename _ExtractKey, typename _Equal,
typename _H1, typename _H2, typename _Hash, typename _RehashPolicy,
typename _Traits>
auto
_Hashtable<_Key, _Value, _Alloc, _ExtractKey, _Equal,
_H1, _H2, _Hash, _RehashPolicy, _Traits>::
_M_find_before_node(size_type __n, const key_type& __k,
__hash_code __code) const
-> __node_base*
{
__node_base* __prev_p = _M_buckets[__n];
if (!__prev_p)
return nullptr;
for (__node_type* __p = static_cast<__node_type*>(__prev_p->_M_nxt);;
__p = __p->_M_next())
{
if (this->_M_equals(__k, __code, __p))
return __prev_p;
if (!__p->_M_nxt || _M_bucket_index(__p->_M_next()) != __n)
break;
__prev_p = __p;
}
return nullptr;
}
迭代器
迭代器就是不断的通过_M_nxt访问链表,由于这个本质上是一个单向链表,所以它只有前向迭代(forward_iterator)而不是随机迭代(random_access_iterator)。这里列出了标准的C++迭代器。
__node_type*
_M_begin() const
{ return static_cast<__node_type*>(_M_before_begin._M_nxt); }
/**
* struct _Hash_node_base
*
* Nodes, used to wrap elements stored in the hash table. A policy
* template parameter of class template _Hashtable controls whether
* nodes also store a hash code. In some cases (e.g. strings) this
* may be a performance win.
*/
struct _Hash_node_base
{
_Hash_node_base* _M_nxt;
_Hash_node_base() noexcept : _M_nxt() { }
_Hash_node_base(_Hash_node_base* __next) noexcept : _M_nxt(__next) { }
};
/**
* struct _Hash_node_value_base
*
* Node type with the value to store.
*/
template<typename _Value>
struct _Hash_node_value_base : _Hash_node_base
{
typedef _Value value_type;
__gnu_cxx::__aligned_buffer<_Value> _M_storage;
_Value*
_M_valptr() noexcept
{ return _M_storage._M_ptr(); }
const _Value*
_M_valptr() const noexcept
{ return _M_storage._M_ptr(); }
_Value&
_M_v() noexcept
{ return *_M_valptr(); }
const _Value&
_M_v() const noexcept
{ return *_M_valptr(); }
}
PhysX的实现
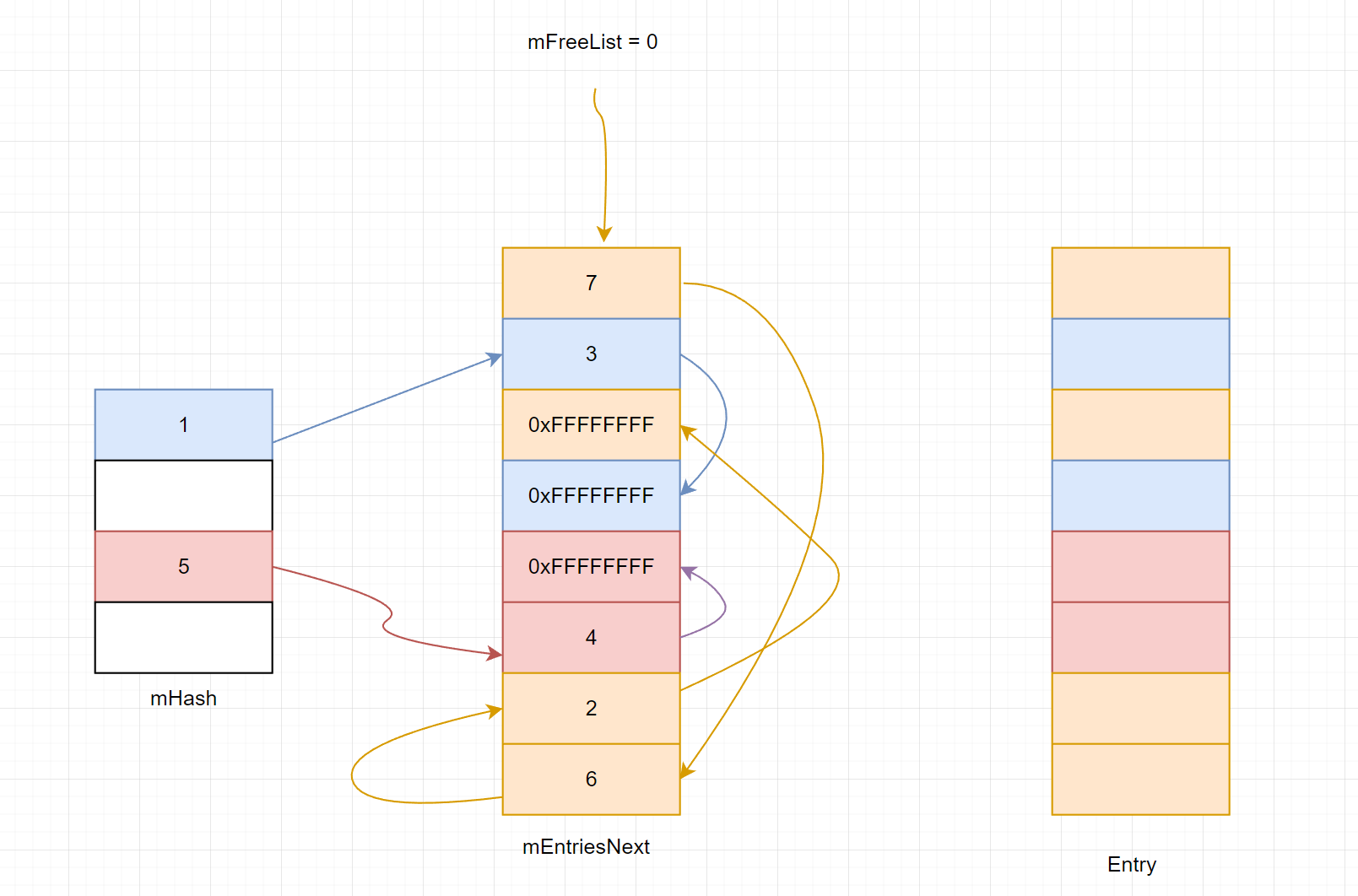
由于hash表是一个基础的数据结构,所以在很多的大中型软件中都有实现,下图是PhysX引擎PsHashInternals.h中HashBase类的实现。其中的mEntriesNext和mEntries数组大小相同,相当于为每个节点配置了一个next指针,但是这个next指针的意义根据它在不同的链表有不同的意义:如果在free链表则表示是free节点,如果是在某个hash桶中则表示某个hash值的节点。
迭代器
这遍历其实比较直观,关键是记录了上次遍历的桶(mBucket)和桶内部的位置(mEntry),在迭代器中要注意自动跨过(skip)桶的边界。
PX_INLINE void skip()
{
while(mEntry == mBase.EOL)
{
if(++mBucket == mBase.mHashSize)
break;
mEntry = mBase.mHash[mBucket];
}
}
压缩(compact)模式
有意思的是它还提供了一个compact模式,这个模式会尽量保证对象池中只是用前面的部分,也就是所有使用部分在前,所有空闲部分在后。这种实现的一个明显有点是可以减少内存足迹。
但是,这个实现其实是通过执行析构/拷贝构造来移动之前已经存在对象的位置,从而保持在用空间的compact,对于存储了对象下标、或者构造/析构支持不是很完善的对象,这种方法并不适用。
PX_INLINE void replaceWithLast(uint32_t index)
{
PX_PLACEMENT_NEW(mEntries + index, Entry)(mEntries[mEntriesCount]);
mEntries[mEntriesCount].~Entry();
mEntriesNext[index] = mEntriesNext[mEntriesCount];
uint32_t h = hash(GetKey()(mEntries[index]));
uint32_t* ptr;
for(ptr = mHash + h; *ptr != mEntriesCount; ptr = mEntriesNext + *ptr)
PX_ASSERT(*ptr != EOL);
*ptr = index;
}
总结
stl库通过将所有的使用中对象链接在同一个链表中,这样遍历所有对象的时候非常紧凑,是一种比较有特点的实现范式。
但是代价是在查找的时候不同通过一个特殊值表示所在bucket结束,也就是hash的计算可能会更频繁一些(在查找的时候)。



